1. Introduction
Over the past two decades, the staff scheduling problem has received a great deal of attention from researchers in related research fields such as operations research, management science and computer science. There have been many studies on the staff scheduling problem, which can be categorized into two types: exact methods and metaheuristic methods [1]. The exact methods mainly include integer programming [2-4] and constraint programming [5-7], in which the exact methods can find the optimal solution under a specific problem size, but with the increase of the problem size and problem complexity, their time cost becomes very expensive and generally unacceptable. To solve this problem, researchers have proposed meta-heuristics, including variable neighborhood search, genetic and stochastic algorithms, and various customized heuristics [8-10], which can generate relatively high-quality feasible solutions in a short period of time.
Traditional scheduling management often uses manual scheduling, need to take into account the staff's personal factors, business needs, rest time and other factors, heavy workload, high difficulty, error-prone. Moreover, once there is a scheduling error or changes in employee demand, the need to re-establish the scheduling plan, which will bring a lot of unnecessary trouble to the enterprise and employees.
Intelligent scheduling system can effectively improve the efficiency and quality of scheduling management, reduce the cost and workload of scheduling management, but also to meet the needs of employees, improve employee motivation and satisfaction. It can be said that intelligent scheduling system is an innovation in enterprise management and human resource management, which is of great significance in promoting social progress and economic development.
Genetic algorithm (GA) as a general search algorithm for solving complex system optimization problems, compared with the traditional search algorithm, genetic algorithm has the following characteristics:
(1) Genetic algorithm has hidden parallelism, unlike other search algorithms, genetic algorithm is no longer a point in the solution space as the starting point, but a group of points as the starting point. These search points do not interfere with each other, and carry out iterative search on their own, which covers a larger solution space and improves the probability of convergence to the global optimal solution.
(2) Genetic algorithm does not need to use external information such as derivation, and directly uses its own fitness function as the basis for search, and there is no restriction of continuous minimization. This makes the genetic algorithm suitable for many applications, such as the typical shop floor tuning problem, the optimization of aviation control system, and the optimization of the airborne control system.
The genetic algorithm can be used in many applications, such as typical shop-floor tuning problems, aviation control system optimization problems, and artificial neural networks, which have become more and more popular in recent years.
(3) Genetic algorithms use probabilistic search techniques. Most of the other optimization algorithms use deterministic search techniques, i.e., searching according to specific methods and rules. Such deterministic rules, in turn, limit the scope of application. The genetic algorithm is an adaptive probabilistic search technique, which is more flexible.
(4) Self-organization, self-adaptation and self-learning. Genetic algorithm in the evolutionary process will eliminate the poor individuals, retain the good individuals, and the remaining individuals have good adaptability.
(5) Genetic algorithms can also use dynamic adaptive technology, adaptive technology has been used in the improvement of genetic algorithms.
However, due to the complexity of the mathematical model of the scheduling problem, the standard genetic algorithm (SGA) can easily fall into the local optimal solution, and the convergence speed is also slow. In order to solve these problems, we propose a stochastic singular variant and switched variant genetic algorithm (SVGA), which can increase the population diversity, reduce the risk of falling into local optimal solutions, and explore the solution space better to improve the probability of finding the global optimal solution by introducing stochastic variants.
2. Genetic Algorithm
In this paper, the multi-preference intelligent scheduling problem is modeled as a variational combinatorial optimization problem and is solved using a genetic algorithm, next we give an introduction to genetic algorithms.
Genetic Algorithm (GA) is a computational method based on the principles of biogenetics and evolutionary theory, which aims to solve the optimization problem by simulating the natural evolutionary process, using selection operators and other operators to evolve and screen the original population, and obtaining the possible optimal solution after iteration. Genetic algorithm is the American computer scientist John Henry Holland (John Henry Holland) in the 1975s, and the application of genetic algorithm successfully solved a number of optimization problems.
Genetic algorithms have the advantages of global search ability and robustness, and are widely used in solving NP problems, machine learning, optimization design and other fields. The definitions of genetic algorithms are given below.
Definition 1 (Individual): A solution to a problem, consisting of a set of genes, usually expressed as a vector or a string.
Definition 2 (population): the set of all individuals, usually consisting of multiple individuals, with the initial population consisting of randomly generated individuals.
Definition 3 (gene): a part of a body, usually expressed as a binary code, a number, a character, etc.
Definition 4 (Chromosome code): A sequence of all the genes of an individual, a transformation method that converts a feasible solution to a problem from its solution space to a search space that can be handled by a genetic algorithm.
Definition 5 (fitness function): the fitness value is used to evaluate the degree of individual strengths and weaknesses, in general, the larger the fitness value, the better the individual; on the contrary, the smaller the fitness, the worse the individual. For specific problems, we can choose the fitness value function which is suitable for the problem, as the standard of individual evaluation.
Definition 6 (Genetic operation operator): The operation operator of genetic algorithm includes three basic forms of selection, crossover and mutation, which form the basis of efficient search capability of genetic algorithm, and it is the main carrier to simulate the reproduction, crossbreeding and mutation phenomena occurring in the process of natural selection and heredity. The selection operation embodies the principle of survival of the fittest, selecting high-quality individuals and discarding poor-quality individuals through the fitness value; the crossover operation generates new individuals by exchanging genetic information between individuals; and the mutation operator obtains unexploited genetic information by mutating some of the loci information to prevent the individuals from converging prematurely during the process of forming the optimal solution.
The process of genetic algorithm is roughly described as follows: firstly, a certain number of individuals are randomly generated and given random genotypes; then, the algorithm calculates the fitness value of each individual, i.e., the value of the objective function of the problem or other evaluation indexes, until a specific termination condition is met (the termination condition is usually a specified number of iterations or a change in the value of the optimum fitness is below a certain threshold), and returns the optimal solution found so far; according to the fitness value, the solution is eliminated, and the optimal solution is formed by the mutation operator. According to the fitness value, eliminate the non-excellent individuals, and add the newly generated individuals to the population, and select a certain number of individuals as "parents" for the next step of reproduction. The key of the algorithm is the coding method of chromosome, the setting of fitness value function and the setting of genetic operation operators such as selection, crossover and mutation.
3. Mathematical modeling of intelligent scheduling
3.1. research problem
In many ordinary stores, the staff scheduling work is mainly based on the store's projected customer flow, the store's second area, the staff's preference for shifts, for each day of each post to allocate the right staff, the ultimate goal is to make the store with the optimal scheduling so that the staff to complete the work.
3.2. Algorithmic Modeling of Intelligent Scheduling Problem
We will model scheduling on a weekly basis.
The model is as follows:
Table 1. Name and significance
name | significance |
\( Size \) | Store size |
\( PreModle \) | The number of customers during working hours of the store, in 0.5 hour units |
\( preWorkTime \) | Number of hours of preparatory work before opening, in multiples of 0.5 |
\( StoreSizeNeedBefore \) | For calculating the number of employees needed before opening the store |
\( passengerFlowNeed \) | For calculating the number of employees needed at work |
\( free\_population \) | Number of people on duty when traffic is zero |
\( aftWorkTime \) | The number of hours of preparatory work after closing, in multiples of 0.5. |
\( StoreSizeNeedAfter \) | The number of people needed after closing the store |
\( preNum=(int)(\frac{Size}{StoreSizeNeedBefore}) \) | Number of people needed before opening |
\( PassFlowNum=(int)(\frac{PreModle}{passengerFlowNeed}) \) | Number of employees required to be on duty |
\( FreeNum=(int)(free\_population) \) | Number of persons required to be on duty when the passenger flow is 0 |
\( AftNum=(int)(\frac{Size}{StoreSizeNeedAfter}) \) | Calculation of the number of people needed after the closure of the store |
\( X=\lbrace 1,2,3,4,⋯,Sum\rbrace \) | \( Sum \) is the total number of soft condition constraints |
\( Check \) array constraints | \( check = [[]] \) , a checklist of whether a particular task has been completed, with a value of 0 or 1, where 0 means it can be worked on and 1 means it cannot be worked on. |
\( status \) array constraints | \( status = [[]] \) , a status list that records whether a particular task has been assigned to a group or not, with values 1, 2, 3, 1 for available, 2 for in progress, 3 for not available. 1 means that you can work at this time, 2 means that you are working, and 3 means that you cannot work at this time. |
\( {S_{1}} \) Continuous operating hours constraint | The length of continuous work of each employee can not exceed the limit range of the given hard conditions, otherwise it will cause physical and mental exhaustion of the employee, the value of the punishment is assigned to 3. |
\( {S_{2}} \) Hours of work constraints | The daily working hours of each employee can not exceed the limits of the given hard conditions, otherwise it will cause physical and mental exhaustion of the employee, the penalty value is assigned to 3. |
\( {S_{3}} \) Employee preference constraints | Scheduling employees to work according to their preferred shifts and assigning a penalty value of 3 for violations. |
The purpose of the scheduling algorithm is to automatically select qualified employees from the preference array for scheduling according to the given constraints, the mathematical nature of the problem is to seek the global optimal solution under multi-dimensional constraints, in the group volume problem, the constraints are the employee's preferences for shifts, so each employee's preferences for shifts can be described by a one-dimensional vector \( Q=({a_{1}},{a_{2}},{a_{3}},⋯,{a_{n}}) \) , where n denotes the preferred shift setting value of each employee, and n denotes the preferred shift setting value of each employee, where n denotes the preferred shift setting value of each employee. where n denotes the set value of each employee's preferred shift. The shift preferences of \( m \) employees form an \( n×m \) preference matrix \( D \) .
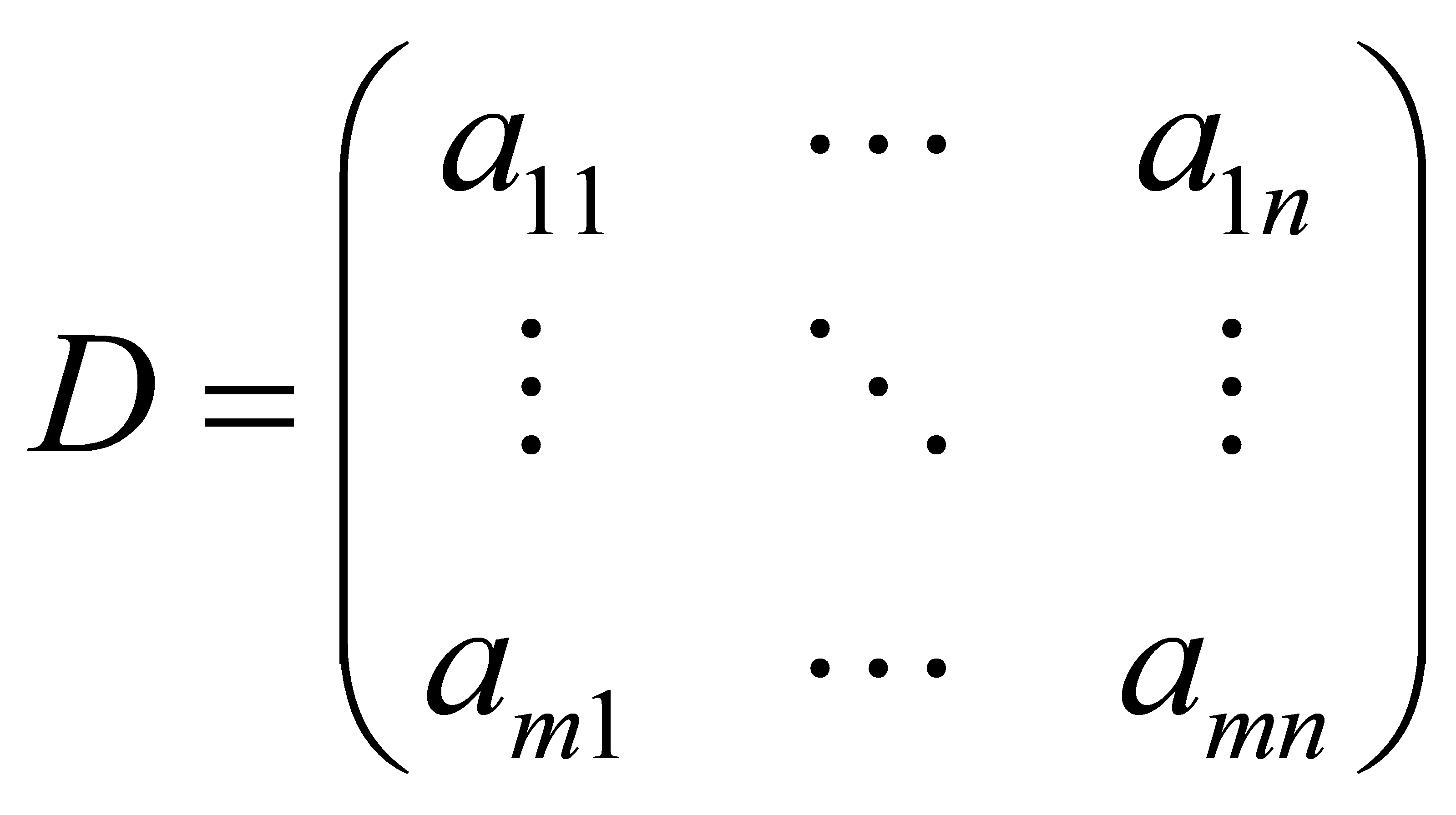
The process of scheduling is the process of selecting a subset matrix from the preference matrix D that satisfies the constraints. The scheduling model takes four attributes as the constraints, namely, no preference, daily working time preference, weekday preference, and working time preference, and the constraints on the attributes and the selection of the objective function are shown as follows.
• (1) No preference: no preference means that employee \( i \) can go to work at any time, and the value of employee \( i \prime s \) preference array is zero.
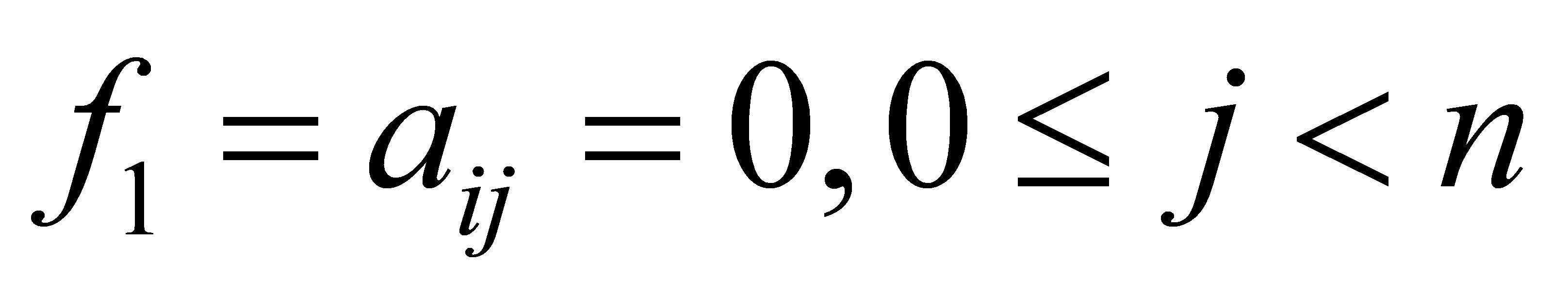
Where \( {a_{ij}} \) that employee \( i \prime s \) preference array of the \( jth \) position, \( n \) that each employee's shift preferences set value.
• (2) workday preference: workday preference indicates that employee i's like to work on what day of the week, and a_i0 is set to 1, indicating that the employee is workday preference.

where \( {a_{ij}} \) denotes the \( jth \) position of employee \( i \prime s \) preference array, \( 1≤j≤7 \) represents the \( jth \) day of the week.
• (3) work time preference: work time preference indicates employee \( i \prime s \) preferred work time period, in order to prevent conflict between work time preference array position and workday preference array position, work time preference array position starts from the 8th position, set \( {b_{0}} \) as employee \( i \prime s \) preferred work time, \( {b_{1}} \) as employee i's preferred off work time, and \( {a_{i0}} \) is set to 2, which indicates that the employee's work time preference.

Where \( {a_{ij}} \) denotes the \( jth \) position of employee \( i \prime s \) preference array, \( {b_{0}} \) is in the format of \( (HH:MM) \) , \( {b_{1}} \) is in the format of \( (hh:mm) \) , \( {b_{01}} \) denotes \( HH \) , \( {b_{02}} \) denotes \( MM \) , \( {b_{11}} \) denotes \( hh \) , and \( {b_{12}} \) denotes \( mm \) .
• (4) daily working time preference: employee \( i \prime s \) daily working time \( c \) that is, employee \( i \prime s \) preferred working time of the day, in order to prevent the daily working time preference array position and working time preference array position conflict, the daily working time preference array position is set to the 32nd position, and \( {a_{i0}} \) is set to 3, which indicates that the employee for the daily working time preference.(3) work time preference: work time preference indicates employee \( i \prime s \) preferred work time period, in order to prevent conflict between work time preference array position and workday preference array position, work time preference array position starts from the 8th position, set \( {b_{0}} \) as employee \( i \prime s \) preferred work time, \( {b_{1}} \) as employee i's preferred off work time, and \( {a_{i0}} \) is set to 2, which indicates that the employee's work time preference.
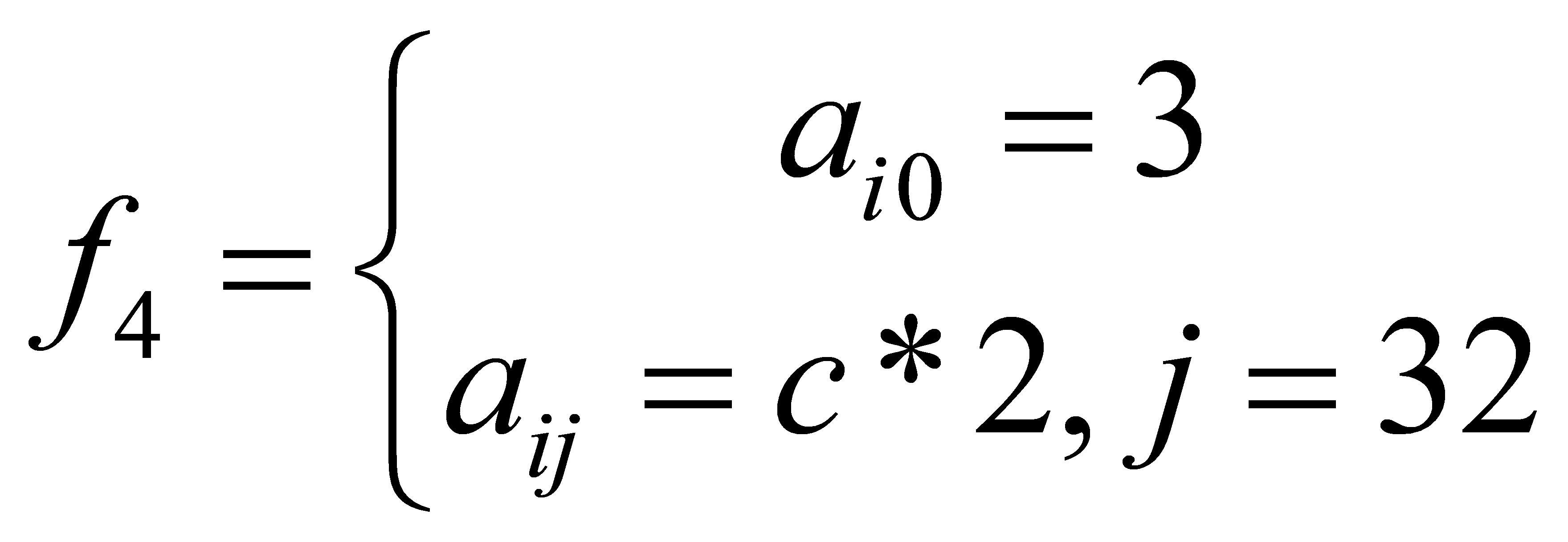
Where \( {a_{ij}} \) denotes the \( jth \) position of employee \( i \prime s \) preference array, \( c \) represents employee \( i \prime s \) daily working hours \( c \) .
4. Algorithm Detailed Procedure
Table 2. Improved Genetic Algorithm for Solving Intelligent Scheduling Problems
Table 2. (continued).
|
• (1) Chromosome coding mode
We represent each employee's chromosome as a binary vector
Among them, \( Size \) is the number of employees, \( {c_{i}} \) indicates whether the \( ith \) employee among the employees is working in the time period, if \( {c_{i}}=1 \) , it represents that the ith employee is working in the time period; if \( {c_{i}}=0 \) , it represents that the ith employee is not working in the time period. For example an employee has chromosome locus \( C=\lbrace 0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0\rbrace \) , if the first locus denotes 08:00-08:30, the chromosome denotes that the employee needs to be at work from 09:00-11:00.
• (2) Initializing populations

In this method, a single-point mutation is used to generate the initial candidate solution population, the algorithm can ensure the diversity of the initial population as much as possible under the condition of satisfying the specified conditions, the detailed process of the algorithm is first \( while \) loop, each loop traverses each employee, and at the same time, randomly generates a floating-point number between -1 and 1, and determines whether the floating-point number is less than \( pm \) , if it meets the requirements, the employee's The first gene is mutated until the sum of the first gene of all employees is equal to \( PreNum \) , then exit the loop. The value of \( pm \) is 0.5, where \( Size \) denotes the population size.
• (3) chosen operator (math.)
The selection operator is used to determine which individuals to recombine or crossover, and how many offspring individuals will be produced by the selected individuals. The selection operator is an operation based on the fitness value, and individuals with higher fitness are more likely to be selected. The fitness function in this method is the \( Multi-WorkTime \) function, which is used to calculate the sum of the average work time of each employee in the scheduling result, and the smaller the value, the better the result.
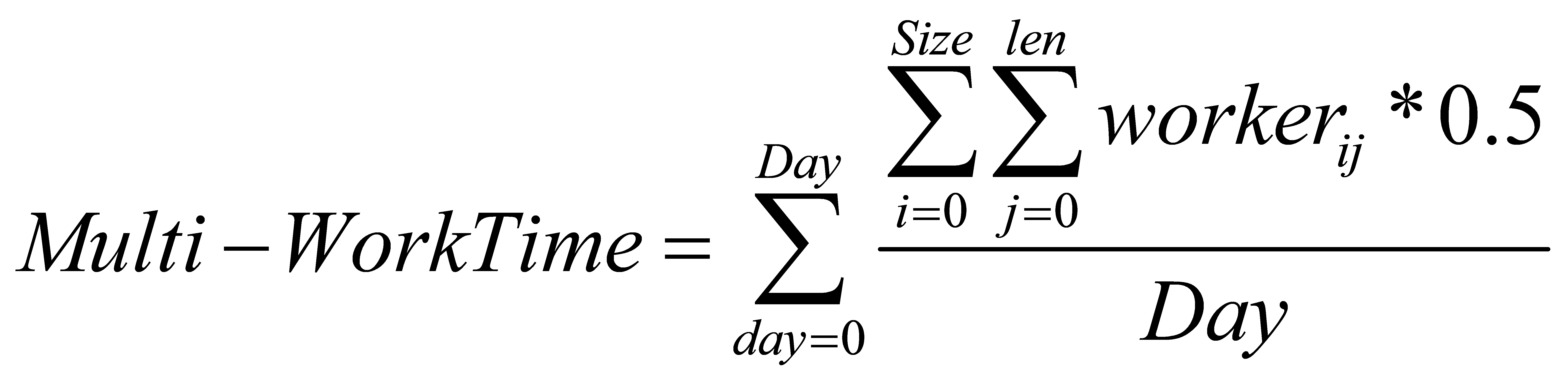 \( \)
\( \)
In the above equation, the value of \( Day \) is 7 (i.e. 7 days), \( Size \) denotes the population size, and \( len \) denotes the chromosome length.
• (4) commutative operator (math.)
The exchange operator operates on an existing chromosome to produce a new chromosome. The parameter \( {P_{c}} \) is the probability that two genes on the chromosome will be exchanged, and under the satisfaction of \( {P_{c}} \) , the values at the two loci are randomly selected and their positions are exchanged. For example, in the exchange operator, one individual is selected as the parent individual for the
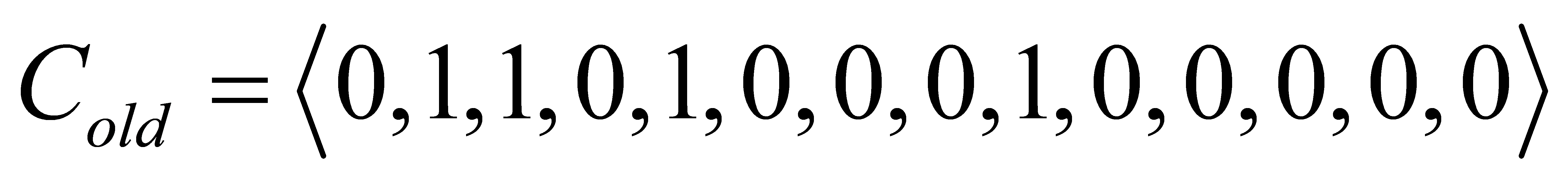
After the exchange operator operation, the individuals of the obtained offspring are as follows
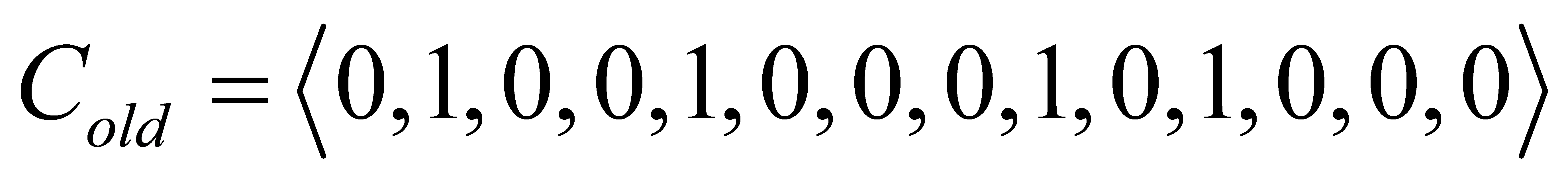
It can be seen that before and after the exchange, a total of two positions of genes are exchanged, resulting in a new individual that is different from the parent. It should be noted that in some cases, such as the first and fourth gene positions in this example, the genes may have been exchanged, but because the positions were zero in the parent, the new genotype was not created in the offspring.
• (5) the calculus of variations (math.)
In crossover arithmetic, individuals of a parent generation are crossed over to obtain new genotypes to form new offspring. However, if the genotypes of the parents are the same at a certain gene position, it is impossible for the offspring to produce new genotypes. Therefore, the algorithm will introduce a mutation operator to ensure the diversity of the population. The parameter \( {P_{m}} \) is used to specify the probability of mutation at each locus of the offspring produced by the crossover operator, i.e., the probability of mutation from 0 to 1 or from 1 to 0, with \( 0 \lt {P_{m}} \lt 1 \) . The value of \( {P_{m}} \) is usually very small, because the mutation operator cannot change the genotype of the population significantly.
• (6) reinsertion
The new individuals obtained from the selection, crossover and mutation operators need to be reinserted into the original population to form the next generation population. In this case, the fitness values of the individuals in the original population and the newly generated individuals should be calculated, and the one with the highest fitness value should be selected to form the new population. Therefore, the poorly adapted individuals in the original population will be replaced by the newly generated individuals with higher fitness values.
5. Algorithmic improvements
5.1. A Gaussian perturbation based on the standard deviation of population fitness and an operation to increase the probability of variation
Since the number of populations is limited, it is not difficult to foresee that after many iterations of evolution, the good individuals in the population will expand rapidly and occupy a large proportion of the population after evolutionary reproduction. When this process continues without external control interference, it will lead to a single population, then selection and cross mutation operations can not play its due role, and ultimately lead to the algorithm converge to the local optimal solution earlier, the genetic algorithm into the local optimal solution is the essence of the evolution, the population of chromosomes between individuals gradually close to each other, the emergence of the phenomenon of focusing.
How to avoid the genetic algorithm falling into local optimal solution is the key problem in designing genetic algorithm. At the late stage of evolution, the "super individuals" in the population have accounted for most of the individuals, at this time, the traditional crossover operation is no longer effective, and no new individuals can be generated. Although the mutation operation can provide new individuals to the algorithm. However, the mutation operation can only play an auxiliary role in the generation of new individuals by the genetic algorithm, which is a small probability event. Blindly increasing the mutation probability may destroy the original good individuals in the population and affect the next evolution of the algorithm. Aiming at the problem that the genetic algorithm is easy to fall into the local optimal solution, the team used a Gaussian perturbation based on the standard deviation of the population fitness and increased the probability of variation operation. Assuming that the number of individuals in the population is \( N \) , the fitness function value of the ith chromosome individual is \( {f_{i}}(g) \) , and the average fitness function value of the current population is \( faverage(g) \) , the standard deviation \( s \) is defined as shown in the following equation:

The standard deviation of the fitness value \( s \) is used to describe the focusing degree of the current population, the larger the \( s \) is, the greater the degree of difference between chromosomes in the population, the smaller the \( s \) is, the poorer the difference of the current population, if \( s=0 \) , then the algorithm is likely to have already fallen into a sluggish state of the search, and fall into the local optimal solution. In order to make the algorithm jump out of the local optimal solution and continue to search effectively, a threshold \( τ \) is set for the standard deviation of the individual fitness value of the population, assuming that the number of termination iterations is set to be \( T \) , and the number of times \( σ≤τ \) is recorded as count, with the initial value of 0. For every occurrence of \( σ≤τ \) , \( count = count +1 \) , and for every occurrence of \( σ \gt τ \) , \( count \) is reset to 0. In the iteration of the algorithm, the count = count + 1; in the case of s=0, the algorithm is likely to have fallen into a sluggish state of search, falling into the local optimal solution. Before the algorithm iterates to \( [T/2] \) times, if the algorithm has \( σ≤τ \) for L consecutive iterations, i.e., \( count=L \) , then the algorithm is determined to be trapped in a local optimal solution. Then the current algorithm is forced to jump out of the local optimum by Gaussian perturbation of the current population data and increasing the variance probability \( Pm \) so that the current variance probability \( Pm \) is changed to \( 2Pm \) .
6. Experiments
In this paper, the clothing store staff scheduling as an example, selected a week in April 2023 for the required scheduling of the week, the number of days in a week for Day = 7 days, the number of employees in the clothing store 25 people, the store area of 200, the need to do preparatory work before opening the store for 1 hour, after the store closure need to do preparatory work for 2 hours for the calculation of the number of employees before the opening of the store for the number of people for the calculation of the number of people after the closure of the store need to be The number of people is 2, the number of people who need to be on duty when the customer flow is 0 is 1, and StoreSizeNeedAfter is set to 3.8.
In order to show the superiority of the improved genetic algorithm, the Simple Genetic Algorithm (SGA) is used as the comparison algorithm in this paper. In addition, this paper also takes ECORA algorithm as the comparison algorithm, which consists of two parts, one is the potential game to realize the current optimal unloading decision, and the other is the resource allocation to realize the allocation of the working time of each employee. The specific simulation parameters are shown in the following table.
Table 3. Simulation parameters
Simulation parameters | Value |
Crossover probabilities for simple genetic algorithms \( {p_{c}} \) | 0.5 |
Range of values of crossover probability \( {p_{c}} \) for improved genetic algorithm | [0.25,0.8] |
Probability of variation \( {p_{m}} \) for simple genetic algorithms | 0.5 |
Improved genetic algorithm with range of values for the probability of variation \( {p_{m}} \) | [0,0.2] |
Standard deviation of population individual fitness values \( τ \) | [0,1] |
Threshold for the number of iterations in which populations experience focusing effects \( L \) | 5 |
Under the same batch of data, the same equipment and the results meet the constraints, the experimental results are shown in the following table.
Table 4. Results of the experiment
algorithms | Running time/one-time schedule | Multi-WorkTime/One Time Scheduling |
Improved genetic algorithms | 13.45s | 115h |
Traditional genetic algorithms | 64.34s | 130.5h |
ECORA algorithm | 36.75s | 64.5h |
From the table 4, under the same batch of data and satisfying the respective constraints, for Runtime, the improved algorithm has the shortest time, i.e., it runs the fastest, and for Multi-WorkTime, the value of the improved algorithm is the smallest, i.e., it outputs the lowest total working hours of the employees in the scheduling table.The results show that the improved genetic algorithm converges faster and is less precocious than the unimproved genetic algorithm, and compared with the existing algorithms, the genetic algorithm can obtain a lower average cost of the system while maintaining a smaller computational complexity. In addition, the operation of increasing the probability of variation according to the standard deviation of the fitness of the population can make the algorithm to maintain the diversity of the population at the beginning of the iteration, avoiding the algorithm's over-representation. In addition, the operation of increasing the probability of variation according to the standard deviation of the fitness of the population can keep the diversity of the population when the fitness values are concentrated in the early iteration and avoid the premature convergence of the algorithm.
7. conclusion
We propose a method based on improved genetic algorithm to solve the multi-preference intelligent scheduling problem for supermarket employee scheduling. According to the experimental results, our proposed method converges faster and is not prone to precociousness, and compared with the existing algorithms and while maintaining a small computational complexity, it is able to obtain a lower average cost of the system.
References
[1]. DE C P, BERGHE G V. A categorisation of nurse rostering problems[J]. Journal of Scheduling, 2011, 14(1): 3-16.
[2]. YANG K, CAO S Q. Research on nurse scheduling model of operating room based on integer programming and transformation rule optimization algorithm[J]. Hospital Management Forum, 2020, 37(7): 65-68.
[3]. CHENG Y J, LUO L . A bank teller resilient scheduling model based on queuing theory and integer programming[J]. Chinese Journal of Management, 2010, 7(10): 1558-1565.
[4]. M’HALLAH R, ALKHABBAZ A. Scheduling of nurses: a case study of a kuwaiti health care unit[J]. Operations Research for Health Care, 2013, 2(1-2): 1-19.
[5]. CHEN Z P, LIU J, CHENG B. Probabilistic constraint programming model and effective solution of intelligent scheduling problem[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2010 , 27(6): 975-985.
[6]. SHEN Y D, SU G P. Constrained nurse scheduling model and optimization algorithm based on transformation rules[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2010, 32(7): 99-103.
[7]. SOTO R, CRAWFORD B, MONFROY E, et al. Nurse and paramedic rostering with constraint programming: a case study [J]. Romanian Journal of Information Science and Technology, 2013, 16(1): 52-64.
[8]. ANG C. Research on variable neighborhood search algorithm in personnel scheduling problem[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2013.
[9]. RAHIMIAN E, AKARTUNALI K, LEVINE J. A hybrid integer programming and variable neighbourhood search algorithm to solve nurse rostering problems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 258(2): 411-423.
[10]. LI J H, LI Y B. Civil aviation crew scheduling system based on genetic algorithm[J]. Software, 2013, 34(4): 38- 39.
Cite this article
Wang,R.;Cao,Z.;Chen,X.;Wan,C.;Yuan,Z.;Shi,L.;Yang,W.;Cao,Z.;Wang,H. (2024). Research on solving multi-preference intelligent scheduling problem based on improved genetic algorithm. Theoretical and Natural Science,56,1-11.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Applied Physics and Mathematical Modeling
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. DE C P, BERGHE G V. A categorisation of nurse rostering problems[J]. Journal of Scheduling, 2011, 14(1): 3-16.
[2]. YANG K, CAO S Q. Research on nurse scheduling model of operating room based on integer programming and transformation rule optimization algorithm[J]. Hospital Management Forum, 2020, 37(7): 65-68.
[3]. CHENG Y J, LUO L . A bank teller resilient scheduling model based on queuing theory and integer programming[J]. Chinese Journal of Management, 2010, 7(10): 1558-1565.
[4]. M’HALLAH R, ALKHABBAZ A. Scheduling of nurses: a case study of a kuwaiti health care unit[J]. Operations Research for Health Care, 2013, 2(1-2): 1-19.
[5]. CHEN Z P, LIU J, CHENG B. Probabilistic constraint programming model and effective solution of intelligent scheduling problem[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2010 , 27(6): 975-985.
[6]. SHEN Y D, SU G P. Constrained nurse scheduling model and optimization algorithm based on transformation rules[J]. Computer Engineering & Science, 2010, 32(7): 99-103.
[7]. SOTO R, CRAWFORD B, MONFROY E, et al. Nurse and paramedic rostering with constraint programming: a case study [J]. Romanian Journal of Information Science and Technology, 2013, 16(1): 52-64.
[8]. ANG C. Research on variable neighborhood search algorithm in personnel scheduling problem[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2013.
[9]. RAHIMIAN E, AKARTUNALI K, LEVINE J. A hybrid integer programming and variable neighbourhood search algorithm to solve nurse rostering problems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 258(2): 411-423.
[10]. LI J H, LI Y B. Civil aviation crew scheduling system based on genetic algorithm[J]. Software, 2013, 34(4): 38- 39.









