1. Introduction
In the research on coal multimodal transportation, scholars typically focus on two aspects: model construction and algorithm optimization [1]. In terms of model development, researchers generally establish multi-objective decision-making models aimed at minimizing total transportation costs and reducing carbon emissions. For algorithm optimization, efforts are primarily dedicated to improving methodologies such as genetic algorithms to enhance the accuracy and reliability of solutions. Regarding model construction, Li Na proposed a coal multimodal transportation optimization model incorporating external costs, solved using the NSGA-II algorithm, and further analyzed the impact of external costs on optimal transportation routes [2]. Yang Yang developed a multimodal transportation path optimization model for coal logistics based on the objective of minimizing economic costs and solved case studies using genetic algorithms [3]. Zhang M constructed a multi-objective fuzzy chance-constrained model under conditions of time uncertainty [4]. In the realm of algorithm optimization, Zhou Jiajie introduced an improved K-shortest path algorithm based on arc-path modeling and validated it through case studies on coal transportation in Shanxi Province [5]. Zhang H proposed a novel solution strategy utilizing the sparrow search algorithm. Zheng C enhanced the particle swarm optimization algorithm [6], while Huang Qin optimized the Harris hawk algorithm [7]. Additionally, Wan Jie designed an improved fireworks algorithm and developed a multi-objective optimization method based on the DE-NSGA-I algorithm [8].
Against this backdrop, this paper constructs a multi-objective optimization model considering transportation costs, carbon emissions, and transit time under the context of Jining Port's operational launch, aiming to provide a more scientific planning framework for coal transportation networks.
2. Model construction
Based on the aforementioned assumptions and aligned with relevant literature and practical scenarios, the parameters and variables of the proposed model are defined as follows:N: Set of all nodes in the transportation network;M: Set of transportation modes, M={1,2,3}, where 1: road transport, 2: rail transport, 3: waterway transport;i: Origin node of goods, i∈N;j: Destination node of goods, j∈N;k: Transportation mode,k∈M;Q: Total coal transportation volume;Tij: Total permissible transportation time;Cijk: Transportation cost from origin ii to destination j using mode k;Eijk: Carbon emissions from origin i to destination j using mode k;Tijk: Transportation time from origin i to destination j using mode k;Lijk: Transportation distance from origin ii to destination jj using mode k;Vk: Average speed of transportation mode k;Wj: Unit inventory cost at destination j;ek: Unit carbon emissions of transportation mode k;ek1k2: Unit carbon emissions during mode transfer from k1 to k2;sk1k2: Unit transfer cost for shifting goods from mode k1 to k2;ck: Unit freight rate of transportation mode k;e: Unit carbon tax value (tax per unit of carbon emissions);p: Unit penalty cost for delivery delays (cost per unit of goods delayed);xijk: Binary decision variable (1 if mode k is selected from i to j; 0 otherwise);yij: Binary decision variable (1 if goods are transferred between i and j; 0 otherwise);
To facilitate model resolution, environmental benefits are quantified as carbon emission costs. The objective function integrates three components:transportation costs;time costs;carbon emission costs
\( {TC_{1}}=\sum _{i∈N,j∈N,k∈M}Q{c_{k}}{L_{ijk}}{x_{ijk}} \) (1)
\( {TC_{2}}=\sum _{i∈N,j∈N,k∈M}Qs_{k2}^{k1}{y_{ij}} \) (2)
\( {TC_{3}}=\sum _{i∈N,j∈N,k∈M}Q({T_{ij}}-{T_{ijk}}){W_{j}} \) (3)
\( {TC_{3}}=\sum _{i∈N,j∈N,k∈M}Q({T_{ijk}}-{T_{ij}})p \) (4)
\( {TC_{E}}=\sum _{i∈N,j∈N,k∈M}eQ{L_{ijk}}{e_{k}}{x_{ijk}}+\sum _{i∈N,j∈N,k∈M}eQe_{k2}^{k1}{y_{ij}} \) (5)
In Equation (1), TC1 represents the transportation cost during transit;In Equation (2), TC2 denotes the transfer cost during transportation;In Equation (3), TC3 denotes the additional storage cost incurred during transportation when goods arrive early;In Equation (4), TC3 represents the additional penalty cost incurred during transportation due to delayed arrival of goods.In Equation (5);TCE represents the total carbon emission cost generated during the transportation process, which comprises two components:in-transit transportation carbon emission cost [9].
In Equation (6), it is explicitly constrained that each coal shipment from a source location to its destination must exclusively select a single transportation mode;In Equation (7), it is constrained that coal shipments at any node may either adopt a single transfer mode or undergo no transfer;In Equation (8) and Equation (9), coal transportation is restricted to the predefined set of available transportation and transfer modes, with the decision variables in this model formulated as binary (0-1) variables.
\( \sum {x_{ijk}}=1,∀i∈N,j∈N,k∈M \) (6)
\( {y_{ij}}≤1,∀i∈N,j∈N,i=j \) (7)
\( {x_{ijk}}∈\lbrace 0,1\rbrace ,∀i∈N,j∈N,k∈M \) (8)
\( {y_{ij}}∈\lbrace 0,1\rbrace ,∀i∈N,j∈N \) (9)
3. Algorithm design
In this study, the NSGA-II algorithm is employed for model resolution, with the specific implementation outlined as follows:Encoding and Initialization: A real-coded representation is adopted, where each chromosome is divided into two segments – path encoding and transportation mode encoding.Fitness Function: The fitness function integrates transportation cost, transportation time, and carbon emissions, with weight coefficients determined via the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) [10].Non-dominated Sorting: A Pareto optimal solution set is constructed to prioritize non-dominated solutions while maintaining population diversity.Selection, Crossover, and Mutation: Tournament selection and path-specific mutation operators are applied to enhance genetic diversity within the population.Elitism Strategy: High-quality non-dominated individuals are preserved to accelerate convergence efficiency.This formulation ensures adherence to academic conventions, including passive voice, technical terminology precision, and structural clarity.
4. Model solving and analysis
4.1. Instance description
The adoption of containerized transportation for inland coal shipping represents a significant developmental trend. To enhance the practical relevance of this study, all data in this research are standardized using container units. This study employs 40-foot containers as the baseline unit, with a standardized payload of 30 tons per container.Figure 1 shows the simplified transportation network diagram
Figure 1: Multimodal transport network diagram
4.2. Data collection and processing
The railway unit freight rate is 1.85 yuan /TEU·km, and the water freight rate is 3.185 yuan /TEU·km. The average railway transport speed is 60km/h, and the unit carbon emission is 0.56kg/TEU·km. The average water transport speed is 30km/h, and the unit carbon emission is 1kg/TEU·km. The unit cost of converting the transportation mode between hot metal is 200 yuan /TEU, the unit transfer time is 0.08h/TEU, and the unit carbon emission is 1.92kg/TEU. Comprehensive different schemes, this paper uses 45 yuan/ton carbon dioxide emission tax rate for analysis.
4.3. Model solving analysis
Under deterministic conditions excluding uncertainty factors, the optimal route minimizing the combined transportation and carbon emission costs demonstrated operational metrics including transportation cost, carbon emission volume, carbon taxation expenditure, and transit duration, as detailed in Table 1.
Table 1: Cost, carbon emissions and transit time under optimal routes
Optimal path | Transportation cost(Yuan) | Carbon emission(kg) | Carbon emission cost(Yuan) | Transit time(h) |
1T2W5W7W8W10 | 101475 | 27628.80 | 1254.20 | 28.97 |
For 30TEU coal shipments originating from Watang, the identified optimal logistics pathway involves rail transportation to Jining, followed by inland waterway shipping via the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal, traversing strategic nodes including Xuzhou, Huaian, and Zhenjiang before final delivery to Shanghai.
Sensitivity Analysis Protocol: To verify the model's robustness and operational adaptability, this study conducted systematic sensitivity testing on critical parameters:Systematic parameter testing was conducted by adjusting rail freight rates to 0.35–3.35 yuan/TEU·km and waterway rates to 1.185–8.185 yuan/TEU·km. Subsequent observations quantified the resultant variations in transportation costs and carbon emission expenditures across these rate intervals, with parametric relationships graphically demonstrated in Figures 2 and 3.
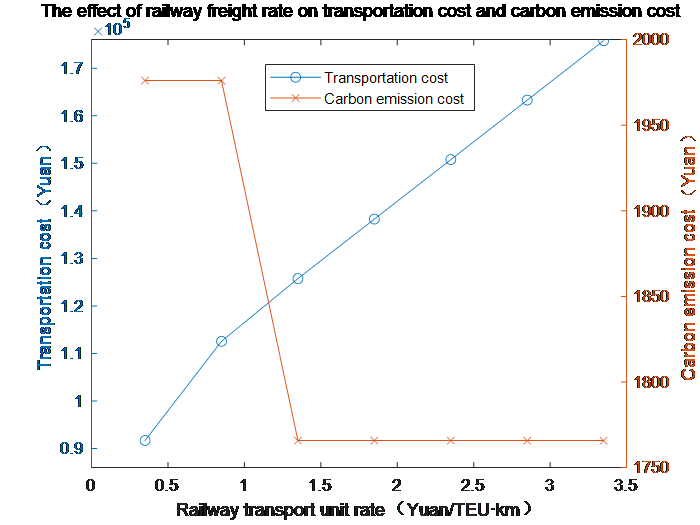
Figure 2: Sensitivity analysis diagram of railway unit rate
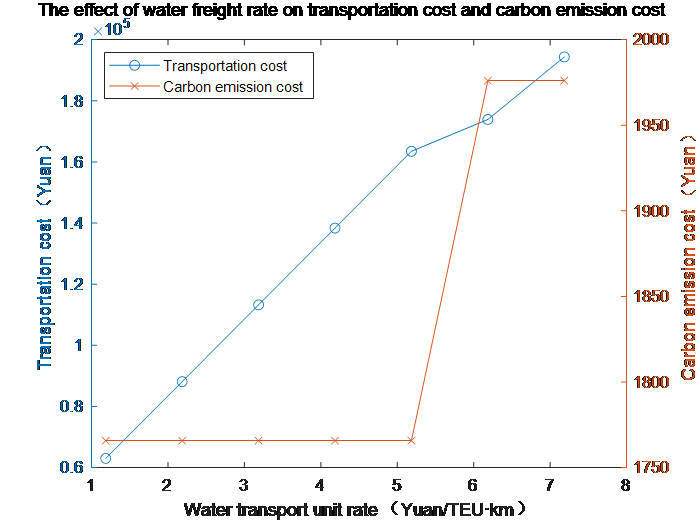
Figure 3: Sensitivity analysis diagram of waterway unit rate
The cost-effectiveness of coal transportation routes exhibits dynamic variations under different freight rate conditions. When railway rates fall below 1.35 yuan/TEU·km, Route 1T4W10 (via Wari Railway to Rizhao Port with maritime transfer) emerges as optimal. Conversely, above this threshold, Route 1T2W5W7W8W10 (rail-to-Jining followed by Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal inland waterway transit) becomes preferable. The canal route maintains cost superiority when waterway rates remain below 5.135 yuan/TEU·km, while maritime routing regains advantage beyond this critical value. Notably, despite Route 1T4W10's longer transportation distance and higher carbon emission costs under standard freight rates, its total costs remain lower than the canal alternative, demonstrating the comprehensive benefits of long-distance(intensive transportation) through optimized multimodal coordination. This cost paradox highlights the critical role of route-specific scale economies in intermodal transportation systems.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, the coal transportation route from Shanxi to Shanghai is optimized by constructing a multi-objective optimization model, considering transportation cost, carbon emission and transportation time. Studies have shown that railway and inland waterway transport have significant advantages in terms of cost and environmental benefits. The sensitivity analysis verifies the adaptability of the model, showing that the carbon tax rate has little effect on the total transportation cost, while the change of freight rate has a significant effect on route selection. This paper provides theoretical and practical reference for multimodal transport route optimization.
References
[1]. Zhang M.Optimization of Multimodal Transport Routes ConsideringCarbon Emissions in Fuzzy Scenarios [J].International Core Journal of Engineering,2022,8(4):267-281.
[2]. Zhang H,Huang Q,Ma L,et al.Sparrow search algorithm with adaptivet distribution for multi-objective low-carbon multimodal transportationplanning problem with fuzzy demand and fuzzy time [J].Expert Systemswith Applications,2024,238:122042.
[3]. Zheng C,Sun K,Gu Y,et al.Multimodal Transport Path Selection of Cold Chain Logistics Based on Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm[J].Journal of Advanced Transportation,2022(Pt.7):1.1-1.12.
[4]. Rademeyer M, Minni Tt R, Falcon R. Multi-product coal distribution and price discovery for the domestic market via mathematical optimisation[J]. Mineral Economics, 2020, 34: 113-126.
[5]. Botha A, Badenhorst-Weiss J A. Risk management in a bulk coal export logistic chain: A stakeholder perspective[J]. Journal of transport and supply chain management, 2019, 13: 316-324.
[6]. Biswal J N, Muduli K, Satapathy S, et al. A TISM based study of SSCM enablers: an Indian coal-fired thermal power plant perspective[J]. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 2019, 10(1): 126-141.
[7]. Mitra S, Avittathur B. Application of linear programming in optimizing the procurement and movement of coal for an Indian coal-fired power-generating company[J]. DECISION, 2018, 45(3): 207–224.
[8]. Rosyid F A, Adachi T. Optimization on long term supply allocation of Indonesian coal to domestic market[J]. Energy Systems, 2018, 9(2): 385–414.
[9]. Lv H D, Zhou J S, Yang L, et al. An accounting of the external environmentalcosts of coal in Inner Mongolia using the pollution damage method[J]. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 2020, 22(2): 1299-1321.
[10]. Li H., Su L. Multimodal transport path optimization model and algorithm considering car bon emission multitask[J]. The Journal of Supereomputing, 2020, 76(12):9355-9373
Cite this article
Jiang,J.;Wang,Z. (2025). Path Selection of Multimodal Transport for Coal Based on Economic and Environmental Benefits. Theoretical and Natural Science,109,18-23.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MPCS 2025 Symposium: Leveraging EVs and Machine Learning for Sustainable Energy Demand Management
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Zhang M.Optimization of Multimodal Transport Routes ConsideringCarbon Emissions in Fuzzy Scenarios [J].International Core Journal of Engineering,2022,8(4):267-281.
[2]. Zhang H,Huang Q,Ma L,et al.Sparrow search algorithm with adaptivet distribution for multi-objective low-carbon multimodal transportationplanning problem with fuzzy demand and fuzzy time [J].Expert Systemswith Applications,2024,238:122042.
[3]. Zheng C,Sun K,Gu Y,et al.Multimodal Transport Path Selection of Cold Chain Logistics Based on Improved Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm[J].Journal of Advanced Transportation,2022(Pt.7):1.1-1.12.
[4]. Rademeyer M, Minni Tt R, Falcon R. Multi-product coal distribution and price discovery for the domestic market via mathematical optimisation[J]. Mineral Economics, 2020, 34: 113-126.
[5]. Botha A, Badenhorst-Weiss J A. Risk management in a bulk coal export logistic chain: A stakeholder perspective[J]. Journal of transport and supply chain management, 2019, 13: 316-324.
[6]. Biswal J N, Muduli K, Satapathy S, et al. A TISM based study of SSCM enablers: an Indian coal-fired thermal power plant perspective[J]. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 2019, 10(1): 126-141.
[7]. Mitra S, Avittathur B. Application of linear programming in optimizing the procurement and movement of coal for an Indian coal-fired power-generating company[J]. DECISION, 2018, 45(3): 207–224.
[8]. Rosyid F A, Adachi T. Optimization on long term supply allocation of Indonesian coal to domestic market[J]. Energy Systems, 2018, 9(2): 385–414.
[9]. Lv H D, Zhou J S, Yang L, et al. An accounting of the external environmentalcosts of coal in Inner Mongolia using the pollution damage method[J]. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 2020, 22(2): 1299-1321.
[10]. Li H., Su L. Multimodal transport path optimization model and algorithm considering car bon emission multitask[J]. The Journal of Supereomputing, 2020, 76(12):9355-9373









