1. Introduction
The Indus Delta, a tropical monsoon-climate alluvial plain in southern Pakistan’s Sindh Province, faces compounded water management challenges from climatic extremes and human interventions. Monsoonal rains (June–August) deliver concentrated heavy precipitation to southern Sindh [1], often causing riverbed overflow, embankment breaches, and urban waterlogging. Aging irrigation infrastructure [2] exacerbates groundwater table elevation via leakage, triggering soil salinization that reduces crop yields and alters wetland vegetation. Climate change amplifies these risks, intensifying seasonal waterlogging-drought cycles, while human activities like inefficient irrigation, urban sprawl, and upstream dams worsen systemic vulnerabilities. Hardened surfaces accelerate runoff, impeding natural drainage, while disrupted water-sediment balances drive coastal erosion and mangrove degradation.
This study investigates multidimensional impacts of climate-human interactions on the delta, focusing on: (1) climate-altered water cycles and hazard patterns (e.g., intensified monsoons, prolonged droughts); (2) anthropogenic drivers of ecological degradation (e.g., irrigation-induced salinization, land-use changes); and (3) integrated strategies for sustainable delta management. By synthesizing hydrological data, remote sensing, and literature, the research aims to establish a scientific basis for water governance and ecological restoration, offering adaptive insights for global deltaic systems.
2. Natural environmental characteristics of Indus River Delta
2.1. Topographic features
The Indus River Delta, a low-lying alluvial plain (average elevation less than10m) in southern Pakistan, formed by millennia of sediment deposition at the Arabian Sea. Its flat terrain features intricate river networks, meandering streams, and abandoned channels, flanked by saline mudflats, marshes, and eroding sandbars. Reduced river sediment and coastal erosion drive shoreline retreat. Fertile alluvial soils dominate, yet irrigation-intensive agriculture has triggered localized salinization. Monsoon dynamics and tidal influences shape this ecologically fragile zone, balancing agricultural productivity with wetland vulnerability to both natural hydrological shifts and human exploitation.
2.2. Climatic and hydrological characteristics
The Indus River Delta exhibits a tropical arid/semi-arid climate marked by monsoonal extremes, with 80% of annual rainfall (average <100 mm at Kotti station, Figure 1) concentrated in June–August under monsoon winds, while other months remain dry. High temperatures (annual mean 25–30°C; summer peaks >40°C) drive evaporation rates exceeding precipitation, intensifying aridity. Projected La Niña effects in 2024 may further elevate rainy-season temperatures in southwestern Pakistan, increasing drought recurrence risks [1].
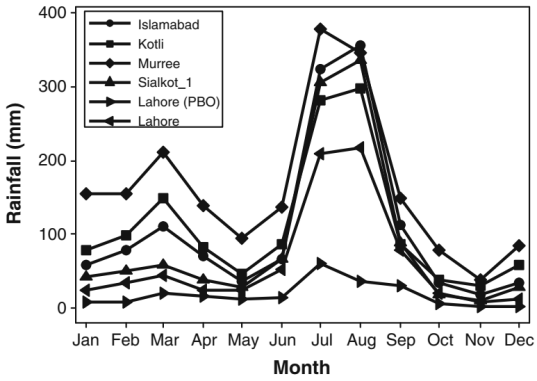
Figure 1: Sum of monthly precipitation from January 1976 to December 1997 of each city [3]
River discharge exhibits strong seasonality [3], driven by glacial melt (53% of upper-basin runoff from Tibetan Plateau glaciers) and irrigation demands. Summer floods deliver 70% of annual flow due to accelerated melt under warming [4], contrasting with winter deficits from reduced melt and negligible precipitation. Mid-lower reaches experience dry-season flow cessation from irrigation withdrawals, exacerbated by high evaporation/infiltration in tropical deserts. Seawater intrusion impedes sediment deposition, inhibiting delta accretion and accelerating erosion. Hydrology integrates climatic (monsoonal recharge, La Niña-amplified extremes [1]) and anthropogenic controls: meltwater-driven surges vs. extraction-induced deficits disrupt sediment transport (critical for delta stability), while warming exacerbates cryospheric vulnerability and irrigation pressures.
2.3. Groundwater distribution and dynamics
The groundwater distribution dynamics in the Indus Basin of Pakistan have undergone significant changes. In the early days, groundwater levels were low due to limited sources of irrigation water. With the expansion of irrigation systems, especially with the widespread use of tube wells after the 1960s, groundwater recharge increased and water levels rose rapidly, leading to extensive waterlogging and salinization (Figure 2). This is particularly severe in the central and southern regions, where groundwater is mostly highly saline due to low-lying and poorly drained areas. Groundwater problems persist despite a variety of measures, including reducing channel leakage, improving field drainage, and using tube wells for drainage [5]. Currently, groundwater management is facing challenges, and further optimization of irrigation management, improvement of drainage systems, and consideration of salt balance and salt disposal issues are needed to ensure sustainable agricultural development.
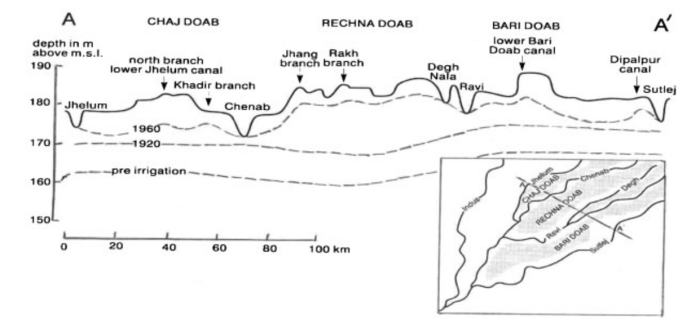
Figure 2: Irrigation induced rises of the water tables in a cross-section over the irrigated land of Northern Punjab, 1860-1950[5]
3. Single-factor drivers
3.1. Climate change
Pakistan ranks among the most climate-vulnerable nations, exhibiting paradoxical coexistence of "drought normalization" and "storm extremes." Hussain [3] employed Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) and Hovmöller diagrams to project drought severity in Sindh (Figure 3). Under RCP2.6, drought mitigation occurs except in the southeastern Indus Delta, while RCP8.5 predicts extreme drought replacing concentrated precipitation during non-monsoon periods. Contrastingly, Atif [6] documented recurring heavy rainfall (2003, 2005, 2006, 2010-2012, 2015-2016), with 2011 delivering Sindh's record rainfall causing province-wide inundation (4-month flood lag). Despite reduced 2012 rainfall, residual soil saturation from prior floods prolonged flood persistence.
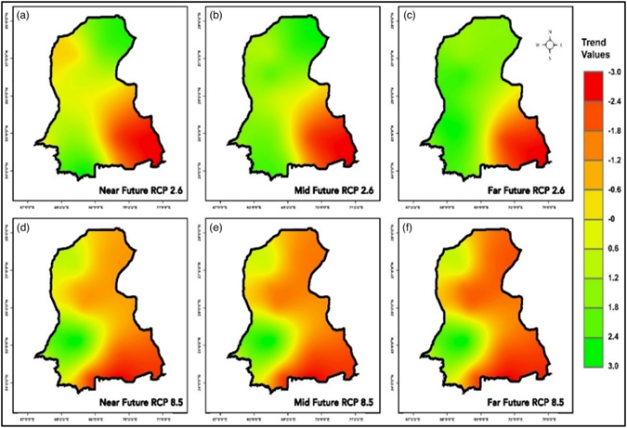
Figure 3: Future drought trends during near-future, mid-future, and far-future periods under RCP 2.6 (a–c) and RCP 8.5 (d–f) [3]
Hydrologically, droughts and floods in the delta stem from climate-driven water cycle imbalances: warming disrupts moisture transport, concentrating rainfall into monsoonal floods (underutilized for water storage) while exacerbating dry-season droughts. This bifurcation reflects precipitation phase-locking – intense wet-season downpours amplify flood risks through rapid surface runoff, whereas inadequate groundwater recharge intensifies dry-season water scarcity. The system’s vulnerability thus arises from amplified hydroclimatic extremes (erratic vapor fluxes) and anthropogenic constraints (inefficient water harvesting), creating a self-reinforcing crisis where flood damage undermines drought resilience and vice versa.
3.2. Human activities
Pakistan’s agriculture (20% GDP [7]) uses 95% of water resources [8], plagued by inefficiencies: flood irrigation wastes >50% water [7], while drip/sprinkler adoption lags due to technological barriers [9]. Uneven water distribution exacerbates dry-season scarcity. Climate change intensifies floods/droughts and reduces glacial-fed river flows, threatening irrigation sustainability. Systemic reforms in water management and irrigation modernization are critical to prevent agricultural crises.
Meanwhile, construction of a dam in the upper reaches of a river can have a number of adverse effects upstream and downstream of the river. For the upstream, reservoir impoundment will lead to localized elevation of the erosion datum, slowing of flow velocity, enhanced sediment deposition, possible formation of backwater deltas and gradual siltation of the reservoir. For the downstream, sediment deposition in the upstream and reduced sediment transport in the downstream will exacerbate coastal erosion, resulting in a shrinking delta area and possible destruction of ecological facilities such as mangrove forests. Moreover, the storage of river water in the dam would allow downstream areas to have access to irrigation water during the dry season, which could exacerbate salinization and waterlogging as mentioned in the context of irrigation issues.
4. Results and feedback
4.1. Ecosystem degradation
Ecosystem degradation in the Indus Delta stems primarily from reduced water/sediment fluxes caused by large-scale hydraulic infrastructure. Pre-20th century sediment discharge exceeded 250 Mt/year, but post-barrage construction triggered progressive declines in both water and sediment flows [10]. This disruption is evidenced by shoreline dynamics: 1972–2017 data show accretion rates substantially outpaced by erosion [11], while Figure 4 reveals reduced deepwater depths (1850–1995), indicating sediment accumulation in offshore zones.
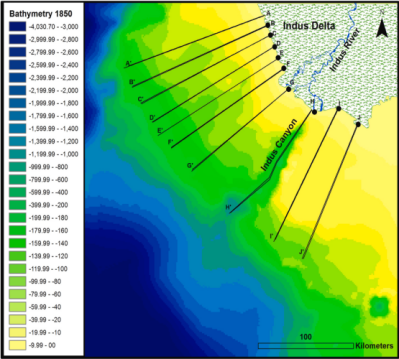
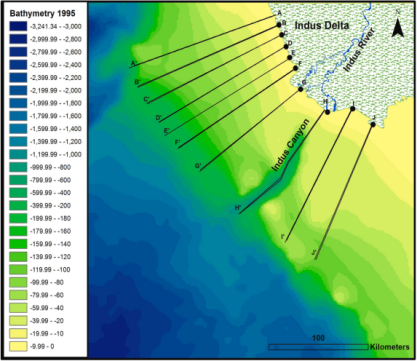
Figure 4: Bathymetry map of offshore Indus Delta, surveyed between 1850 and 1995 [11]
Anthropogenic pressures extend to groundwater systems – intensive irrigation withdrawals have forced overexploitation, creating regional subsurface funnels and exacerbating seawater intrusion.
This has caused severe land salinization, converting fertile agricultural zones to barren land. The delta hosts >90% of Pakistan’s mangroves, occupying 25% of the national coastline. However, human activities drove 96.1 km² mangrove loss in the western delta (1990–2020) [12], with central/western coastlines experiencing severe erosion. These changes degrade critical habitats, accelerating biodiversity loss and amplifying ecosystem vulnerability.
Cumulatively, these perturbations – sediment starvation, hydrological regime alteration, coastal erosion, and biosphere degradation – threaten local livelihoods while impacting global biodiversity networks and climate feedback systems through carbon sink reduction and coastal protection loss.
4.2. Salinization and urban waterlogging
Soil salinization arises from natural and anthropogenic factors. Natural drivers include salt transport via deep rainfall infiltration, flood-induced salt deposition, and poor drainage from hard soils. Human activities exacerbate salinity through unlined irrigation canals (seepage losses), over-irrigation, upland hydraulic salt migration, and infrastructure (roads/railroads) blocking natural drainage. Annually, Indus irrigation diverts 33 million tons of salt, with only 16.4 million tons reaching the sea, accumulating ~16.6 million tons in the delta [2]. Subsurface seawater intrusion affects 88% of the delta [13], causing soil compaction, reduced infiltration, and intensified waterlogging while diminishing vegetation’s flood buffering capacity.
Sindh faces riverine/flash floods (driven by extreme monsoon rainfall) and urban waterlogging (linked to impervious surfaces [14]). Natural surfaces enable rainwater infiltration and purification via soil-vegetation-microorganism systems, while impermeable surfaces force rapid runoff, overwhelming drainage systems. Groundwater recharge is disrupted, and runoff velocity/volume surges, creating a vicious cycle: “infiltration blockage→runoff surge→storage failure.” Surface hardening further disrupts evapotranspiration, amplifying water cycle imbalances.
5. Sustainable management strategies and recommendations
To address Indus Delta flooding and salinity, the Sindh Irrigation Department constructed eight small dams in the Lat Nai basin. Proposed engineering measures include smart drainage upgrades, modular pumping stations, and underground cisterns to counter low-lying topography, with IoT-enabled flow regulation and GIS/remote sensing-based water inventories mitigating monsoon waterlogging. Ijaz et al. [15] recommend increasing freshwater flows to 250 m³/s (~94% salinity reduction at saline-freshwater interfaces) and deploying ecological breakwaters (oyster reefs, mangrove piles) in erosion-prone western zones.
Mangrove restoration is critical: their ecosystems reduced DOC and POC concentrations by 19.3% and 22.7% respectively [16]. Strategies include artificial wetland-agricultural buffers (planting salt-adsorbing reeds/balsam ferns) and ecological ditch networks to divert waterlogged water for purification/groundwater recharge. To safeguard livelihoods, saline-adapted agriculture and small-scale solar desalination units are proposed for 500,000 farmers.
6. Conclusion
The Indus Delta faces intertwined climatic and anthropogenic crises. Climate warming disrupts precipitation patterns, intensifying waterlogging-drought cycles and complicating water governance. Human interventions exacerbate risks: outdated irrigation accelerates groundwater salinization, urban sprawl degrades natural drainage, and upstream dams trap sediment (aggravating coastal erosion). Ecosystem degradation manifests as mangrove loss, soil fertility decline, and biodiversity collapse, directly threatening agriculture and livelihoods.
This study proposes a "nature-engineering-society" governance framework: (1) Engineering solutions (drainage optimization, freshwater replenishment); (2) Policy innovations (cross-regional cooperation, water quotas); (3) Ecological restoration (mangrove rehabilitation, constructed wetlands). These aim to mitigate salinization, flooding, and erosion while enhancing resilience, balancing short-term mitigation with long-term adaptation to avoid environmental risks.
Key limitations include: (1) Insufficient spatiotemporal data resolution and incomplete hydrological records; (2) Oversimplified climate-human interaction models lacking quantitative driver analysis; (3) Underexplored socioeconomic factors (e.g., farmer water-use behaviors, policy implementation efficacy).
Future priorities involve: (1) Integrating high-resolution remote sensing with field data for dynamic water-salinity models; (2) Multi-scenario simulations (RCP4.5/8.5 climate trajectories, governance synergies); (3) Interdisciplinary frameworks incorporating social behavior models to decode policy-economic-cultural drivers. Coastal-marine interactions (e.g., sea-level rise impacts on saltwater intrusion) require urgent attention for adaptive planning. This multidimensional strategy could guide sustainable delta management, offering insights for global coastal systems.
References
[1]. Government of Pakistan. (2024) Contingency plan 2024. https://www.mowr.gov.pk/
[2]. Asad Sarwar Qureshi. (2011) Water Management in the Indus Basin in Pakistan: Challenges and Opportunities. Mountain Research and Development, 31(3):252-260.
[3]. Zafar Hussain, Zongmin Wang, et al. (2024) CORDEX Ensemble-based drought projections for Sindh Province of Pakistan under climate change. Journal of Water and Climate Change, 1 November; 15 (11): 5501–5517.
[4]. Ajit T. Singh, C.M. Laluraj, Parmanand Sharma, et al. (2021) Hydrograph apportionment of the Chandra River draining from a semi-arid region of the Upper Indus Basin, western Himalaya, Science of The Total Environment, Volume 780, 146500.
[5]. Bhutta, M.N. and Smedema, L.K. (2007) One hundred years of waterlogging and salinity control in the Indus valley, Pakistan: a historical review†. Irrig. and Drain, 56: S81-S90.
[6]. Atif, S., Umar, M. & Ullah, F. (2021) Investigating the flood damages in Lower Indus Basin since 2000: Spatiotemporal analyses of the major flood events. Nat Hazards, 108, 2357–2383.
[7]. Rehman, A., Ma, H., Oláh, J., Alvarado, R., & Işık, C. (2023). Agricultural machinery, irrigation systems and food grains: A symmetric novel analysis. Cogent Food & Agriculture, 9(2).
[8]. Government of Pakistan (2018) National Water Policy. https://www.mowr.gov.pk/
[9]. Adnan M., Xiao B., Bibi S., et al. (2024) Known and Unknown Environmental Impacts Related to Climate Changes in Pakistan: An Under-Recognized Risk to Local Communities. Sustainability, 16(14):6108.
[10]. Gohar Ali Mahar, Nayyer Alam Zaigham, Muhammad Azam, Syed Ikhlaq Hussain. (2022) Morphological evolution of Indus shelf region under the influence of hydrodynamic conditions in 20th century, Journal of Sea Research, Volume 184, 102216.
[11]. Altaf Ali Siyal, Ghulam Shabir Solangi, et al. (2022) Shoreline change assessment of Indus delta using GIS-DSAS and satellite data, Regional Studies in Marine Science, Volume 53, 2022102405.
[12]. Hafsa Aeman, Hong Shu, Sawaid Abbas, Hamera Aisha, Muhammad Usman. (2023) Sinking delta: Quantifying the impacts of saltwater intrusion in the Indus Delta of Pakistan, Science of The Total Environment, Volume 880, 2023, 163356.
[13]. Solangi, Ghulam Shabir; Siyal, Altaf Ali; Siyal, Pirah. (2023) Indication of subsurface seawater intrusion into the Indus delta, Sindh, Pakistan. Mehran University Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, [S.l.], v. 42, n. 1, pp. 9-16.
[14]. Yuqin Huang, Jinyao Lin, Xiaoyu He, Zhuochun Lin, Zhifeng Wu, Xinchang Zhang. (2024) Assessing the scale effect of urban vertical patterns on urban waterlogging: An empirical study in Shenzhen, Environmental Impact Assessment Review, Volume 106, 107486.
[15]. Muhammad Wajid Ijaz, Rasool Bux Mahar, Kamran Ansari, Altaf Ali Siyal. (2019) Optimization of salinity intrusion control through freshwater and tidal inlet modifications for the Indus River Estuary, Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, Volume 224, pp. 51-61.
[16]. Waqar Ahmed, Ying Wu, Samina Kidwai, Xiuzhen Li, Tariq Mahmood, Jing Zhang. (2021) Do Indus Delta mangroves and Indus River contribute to organic carbon in deltaic creeks and coastal waters (Northwest Indian Ocean, Pakistan)? Continental Shelf Research, Volume 231, 104601.
Cite this article
Xu,A. (2025). The Indian River Delta under the Interweaving of Climate Change and Human Activities: Multidimensional Impacts from Waterlogging to Salinization. Theoretical and Natural Science,102,69-74.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of ICEGEE 2025 Symposium: Impact of Technological Innovation on Energy Efficiency in European Countries
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Government of Pakistan. (2024) Contingency plan 2024. https://www.mowr.gov.pk/
[2]. Asad Sarwar Qureshi. (2011) Water Management in the Indus Basin in Pakistan: Challenges and Opportunities. Mountain Research and Development, 31(3):252-260.
[3]. Zafar Hussain, Zongmin Wang, et al. (2024) CORDEX Ensemble-based drought projections for Sindh Province of Pakistan under climate change. Journal of Water and Climate Change, 1 November; 15 (11): 5501–5517.
[4]. Ajit T. Singh, C.M. Laluraj, Parmanand Sharma, et al. (2021) Hydrograph apportionment of the Chandra River draining from a semi-arid region of the Upper Indus Basin, western Himalaya, Science of The Total Environment, Volume 780, 146500.
[5]. Bhutta, M.N. and Smedema, L.K. (2007) One hundred years of waterlogging and salinity control in the Indus valley, Pakistan: a historical review†. Irrig. and Drain, 56: S81-S90.
[6]. Atif, S., Umar, M. & Ullah, F. (2021) Investigating the flood damages in Lower Indus Basin since 2000: Spatiotemporal analyses of the major flood events. Nat Hazards, 108, 2357–2383.
[7]. Rehman, A., Ma, H., Oláh, J., Alvarado, R., & Işık, C. (2023). Agricultural machinery, irrigation systems and food grains: A symmetric novel analysis. Cogent Food & Agriculture, 9(2).
[8]. Government of Pakistan (2018) National Water Policy. https://www.mowr.gov.pk/
[9]. Adnan M., Xiao B., Bibi S., et al. (2024) Known and Unknown Environmental Impacts Related to Climate Changes in Pakistan: An Under-Recognized Risk to Local Communities. Sustainability, 16(14):6108.
[10]. Gohar Ali Mahar, Nayyer Alam Zaigham, Muhammad Azam, Syed Ikhlaq Hussain. (2022) Morphological evolution of Indus shelf region under the influence of hydrodynamic conditions in 20th century, Journal of Sea Research, Volume 184, 102216.
[11]. Altaf Ali Siyal, Ghulam Shabir Solangi, et al. (2022) Shoreline change assessment of Indus delta using GIS-DSAS and satellite data, Regional Studies in Marine Science, Volume 53, 2022102405.
[12]. Hafsa Aeman, Hong Shu, Sawaid Abbas, Hamera Aisha, Muhammad Usman. (2023) Sinking delta: Quantifying the impacts of saltwater intrusion in the Indus Delta of Pakistan, Science of The Total Environment, Volume 880, 2023, 163356.
[13]. Solangi, Ghulam Shabir; Siyal, Altaf Ali; Siyal, Pirah. (2023) Indication of subsurface seawater intrusion into the Indus delta, Sindh, Pakistan. Mehran University Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, [S.l.], v. 42, n. 1, pp. 9-16.
[14]. Yuqin Huang, Jinyao Lin, Xiaoyu He, Zhuochun Lin, Zhifeng Wu, Xinchang Zhang. (2024) Assessing the scale effect of urban vertical patterns on urban waterlogging: An empirical study in Shenzhen, Environmental Impact Assessment Review, Volume 106, 107486.
[15]. Muhammad Wajid Ijaz, Rasool Bux Mahar, Kamran Ansari, Altaf Ali Siyal. (2019) Optimization of salinity intrusion control through freshwater and tidal inlet modifications for the Indus River Estuary, Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, Volume 224, pp. 51-61.
[16]. Waqar Ahmed, Ying Wu, Samina Kidwai, Xiuzhen Li, Tariq Mahmood, Jing Zhang. (2021) Do Indus Delta mangroves and Indus River contribute to organic carbon in deltaic creeks and coastal waters (Northwest Indian Ocean, Pakistan)? Continental Shelf Research, Volume 231, 104601.









