1. Introduction
1.1. Alias-free generative adversarial networks
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have significantly advanced, producing higher-quality and more detailed images. These improvements have expanded their use in fields like image editing, domain translation, and video creation. One of the latest models, StyleGAN3, specifically addresses issues that previous models had with image quality and realism.
StyleGAN3 stands out because it creates images without aliasing, a problem where fine details appear fixed and unnatural. The creators of StyleGAN3 note that “current GAN architectures do not synthesize images in a natural hierarchical manner,” (Karras) which means that while coarse features control the presence of finer ones, they don't determine their exact positions.
To address this, StyleGAN3 uses a novel approach to ensure that details move naturally with their larger features, similar to how skin pores move when a head turns. By focusing on continuous signal processing, the model ensures details are generated correctly no matter the pixel coordinates. This helps to eliminate "texture sticking," (Karras) where fine details remain in place, disrupting the realistic movement of objects.
The result is a generator that attaches details to surfaces correctly, promising significant improvements in video and animation. According to the authors, StyleGAN3 "matches StyleGAN2 in terms of FID," (Karras) but with a more sophisticated method that demands slightly more computational power.
This paper investigates how well people can identify images created by StyleGAN3. Our goal is to understand the accuracy of human detection and the factors that affect it. This research is crucial for enhancing detection tools and addressing the ethical implications of highly realistic AI-generated images.
2. Artificial discrimination
2.1. Sample generation
In this study, we selected two types of images for manual classification: human faces and animals. For human face generation, we used the FFHQ dataset with a truncation value set to 0.7. For animal image generation, we used the AFHQv2 dataset with the truncation value also set to 0.7. We will randomly select 100 images from each dataset for analysis.


Figure 1: Dataset of generated images
2.2. Analysis of face picture
We judged whether a picture has been generated successfully (whether it can be recognized by the human eye as a computer-generated image) based on the following factors: hair, facial features, accessories, muscles, and background. Here are the initial data we have analyzed and statistically calculated:
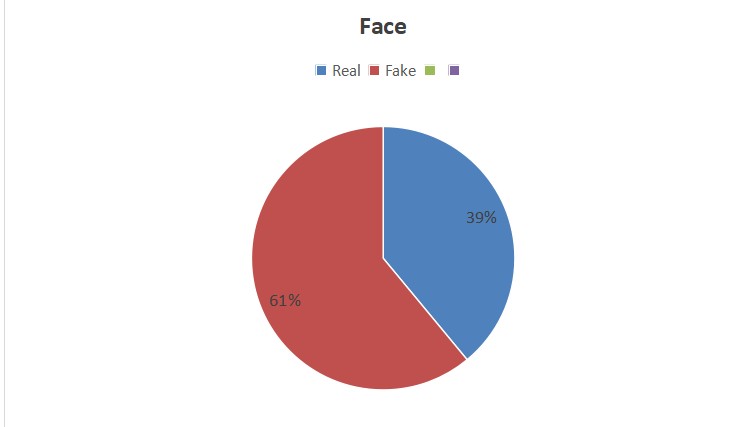
Figure 2: Percentage of people identifying the face as fake or real
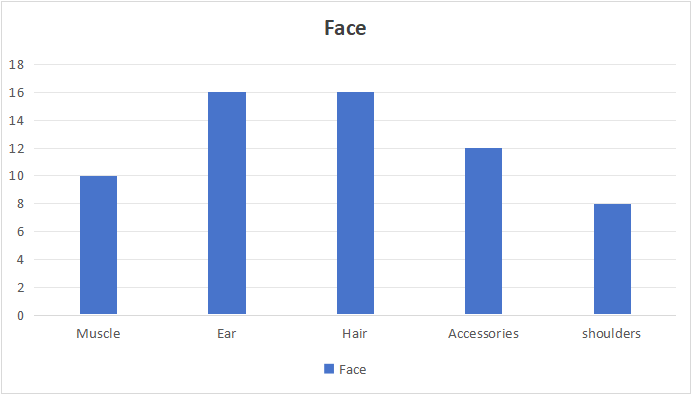
Figure 3: Different elements that determines the generated image as fake
Conclusion: Gan3 exhibited relatively weak capabilities in generating human faces, particularly evident in the representation of ears and hair. It was observed that as the number of elements to be generated in an image increases, the likelihood of generation failure also rises. This is notably manifested when individuals are adorned with numerous accessories (such as glasses, hairpins, hats, etc.), resulting in blurred hair quality or distorted ear shapes, as illustrated in Figure 2 and Table 1. Furthermore, it is worth noting that out of the one hundred images examined, two instances of significant generation errors were related to the shoulders.
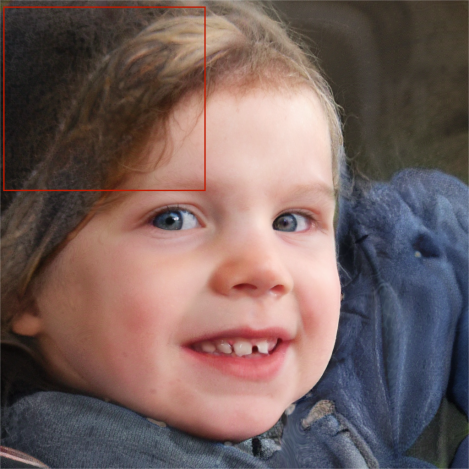
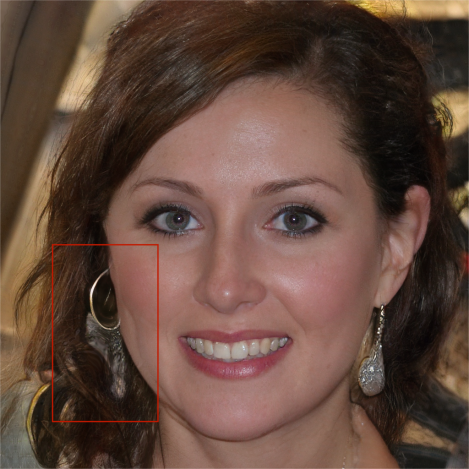


Figure 4: Image of a small child Figure 5: Image of a women
2.3. Animals
Unlike the criteria for recognizing human faces, the elements in animal pictures are relatively fewer. Therefore, we changed the judging criteria to the animal's fur, facial proportions, and the lighting of the background. By analyzing 100 pictures, we obtained the following data:
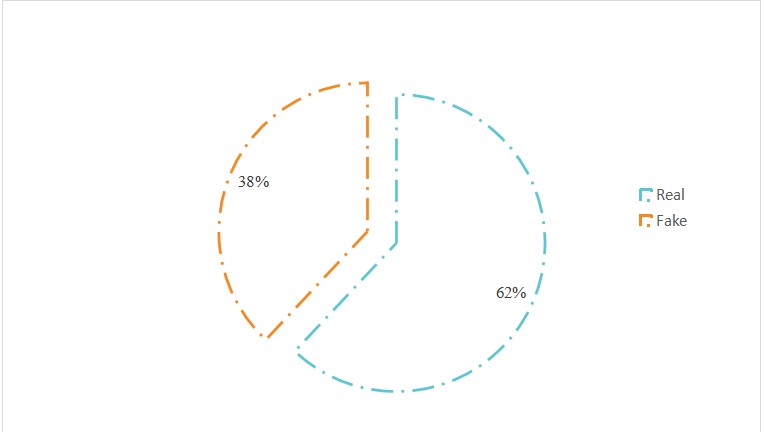
Figure 6: Percentage of real and fake pictures
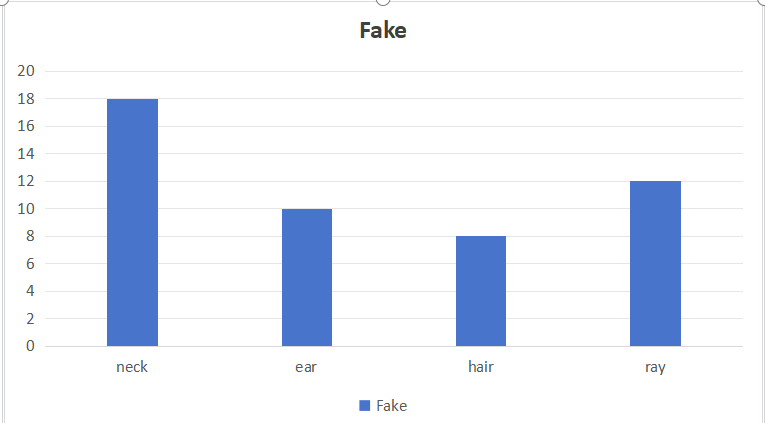
Figure 7: Features indicating fake image
Conclusion: Compared with face generation, gan3 is more powerful for animal generation, especially for feline generation. Of the 19 fake images, only three were of felines, and the vast majority were of canines. Most of this is reflected in the neck parts, such as the ratio of the collar to the neck. I think gan3 needs a lot of work on generating collars. In addition, canine features can be seen in some photos of cats, and vice versa.
2.4. Cross-Entropy Loss [2]
The Cross-Entropy Loss function is a loss function commonly used in classification problems. It measures the difference between the probability distribution predicted by the model and the true label distribution. In information theory, cross-entropy is used to quantify the uncertainty or divergence between two probability distributions. In machine learning and deep learning, the Cross-Entropy Loss function facilitates the learning and optimization of the model by maximizing the likelihood of the data given by the model.
Mathematical Expression and Calculation
For a multi-class classification problem, assume that the output of the model is a probability distribution q(x), and the probability distribution corresponding to the true label p(x) is a one-hot encoding vector. The Cross-Entropy Loss function can be expressed as:
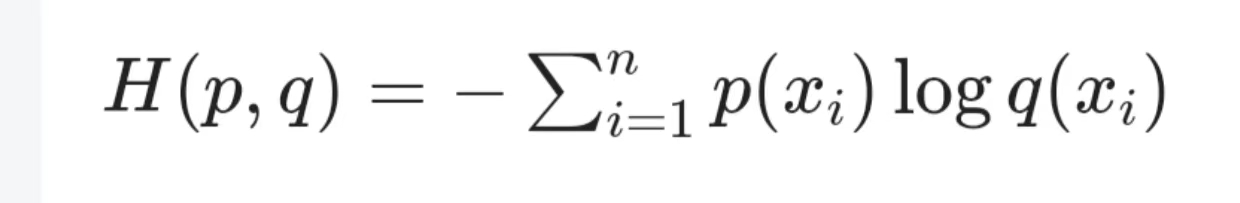
Where n is the total number of classes, p(xi) is the probability that the true label belongs to the i-th class (for one-hot encoding, only the element corresponding to the true class is 1, and the others are 0), and q(xi) is the probability predicted by the model for the i-th class.
In practical applications, the output of the model is usually not a probability distribution but unnormalized scores (logits). Therefore, the Cross-Entropy Loss function is often used in conjunction with the softmax activation function, which converts these scores into a probability distribution. In deep learning frameworks such as PyTorch, there are usually built-in Cross-Entropy Loss functions that incorporate the softmax function internally.
3. Method
3.1. Image generation with StyleGAN3
For the purpose of our research, we used the latest model from NVIDIA of the Generative Adversarial Network, StyleGAN3; these new state-of-the-art architectures have several novel image quality-improving components for realism. Some of its main salient features are Alias-Free Generative and Stochastic Variations. We initialized our process of image generation with pre-trained weights from the repository of StyleGAN3. This gave the model the advantage of broad training on a large scale through datasets that it had previously learned, and the produced image output was high quality.
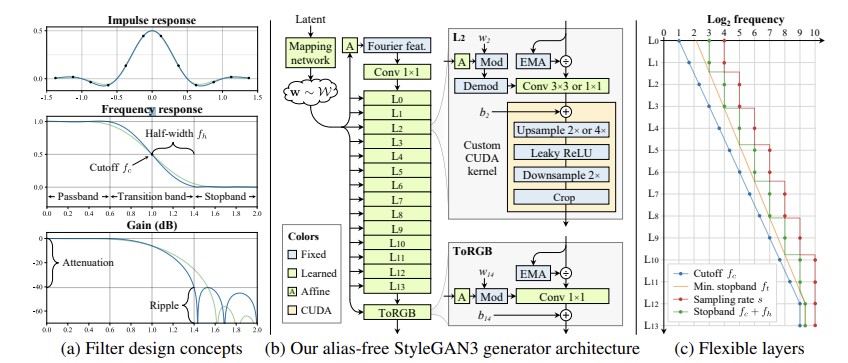
Figure 8: Alias-free StyleGAN3 architecture: filter design, generator architecture, and layer flexibility
We processed 50 images for each parameter set, making this set large enough to ensure an appropriate sample size in the subsequent analysis. The resolution of all produced images was saved at 1024×1024 pixels, according to the default available under StyleGAN3, to maintain consistency across all experiments. Following image generation, we compiled the full dataset for analysis. In the methodology, the first primary objective was testing the realism of images via a double-blind testing protocol to ensure unbiased results. It is worth mentioning that these images came from a model with translation and rotation equivariance. Equivariance of image features to translation and rotation guarantees that the details in an image are left unchanged by these geometric transformations. We can give images from this model a high level of realism and detail fidelity under the influence of different geometric transformations.

Figure 9: Generated faces using StyleGAN3 with FFHQ dataset at truncation level 0.7
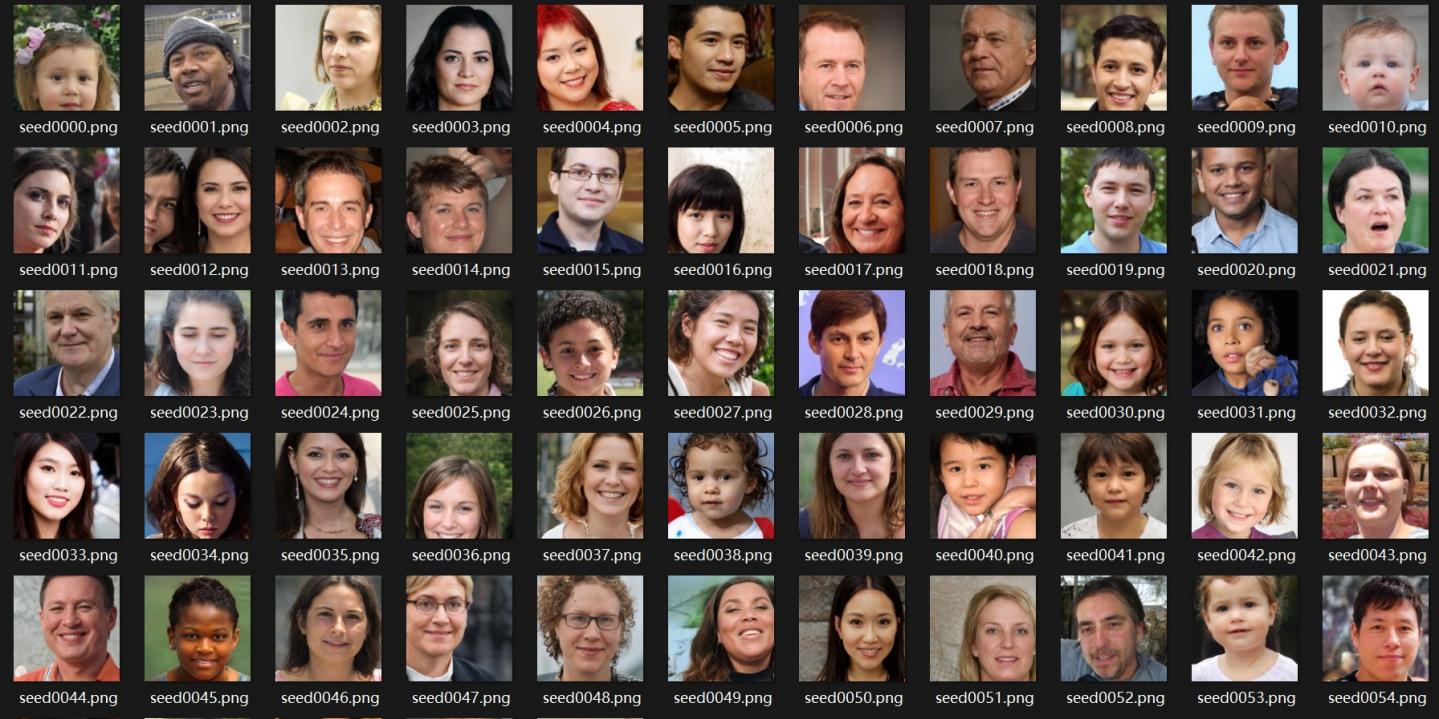

Figure 10: Generated faces using StyleGAN3 with FFHQ dataset at truncation level 0.7

Figure 11: Generated animal faces using StyleGAN3 with AFHQv2 dataset at truncation level 0.7
3.2. Double-blind testing and evaluation criteria
Prior to double-blind testing, the constructed imagery was labeled with the parameters used to construct it, but without the labels being presented to evaluators to avoid any form of perception of bias. The dataset was randomized in order to prevent ordering effects, and images were anonymized to remove identifiability from metadata. Evaluator Selection: We have selected a pool of diverse evaluators with varied experience in the field of image analysis and data science for our evaluation process. Evaluation Criteria: We have used a standard rubric for the evaluators to grade the images on the following criteria:
Visual Realism: The degree to which the image looks like a real photograph. Coherence: the degree and consistency of how all elements work together in an image.
Detail: the level of fine detail and texture in the image
Scoring Process: Each evaluator independently scored a subset of images from the dataset. The images were presented in random order, and evaluators were blinded to the parameters used in their generation.
• 3.3 Analysis of Parameter Impact on Image Realism
• Results from double-blind testing are used to highlight best configurations of parameters in order to make StyleGAN3 realistic. We used the analysis of scoring by experts to trace trends and patterns explaining how perceived realism is affected by various model settings.
4. Conclusion
In conclusion this study is designed to investigate human’s ability to recognize and distinguish between real images taken by cameras and “fake” images generated by the StyleGan3 model. The study especially focused on human’s detection accuracy and the factors that serve as key determination points in the generated picture which leads to the final decision. We decided to conduct a double-blind experiment, which examines the performance of StyleGan3 in generating human faces and animal images to reveal both strengths and weaknesses in the model's outputs.
Our result with human face images implies that StyleGAN3 model’s weakness in generating details such as ears and the texture of hairs. Under the current model, the key problems is that as the image complexity and elements in the image increases, error in the images also rises. Examples in this case are blurred hair quality or distorted ear shapes when individuals wore accessories like glasses or hats.
Unlike generating human faces, the StyleGan3 model has a much better performance when generating animal images. However, there are still weaknesses with generating collars accurately and sometimes the model would mix features between different animal types.
In conclusion, the StyleGan3 model has a significant advancement compared to the older StyeGan2 model at the accuracy of image generation. There are still obvious flaws that are easy to detect when generating human faces. But has a better performance in animal image generation. The overall detection rate of “fake images” is relatively low and is suitable to be considered a reliable and accurate image generation tool.
References
[1]. Karras, Tero, et al. "Alias-free generative adversarial networks." Advances in neural information processing systems 34 (2021): 852-863.
[2]. Connor R ,Dearle A ,Claydon B , et al.Correlations of Cross-Entropy Loss in Machine Learning[J].Entropy,2024,26(6):491-.
[3]. Karras, Tero, et al. “Analyzing and Improving the Image Quality of StyleGAN” Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition arXiv:1912.04958 [cs.CV]
[4]. Wang, Y., Jiang, L., & Loy, C. C. (2023). Styleinv: A temporal style modulated inversion network for unconditional video generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 22851-22861).
[5]. Bermano, Amit H., et al. "State‐of‐the‐Art in the Architecture, Methods and Applications of StyleGAN." Computer Graphics Forum. Vol. 41. No. 2. 2022.
Cite this article
Wang,N.;Liu,X.;Ji,Y.;Zheng,Y. (2025). Alias-Free Generative Adversarial Networks’ Generated Picture Detection. Theoretical and Natural Science,107,164-170.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Karras, Tero, et al. "Alias-free generative adversarial networks." Advances in neural information processing systems 34 (2021): 852-863.
[2]. Connor R ,Dearle A ,Claydon B , et al.Correlations of Cross-Entropy Loss in Machine Learning[J].Entropy,2024,26(6):491-.
[3]. Karras, Tero, et al. “Analyzing and Improving the Image Quality of StyleGAN” Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition arXiv:1912.04958 [cs.CV]
[4]. Wang, Y., Jiang, L., & Loy, C. C. (2023). Styleinv: A temporal style modulated inversion network for unconditional video generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 22851-22861).
[5]. Bermano, Amit H., et al. "State‐of‐the‐Art in the Architecture, Methods and Applications of StyleGAN." Computer Graphics Forum. Vol. 41. No. 2. 2022.









