1. Introduction
Electromyography (EMG) is a powerful technique used to measure the electrical activity of muscles. By detecting the electrical signals produced by muscle contractions, EMG provides insights into muscle function and health. Surface electromyography (sEMG) is a non-invasive variant of EMG that involves placing electrodes on the skin surface above the muscle [1]. This method is widely used in various applications, from clinical diagnostics to interactive control systems[2].
By measuring muscle electrical activity through EMG, the working status of muscles can be monitored in real time, and assistive devices such as wheelchairs and prosthetics can be controlled to respond to user intentions and improve quality of life. Meanwhile, EMG sensors can be designed as small, lightweight wearable devices that do not require invasive operations. Intramuscular needle EMG electrodes are predominantly used to evaluate motor unit (MU) function but since it is a painful procedure, sEMG constitutes a good alternative, which is particularly important for fields such as medical research, rehabilitation, and sports science.
The integration of sEMG with microcontroller platforms like the Arduino Uno represents a significant advancement in the development of real-time control systems. The Arduino Uno, an open-source microcontroller, is known for its simplicity and affordability, making it an ideal platform for prototyping and implementing control systems (Arduino, 2023). This study explores the use of Arduino Uno in conjunction with sEMG electrodes to create a system that can control servo motors based on muscle activity, aiming to enhance assistive technologies and human-computer interaction devices.
Recent developments in microcontroller technology and sensor accuracy have expanded the potential applications of sEMG. Advances in wearable sensors and signal processing techniques have made it possible to develop more sophisticated and accessible control systems . This research builds on these advancements to explore the practical implementation of sEMG-based servo control, with a focus on improving the responsiveness and accuracy of the control system.
The use of EMG signals for device control has been a topic of extensive research demonstrated that EMG signals could control robotic arms, showing promising results in terms of accuracy and responsiveness[3]. Similarly, the use of sEMG for controlling virtual reality environments highlighted the versatility of sEMG in interactive applications[4].
Recent studies have addressed challenges related to signal quality and control precision. For example, reviewing advancements in wearable technology, noting improvements in sensor resolution and signal acquisition systems[5]. These advancements have facilitated more accurate and reliable EMG-based control systems. However, issues such as noise interference and data processing delays remain significant challenges that impact the performance of EMG-based systems.
The integration of advanced control algorithms has been proposed to enhance system performance, such as the use of PID controllers in various applications, including robotic control systems[6]. PID controllers, which adjust system output based on proportional, integral, and derivative feedback, offer a robust solution for maintaining control accuracy and stability. Incorporating such algorithms with sEMG-based systems could address some of the current limitations, improving overall system performance.
2. Methods
2.1. Hardware Setup
2.1.1. Arduino Uno and EMG Shield
The Arduino Uno serves as the central processing unit for the system, interfacing with the EMG shield to acquire and process muscle electrical signals. The EMG shield converts differential analog signals from the sEMG electrodes into single-ended analog outputs that the Arduino Uno can read. This setup allows for efficient data acquisition and processing. The EMG shield provides a convenient way to connect the sEMG electrodes and interface with the microcontroller, facilitating real-time signal processing.
2.1.2. Servo Motor
A standard servo motor was chosen for this study to demonstrate the servo control capabilities of the system. Connected to GPIO 3 on the Arduino Uno, the servo motor’s position was controlled based on RMS voltage values computed from the EMG signals. The use of a standard servo motor ensures that the system remains affordable and accessible while providing adequate performance for evaluating the proposed control mechanism.
2.2. Software Configuration
2.2.1. Arduino IDE Setup
The Arduino Integrated Development Environment (IDE) was used to program the Arduino Uno and configure the system for data acquisition and signal processing. The ElecGuru40 demo code, obtained from the Olimex store, provided a starting point for the experiments. The FlexiTimer2 library was also installed to enable precise timing and control of data acquisition tasks. This library is essential for handling high-frequency data sampling and processing, which is critical for accurate EMG signal analysis.
2.2.2. Signal Acquisition and Processing
To capture and process EMG signals, the Arduino IDE was configured to run the demo code in Figure 1, which initializes the data collection process. The initial experiments focused on measuring the amplitude and frequency of EMG signals under different hand postures. The BetterSerialPlotter tool was used to visualize the EMG signals, providing a more detailed view of signal variations and facilitating data analysis.
2.2.3. RMS Voltage Calculation
To calculate the root mean square (RMS) voltage of the EMG signals, the data packet transmission lines in Figure 2 were commented out. Custom code was added to compute RMS voltage values based on a set of 30 samples. These values were transmitted to the computer via serial communication for further analysis. RMS voltage is a key metric in evaluating muscle activity, providing a measure of signal strength that can be used for controlling external devices.
2.2.4. Servo Control Implementation
The Servo.h library was included in the Arduino code to control the servo motor. A servo object was created and attached to GPIO 3. The position of the servo motor was adjusted based on the computed RMS voltage values. This integration in Figure 3 allows for precise control of the servo motor, enabling real-time adjustment of its position in response to changes in muscle activity.
2.3. Data Acquisition and Processing
2.3.1. Signal Acquisition
The EMG electrodes were placed on the forearm of the subject to measure muscle electrical activity during hand movements. The green and red electrodes were positioned on areas with high muscle activity, while the yellow electrode served as a reference. Data were collected while the subject performed hand opening and closing movements, allowing for analysis of signal variations associated with different muscle states.
2.3.2. Signal Processing
The raw EMG signals were processed to remove noise and artifacts. Low-pass filters were used to eliminate high-frequency noise, while smoothing techniques were applied to reduce signal fluctuations. The processed signals were analyzed to compute RMS voltage values, which reflect the overall muscle activity. Signal processing is crucial for ensuring accurate measurement and interpretation of EMG signals, as it helps to eliminate interference and improve signal quality.
2.4. Comparison of differences between China and foreign countries
The question of whether there are differences in electromyography (EMG) signals between individuals from China and those from other parts of the world is a complex one. Collect data of five Chinese people and five white people of the same body size and age, measure and compare their EMG signals and motor rotation amplitude respectively.
3. Results
The EMG signals in Figure 4 displayed distinct patterns corresponding to different hand postures. During hand opening, the amplitude of the signals increased, reflecting higher muscle activity. Conversely, during hand closing, the amplitude decreased. These observations validate the hypothesis that sEMG signals can differentiate between various muscle states. The ability to accurately measure and interpret muscle activity is essential for developing effective control systems.
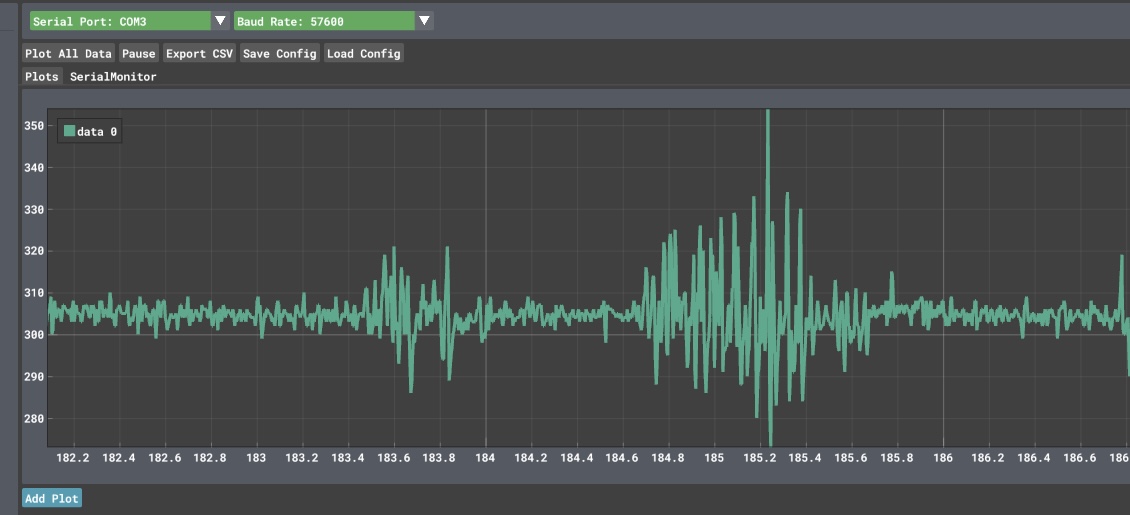
Figure 4: the amplitude and frequency of EMG signals under different hand postures
The RMS voltage values in Table 1 calculated from the EMG signals showed clear variations based on hand posture. When the hand was open, the RMS voltage was approximately 0.000874V. When the hand was closed, the RMS voltage was around 0.000883V. These values are consistent with expected changes in muscle activity and confirm the system’s ability to accurately reflect muscle state changes. The RMS voltage values provide a quantitative measure of muscle activity, which is used to control the servo motor.
Table 1: the root mean square (RMS) voltage of the EMG signals
RMS voltage when the hand was opened | RMS voltage when the hand was closed |
0.000875 | 0.000881 |
0.000876 | 0.000910 |
0.000875 | 0.000880 |
0.000873 | 0.000893 |
0.000875 | 0.000902 |
0.000874 | 0.000881 |
0.000873 | 0.000904 |
The servo motor responded accurately to changes in RMS voltage values. When the hand was opened, the servo motor’s position approached 180 degrees, while during hand closing, it moved towards 0 degrees. This responsiveness demonstrates that the servo control system effectively mirrors hand movements, indicating successful implementation of the EMG-based control mechanism. The ability to control mechanical devices based on muscle activity highlights the practical application of the system in assistive technologies and human-computer interaction.
To contextualize the findings, it is useful to compare this system with other EMG-based control systems. Studies such as those by Doud et al.[3]and Choi et al.[4] have employed more complex setups and algorithms. This work provides a simpler and more cost-effective alternative, suitable for applications where high precision and advanced control are not critical.
The China and foreign difference experiment showed that in the case of similar age and body size, when opening and closing the hand, the majority of white people (4/5) had a larger frequency and amplitude of EMG and a higher RMS voltage, resulting in a larger rotation amplitude of the servo motor. For different experimental results, it may be due to biological variability, muscle development size, health status, and small sample size.
Table 2: Comparison of different races
Race | RMS voltage(open) | Servo motor amplitude (degree) |
Chinese 1/White 1 | 0.000874/0.000879 | 169/171 |
Chinese 2/White 2 | 0.000871/0.000867 | 166/163 |
Chinese 3/White 3 | 0.000863/0.000881 | 161/175 |
Chinese 4/White 4 | 0.000877/0.000891 | 171/180 |
Chinese 5/White 5 | 0.000872/0.000904 | 167/180 |
4. Discussion
The results confirm the effectiveness of using EMG signals for servo control. The system successfully reflects hand movements in real-time, demonstrating its potential for applications in prosthetics and rehabilitation. By translating muscle activity into control signals for mechanical devices, the system offers a practical solution for adaptive control in various fields. However, several areas for improvement have been identified:
Signal Quality Enhancement and noise reduction: The integration of high-pass filters alongside low-pass filters could further improve signal quality by reducing high-frequency noise. High-pass filters can eliminate unwanted high-frequency components, while low-pass filters can reduce low-frequency noise. Combining these filters would enhance the accuracy of the EMG signal measurements and improve overall system performance.
In addition to filtering, employing advanced noise reduction techniques, such as adaptive filtering or wavelet transform, could further improve signal clarity. Adaptive filtering adjusts the filter parameters dynamically based on the signal characteristics, while wavelet transform provides a multi-resolution analysis that can isolate noise from the actual signal.
Advanced Signal Processing: The current signal processing approach involves basic filtering and smoothing techniques. Future research could explore more advanced signal processing methods, such as principal component analysis (PCA) or independent component analysis (ICA). PCA reduces the dimensionality of the data, which can help in identifying significant features of the EMG signals. ICA separates mixed signals into independent components, potentially isolating useful information from artifacts. These techniques can enhance the accuracy of signal interpretation and improve the performance of the control system.
PID Controller Integration: Incorporating a PID controller could provide smoother control of the servo motor, reducing overshoot and improving response time. PID controllers are known for their ability to maintain system stability and improve performance by adjusting output based on proportional, integral, and derivative feedback. Integrating a PID controller could enhance the precision and responsiveness of the servo motor control, making the system more effective in practical applications.
Future research could focus on several key areas:
Integration of Machine Learning: Exploring machine learning algorithms to enhance signal processing and control strategies could significantly improve system performance and adaptability.
Extended Applications: Expanding the system to include additional sensors and actuators could broaden its applications, including more complex prosthetic devices and interactive rehabilitation systems.
User Studies: Conducting user studies to gather feedback from individuals using the system in real-world scenarios could provide valuable insights into its usability and effectiveness.
Long-Term Testing: Implementing long-term testing to assess the system's durability and reliability over extended periods would help validate its practicality for daily use.
5. Conclusion
This thesis introduces a novel method using Arduino Uno and surface electromyography (sEMG) electrodes for muscle signal measurement and servo control. The results validate the effectiveness of sEMG in controlling mechanical devices based on muscle activity, highlighting its potential in biomedical engineering and assistive technologies.
The system demonstrated precise measurement of sEMG signals, with RMS voltage values of approximately 0.000874V when the hand was open and 0.000883 V when closed, reflecting accurate muscle state changes. The servo motor's responsive adjustment from 0 to 180 degrees, based on these RMS values, showcases the practical application of sEMG for real-time control in prosthetics and rehabilitation. This approach offers significant advancements in adaptive device technology.
The EMG-based servo control system has significant potential in various fields, including rehabilitation medicine, prosthetic control, and human-computer interaction. Future research could explore integrating more advanced signal processing techniques and control algorithms to enhance system capabilities. Expanding the system to include additional sensors and actuators could further extend its applications and improve its functionality.
References
[1]. Hermens, H. J., Freriks, B., & Merletti, R. (2000). European Recommendations for Surface Electromyography. Roessingh Research and Development, 1(2), 11-33.
[2]. Hogrel, J. Y. (2005). Surface electromyography in the assessment of muscle function: Theoretical and clinical aspects. Muscle & Nerve, 32(5), 506-515.
[3]. Doud, A. J., He, B., & Liu, J. (2012). EMG-based control of a robotic arm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 20(2), 139-148.
[4]. Choi, J., Lee, H., & Park, K. (2014). EMG-based control of a virtual reality environment. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development, 51(7), 105-114.
[5]. Zhao, J., Zhang, X., & Wang, L. (2020). Advances in wearable technology for EMG signal acquisition and processing. Sensors, 20(15), 4156.
[6]. Hsu, S. H., Liu, Y. Y., & Wu, T. L. (2015). PID control strategy for robotic applications. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 61(3), 52-60.
Cite this article
Liu,W. (2025). Using Arduino Uno and EMG Electrodes for Electromyographic Signal Measurement and Servo Control. Theoretical and Natural Science,86,37-44.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Hermens, H. J., Freriks, B., & Merletti, R. (2000). European Recommendations for Surface Electromyography. Roessingh Research and Development, 1(2), 11-33.
[2]. Hogrel, J. Y. (2005). Surface electromyography in the assessment of muscle function: Theoretical and clinical aspects. Muscle & Nerve, 32(5), 506-515.
[3]. Doud, A. J., He, B., & Liu, J. (2012). EMG-based control of a robotic arm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 20(2), 139-148.
[4]. Choi, J., Lee, H., & Park, K. (2014). EMG-based control of a virtual reality environment. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development, 51(7), 105-114.
[5]. Zhao, J., Zhang, X., & Wang, L. (2020). Advances in wearable technology for EMG signal acquisition and processing. Sensors, 20(15), 4156.
[6]. Hsu, S. H., Liu, Y. Y., & Wu, T. L. (2015). PID control strategy for robotic applications. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 61(3), 52-60.









