1. Introduction
The WASP-12 system, an intriguing extrasolar planetary system, has garnered significant attention in the field of astronomy due to its basic parameters and characteristics. The system is located in the constellation Auriga, approximately 1,300 light-years away from Earth 1] or 600 light-years [2], noting that distance estimates may vary depending on observation methods and data). WASP-12 is a G-type main-sequence star or subgiant (depending on its specific evolutionary stage classification), with a visual magnitude of 11.7 [1], a mass ranging from approximately 1.35 to 1.43 times the mass of the Sun [2,3], and a radius of about 1.56 to 1.6 times the solar radius [3,4]. Nevertheless, through high-resolution imaging and spectroscopic analysis, researchers have discovered at least two companion stars, WASP-12B and WASP-12C [5]. These two companions are M-type red dwarfs with masses of approximately 0.38 and 0.37 times the mass of the Sun, respectively [5], and they are located relatively far from WASP-12, at distances of about 2,100 AU and 4,300 AU, respectively [5].
WASP-12b, the planet in this system, was first discovered in 2008 by the Wide Angle Search for Planets (SuperWASP) project [1]. It is a typical hot Jupiter, with a mass of approximately 1.41 times that of Jupiter [1,2] but an unusually large volume, about 1.79 times the volume of Jupiter [6], resulting in a lower density that is roughly half of Jupiter's. WASP-12b has an extremely short orbital period of just 1.09142 days [1], meaning it completes one orbit around WASP-12 at close quarters almost every day. Furthermore, its orbital semi-major axis is only 0.02294 astronomical units (AU), which is about 1/44 of the distance from Earth to the Sun [1].
For WASP-12b, there was one interesting phenomenon based on continuous detection and supervision to the light curve, which was claimed to an orbital period variation. According to recent research, its orbit is decaying at a rate of approximately 32.53 milliseconds per year, far exceeding previous expectations. It is predicted that WASP-12b will ultimately face destruction due to its orbital decay in approximately 29 million years.
In this article, we draw upon previously published articles concerning WASP-12, focusing specifically on its periodic characteristics. Our objective is to conduct a statistical analysis and synthesis of its period, aiming to organize and elucidate the patterns of periodicity observed. Furthermore, we intend to delve into the underlying mechanisms responsible for these periodic variations. By referencing established research, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of WASP-12's periodic behavior and contribute to the ongoing discourse in this field.
2. Past orbital period detections
2.1. L. Hebb et al., 2009[1]
L. Hebb et al. groundbreakingly announced the discovery of the hottest and largest hot Jupiter WASP-12b that have ever detected using transit method [1]. The study utilized photometric data from the SuperWASP survey to identify periodic dips in the brightness of the F9V host star, indicating transits caused by a closely orbiting planet. Subsequent follow-up observations refined the orbital and physical parameters of the system, establishing a detailed foundation for future research on WASP-12b. The orbital period of WASP-12b revealed a periodicity of 1.09142±0.000003 days, supported by a Monte Carlo Markov Chain (MCMC) analysis. This short period signified WASP-12b as one of the closest-in hot Jupiter known at the time.
Follow-up photometric and spectroscopic campaigns corroborated the transit signal, ruling out false positives like eclipsing binaries. Spectroscopy from the SOPHIE spectrograph provided radial velocity data, confirming the planetary nature of the companion and constraining its mass to \( 1.41 ±0.10 {M_{J}} \) . Combining radial velocity and transit data, the study estimated the planet’s semi-major axis at \( 0.0229 AU \) , a critical metric for its intense stellar irradiation and rapid orbital evolution.
2.2. G. Maciejewski et al., 2011, 2013, 2016, 2018, 2020 [4] [7] [8] [9] [10]
2.2.1. 2011 Work[4]
G. Maciejewski et al. did an improvement to the results from Hebb et al.’s work of presenting the systematic parameters of WASP-12b using MCMC analysis. The authors observed two transits of WASP-12b in February 2010 using the 2.2-meter telescope at the Calar Alto Observatory. By employing high-precision photometry, they modeled the light curves with various limb-darkening laws to refine the parameters of the planetary system. After comparing data, the author found that the square-root model produced the best fit to their data, offering the lowest residuals and the most realistic parameter values. Having a long time span of observations, the author redetermined an improved ephemeris. As a result of fitting a linear function of the epoch and orbital period Pb, they obtained a new orbital period of \( 1.09142245±0.00000033 \) days and a mid-transit time \( {T_{0}}=2454508.97682±0.00020 {BJD_{TDB}} \) .
2.2.2. 2013 Work[7]
Following a two-year period, the team re-conducted the observation to refresh the data for WASP-12b. The writers coordinated a campaign across multiple telescopes to monitor transits of WASP-12b, collecting 61 transit light curves. Through analysis of the best data sets, they refined the parameters, which align with those reported in previous articles. The residuals from a linear ephemeris indicated a possible periodic signal, which might be modeled by a sinusoidal function with an amplitude of 0.00068 ± 0.00013 days and a period of 500 ± 20 orbital cycles of WASP-12b. The combined examination of timing data and radial velocity measurements led to an additional planet model, which better explained the observations compared to single-planet scenarios. The authors hypothesize that WASP-12 b may not be the only planet in the system and suggest the presence of an additional 0.1 MJup body on a 3.6-day eccentric orbit. Furthermore, the analysis shows that the proposed new system will remain stable over long timescales.
2.2.3. 2016 Work[8]
In their third analysis of WASP-12b, they acquired 31 complete light curves for 29 transits between November 2012 and February 2016 utilizing seven telescopes. Combining all light curves newly acquired and former light curves, the authors were able to reevaluate the WASP-12b’s ephemeris, which turned out to fail to fit with a linear ephemeris rather than a quadratic ephemeris. This indicates a period change to WASP-12b’s orbital period. Using a quadratic ephemeris function of \( {T_{mid}}={T_{0}}+{P_{b}}E+\frac{1}{2}δ{P_{b}}{E^{2}} \) where \( E \) is the transit number from the cycle-zero epoch \( {T_{0}} \) and \( δ{P_{b}} \) is the change in the orbital period between succeeding transits. They yielded a result a much better fit with \( {{χ_{red}}^{2}}= 1.03 \) , comparing to a larger departure of \( {{χ_{red}}^{2}}=4.01 \) under a linear ephemeris. Therefore, the authors reclaimed that WASP-12b might exhibit a period decay, with a rate of change of orbital period of \( \dot{{P_{b}}}=-2.56 ± 0.40 × {10^{-2}}s/yr \) . Apart from this conclusion, the authors reevaluated the systematic parameters of WASP-12b with a period of \( {P_{b}} = 1.09142162 ± 0.00000021 day \) and a mid-transit time \( {T_{0}}= \) 2454 508.97696 ± 0.00016 \( {BJD_{TDB}} \) .
2.2.4. 2018 Work[9]
With a similar technique applied in their 2016 work, G. Maciejewski et al. acquired 22 new high-quality transit light curves for WASP-12b from 10 different telescopes, which allowed them to refine the transit parameters with uncertainties comparable to or better than previous studies. The new transit times follow a quadratic ephemeris very well, indicating an orbital period decay.
With a best-fit model disparity of \( {{χ_{red}}^{2}}=0.9 \) ,the best-fit model for the orbital period decay rate is consistent with but more precise than previous measurements. This corresponds to a tidal quality factor of the host star \( Q_{*}^{ \prime } \) \( = (1.82 ± 0.32) × {10^{5}}, \) in agreement with theoretical predictions for subgiant stars.
2.3. Tucker Chan et al., 2011[11]
This article focused on refining the parameters of several transiting exoplanets, including WASP-12b, as part of the Transit Light Curve Project (TLCP). This study provided updated system parameters based on additional transit observations, leveraging high-precision photometry to validate previous findings and explore anomalies in planetary radii. Since WASP-12b was highlighted as a "bloated" planet, with a radius exceeding standard expectations for its mass, Chan et al. sought to confirm this anomaly through new observations and to refine the orbital ephemeris, enhancing the precision of the planet's period and transit timing. By employing photometry from the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory and the Nordic Optical Telescope, they acquired transit light curves of WASP-12b, then applied quadratic limb darkening laws [32] and Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm, Chan et al. finally reached an updated systematic parameter for WASP-12b.
2.4. David K. Sing et al., 2013[12]
David K. Sing et al presented another survey on WASP-12b using Hubble Space Telescope (HST) optical transmission spectra to resolve WASP-12 system, revealing it to be a close binary M0V pair. From the spectra, they managed to exclude prominent absorption by TiO, strong pressure-broadened elements of Na and K, and significant metal-hydride features in the exoplanet's atmosphere. They also presented corrections for the systematic parameters for WASP-12b.
2.5. Karen A. Collins et al., 2017[2]
Karen A. Collins et al. presented a detailed analysis of TTVs in the WASP-12b. The authors collected 23 new transit light curves from the Moore Observatory Ritchie–Chretien (MORC) 0.6 m telescope and performed global fits to all available data, including spectroscopic and radial velocity measurements from the literature. The goal was to refine the system parameters and search for evidence of additional perturbing bodies in these systems, as suggested by previous studies. For the WASP-12b system, previous work by Maciejewski et al. [7] found tentative evidence for a TTV signal, which has a period of 545±22 days and a semi-amplitude of 59±11 s, and they suggest that the possible perturbing body has a mass of M 0.1 J and a 3.6-day eccentric orbit. Based on hypothesis, Collins et al. did global fit to the linear ephemeris and eventually found no presuasive evidence for sinusoidal TTVs with a semi-amplitude of more than ∼35s in datasets, indicating a contradiction to Maciejewski et al. [7].
3. Past data analysis
Since the discovery of WASP-12b [1], there are many articles measuring the orbital period of the hot Jupiter, as well as analysis of the orbital decay on theoretical basis. They reached an agreement that WASP-12b does not have a general decay of its orbital period. However, in our literature review, we’d like to affirm the consistency by applying a linear regression for all measure parameters from past articles. Theoretically, the decay motion follows a linear relation with respect to time, and hence, we’d like to apply a linear regression of \( P={mT_{0}}+b \) to all data, where \( m \) is the decay rate \( \dot{P} \) of WASP-12b. The table below shows the values mid-transit time \( {T_{0}} \) and period \( P \) of a collection of past articles categorized by published years in ascending order.
Table 1: Summary of WASP-12b orbital parameters
Source | Year | T0(BJDTDB)+2450000 | P(days) |
Hebb et al.[1] | 2009 | \( 4508.9761±0.0002 \) | \( 1.091423±0.000003 \) |
Tucker Chan et al.[2] | 2011 | \( 4508.97605±0.00028 \) | \( 1.0914222±0.0000011 \) |
Southworth et al.[13] | 2012 | \( N/A \) | \( 1.0914222±0.0000011 \) |
Albrecht et al.[14] | 2012 | \( 4508.97605±0.00146 \) | \( N/A \) |
G.Maciejewski et al.[7] | 2013 | \( 4508.97718±0.00022 \) | \( 1.0914209±0.0000002 \) |
Turner et al[15]. | 2016 | \( 5147.45820±0.00013 \) | \( 1.09142119±0.00000021 \) |
G.Maciejewski et al.[8] | 2016 | \( 4508.97696±0.00016 \) | \( 1.09142162±0.00000021 \) |
Bonomo et al.[16] | 2017 | \( 4508.97718±0.00022 \) | \( 1.09142090±0.00000020 \) |
Stassun et al.[17] | 2017 | \( N/A \) | \( 1.09142245±0.00000033 \) |
Collins et al.[2] | 2017 | \( 6176.668258 0.000077650773 \) | \( 1.0914203 \) 0.0000014432653 |
C. Patra et al.[18] | 2017 | \( 6305.455790 \) | \( 1.091420078 \) |
G.Maciejewski et al.[9] | 2018 | \( 4508.97694 \) | \( 1.09142172 \) |
Sing et al.[12] | 2018 | \( 4508.977005±0.00031 \) | \( 1.09142166_{-0.00000031}^{+0.00000032} \) |
Baluev et al.[19] | 2019 | \( 5197.5 \) | \( 1.091421080 \) |
Chakrabarty et al.[20] | 2019 | \( N/A \) | \( 1.09142000000±0.00000014432 \) |
Öztürk et al.[21] | 2019 | \( 4508.97824±0.00027 \) | \( 1.0914199±0.0000002 \) |
Turner et al.[22] | 2020 | \( 6305.455795± \) 0.000038 | 1.091420090±0.000000041 |
Ivshina et al.[23] | 2022 | \( 7010.512173±0.000070 \) | \( 1.091419108±0.000000055 \) |
Kokori et al.[24] | 2022 | \( 6594.68160±0.00004 \) | \( 1.09141964±0.00000004 \) |
Kokori et al.[25] | 2023 | \( 7036.706177±0.000055 \) | \( 1.091419179±0.000000043 \) |
Furthermore, a linear regression was applied for all measure parameters from past articles to learn the decay rate. Our hypothesis is, the decay motion follows a linear relation with respect to time, hence a linear regression of \( P={mT_{0}}+b \) would fit to all data, and \( m \) is hereby the decay rate \( \dot{P} \) of WASP-12b.
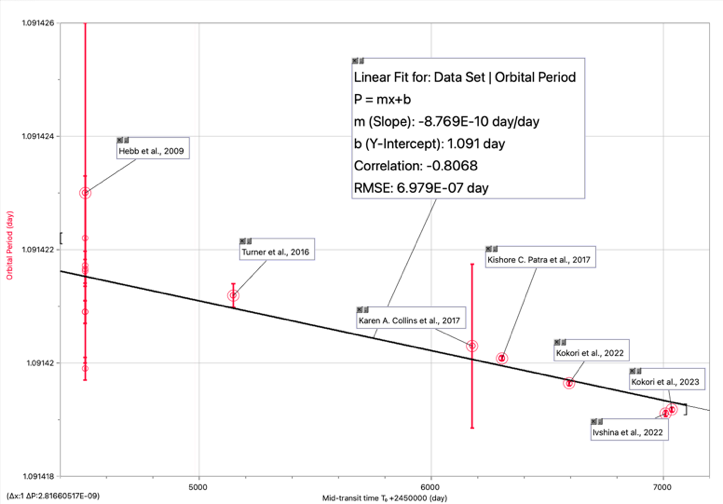
Figure 1: Regression results
Table 2: Comparison to past results
Source | Decay Rate \( \dot{P} \) ( \( ms/yr) \) | Discrepancy (%) |
This work | \( -27.654_{-39.697}^{+39.697} \) | N/A |
Patra et al., 2017[18] | \( -29 \) | 4.64 |
Yee et.al, 2020[26] | \( {-31.536^{*}} \) | 12.31 |
Turner et al., 2020[22] | \( -32.53 \) | 14.99 |
*Converted Unit | ||
By conversion the unit from day/day into ms/yr, a decay rate for WASP-12b orbital period is \( \dot{P}=-27.6539184 ms/yr \) . That’s to say, after applying a linear regressing to observational parameters of WASP-12b, we lead to a conclusion that the planet has a decay timescale, according to this work, of \( 3.4925Myr \) ( \( P \) adopted from [25]) Comparing with past results [18,26,22], we are able to see the accuracy and alignment of our result.
The uncertainty calculation is based on the equation \( uncertainty=1.96×\sqrt[]{\frac{\sum _{i=0}^{n}{{(y_{i}}-f(x))^{2}}}{\sum _{i=0}^{n}{{(x_{i}}-\bar{x})^{2}}}} \) , which is then calculated to be \( 1.2587853×{10^{-9}}day/day \) , which is \( 39.697ms/yr \) . This error greater than 100% of the actual value may be caused by some reasons: First, the data set was mostly crowded around the x value of 4508 \( {BJD_{TDB}} \) , making fewer significant data that participated in and affected the regression result. Second, as for the large uncertainty, we consider that the order of magnitudes of x and y values have a great difference that leads to a larger degree of freedom to the regression result. Third, regarding the actual model would a non-linear ephemeris relation of orbital period in terms of year, this linear fit curve may appear to have some systematic disparity to the actual condition. Multiple ways to reduce the uncertainty involve selecting and applying different and more random mid-transit times in order to have more data points available and effective for regression.
Nevertheless, we conducted another comparison with the former computed decay rate, shown in the table. With the largest discrepancy of less than 15.00%, we can tell that the linearized result is aligned with the general value for the WASP-12b decay rate. Therefore, though the uncertainty of the regression results is large, it is unanimously agreed that the decay trend is considered from the trend of the fitted curve and previous results.
4. Explanations for orbital period change
Nowadays, three main possible reasons for a hot Jupiter to present a period change are tidal dissipation, mass loss, and apsidal precession [26]. First, the mechanism of tidal dissipation involves the transfer of angular momentum between a close-in planet and its host star due to tidal interactions [27]. In solar-like stars, this dissipation is primarily driven by the eddy viscosity in the convective envelope. The rate of this tidal transfer depends on factors such as the stellar mass, radius, and convective zone properties, as well as the planet's mass and orbital separation. If the tidal pumping period is shorter than the eddy turnover timescale, the dissipation can be significantly reduced, leading to a longer orbital decay timescale. This tidal dissipation can have important implications for the long-term stability of planetary orbits, potentially leading to the engulfment of planets like Earth during the host star's red-giant phase.
The second should be apsidal precession [28]. Many reasons can cause a planet to exhibit an apsidal precession. The key factor is merely relativistic effects. General relativity (Miralda-Escudé, 2002[28]) predicts that a planet's orbit around its host star will slowly precess due to the curvature of spacetime caused by the star's mass. This effect is especially significant for close-in exoplanets like hot Jupiter. The relativistic precession rate [29] is given by \( \dot{ ω}=\frac{3n}{1-{e^{2}}}{(\frac{na}{c}) ^{2}} \) where \( ω \) is the periastron, \( n \) is the orbital frequency, \( e \) is the eccentricity, and \( a \) is the semi-major axis. The quadrupole moment of the host star can also cause precession of the periastron(Miralda-Escudé, 2002[28]). This precession rate (Binney & Tremaine,1987[30]) is given by \( \dot{ω}=n-κ=\frac{3{J_{2}}R_{S}^{2}}{2{a^{2}}}n \)
Last, the gravitational influence of a second planet in the system can induce precession of the periastron of the transiting planet (Miralda-Escudé, 2002[28]). The precession rate due to this effect is given by \( \dot{ω}=\frac{3{M_{2}}{A^{3}}}{4{M_{S}}a_{2}^{3}} \)
4.1. Kishore C. patra et al., 2017[18]
This article presents transit and occultation observations of the hot Jupiter exoplanet WASP-12b. The data are compatible with a constant period derivative, suggesting the planet's orbit is decaying due to tidal interactions with its host star. However, the data could also be explained by a portion of a 14-year apsidal precession cycle. If interpreted as orbital decay, the inferred tidal quality parameter of the star is about \( 2x{10^{5}} \) . If interpreted as precession, the planet's Love number is \( 0.44±0.10. \) The decay model is favored by the data, but distinguishing between the two scenarios will likely require several more years of monitoring, particularly occultation timing in 2019 and beyond. They observed seven transits of WASP-12 between 2016 October and 2017 February and two new occultation times from Spitzer project. After fitting with both precession model and decaying model [8], they found it was more fit with the latter, with a \( {{χ_{min}}^{2}}=118.5 \) , comparing with \( {{χ_{min}}^{2}}=124.0 \) for the precession model. Consequently, the article ultimately concluded that the constant period model has been excluded, while orbital decay is preferred over apsidal precession to be the most suitable explanation.
4.2. R.V. Baluev, 2019[19]
The writer emphasized the utilization of transit light curves along with radial velocity(RV) techniques to confirm that WASP-12 is a triple star system, featuring a stellar companion that resembles a binary. The total mass of these two companions WASP-12B and WASP-12C is 0.75 \( {M_{⊙}} \) , and they may induce a radial acceleration of \( 0.33 m{s^{-1}}/yr \) max on WASP-12A. Yet, the observed \( -7.5 m{s^{-1}}/yr \) radial acceleration would belong to some other unidentified companions or other distant planets, e.g brown dwarfs. The article mentioned that any object or several objects causing this radial acceleration must also produce a quadratic trend in transit timing variations (TTV). Although the trend wasn't significant, it ought to be incorporated into the model to ascertain a more accurate uncertainty of the tidal component of the TTV. Moreover, they performed a brief additional calculation to determine how much the tidal component is less than the overall measured TTV and the uncertainty associated with this value. They noticed that the data about the RV and TTV trends have been revealed to come from qualitatively different observations, so these two quantities may be expected to be independent.
In conclusion, the authors confirmed the nonlinear TTV trend, which may be partially explained by the light-travel (Roemer) effect due to unseen distant companions.
4.3. Samuel W. Yee, 2020[26]
In this article, 10 transiting light curves of WASP-12b between 2017 November and 2019 January and four occultations of WASP-12b in 2019 January and February had been newly acquired for a parameter refinement of the planet. Combining data from radial velocity methods [31] and former transits & occultation data, they applied a comprehensive analysis to those data under three common model of orbital change. In the end, Yee et al. measured a shift in transit and occultation times of about 4 minutes in a decade, corresponding to a decay constant of \( \dot{P} = -29 2ms/yr \) . Furthermore, the measurement of \( \frac{dP}{dN} = -10.0_{-0.69}^{+0.68}×{10^{-10}} \) days/epoch is consistent with the rate of \( -10.2 1.1×{10^{-10}} \) days/orbit (Patra et al., 2017[18]), and with the rate of \( \frac{dP}{dN} =-9.67 0.73×{10^{-10}} \) days/orbit [9]. This marks the first discovery of a hot Jupiter being observed to behave a spiraling motion towards its host star. It is probable that it will be destroyed within a timeframe of \( τ≈3.25Myr \) .
5. Conclusion
WASP-12b is an exoplanet located in the constellation of Auriga that was discovered by SuperWASP project in 2008 and established its existence in 2009 by Hebb et al.[1]. Classified as a hot Jupiter, WASP-12b has a mass approximately 1.41 \( {M_{Jupiter}} \) and a volume about 1.79 times larger. It orbits its host star WASP-12 at an exceptionally close distance of only 0.02294 AU, with an orbital period of roughly 1.09 days, which is the shortest orbital period known for exoplanets ever detected. WASP-12b's orbital period variation has been a significant interest in exoplanetary studies. Over more than a decade of continuous observations, scientists have detected a decline in the orbital period at a rate of approximately 30 milliseconds per year. Based on these findings, the predicted decay timescale for the orbit of WASP-12b is roughly \( \dot{P}=3.25Myr \) . In this article, we categorized, compiled, and analyzed previous studies on WASP-12b concentrated on the variations in the orbital period derived from transit & occultation light curve observations. We also applied a linear regression to the period-time graph based on our assumption that the planet in a short period will exhibit a constant decay rate, and an empirical orbital decay rate of 27.65 milliseconds per year for WASP-12b was obtained. This value presents a consistency with observational data reported in various studies, with discrepancies within a 15% margin of error. Furthermore, based on fitting results of three models, the potential mechanism for the tidal orbital decay showed a more consistency with the tidal dissipation, regarding apsidal precession and mass loss by escaping wind or Roche lobe overflow as two other proposed mechanism. Therefore, according to our analysis on past articles, tidal dissipation emerges as the most plausible explanation.
Looking forward, future research on WASP-12b will continue to monitor its orbital period variations using advanced observational techniques. The James Webb Space Telescope, in particular, offers the potential for more precise data collection, enabling further refinement of the parameters of the planet.
References
[1]. Hebb, L., Collier Cameron, A., Loeillet, B., et al. (2009). WASP-12b: The hottest transiting extrasolar planet yet discovered. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 499(2), L21-L25.
[2]. Collins, K. A., Kielkopf, J. F., Stassun, K. G., & Hessman, F. V. (2017). WASP-12: Constraints on planet mass from stellar line-bisector spans and revised system parameters. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 467(2), 1714-1726.
[3]. Fossati, L., Haswell, C. A., Froning, C. S., et al. (2010). The extremely irradiated hot Jupiter WASP-12b: Detection of iron in the planet's atmosphere and implications for its loss of mass. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 517, A56.
[4]. Maciejewski, G., Dimitrov, D., Neveu-VanMalle, M., et al. (2011). Transit timing variations of WASP-12. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 411(1), 1204-1218.
[5]. Bechter, E. B., Crepp, J. R., Ngo, H., et al. (2014). Stellar companions to exoplanet host stars: A high-resolution imaging survey. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 788(1), L9.
[6]. Li, S.-L., Miller, N., Lin, D. N. C., & Fortney, J. J. (2010). Atmospheric escape and evolution of WASP-12b and other hot Jupiters. Nature, 463(7282), 1054-1056.
[7]. G.Maciejewski,D.Dimitrov,M.Seeliger,St.Raetz,Ł.Bukowiecki,M.Kitze,R.Errmann,G.Nowak,A.Niedzielski, V. Popov,C.Marka,K.Go´zdziewski, R. Neuhäuser,J.Ohlert,T.C.Hinse,J.W.Lee, C.-U. Lee, J.-N.Yoon,A.Berndt,H.Gilbert,Ch.Ginski,M.M.Hohle,M.Mugrauer,T.Röll,T.O.B.Schmidt,N.Tetzlaff,L.Mancini,J.Southworth,M.Dall’Ora,S.Ciceri,R.Zambelli,G.Corfini,H.Takahashi,K.Tachihara,J.M.Benk˝ oK. Sárneczky,Gy. M. Szabo,T.N.Varga,M.Vaˇnko, Y. C. Joshi,andW.P.Chen(2013),Multi-site campaign for transit timing variations of WASP-12 b: possible detection of a long-period signal of planetary origin
[8]. G.Maciejewski,D.Dimitrov,M.Seeliger,St.Raetz,Ł.Bukowiecki,M.Kitze,R.Errmann,G.Nowak,A.Niedzielski, V. Popov,C.Marka,K.Go´zdziewski, R. Neuhäuser,J.Ohlert,T.C.Hinse,J.W.Lee, C.-U. Lee, J.-N.Yoon,A.Berndt,H.Gilbert,Ch.Ginski,M.M.Hohle,M.Mugrauer,T.Röll,T.O.B.Schmidt,N.Tetzlaff,L.Mancini,J.Southworth,M.Dall’Ora,S.Ciceri,R.Zambelli,G.Corfini,H.Takahashi,K.Tachihara,J.M.Benk˝ oK. Sárneczky,Gy. M. Szabo,T.N.Varga,M.Vaˇnko, Y. C. Joshi,andW.P.Chen(2013),Multi-site campaign for transit timing variations of WASP-12 b: possible detection of a long-period signal of planetary origin
[9]. Planet-star interactions with precise transit timing. I. The refined orbital decay rate for WASP-12 b and initial constraints for HAT-P-23 b, KELT-1 b, KELT-16 b, WASP-33 b, and WASP-103 b(2018)G.Maciejewski et al
[10]. An Apparently Eccentric Orbit of the Exoplanet WASP-12 b as a Radial Velocity Signature of Planetary-induced Tides in the Host Star(2020)Maciejewski, G
[11]. Tucker Chan et.al(2011), The Transit Light-Curve Project. Xiv. Confirmation Of Anomalous Radii For The Exoplanets Tres-4b, HAT-P-3b, and WASP-12b
[12]. D.K Sing et al. The Complete Transmission Spectrum of WASP-39b with a Precise Water Constraint, 2018
[13]. Southworth et al., Transmission photometry of WASP-12b: simultaneous measurement of the planetary radius in three bands, 2012
[14]. Albrecht et al, Optical coherence tomography in parkinsonian syndromes,2012
[15]. Turner et al. Ground-based near-UV observations of 15 transiting exoplanets: Constraints on their atmospheres and no evidence for asymmetrical transits,2016
[16]. Bonomo et al. The GAPS Programme with HARPS-N at TNG . XIV. Investigating giant planet migration history via improved eccentricity and mass determination for 231 transiting planets,2017
[17]. Stassun et al.(2017), Transit Timing Variation Measurements Of WASP-12b and QATAR-1b: No Evidence Of Additional Planets
[18]. Stassun et al.(2017), Transit Timing Variation Measurements Of WASP-12b and QATAR-1b: No Evidence Of Additional Planets
[19]. R.V. Baluev et al. WASP-4 transit timing variation from a comprehensive set of 129 transits,2019
[20]. Chakrabarty et al. Precise Photometric Transit Follow-up Observations of Five Close-in Exoplanets: Update on Their Physical Properties,2019
[21]. Öztürk et al. New photometric analysis of five exoplanets: CoRoT-2b, HAT-P-12b, TrES-2b, WASP-12b, and WASP-52b,2019
[22]. Jake D. Turner et al. Decaying Orbit of the Hot Jupiter WASP-12b: Confirmation with TESS Observations,2020
[23]. Ivshina et al. TESS Transit Timing of Hundreds of Hot Jupiters,2022
[24]. Kokori et al. ExoClock Project. II. A Large-scale Integrated Study with 180 Updated Exoplanet Ephemerides,2022
[25]. Kokori et al. ExoClock Project. III. 450 New Exoplanet Ephemerides from Ground and Space Observations,2023
[26]. The Orbit of WASP-12b Is Decaying,(2020 Yee et,al
[27]. Tidal Decay of Close Planetary Orbits, (F. A. Rasio, 1996)
[28]. Miralda-Escudé, Orbital Perturbations of Transiting Planets: A Possible Method to Measure Stellar Quadrupoles and to Detect Earth-Mass Planets, 2002
[29]. Landau, L. D., & Lifshitz, E. M. 1951, The Classical Theory of Fields
[30]. Binney & Tremaine, Galactic dynamics,1987
[31]. Knutson et al., 2014, Friends Of Hot Jupiters. I. A Radial Velocity Search For Massive, Long-Period Companions To Close-In Gas Giant Planets
[32]. K. Mandel & E.Agol, 2002, Analytic Light Curves for Planetary Transit Searches
Cite this article
Miao,H.;Feng,R. (2025). Literature Review for WASP-12b Orbital Decay. Theoretical and Natural Science,107,74-82.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Hebb, L., Collier Cameron, A., Loeillet, B., et al. (2009). WASP-12b: The hottest transiting extrasolar planet yet discovered. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 499(2), L21-L25.
[2]. Collins, K. A., Kielkopf, J. F., Stassun, K. G., & Hessman, F. V. (2017). WASP-12: Constraints on planet mass from stellar line-bisector spans and revised system parameters. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 467(2), 1714-1726.
[3]. Fossati, L., Haswell, C. A., Froning, C. S., et al. (2010). The extremely irradiated hot Jupiter WASP-12b: Detection of iron in the planet's atmosphere and implications for its loss of mass. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 517, A56.
[4]. Maciejewski, G., Dimitrov, D., Neveu-VanMalle, M., et al. (2011). Transit timing variations of WASP-12. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 411(1), 1204-1218.
[5]. Bechter, E. B., Crepp, J. R., Ngo, H., et al. (2014). Stellar companions to exoplanet host stars: A high-resolution imaging survey. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 788(1), L9.
[6]. Li, S.-L., Miller, N., Lin, D. N. C., & Fortney, J. J. (2010). Atmospheric escape and evolution of WASP-12b and other hot Jupiters. Nature, 463(7282), 1054-1056.
[7]. G.Maciejewski,D.Dimitrov,M.Seeliger,St.Raetz,Ł.Bukowiecki,M.Kitze,R.Errmann,G.Nowak,A.Niedzielski, V. Popov,C.Marka,K.Go´zdziewski, R. Neuhäuser,J.Ohlert,T.C.Hinse,J.W.Lee, C.-U. Lee, J.-N.Yoon,A.Berndt,H.Gilbert,Ch.Ginski,M.M.Hohle,M.Mugrauer,T.Röll,T.O.B.Schmidt,N.Tetzlaff,L.Mancini,J.Southworth,M.Dall’Ora,S.Ciceri,R.Zambelli,G.Corfini,H.Takahashi,K.Tachihara,J.M.Benk˝ oK. Sárneczky,Gy. M. Szabo,T.N.Varga,M.Vaˇnko, Y. C. Joshi,andW.P.Chen(2013),Multi-site campaign for transit timing variations of WASP-12 b: possible detection of a long-period signal of planetary origin
[8]. G.Maciejewski,D.Dimitrov,M.Seeliger,St.Raetz,Ł.Bukowiecki,M.Kitze,R.Errmann,G.Nowak,A.Niedzielski, V. Popov,C.Marka,K.Go´zdziewski, R. Neuhäuser,J.Ohlert,T.C.Hinse,J.W.Lee, C.-U. Lee, J.-N.Yoon,A.Berndt,H.Gilbert,Ch.Ginski,M.M.Hohle,M.Mugrauer,T.Röll,T.O.B.Schmidt,N.Tetzlaff,L.Mancini,J.Southworth,M.Dall’Ora,S.Ciceri,R.Zambelli,G.Corfini,H.Takahashi,K.Tachihara,J.M.Benk˝ oK. Sárneczky,Gy. M. Szabo,T.N.Varga,M.Vaˇnko, Y. C. Joshi,andW.P.Chen(2013),Multi-site campaign for transit timing variations of WASP-12 b: possible detection of a long-period signal of planetary origin
[9]. Planet-star interactions with precise transit timing. I. The refined orbital decay rate for WASP-12 b and initial constraints for HAT-P-23 b, KELT-1 b, KELT-16 b, WASP-33 b, and WASP-103 b(2018)G.Maciejewski et al
[10]. An Apparently Eccentric Orbit of the Exoplanet WASP-12 b as a Radial Velocity Signature of Planetary-induced Tides in the Host Star(2020)Maciejewski, G
[11]. Tucker Chan et.al(2011), The Transit Light-Curve Project. Xiv. Confirmation Of Anomalous Radii For The Exoplanets Tres-4b, HAT-P-3b, and WASP-12b
[12]. D.K Sing et al. The Complete Transmission Spectrum of WASP-39b with a Precise Water Constraint, 2018
[13]. Southworth et al., Transmission photometry of WASP-12b: simultaneous measurement of the planetary radius in three bands, 2012
[14]. Albrecht et al, Optical coherence tomography in parkinsonian syndromes,2012
[15]. Turner et al. Ground-based near-UV observations of 15 transiting exoplanets: Constraints on their atmospheres and no evidence for asymmetrical transits,2016
[16]. Bonomo et al. The GAPS Programme with HARPS-N at TNG . XIV. Investigating giant planet migration history via improved eccentricity and mass determination for 231 transiting planets,2017
[17]. Stassun et al.(2017), Transit Timing Variation Measurements Of WASP-12b and QATAR-1b: No Evidence Of Additional Planets
[18]. Stassun et al.(2017), Transit Timing Variation Measurements Of WASP-12b and QATAR-1b: No Evidence Of Additional Planets
[19]. R.V. Baluev et al. WASP-4 transit timing variation from a comprehensive set of 129 transits,2019
[20]. Chakrabarty et al. Precise Photometric Transit Follow-up Observations of Five Close-in Exoplanets: Update on Their Physical Properties,2019
[21]. Öztürk et al. New photometric analysis of five exoplanets: CoRoT-2b, HAT-P-12b, TrES-2b, WASP-12b, and WASP-52b,2019
[22]. Jake D. Turner et al. Decaying Orbit of the Hot Jupiter WASP-12b: Confirmation with TESS Observations,2020
[23]. Ivshina et al. TESS Transit Timing of Hundreds of Hot Jupiters,2022
[24]. Kokori et al. ExoClock Project. II. A Large-scale Integrated Study with 180 Updated Exoplanet Ephemerides,2022
[25]. Kokori et al. ExoClock Project. III. 450 New Exoplanet Ephemerides from Ground and Space Observations,2023
[26]. The Orbit of WASP-12b Is Decaying,(2020 Yee et,al
[27]. Tidal Decay of Close Planetary Orbits, (F. A. Rasio, 1996)
[28]. Miralda-Escudé, Orbital Perturbations of Transiting Planets: A Possible Method to Measure Stellar Quadrupoles and to Detect Earth-Mass Planets, 2002
[29]. Landau, L. D., & Lifshitz, E. M. 1951, The Classical Theory of Fields
[30]. Binney & Tremaine, Galactic dynamics,1987
[31]. Knutson et al., 2014, Friends Of Hot Jupiters. I. A Radial Velocity Search For Massive, Long-Period Companions To Close-In Gas Giant Planets
[32]. K. Mandel & E.Agol, 2002, Analytic Light Curves for Planetary Transit Searches









