1. Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected the world since its emergence in December 2019. It has caused significant disruptions to daily life, including widespread lock-downs, economic downturns, and strained healthcare systems. While research on the pandemic has focused on its direct impact, there is a growing recognition of the pandemic's indirect effects, such as its impact on mental health, the economy, and livelihoods. This review will explore how the pandemic has impacted healthcare, economics, livelihoods, and mental health. By examining both specific research on COVID-19 and broader research on similar topics, this review will identify knowledge gaps and limitations in the existing literature. Ultimately, this paper seeks to provide insight into the importance of understanding the full range of pandemic impacts and identifying opportunities for intervention and support.
2. Methodology
This literature review focuses on three main topics that have been indirectly impacted by the pandemic: mental health, health care, and the economy. A systematic search was conducted in research databases (ProQuest, JSTOR, and Google Scholar) using the selected keywords "mental health," "healthcare," and "economy". The search was limited to articles published in English between 2019 and the present. Primary research was also conducted through interviews to gain insight through individual perspectives. Through the review of current studies, this literature review aims to identify and discuss gaps in research regarding groups of people who have been indirectly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. The discussion of these gaps will highlight the need for further relevant research to fill in these gaps.
3. Results
Upon reviewing the literature on several key themes that were selected for studies, the following themes were analyzed: 'mental health,' 'healthcare,' and 'economy'. The subsequent sections will provide a summary of the results related to each of these themes.
3.1. Mental health
The negative impact of COVID-19 regulations on mental health has been observed in many countries, despite efforts by public health officials to prevent outbreaks. For instance, in Canada, there has been a 13% decline in the number of citizens reporting excellent or very good mental health compared to pre-COVID years [1]. This decline is largely attributed to anxiety and pressure caused by factors such as uncertain income and continuous social isolation, which have been shown to affect adults and teenagers differently. Studies reveal that among adults, employment status is linked to mental health during the pandemic, with those absent from work due to COVID-19 reporting the lowest levels of excellent mental health [1]. Furthermore, the pandemic-induced uncertainty has led to stress, anxiety, insecurity, frustration, and other emotional outcomes among employees in quarantine, significantly disrupting their mental status. Interestingly, teenagers have taken a more negative approach to cope with the sudden emotional outburst caused by the pandemic. According to Statistics Canada, teenagers between 15 to 35 years old have shown a significant increase in substance use due to poor mental health, with cannabis use experiencing the greatest decline since the pandemic began. This result emphasizes the negative impact of COVID-19 and its regulations on teens and their mental health.
Overall, the results of the studies reviewed demonstrate the significant negative impact that COVID-19 and its regulations have had on the mental health of individuals in various countries, including Canada. The findings highlight the need for continued efforts to support mental health and well-being during and after the pandemic. It is clear that the pandemic has caused widespread disruption and uncertainty, leading to stress and anxiety that have affected both adults and teenagers. It is important for public health officials and policymakers to take these findings into consideration when developing strategies to address the ongoing mental health crisis. By recognizing and addressing the challenges faced by individuals during the pandemic, society can work towards a healthier and more resilient future.
3.2. Health care
The COVID-19 pandemic has had far-reaching effects on healthcare systems globally, including weakened healthcare services resulting from resource and provider shortages, primarily in COVID-19-related areas. An article highlights the impact of COVID-19 on healthcare in Italy, one of the countries hardest hit by the pandemic. It was noted that healthcare systems were overwhelmed, with shortages of hospital beds, ICU beds, and healthcare workers, leading to resource allocation challenges and a reduction in the quality of care [2]. According to Dr. Dan, who currently works in a provincial hospital, the sudden influx of walk-inpatients due to COVID-19 infections caused staff shortages, stressing the operation of other departments. This situation presented challenges for hospital management, with overworked staff and concerned patients seeking care beyond COVID-19 infections. Though, despite the difficulties, healthcare professionals have continued to work tirelessly to provide care to those in need during this unprecedented time.
3.3. Economics
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has also expanded to the global economy. From larger countries to smaller individuals, many have experienced a crash in economic growth. The sharp decline in global economic activity caused a loss of over two trillion US dollars of economic output in 2020, with the global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) decreasing by 3.4%. Additionally, there was a decline of 11.6% change in global goods trade volume as of April 2020 [3]. However, these losses were followed by a V-shaped recovery in later 2020 [4]. While larger countries have experienced a quicker recovery, smaller countries with strong dependence on tourism as their primary source of GDP have struggled to recover. A recent 2022 report from the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) noted that “the pandemic caused an unprecedented disruption to tourism, with a massive fall of international demand amid widespread lock-downs and travel restrictions” [5]. According to the World Tourism Organization, 2020,the year that marks the start of the pandemic, was the worst year on record for tourism. In the same year, international tourism rates experienced sudden declines in numbers since January 2020; with a -72% change in comparison with 2019, the international tourists arrivals in 2020 remained low after the first three months of the pandemic, only having a steady increase since the beginning of 2022 [5] (Figure 1).
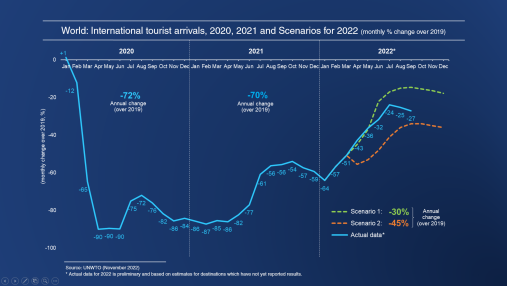
Figure 1. Impact assessment of the COVID-19 outbreak on international tourism [5].
The disruptive hit on the tourism economy can also be reflected in the loss in Tourism Direct Gross Domestic Product (TDGDP), from a total of 3.5 trillion in 2019 to only 1.7 trillion US dollars in 2020. In fact, as recently as 2022, international travel has yet to recover from the downfall since COVID-19 hit; by September 2022, only 57% of 2019 levels were recovered in the world. Especially for the Asia Pacific regions, less than one-fifth of international tourist arrivals were recovered in 2022 [5]. (Figure 2)
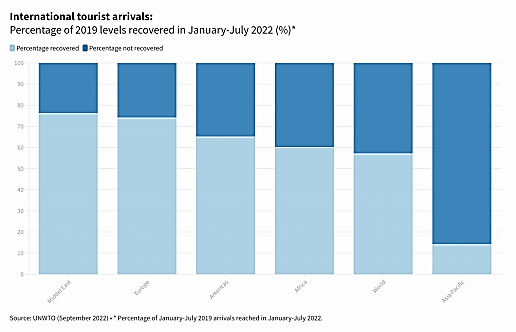
Figure 2. Impact assessment of the COVID-19 outbreak on international tourism [5].
In conclusion, the pandemic has had a severe impact on the global economy, with smaller countries heavily dependent on tourism experiencing significant economic losses. Although larger countries have seen a quicker recovery, the international travel industry has yet to fully recover.
4. Discussion
The reviewed articles highlight the far-reaching effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, demonstrating its negative impact on people's lives in various aspects. The evidence indicates a significant decline in public mental health during lock-downs, weakened healthcare experienced by patients and healthcare workers, and a massive loss in the global tourism economy that is still struggling to recover. These findings underscore the urgent need for continued research and targeted interventions to mitigate the pandemic's impact and support affected individuals and communities. However, while the literature on the impact of the pandemic has extensively covered certain areas, there are still neglected areas that require attention. By exploring these overlooked areas, a more nuanced understanding of the impact of the pandemic will be gained. In particular, declined mental health of healthcare providers, the fragility of the global healthcare system, and the disruption to local small businesses will be focused on to shed light on their significance and implications.
First, in addition to articles that examine the impact of the pandemic on the general public's mental health, there should be extended studies that highlight the mental health challenges faced by healthcare workers during the pandemic. [6] provided their unique perspective by focusing on this specific group and their experiences and struggles during this difficult time. The mental health of healthcare workers has been identified as a critical concern during the COVID-19 pandemic, given the decline in their mental well-being with “7 in 10 healthcare workers who participated in a crowd sourcing initiative reported worsening mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic” [7]. In Italy, a survey of front-line and second-line healthcare workers revealed symptoms of post-traumatic stress and depression. Similar studies in China reported high levels of stress-related mental health issues, including insomnia, depression, and anxiety, among healthcare workers with direct contact with COVID-19 patients. To summarize, these findings highlight the impact of the overwhelming and stressful environment that healthcare workers face in the fight against the pandemic, and the importance of addressing and aiding their mental health needs. It is crucial to expand the current research on mental health impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic to address the challenges faced by healthcare workers, as their mental health needs are equally important.
Second, The COVID-19 pandemic has also underscored the need for global preparedness in the face of health crises, revealing the fragility of healthcare systems worldwide. Despite the challenges posed by the pandemic, healthcare professionals have shown remarkable dedication and resilience in providing care to those in need. Moving forward, confronting the systemic issues that contributed to weakened healthcare services during the pandemic and developing strategies to strengthen healthcare systems are crucial steps to better prepare for future health crises. The pandemic's impact on global healthcare systems affected not only patients and providers but also other individuals who lost access to essential equipment and resources for treatment. Moreover, the overwhelming demands on doctors and other healthcare providers caused associated medical resources to become scarce due to limited numbers. As a result, the pandemic disrupted cancer screening in the community, which may lead to an increase in cancer rates and deaths, as suggested by a study by Yong that found a correlation between the length of screening interruption and the corresponding number of cancer cases [8]. (Figure 3) In conclusion, the revealed vulnerability of healthcare systems demands the need for greater preparedness and investment in healthcare infrastructure to ensure a better response to future health crises.
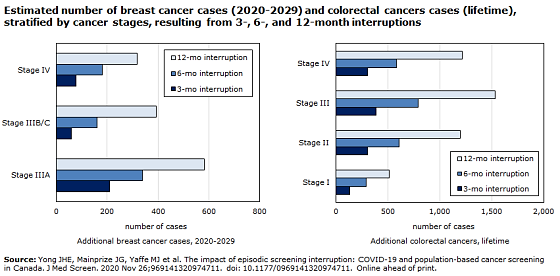
Figure 3. The impact of episodic screening interruption: COVID-19 and population-based cancer screening in Canada [8].
Third, the pandemic's impact was not limited to the economy of the tourism industry studied in most literature reviewed. Small businesses, which constitute a significant portion of the market in many countries, have also been adversely affected. As indicators of the national economy, they take up a great part of the overall market in countries. For context, in Canada, small businesses employ about two-thirds of the total labor force in the country [9], and in the United States, they employ almost half of all American workers [10]. The restrictions and regulations including social distancing and quarantine plans for containing the spread of the virus largely affected these businesses. As of April 2020, 43% of businesses were temporarily closed [10]. To some, the temporary closure was a challenge to their survival as a business. Researches suggest that options left for these businesses are “dramatically cut expenses, take on additional debt, or declare bankruptcy”, by which many were forced to make the cut in employed workers, with a 40% fall in employment rate since businesses’ closures [10, 11]. Furthermore, the closures of businesses have not only caused high rates of unemployment and bankruptcy but also triggered a chain reaction that has had extensive consequences on the local economy. The resulting poverty, worsened mental health, and poor livelihoods affect more people, exacerbating the pandemic's negative impact on communities. It is why this aspect should be examined more in the global recovery from the pandemic.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, the reviewed literature has provided evidence of the negative impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on various aspects of people's lives, including mental health, healthcare, and the economy. It is clear that the pandemic has exposed and exacerbated existing societal inequalities, and urgent interventions are needed to mitigate its impact and support affected individuals and communities. Further research is necessary to better understand the specific challenges and needs of different populations and to ensure an inclusive global recovery plan that covers all affected.
References
[1]. Impacts on Mental Health. (2020, October 20). Statistics Canada. Retrieved March 5, 2023, from https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/11-631-x/2020004/s3-eng.htm
[2]. Livingston, E., & Bucher, K. (2020). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. JAMA, 323(14), 1335. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.4344
[3]. Impact of the coronavirus pandemic on the global economy - Statistics & Facts. (2023, January 17). Statista. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www.statista.com/topics/6139/COVID-19-impact-on-the-global-economy/#topicOverview
[4]. Arriola, C., Cadestin, C., Kowalski, P., & Tongeren, F. V. (2022, March 10). International trade during the COVID-19 pandemic: Big shifts and uncertainty. OECD. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/international-trade-during-the-COVID-19-pandemic-big-shifts-and-uncertainty-d1131663/
[5]. Impact assessment of the COVID-19 outbreak on international tourism. (2022). UNWTO. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www.unwto.org/impact-assessment-of-the-COVID-19-outbreak-on-international-tourism
[6]. Guerrini, C. J., Storch, E. A., & McGuire, A. L. (2020). Essential, not peripheral: Addressing health care workers’ mental health concerns during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Occupational Health, 62(1) https://doi.org/10.1002/1348-9585.12169
[7]. COVID-19 in Canada: A One-year Update on Social and Economic Impacts. (2021, March 11). Statistique Canada. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/11-631-x/11-631-x2021001-eng.htm#a3
[8]. Yong JHE, Mainprize JG. Yaffe MJ et al. The impact of episodic screenning interruption: COVID-19 and population-based cancer screening in Cnada. J med Screen. 2020 Nov 26;969141320974711. doi:10.1177/0969141320974711
[9]. Li, B., Sood, S., & Johnston, C. (2022, January 6). Data to Insights for a Better Canada Impact of COVID-19 on small businesses in Canada,fourth quarter of2021. Statistique Canada. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/45-28-0001/2021001 /article/00043-eng.htm
[10]. Bartik, A. W., Marianne, M., Cullen, Z., Glaeser, E. L., Luca, M., & Stanton, C. (2020, July 10). PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES, 117(30). https://doi. org/10.1073/pnas.2006991117
[11]. Sundaram, A. (2020, September 16). Yelp data shows 60% of business closures due to the coronavirus pandemic are now ermanent. CNBC. Retrieved March6, 2023, from https://www.cnbc.com/2020/09/16/yelp-data-shows-60percent-of-business-closures-due-to-the-coronavirus-pandemic-are-now-permanent.html
Cite this article
Wang,Z. (2023). The extensive impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on various aspects of people's lives: A literature review. Theoretical and Natural Science,7,33-38.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Environmental Geoscience and Earth Ecology
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Impacts on Mental Health. (2020, October 20). Statistics Canada. Retrieved March 5, 2023, from https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/11-631-x/2020004/s3-eng.htm
[2]. Livingston, E., & Bucher, K. (2020). Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. JAMA, 323(14), 1335. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.4344
[3]. Impact of the coronavirus pandemic on the global economy - Statistics & Facts. (2023, January 17). Statista. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www.statista.com/topics/6139/COVID-19-impact-on-the-global-economy/#topicOverview
[4]. Arriola, C., Cadestin, C., Kowalski, P., & Tongeren, F. V. (2022, March 10). International trade during the COVID-19 pandemic: Big shifts and uncertainty. OECD. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www.oecd.org/coronavirus/policy-responses/international-trade-during-the-COVID-19-pandemic-big-shifts-and-uncertainty-d1131663/
[5]. Impact assessment of the COVID-19 outbreak on international tourism. (2022). UNWTO. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www.unwto.org/impact-assessment-of-the-COVID-19-outbreak-on-international-tourism
[6]. Guerrini, C. J., Storch, E. A., & McGuire, A. L. (2020). Essential, not peripheral: Addressing health care workers’ mental health concerns during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Occupational Health, 62(1) https://doi.org/10.1002/1348-9585.12169
[7]. COVID-19 in Canada: A One-year Update on Social and Economic Impacts. (2021, March 11). Statistique Canada. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/11-631-x/11-631-x2021001-eng.htm#a3
[8]. Yong JHE, Mainprize JG. Yaffe MJ et al. The impact of episodic screenning interruption: COVID-19 and population-based cancer screening in Cnada. J med Screen. 2020 Nov 26;969141320974711. doi:10.1177/0969141320974711
[9]. Li, B., Sood, S., & Johnston, C. (2022, January 6). Data to Insights for a Better Canada Impact of COVID-19 on small businesses in Canada,fourth quarter of2021. Statistique Canada. Retrieved March 6, 2023, from https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/45-28-0001/2021001 /article/00043-eng.htm
[10]. Bartik, A. W., Marianne, M., Cullen, Z., Glaeser, E. L., Luca, M., & Stanton, C. (2020, July 10). PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES, 117(30). https://doi. org/10.1073/pnas.2006991117
[11]. Sundaram, A. (2020, September 16). Yelp data shows 60% of business closures due to the coronavirus pandemic are now ermanent. CNBC. Retrieved March6, 2023, from https://www.cnbc.com/2020/09/16/yelp-data-shows-60percent-of-business-closures-due-to-the-coronavirus-pandemic-are-now-permanent.html









