1.Introduction
A sensor is a device used to recognize properties from the environment it is in and convert them into electricity [1]. A biosensor is a specialized type of sensor that monitors biological processes and translates them into electronic outputs [2]. Biosensors consist of several critical components: the analyte (the substance being measured), the bioreceptor (which identifies the analyte), the transducer (which converts the bioreceptor’s response into a measurable signal), the electronics (which process and refine the signal), and the display (which presents the results to the user) [2].
Quantum dots (QDs) are a class of zero-dimensional (0D) nanomaterials, characterized by their extremely small dimensions, typically between 2 and 10 nanometers in diameter [2], [3]. They have been widely used in biosensors [2]. When light hits them, quantum dots emit fluorescence using bandgap energy [4]. This energy moves an electron to a higher energy level and releases light when the electron goes back to its original state. Sensors can detect changes in the light while the QDs respond to the analyte [5]. A QD's size affects its color [4].
QDs are sometimes made of heavy metals [6]. However, they could harm organisms [4]. Because of this, carbon and graphene QDs are used [4]. In addition to being less toxic, they dissolve better and are more versatile [4]. Compared to traditional fluorophores, quantum dots have many advantages in biosensor use, including decreased photobleaching, larger size, and increased sensitivity [7].
This paper aims to review quantum dots-based biosensors’ parts and applications, making the large amount of information on QD-based biosensors within reach. This provides researchers with knowledge that they can use to make improved biosensors.
2.Working Principles and Components of Quantum Dot Biosensors
The synthesis of quantum dots (QDs) can be achieved through two main approaches: top-down and bottom-up [8]. In a top-down approach, a large piece is broken into smaller pieces, making quantum dots. In a bottom-up approach, minuscule molecules form the quantum dots [8].
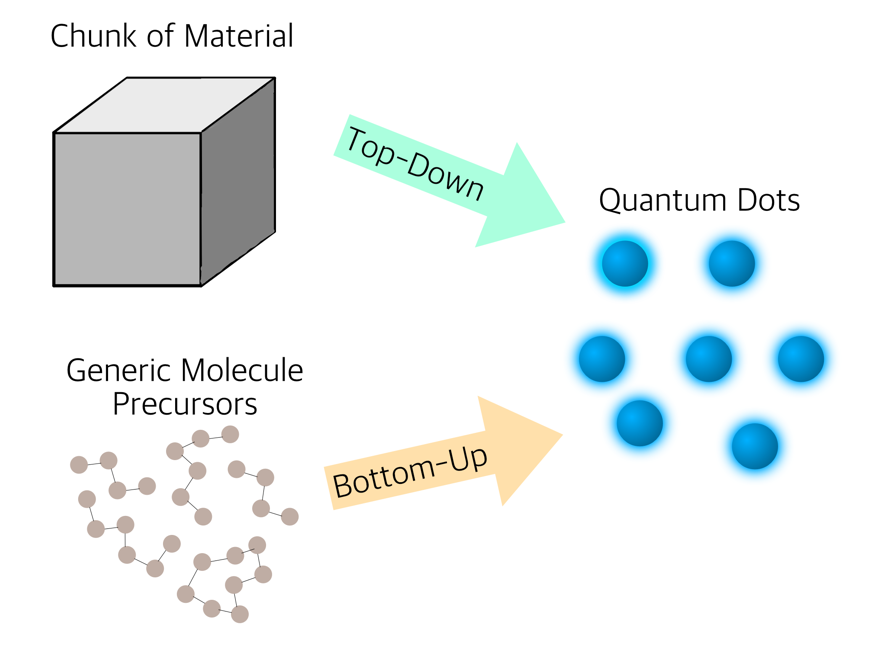
Figure 1: Top-down vs. bottom-up synthesis of quantum dots [8].
2.1.Bottom-Up Synthesis
One example of a bottom-up approach is deposition, where chemical reactions at high temperatures result in the formation of QDs on a substrate’s surface [9]. Another bottom-up approach is the solvothermal method [9]. Sustainable biomass goes through various reactions while intensely pressurized and heated, forming QDs made out of carbon.
2.2.Top-Down Synthesis
One example of a top-down approach is laser ablation [8]. A high-energy laser breaks down metal or crystals into quantum dots. Other top-down methods include chemical ablation, in which a large chunk is oxidized and broken down into QDs [9].
2.3.Functionalization of the Bioreceptor
Once QDs are synthesized, they must be functionalized to bind to specific analytes. Examples include molecularly imprinted polymers, aptamers, and antibodies [10]. These many options are an advantage of quantum dots because they can be customized depending on what the biosensor will be used for.
Molecularly imprinted polymers are monomers that become polymers, organized in a way that allows them to attach to a particular analyte [10]. Aptamers are nucleic acids with one strand [10]. They are excellent for putting in sensors because they are less likely to result in an immune response, cheap, long-lasting, and simple to alter. They also have a great binding affinity. Antibodies can bind to antigens [10]. Their advantages include high sensitivity, not being susceptible to interference, and adaptability.
2.4.Transducer
Quantum dots are both bioreceptors and transducers. As mentioned before, the analyte affects the fluorescence of the QD, which can then be detected [2], [5]. In other words, the quantum dots change their signal from the analyte to a light signal that can be sensed.
2.5.Power Source
Traditional quantum dot biosensors rely on an external light source to excite QDs, initiating fluorescence [11]. Currently, there are QD sensors without power sources. Li et al. created an exceptionally thin (just 40 nanometers) quantum dot sensor for people to wear and measure their heart rate [12]. It powered itself using the photovoltaic effect. To prevent people from being harmed by toxicity, the sensor used quantum dots that didn’t contain heavy metals. The resulting sensor had extremely good specific detectivity and was very flexible physically [12].
3.Applications
Quantum dot biosensors have a wide variety of purposes. Each of the following QD biosensors were better than traditional methods.
3.1.Cancer Detection
Cui et al. created a quantum dot biosensor that detected circulated tumor cells (CTCs) [13]. This is important because cancer can put CTCs into the blood and metastasize (spread throughout the body). Past methods took a lot of time and were costly. By attaching aptamers to the dots, the sensor could find cell-surface epithelial cell adhesion molecules, which are related to CTCs. It could detect CTCs in just 15 minutes and was very sensitive [13].
Liu et al. constructed a QD biosensor that indirectly detected cancer [14]. It looked for the Pax-5 gene, which is linked to acute lymphoblastic leukemia. They used a dual-signal sensor to decrease the effect of other substances. They made the dots utilizing molybdenum disulfide and altered them using zinc. They tested it on human serum, and the sensor performed well. It had a detection limit of 0.52 pM [14].
Kalkal et al. made a QD biosensor to detect small cell lung cancer (SCLC) [15]. SCLC is a type of cancer that is challenging to cure and metastasizes quickly. Specifically, the sensor detected neuron-specific enolase, which is found in larger amounts in people with SCLC. Previous sensors used organic dyes, which are harmful and can lose their fluorescence after being exposed to light. They used gold nanoparticles and graphene quantum dots in the sensor. They tested it on serum from a human in good health. The sensor was very sensitive (0.09 pg mL-1), quick (16 minutes), and selective [15].
Liu et al. built an optical QD biosensor to detect breast cancer [16]. Patients with breast cancer, as well as many other cancers, have different activity of methyltransferase like 14 protein and methyltransferase like 3 proteins (METTL3/14). Traditional options were too expensive and not specific enough or used hazardous substances. The sensor was selective because the authors tested its detection of METTL3/14 while there were pollutants. Then, they tested the sensor on breast tissue, and it could distinguish between healthy and cancerous tissue. Its limit of detection was 3.11*10-17 M [16].
3.2.Coronavirus Detection
SARS-Cov-2, more commonly known as COVID-19, resulted in a pandemic that affected many people across the world [17]. Prior methods of detection were not sensitive enough or too expensive and complicated [17].
Zhang et al. created the first quantum dot sensor for detecting SARS-CoV-2 [17]. It worked by detecting a gene on SARS-CoV-2. They tested it on various clinical samples. It took less than an hour to sense the protein and could distinguish coronavirus from other illnesses. Additionally, it was very cheap, with one test costing under $1.50. Its detection limit was 1 virus/mL. The sensor could be stored at room temperature for at least three months [17].
A few years later, Wu et al. built a quantum dot biosensor for sensing a SARS-Cov-2 protein [18]. Unlike the other sensor, they used an aptamer and an antibody in the sensor and made it water soluble by adding a coreactant. They tested it on real human serum. Its detection limit was 3.0 picogram/ mL-1, and it was reproducible and not easily affected by interference. The sensor could be stored at 4 degrees Celsius for a minimum of a month [18].
3.3.Tuberculosis Detection
Bakhori et al. manufactured a sensor to detect Mycobacterium Tuberculosis using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots and nanoparticles [19]. Detecting these bacteria is crucial because it causes tuberculosis, the top killer amidst bacterial infections. These nanomaterials allowed the sensor to be more specific and sensitive, with a detection limit of 1.5 * 10-10 g/mL. It had high reproducibility [19].
3.4.Salmonella Detection
Ding et al. made an optical QD biosensor to detect Salmonella in milk [20]. Salmonella is a foodborne bacterium that harms humans if ingested. Previous methods had various disadvantages such as causing false negatives, requiring a lot of time, or being high-priced. They connected the dots to poly-L-lysine, resulting in a sensor that detected Salmonella 10 times superior to a previous method. Specifically, its limit of detection was 4.9 * 103 cfu/mL. Also, it only took an hour to detect Salmonella. [20].
4.Environmental Effects
Despite the numerous advantages of quantum dot-based biosensors, their environmental impact remains a significant concern. Quantum dots can enter the environment at various stages of their lifecycle [21]. During synthesis, large amounts of chemical waste are generated [21]. While being moved, they could be damaged. Also, when people use the QDs, they could be released, but fewer QDs will enter the environment because of sensors compared to packaging and other uses. After their life cycle, they could end up in landfills, releasing metals. They could also be burned, going to the atmosphere and creating extremely harmful waste. Even if they are recycled, people might be harmed by toxic metals in the QDs, especially in developing countries with fewer safety laws [21].
After entering the environment, QDs can go into organisms [21]. They can harm their DNA, immune system, and reproduction [21]. QDs can also decrease growth and cause deformities in descendants [21]. For example, Li et al. conducted a study on the effects of carbon quantum dots on organisms in saltwater. They found that Phaeodactylum tricornutum, an autotroph, completely stopped getting bigger when exposed to CQDs at a concentration of 500 mg/L. At 100 mg/L, it got larger by 81.11% less than the control [22].
Recently in March of 2024, the European Commission made a decision about cadmium quantum dots in displays and lights. They made a exception for putting cadmium in QDs in LED chips in displays and rejected two other proposals [23]. By decreasing motivation, this could hinder future progress of synthesizing more environmentally-friendly quantum dots to replace cadmium.
5.Future Directions
This section explores the future directions of quantum dot-based biosensors, focusing on material advancements, sustainability, and emerging applications.
5.1.Carbon Quantum Dots
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) are expected to play a larger role in the development of biosensors due to their numerous advantages. Those advantages will improve biosensors because heavy metal QDs need to be covered with a shell that harms the specificity of the sensor by making the QDs bigger [9]. It will also make sensors less dangerous to people’s health since CQDs are less harmful than heavy metal QDs [9]. Additionally, CQDs are cheaper, allowing more sensors to integrate quantum dots into their designs [9]. Their improved solubility and versatility [4] could also improve sensors.
5.2.Environmental Sustainability
Future advancements in QD synthesis are likely to prioritize environmental sustainability. One promising method is hydrothermal synthesis, in which eco-friendly precursors are dissolved in water, followed by heating and pressurization at relatively low temperatures to produce CQDs [24]. This is very similar to the solvothermal method, another environmentally-friendly approach that was mentioned before, but it uses water instead of other solvents [9], [24], [25].
Zhao et al. created quantum dots employing the hydrothermal method. They used orange peel as the precursor. The resulting QDs were blue with excitation and emission wavelengths of 370 nm and 440 nm, respectively. Then, they used them in a sensor to detect folic acid, iron, and calcium [26].
Another technique is microwave-assisted synthesis [24]. Environmentally safe precursors undergo reactions caused by microwave radiation. This method has less energy usage and harmful waste. It is also quicker and can be used to make QDs in large quantities [24].
Yalshetti et al. used the microwave-assisted synthesis method to make carbon quantum dots from Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaves. The dots helped treat wounds, prevented inflammation, and were not toxic, so they could be used for biomedical purposes [27].
Quantum dots have also been synthesized in microorganisms [24]. The CQDs’ properties can be adjusted by changing the organisms’ environment. This method uses eco-friendly precursors, consumes less energy, and doesn’t create a lot of harmful byproducts [24].
5.3.Applications in Emerging Fields
In the future, there will be more quantum dot-based biosensors. The line in Figure 2 is going up, showing that the field is expanding. In 2000, there were just 80 results. In 2010, that number increased to 2,480. In 2024, there were 17,600 papers.
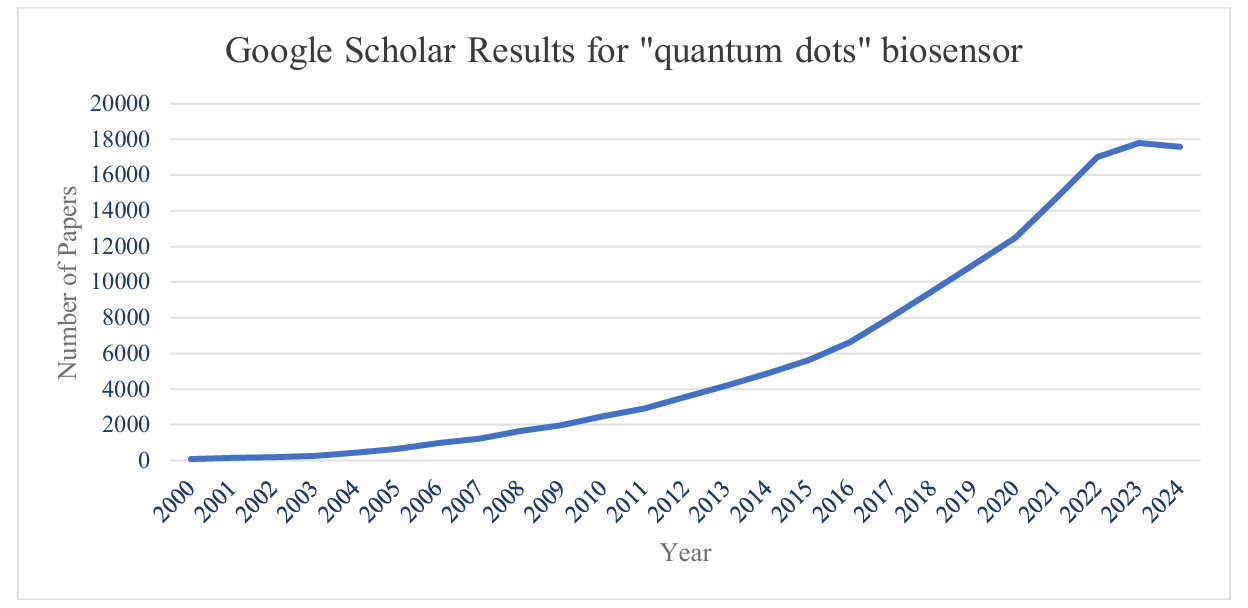
Figure 2: The quantity of search results using “‘quantum dots’ biosensor” by year.
New quantum dots-based biosensors can integrate AI to analyze data, automating the process and improving the biosensors. In the future, QD biosensors could be used more and applied for new purposes.
6.Conclusion
Quantum dots can be used in biosensors since they release light. They can be synthesized using a top-down or a bottom-up method. Then, they need to be completed by adding a bioreceptor. QD biosensors also need a power source to work.
Quantum dots have been applied in biosensors to detect numerous analytes. Some QD sensors can sense cancer and markers of cancer, while others can identify coronavirus. They have also been used to detect tuberculosis and salmonella. These many uses show potential for future biosensors that can detect other analytes. However, quantum dots can enter the environment and harm living things.
The development of carbon quantum dots offers a safer and more sustainable alternative to traditional QDs. Advancements in green synthesis methods, such as hydrothermal and microwave-assisted techniques, are addressing environmental concerns while enhancing scalability. The continued expansion of QD-based biosensors highlights their growing significance in healthcare, environmental monitoring, and beyond.
References
[1]. Javaid, M., Haleem, A., Rab, S., Pratap Singh, R., & Suman, R. (2021). Sensors for daily life: A review. Sensors International, 2, 100121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sintl.2021.100121
[2]. Naresh, Varnakavi., & Lee, N. (2021). A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors, 21(4), 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041109
[3]. Yang, F., Jin, C., Subedi, S., Lee, C. L., Wang, Q., Jiang, Y., Li, J., Di, Y., & Fu, D. (2012). Emerging inorganic nanomaterials for pancreatic cancer diagnosis and treatment. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 38(6), 566–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.02.003
[4]. Jessy Mercy, D., Girigoswami, K., & Girigoswami, A. (2024). A mini review on biosensor advancements-emphasis on quantum dots. Results in Chemistry, 7, 101271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2023.101271
[5]. Safari, M. (2023). Recent Advances in Quantum Dots-Based Biosensors. In J. Thirumalai (Ed.), Quantum Dots—Recent Advances, New Perspectives and Contemporary Applications. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.108205
[6]. Maxwell, T., Nogueira Campos, M. G., Smith, S., Doomra, M., Thwin, Z., & Santra, S. (2020). Quantum Dots. In Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications (pp. 243–265). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816662-8.00015-1
[7]. Sapsford, K. E., Pons, T., Medintz, I. L., & Mattoussi, H. (2006). Biosensing with Luminescent Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Sensors, 6(8), 925–953. https://doi.org/10.3390/s6080925
[8]. Joglekar, P. V., Mandalkar, D. J., Nikam, M. A., Pande, N. S., & Dubal, A. (2019). Review article on Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Application. International Journal of Research in Advent Technology. https://www.ijrat.org/downloads/Vol-7/jan-2019/Paper%20ID-712019113.pdf
[9]. Pourmadadi, M., Rahmani, E., Rajabzadeh-Khosroshahi, M., Samadi, A., Behzadmehr, R., Rahdar, A., & Ferreira, L. F. R. (2023). Properties and application of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) in biosensors for disease detection: A comprehensive review. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 80, 104156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104156
[10]. Ding, R., Chen, Y., Wang, Q., Wu, Z., Zhang, X., Li, B., & Lin, L. (2022). Recent advances in quantum dots-based biosensors for antibiotics detection. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 12(3), 355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2021.08.002
[11]. Sapsford, K. E., Pons, T., Medintz, I. L., & Mattoussi, H. (2006). Biosensing with Luminescent Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Sensors, 6(8), 925–953. https://doi.org/10.3390/s6080925
[12]. Li, S., Jang, J. H., Chung, W., Seung, H., Park, S. I., Ma, H., Pyo, W. J., Choi, C., Chung, D. S., Kim, D.-H., Choi, M. K., & Yang, J. (2023). Ultrathin Self-Powered Heavy-Metal-Free Cu–In–Se Quantum Dot Photodetectors for Wearable Health Monitoring. ACS Nano, 17(20), 20013–20023. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c05178
[13]. Cui, F., Ji, J., Sun, J., Wang, J., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Ding, H., Lu, Y., Xu, D., & Sun, X. (2019). A novel magnetic fluorescent biosensor based on graphene quantum dots for rapid, efficient, and sensitive separation and detection of circulating tumor cells. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 411(5), 985–995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1501-0
[14]. Liu, J., Chen, J., Zhou, C., & Su, X. (2025). Dual-signal biosensor based on G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme and zinc-doped molybdenum disulfide quantum dots for ultrasensitive detection of tumor biomarker. Talanta, 283, 127179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2024.127179
[15]. Kalkal, A., Pradhan, R., Kadian, S., Manik, G., & Packirisamy, G. (2020). Biofunctionalized Graphene Quantum Dots Based Fluorescent Biosensor toward Efficient Detection of Small Cell Lung Cancer. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 3(8), 4922–4932. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c00427
[16]. Liu, M., Yu, W., Zhao, N., Qiu, J.-G., Jiang, B.-H., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, C. (2023). Development of a N6-methyladenosine-directed single quantum dot-based biosensor for sensitive detection of METTL3/14 complex activity in breast cancer tissues. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1279, 341796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2023.341796
[17]. Zhang, Q., Li, J., Li, Y., Tan, G., Sun, M., Shan, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Song, K., Shi, R., Huang, L., Liu, F., Yi, Y., & Wu, X. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 detection using quantum dot fluorescence immunochromatography combined with isothermal amplification and CRISPR/Cas13a. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 202, 113978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.113978
[18]. Wu, P., Zhang, L., Zhang, G., Cheng, L., Zhang, F., Li, Y., Lei, Y., Qi, H., Zhang, C., & Gao, Q. (2024). Highly Sensitive Electrochemiluminescence Biosensing Method for SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Incorporating the Micelle Probes of Quantum Dots and Dibenzoyl Peroxide Using the Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode Modified with a Carboxyl-Functionalized Graphene. Analytical Chemistry, 96(43), 17345–17352. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.4c04024
[19]. Mohd Bakhori, N., Yusof, N. A., Abdullah, J., Wasoh, H., Ab Rahman, S. K., & Abd Rahman, S. F. (2019). Surface Enhanced CdSe/ZnS QD/SiNP Electrochemical Immunosensor for the Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis by Combination of CFP10-ESAT6 for Better Diagnostic Specificity. Materials, 13(1), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010149
[20]. Ding, S., Hu, H., Yue, X., Feng, K., Gao, X., Dong, Q., Yang, M., Tamer, U., Huang, G., & Zhang, J. (2022). A fluorescent biosensor based on quantum dot–labeled streptavidin and poly-l-lysine for the rapid detection of Salmonella in milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 105(4), 2895–2907. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2021-21229
[21]. Giroux, M. S., Zahra, Z., Salawu, O. A., Burgess, R. M., Ho, K. T., & Adeleye, A. S. (2022). Assessing the environmental effects related to quantum dot structure, function, synthesis and exposure. Environmental Science: Nano, 9(3), 867–910. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00712B
[22]. Li, X., Chen, C. C., Wu, L., Zhou, J., Huang, Y., & Zhu, X. (2024). Neglected negative effect of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) entering the ocean on marine organisms living in different water layers. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 199, 115921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115921
[23]. European Commission. (2024, March 23). Commission Delegated Directive (EU) of 13.3.2024 amending Directive 2011/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards an exemption for cadmium in downshifting quantum dots directly deposited LED semiconductor chips. https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/13468-Hazardous-substances-in-electrical-and-electronic-equipment-exemption-for-cadmium-in-quantum-dots-for-LED-applications_en
[24]. Saadh, M. J., Al-dolaimy, F., Alamir, H. T. A., Kadhim, O., Al-Abdeen, S. H. Z., Sattar, R., Jabbar, A. M., Kadhem Abid, M., Jetti, R., Alawadi, A., & Alsalamy, A. (2024). Emerging pathways in environmentally friendly synthesis of carbon-based quantum dots for exploring antibacterial resistance. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 161, 112012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.112012
[25]. Feng, S., & Guanghua, L. (2011). Hydrothermal and Solvothermal Syntheses. In Modern Inorganic Synthetic Chemistry (pp. 63–95). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53599-3.10004-6
[26]. Zhao, Q., Mao, H.-H., Xue, M., Feng, X.-Z., Han, G.-C., Chen, Z., & Kraatz, H.-B. (2023). One-pot synthesis of environmentally-friendly carbon quantum dots for “on-off” rapid fluorescent sensing of folic acid, Fe3+, and Ca2+. Journal of Luminescence, 263, 120091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2023.120091.
[27]. Yalshetti, S., Thokchom, B., Bhavi, S. M., Singh, S. R., Patil, S. R., Harini, B. P., Sillanpää, M., Manjunatha, J. G., Srinath, B. S., & Yarajarla, R. B. (2024). Microwave-assisted synthesis, characterization and in vitro biomedical applications of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Linn.-mediated carbon quantum dots. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 9915. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60726-y
Cite this article
Zhao,A. (2025). Review of Quantum Dots-Based Biosensor Systems: Construction and Applications. Theoretical and Natural Science,98,16-23.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Javaid, M., Haleem, A., Rab, S., Pratap Singh, R., & Suman, R. (2021). Sensors for daily life: A review. Sensors International, 2, 100121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sintl.2021.100121
[2]. Naresh, Varnakavi., & Lee, N. (2021). A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors, 21(4), 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21041109
[3]. Yang, F., Jin, C., Subedi, S., Lee, C. L., Wang, Q., Jiang, Y., Li, J., Di, Y., & Fu, D. (2012). Emerging inorganic nanomaterials for pancreatic cancer diagnosis and treatment. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 38(6), 566–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.02.003
[4]. Jessy Mercy, D., Girigoswami, K., & Girigoswami, A. (2024). A mini review on biosensor advancements-emphasis on quantum dots. Results in Chemistry, 7, 101271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2023.101271
[5]. Safari, M. (2023). Recent Advances in Quantum Dots-Based Biosensors. In J. Thirumalai (Ed.), Quantum Dots—Recent Advances, New Perspectives and Contemporary Applications. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.108205
[6]. Maxwell, T., Nogueira Campos, M. G., Smith, S., Doomra, M., Thwin, Z., & Santra, S. (2020). Quantum Dots. In Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications (pp. 243–265). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816662-8.00015-1
[7]. Sapsford, K. E., Pons, T., Medintz, I. L., & Mattoussi, H. (2006). Biosensing with Luminescent Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Sensors, 6(8), 925–953. https://doi.org/10.3390/s6080925
[8]. Joglekar, P. V., Mandalkar, D. J., Nikam, M. A., Pande, N. S., & Dubal, A. (2019). Review article on Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Application. International Journal of Research in Advent Technology. https://www.ijrat.org/downloads/Vol-7/jan-2019/Paper%20ID-712019113.pdf
[9]. Pourmadadi, M., Rahmani, E., Rajabzadeh-Khosroshahi, M., Samadi, A., Behzadmehr, R., Rahdar, A., & Ferreira, L. F. R. (2023). Properties and application of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) in biosensors for disease detection: A comprehensive review. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 80, 104156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104156
[10]. Ding, R., Chen, Y., Wang, Q., Wu, Z., Zhang, X., Li, B., & Lin, L. (2022). Recent advances in quantum dots-based biosensors for antibiotics detection. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 12(3), 355–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2021.08.002
[11]. Sapsford, K. E., Pons, T., Medintz, I. L., & Mattoussi, H. (2006). Biosensing with Luminescent Semiconductor Quantum Dots. Sensors, 6(8), 925–953. https://doi.org/10.3390/s6080925
[12]. Li, S., Jang, J. H., Chung, W., Seung, H., Park, S. I., Ma, H., Pyo, W. J., Choi, C., Chung, D. S., Kim, D.-H., Choi, M. K., & Yang, J. (2023). Ultrathin Self-Powered Heavy-Metal-Free Cu–In–Se Quantum Dot Photodetectors for Wearable Health Monitoring. ACS Nano, 17(20), 20013–20023. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c05178
[13]. Cui, F., Ji, J., Sun, J., Wang, J., Wang, H., Zhang, Y., Ding, H., Lu, Y., Xu, D., & Sun, X. (2019). A novel magnetic fluorescent biosensor based on graphene quantum dots for rapid, efficient, and sensitive separation and detection of circulating tumor cells. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 411(5), 985–995. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1501-0
[14]. Liu, J., Chen, J., Zhou, C., & Su, X. (2025). Dual-signal biosensor based on G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme and zinc-doped molybdenum disulfide quantum dots for ultrasensitive detection of tumor biomarker. Talanta, 283, 127179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2024.127179
[15]. Kalkal, A., Pradhan, R., Kadian, S., Manik, G., & Packirisamy, G. (2020). Biofunctionalized Graphene Quantum Dots Based Fluorescent Biosensor toward Efficient Detection of Small Cell Lung Cancer. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 3(8), 4922–4932. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.0c00427
[16]. Liu, M., Yu, W., Zhao, N., Qiu, J.-G., Jiang, B.-H., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, C. (2023). Development of a N6-methyladenosine-directed single quantum dot-based biosensor for sensitive detection of METTL3/14 complex activity in breast cancer tissues. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1279, 341796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2023.341796
[17]. Zhang, Q., Li, J., Li, Y., Tan, G., Sun, M., Shan, Y., Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Song, K., Shi, R., Huang, L., Liu, F., Yi, Y., & Wu, X. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 detection using quantum dot fluorescence immunochromatography combined with isothermal amplification and CRISPR/Cas13a. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 202, 113978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.113978
[18]. Wu, P., Zhang, L., Zhang, G., Cheng, L., Zhang, F., Li, Y., Lei, Y., Qi, H., Zhang, C., & Gao, Q. (2024). Highly Sensitive Electrochemiluminescence Biosensing Method for SARS-CoV-2 N Protein Incorporating the Micelle Probes of Quantum Dots and Dibenzoyl Peroxide Using the Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode Modified with a Carboxyl-Functionalized Graphene. Analytical Chemistry, 96(43), 17345–17352. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.4c04024
[19]. Mohd Bakhori, N., Yusof, N. A., Abdullah, J., Wasoh, H., Ab Rahman, S. K., & Abd Rahman, S. F. (2019). Surface Enhanced CdSe/ZnS QD/SiNP Electrochemical Immunosensor for the Detection of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis by Combination of CFP10-ESAT6 for Better Diagnostic Specificity. Materials, 13(1), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010149
[20]. Ding, S., Hu, H., Yue, X., Feng, K., Gao, X., Dong, Q., Yang, M., Tamer, U., Huang, G., & Zhang, J. (2022). A fluorescent biosensor based on quantum dot–labeled streptavidin and poly-l-lysine for the rapid detection of Salmonella in milk. Journal of Dairy Science, 105(4), 2895–2907. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2021-21229
[21]. Giroux, M. S., Zahra, Z., Salawu, O. A., Burgess, R. M., Ho, K. T., & Adeleye, A. S. (2022). Assessing the environmental effects related to quantum dot structure, function, synthesis and exposure. Environmental Science: Nano, 9(3), 867–910. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EN00712B
[22]. Li, X., Chen, C. C., Wu, L., Zhou, J., Huang, Y., & Zhu, X. (2024). Neglected negative effect of carbon quantum dots (CQDs) entering the ocean on marine organisms living in different water layers. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 199, 115921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115921
[23]. European Commission. (2024, March 23). Commission Delegated Directive (EU) of 13.3.2024 amending Directive 2011/65/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards an exemption for cadmium in downshifting quantum dots directly deposited LED semiconductor chips. https://ec.europa.eu/info/law/better-regulation/have-your-say/initiatives/13468-Hazardous-substances-in-electrical-and-electronic-equipment-exemption-for-cadmium-in-quantum-dots-for-LED-applications_en
[24]. Saadh, M. J., Al-dolaimy, F., Alamir, H. T. A., Kadhim, O., Al-Abdeen, S. H. Z., Sattar, R., Jabbar, A. M., Kadhem Abid, M., Jetti, R., Alawadi, A., & Alsalamy, A. (2024). Emerging pathways in environmentally friendly synthesis of carbon-based quantum dots for exploring antibacterial resistance. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 161, 112012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.112012
[25]. Feng, S., & Guanghua, L. (2011). Hydrothermal and Solvothermal Syntheses. In Modern Inorganic Synthetic Chemistry (pp. 63–95). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53599-3.10004-6
[26]. Zhao, Q., Mao, H.-H., Xue, M., Feng, X.-Z., Han, G.-C., Chen, Z., & Kraatz, H.-B. (2023). One-pot synthesis of environmentally-friendly carbon quantum dots for “on-off” rapid fluorescent sensing of folic acid, Fe3+, and Ca2+. Journal of Luminescence, 263, 120091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2023.120091.
[27]. Yalshetti, S., Thokchom, B., Bhavi, S. M., Singh, S. R., Patil, S. R., Harini, B. P., Sillanpää, M., Manjunatha, J. G., Srinath, B. S., & Yarajarla, R. B. (2024). Microwave-assisted synthesis, characterization and in vitro biomedical applications of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis Linn.-mediated carbon quantum dots. Scientific Reports, 14(1), 9915. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60726-y









