1. Introduction
Artificial Intelligent (AI) is a comprehensive discipline that utilizes computer simulation, extension and extension of human theory, method and technology, and is considered to be one of the three cutting-edge technologies in the 21st century. It covers many fields such as computer science, symbolic logic, bionics, information theory, and cybernetics, and belongs to the three interdisciplinary disciplines of natural science, social science, and technical science [1, 2].
The concept of “AI” has mainly gone through three stages of development since it was proposed at the Dartmouth Conference in 1956, namely 1956-1980 In the initial stage of AI, the prevalence of the expert system from 1980 to 1990, and the deep learning stage from 2000 to the present. At present, AI has become a research and application hot spot in various fields. China is one of the countries with the earliest and fastest action in the field of AI in the world. Since 2015, it has successively promulgated ‘Made in China’. 2025, “Guiding Opinions on Actively Promoting ‘Internet +’ Actions”, “The ‘Thirteenth Five-Year’ National Strategic Emerging Industry Development Plan”, “New Generation of AI Development” Policies such as “Plan” have planned the key development direction of AI in detail from various aspects, and clearly pointed out that AI is the core technology of a new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation [3]. Through figure 1, it can be more intuitive and clearer to indicate the above content [4].
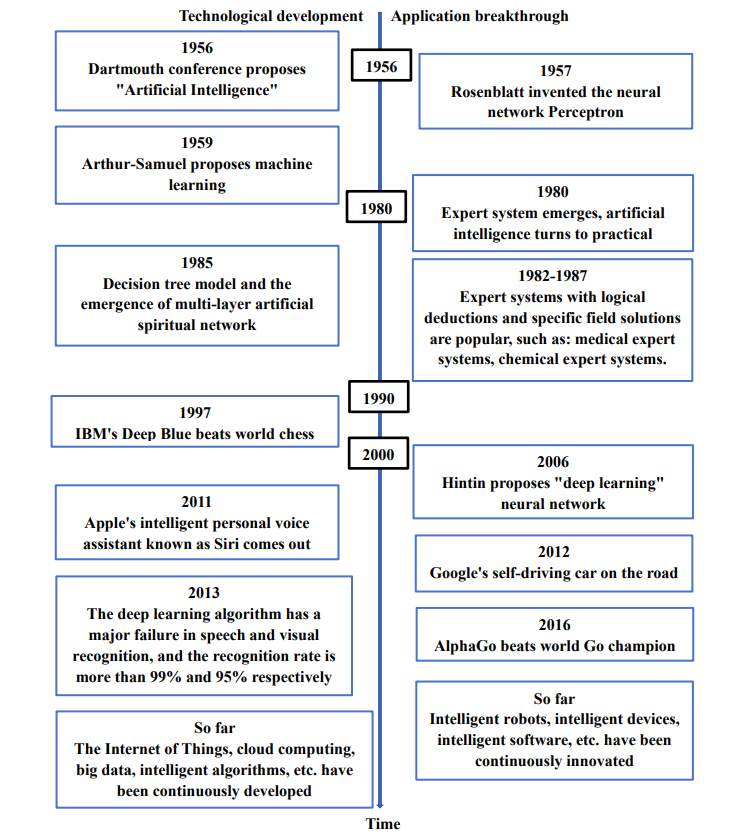
Figure 1. Artificial intelligence development history [4].
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and civil engineering has created an era of change, and the traditional construction process is evolving into an intelligent data-driven system. This transformation of this model not only reshapes the way we conceive and execute civil engineering projects, but also hopes to achieve unprecedented efficiency, sustainability and safety. In an era marked by urbanization and infrastructure needs, it has become imperative to leverage the power of AI [5]. This paper discusses the multi-faceted landscape of the intersection of AI and civil engineering, and reveals the various applications, breakthroughs and impacts of AI to the construction industry. From design optimization and structural health monitoring to robotics and intelligent infrastructure, the emerging field of intelligent buildings is studied, where the capabilities of artificial intelligence are used to redefine the foundations of civil engineering practice.
2. Definition and characteristics of intelligent construction
Intelligent construction refers to a new construction method that combines civil engineering construction with informatization and intelligence, but at present, there is no unified and precise definition of intelligent construction in the industry. Some experts and scholars define intelligent construction as: AI, big data, Building information modeling (BIM) as well as the IoT blockchain to the programme, design, construction and operation and maintenance of civil engineering construction. This system that combines information technology with traditional civil engineering construction is called an intelligent construction technology system. Compared with traditional civil engineering construction, intelligent construction has the characteristics of more comprehensive perception and more realistic analysis, which can control the equipment timelier and continuously monitor and correct it.
(1) Comprehensive perception
As the name suggests, it refers to the use of various types of sensors and related instruments to collect and organize various data during the construction process, and upload and store them. It is beneficial for the staff to remotely obtain the on-site data and analyse it when they cannot arrive at the site, and give technical guidance to the construction site at the first time.
(2) Real analysis
The data collected by devices such as sensors can be used by technicians to analyse and eliminate unreasonable parts, and establish a dimensional model. It is simulated in the simulation laboratory to eliminate the risks that may arise from later construction.
(3) Continuous monitoring
Through intelligent devices, various on-site data can be continuously collected and transmitted to the background database in real time. Background personnel can analyze the same type of data at different times through the corresponding software, so as to eliminate abnormal data, reduce errors, and achieve the expected construction effect. Similarly, it can also be operated on smart devices in the field to achieve automation and unmanned, reducing production risks.
3. Intelligent design
In the design industry, art and technology have always been a combination of art. Not only should the ornamentality and practicality be considered, but also the rationality and aesthetics of the mechanical structure should also be considered. In the traditional civil engineering structural design, due to the serious designer experience dependence on the structural design scheme, there will be unfavorable factors such as time difference, long construction period, and difficult communication when interacting with the shape design and structural design. It is impossible to effectively obtain the global optimal solution for the space-time of complex large systems, so it is impossible to realize the integrated design of geometry and structure.
With the development of the times, AI has developed rapidly in the fields of computer vision and graphics in recent years, especially in deep intelligent algorithms. Relying on its powerful nonlinear expression ability and algorithm optimization, it can provide new theories and methods for the intelligent design of civil engineering. As far as the current development trend is concerned, it is the general trend of the development of the discipline to cross the discipline of AI and civil engineering design. After research, relevant experts put forward the theory and scheme to describe the optimization of art design and geometric constraint structure through mathematics, so as to realize the automation of architectural art design, model the real data and continue to optimize the model, which will be a development trend of the civil engineering architectural design industry in the future. It is mainly used in urban planning and design and selection and optimization of design schemes [6, 7].
3.1. Urban planning and design
Urban planning design refers to the regulation of urban development, the deployment of urban construction, and the study of urban layout. Having a reasonable urban planning is the premise of ensuring the orderly development of the city. In recent years, AI has begun to be applied to urban planning, which is regarded as a huge change in this field. AI can be applied in many links, such as the detection of geological conditions, the investigation of human traffic behavior habits, and AI can be used to reduce planning errors caused by these objective factors. This method is intelligent planning. In 2018, Academician Wu [8] constructed an urban intelligent model based on the actual planning project, and used AI to make an accurate layout of urban planning, and proposed an urban planning method of “fixing by flow”. In the same year, Professor Gan [9] deduced the development paths of various cities in the Yangtze River Delta in the fields of regional infrastructure, ecological resources, land utilization rate, and industrial division of labor in the fields of competition and cooperation in the fields of the Yangtze River Delta.
3.2. Design scheme selection and optimization
Design scheme selection and optimization, also known as expert system, refers to converting the knowledge and experience of existing experts in the field of civil engineering into digital forms in the early stage of AI development, and stored in intelligent computer systems. AI is used to analyze decisions and to solve complexities that require experts to decide in the relevant fields. In 2000, a group of experts led by Professor Zhu [10] conducted the research and development of the foundation pit support structure expert system, which can provide the basis and help for the geotechnical engineers in the subsequent selection of the foundation pit support structure design scheme [11]. In 2021, Nie et al. proposed a generative topology optimization model based on deep learning. The framework is 3 times lower than the traditional Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (CGAN) framework, and the absolute error is reduced by 2.5 times, which greatly improves the prediction accuracy of the topology, as shown in figure 2 [12].
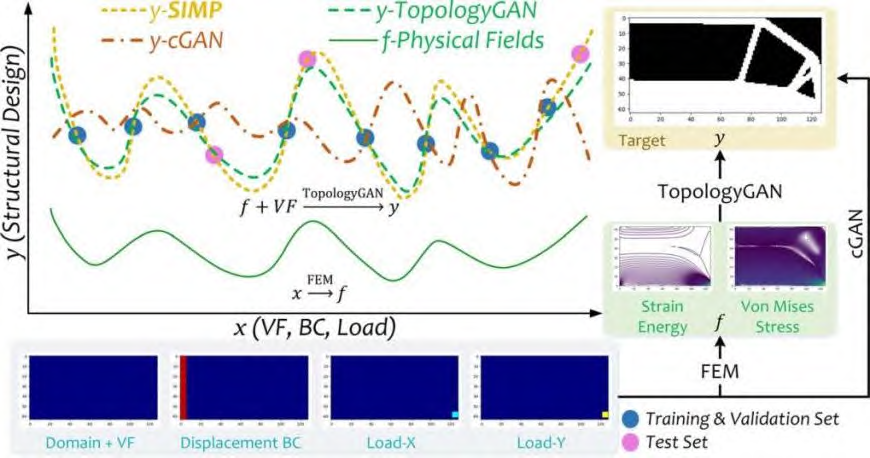
Figure 2. TopologyGAN model based on deep learning [12].
4. Intelligent construction
Intelligent construction is an intelligent construction method, the organic combination of new generation of information technology and engineering construction, and a new development direction in the construction of modern civil engineering. The new generation of technologies includes AI, BIM, 3D printing, Internet of Things and big data.
4.1. BIM
BIM technology adopts digital and modeling to express the physical state and functional characteristics of the structure, which can cover the whole life period from planning and design to construction and maintenance. At different stages, the twin model of the fusion of digital and physical virtual and real is formed by adding, extracting, modifying and updating the structure information to the BIM structural model. In this way, it can not only allow the designer to conduct more scientific design, expansion design, construction drawing design, etc., but also for the construction party to optimize the construction plan, inspect the construction quality, and shorten the construction cycle. Finally, it can also be used by the operation and maintenance party to manage space facilities, check safety hazards, and reduce operation and maintenance costs [8]. In recent years, BIM technology has been applied in practical projects such as the National Convention and Exhibition Center, and has played a significant role in deepening design, auxiliary construction and visual control [13].
4.2. 3D printing
3D printing technology originated in the late 1980s, also known as “additive manufacturing” or “rapid prototype” technology. The basic principle is to superimpose the layered material, and then decompose the three-dimensional model data of the target structure obtained by the information system, and decompose it into a two-dimensional geometric information. The stacked sheet structure of information is then parsed by the Computerized Numerical Control (CNC) system, and then the printing path planning is carried out, so as to achieve mechanized construction of the target structure. It includes 3D modeling and approximation processing, model slice and path planning, layer processing and overlay. According to the different materials and processes, the 3D printing technology of the building can be divided into the additive construction of concrete layered spraying and extrusion, the additive construction of sand and gravel powder layered and superimposed, and the three-dimensional structure construction of the material driven by the large robotic arm.
4.3. The Internet of Things
The Internet of Things was first proposed by Professor Kevin Ash-Ton in 1999, and in the same year at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has established the Auto-Identification Center (Auto-ID). This is the first time the Internet of Things has faced the world. Its concept is “combining all kinds of information sensing devices with the Internet to form a network of interconnection of all things.” Its main role in practice is to the multi-source and heterogeneous data generated by the five elements in the construction process are collected and uploaded to the terminal equipment with different types of sensors, so as to realize the perception of the status, quality and position of the elements during the construction process. For example, Professor LIU Z S once proposed an intelligent construction method based on the digital twin and intelligent decision-making platform through the fused Internet of Things, BIM and finite element models, comparing real-time monitoring and theoretical model data, and then adjusting and correcting the actual construction process of the physical space [14].
4.4. AI and big data
At this stage in the construction industry, the main purpose of AI and big data is to use sensors to collect on-site data and conduct analysis and monitoring, which can identify the safety status of personnel in the construction scenario, the status of construction equipment and risk target identification. By analyzing the video images returned by the sensors, we can identify many unsafe factors in video images by establishing object detection and semantic segmentation models based on convolutional neural network and long and short-term memory networks, such as whether on-site personnel wear protective equipment according to specifications, and whether large-scale construction equipment is in a dangerous state.
5. Intelligent maintenance and disaster prevention and mitigation
The service period of the civil engineering structure is basically decades or even hundreds of years. During this period, it will inevitably suffer from the erosion of the environment, the aging of materials, the power load, and the coupling effect of sudden various disasters, resulting in structural damage, development and accumulation. resulting in continuous decay of service performance. In the operation and maintenance of traditional civil engineering, the inspection personnel mainly pass the visual inspection of the inspection personnel, and combine the relevant standard specifications and experience to give the corresponding damage identification results and status evaluation grades. The traditional mechanics knowledge system plays an important role in dealing with various disasters. These include seismic engineering, wind engineering and fire engineering.
Since the 1990s, the health monitoring technology of the structure has developed rapidly. Through real-time monitoring of environmental load and structural response, the identification of the structural system, the correction of the model and the real-time update of the parameters are carried out, so as to realize the structural state evaluation and diagnose the structural health status. Its main connotation includes the acquisition of structural health monitoring data, combined with the service life of the structure and the current situation, to evaluate the current structural damage status (including determining whether the injury occurs, the damage department Bit determination, damage degree, etc.) then predict the future load environment and structural performance through data model correction, and use the reliability analysis method based on the failure probability to evaluate the residual fatigue life of the structure. However, due to the certain uncertainty of manual inspection and the limited area of sensor coverage, the identification method based on modal analysis is not sensitive to the early small damage of the structure. In this case, it is urgent to develop the system theory and method of intelligent operation and maintenance in civil engineering structure, and excavate and reveal the correlation characteristics and evolutionary laws of structural damage development and performance degradation [15].
6. Conclusion
At present, the combination of civil engineering and AI is still in the development stage. Although there are many researches that use machine learning algorithms to solve problems in the field of civil engineering, there is still a lack of new discoveries and new breakthroughs in the true sense of “from zero to one”. There is still slightly fewer breakthrough research on the fundamental subject problems and technical bottlenecks at the domain of civil engineering. In order to promote new breakthroughs in the field of AI technology, for the situation in civil engineering, it is still necessary to explore the practice.
(1) In terms of intelligent construction, study the semantic modeling and mapping methods of all elements of construction, and establish the number of errors and omissions during the construction process. Twin intelligent diagnosis and recovery deduction system, realize the physical-information simulation, dynamic mapping and visualization of the structural maintenance and modification process.
(2) In terms of intelligent design, the combination of architectural structure and architectural design uses AI to form a new paradigm building that integrates architectural aesthetics and mechanics, and establishes an intelligent design theory that integrates aesthetics and mechanics.
(3) In terms of intelligent operation and maintenance and disaster prevention and mitigation, study the new principles, new technologies, devices, systems and devices of the global perception of structural health status, and propose structural holographic intelligent identification and pre-recognition. The new theories and new methods are obtained, and the precise solution of the structural health diagnosis inversion equation is obtained under the incomplete information, and the civil engineering intelligent operation and maintenance agent and the corresponding scientific theories are formed. This paper studies the intelligent disaster prevention theory and technology that integrates the data and physical models of the complex and large systems of urban engineering, and establishes the theory and technology of multi-disaster simulation, evaluation and prediction, and realizes the intelligent disaster prevention and mitigation of civil engineering under the new data-driven paradigm.
References
[1]. Magaña Martínez D and Fernandez-Rodriguez J C 2015 Artificial intelligence applied to project success: a literature review Int. J. Interact. Multi. 3(5) 77-85
[2]. Wetzstein G, Ozcan A and Gigan S et al. 2020 Inference in artificial intelligence with deep optics and photonics Nature 588(7836) 39-47
[3]. Muthukrishnan N, Maleki F and Ovens K et al. 2020 Brief history of artificial intelligence Neuroimaging Cl. of N. USA. 30(4) 393-399
[4]. Liu H B, Zhang F and Chen Z H et al. 2022 Application research status and prospect of artificial intelligence in civil engineering J. Civil Envir. Eng. 3 1-20
[5]. Hu W, Sun C Y and Zhang D D 2023 Architectural design framework with the participation of artificial intelligence New Arch. 3 50-56
[6]. Schütze M, Sachse P and Römer A 2003 Support value of sketching in the design process RES. in Eng. Desg. 14(2) 89-97
[7]. Qian W, Xv Y and LI H 2022 A self-sparse generative adversarial network for autonomous early-stage design of architectural sketches Computer-Aided Civil Infra. Eng. 37(5) 612-628
[8]. Oliveira V and Ponho P 2010 Evaluation in urban planning: Advances and prospects J. Planning Lit. 24(4) 343-361
[9]. Lin B, Diao R D and Wu Y W 2019 Urban space generative design based on artificial intelligence: Northern extension of central green axis, Wenzhou Planners 35 (17) 44-50
[10]. Lyu J and Chen M N 2009 Automated visual inspection expert system for multivariate statistical process control chart Expert Sys. with App. 36(3) 5113-5118
[11]. Zhu F S, Li X B and WANG S Q et al. 2000 An expert system application to the selection and design of retaining structures J. Ne. Univ. (Natural Sci.) 21(3) 298-300
[12]. Nie Z G, Lin T, Jiang H L et al. 2021 TopologyGAN: Topology optimization using generative adversarial networks based on physical fields over the initial domain J. Mech. Desg. 143(3) 1-18
[13]. Chinese Academy of Architecture 2017 The unified standard for building information model application: GB/T 51212—2016 Beijing: China Construction Industry Press
[14]. Chen S M Griffs F H and Chen P H et al. 2021 Simulation and analytical techniques for construction resource planning and scheduling Auto. in CONST. 21 99-113
[15]. Li H and Bao Y Q 2021 Machine learning paradigm for structural health monitoring Struct. Health. Monit. 20(4) 1353-1372
Cite this article
Liu,Q. (2023). Application and research of artificial intelligence in civil engineering intelligent construction. Theoretical and Natural Science,26,30-36.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Magaña Martínez D and Fernandez-Rodriguez J C 2015 Artificial intelligence applied to project success: a literature review Int. J. Interact. Multi. 3(5) 77-85
[2]. Wetzstein G, Ozcan A and Gigan S et al. 2020 Inference in artificial intelligence with deep optics and photonics Nature 588(7836) 39-47
[3]. Muthukrishnan N, Maleki F and Ovens K et al. 2020 Brief history of artificial intelligence Neuroimaging Cl. of N. USA. 30(4) 393-399
[4]. Liu H B, Zhang F and Chen Z H et al. 2022 Application research status and prospect of artificial intelligence in civil engineering J. Civil Envir. Eng. 3 1-20
[5]. Hu W, Sun C Y and Zhang D D 2023 Architectural design framework with the participation of artificial intelligence New Arch. 3 50-56
[6]. Schütze M, Sachse P and Römer A 2003 Support value of sketching in the design process RES. in Eng. Desg. 14(2) 89-97
[7]. Qian W, Xv Y and LI H 2022 A self-sparse generative adversarial network for autonomous early-stage design of architectural sketches Computer-Aided Civil Infra. Eng. 37(5) 612-628
[8]. Oliveira V and Ponho P 2010 Evaluation in urban planning: Advances and prospects J. Planning Lit. 24(4) 343-361
[9]. Lin B, Diao R D and Wu Y W 2019 Urban space generative design based on artificial intelligence: Northern extension of central green axis, Wenzhou Planners 35 (17) 44-50
[10]. Lyu J and Chen M N 2009 Automated visual inspection expert system for multivariate statistical process control chart Expert Sys. with App. 36(3) 5113-5118
[11]. Zhu F S, Li X B and WANG S Q et al. 2000 An expert system application to the selection and design of retaining structures J. Ne. Univ. (Natural Sci.) 21(3) 298-300
[12]. Nie Z G, Lin T, Jiang H L et al. 2021 TopologyGAN: Topology optimization using generative adversarial networks based on physical fields over the initial domain J. Mech. Desg. 143(3) 1-18
[13]. Chinese Academy of Architecture 2017 The unified standard for building information model application: GB/T 51212—2016 Beijing: China Construction Industry Press
[14]. Chen S M Griffs F H and Chen P H et al. 2021 Simulation and analytical techniques for construction resource planning and scheduling Auto. in CONST. 21 99-113
[15]. Li H and Bao Y Q 2021 Machine learning paradigm for structural health monitoring Struct. Health. Monit. 20(4) 1353-1372









