1. Introduction
The building business has grown rapidly due to its global economic impact. Approximately 20% of occupational fatalities globally occur in the construction business, making it one of the most dangerous. In 2020, the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China reported 689 housing and municipal engineering production safety incidents. These events tragically claimed 794 lives [1]. Construction sites worldwide have at least 60,000 fatalities each year, according to ILO figures. About 1/6 of all work-related fatalities occur at construction sites. In wealthy countries, 25%–40% of construction site fatalities are work-related. Construction workers in some nations have back pain or other musculoskeletal ailments at 30% [2]. The construction sector is globally recognized as one of the industries exhibiting the highest prevalence of occupational disorders and accidents. Additionally, this industry poses significant risks, leading to severe health complications among its workforce and contributing to increased costs associated with safety management [3]. Enhancing safety management within the engineering and construction process is an essential imperative.
The dynamics of the surrounding environment, dispersion of personnel, and the transient nature the varied equipment layouts are the main causes variety of risks that can develop on construction sites[4]. The simple ignorance of workers’ safety issues is another key aspect. The engineering community has discovered recently how hard it is to tackle this management issue by focusing simply on conventional management practices, such having safety supervisors involved. As a result, scientists have developed a wide range of cutting-edge smart technologies, including wearables, cameras, robots, and smartphones, along with computer techniques like cloud computing, Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence (AI), to automate and smarten technology and replace the conventional human-based information decision-making and safety management tools [5].
Among the above methods, Computer Vision (CV) is gaining prominence because to its advantages in processing complicated image data. It can monitor equipment and worker safety on construction sites, recognize visual data such as material quantities and surfaces, track item movement and changes [6]. With the introduction of high-resolution cameras, the rapid rise of computer database capacity, and the development of technologies such as deep learning, knowledge graphs, and neural networks, CV technology is becoming increasingly popular [7]. (1) CV can efficiently integrate and process enormous amounts of complicated data; (2) CV is not impacted by extreme temperatures, dust, electromagnetic fields, explosions, and other dangerous work conditions (3) CV is a non-intrusive technology, which is a critical aspect in using CV technology to building safety monitoring.
Thus, utilizing a study of the literature and an analysis of it, this paper tackles the main directions for future research and evaluates the progress of CV technology in engineering safety management. It focuses on the numerous things that CV technology uses as classification labels for further explanation. These objects cover the four domains of construction scene monitoring, worker behavior and activity guidance and control, safe equipment operation, and material management. In order to assist the rational growth of the engineering sector, this study intends to offer some suggestions for the future application of CV technology in related domains.
2. Research Method
This work aims to elucidate the current status of use of CV technology in the domain of engineering safety management, based on a comprehensive analysis of the existing literature. The present study employs the content analysis methodology, a widely utilized strategy within the realm of social science research. Content analysis is a specialized research technique that employs a systematic, unbiased, and quantitative approach to analyze the content of literature. Its primary purpose is to uncover latent linkages within the literature and generate informed predictions regarding future developments. The mapping of research hotspots in the field of building safety related to CV is conducted using keyword clustering, utilizing bibliometric analysis as provided in this section. Moreover, the emphasis serves as evidence of the neutrality in categorizing the utilization of CV technology in the subsequent section. The foundation of the next section has been established.
2.1. Literature search and selection
The majority of the literature reviewed in this paper comes from the Core Collection database in Web of Science (WOS), which houses the most prestigious academic literature systems in the fields of science and technology, including SCI, SSCI, and others [8]. It also includes the most prestigious and influential academic journals in the world and can be used to track the direction of the major concerns of international scientific researchers. It performs well in the bibliometrics domain for WOS. When it comes to literature measurement, WOS performs well and finds relevant and high-quality literature fast. The present study employs an advanced search methodology that incorporates Boolean operators and synonymous keywords to accurately and thoroughly retrieve relevant literature. The approach to searching is “TS=(CV OR based vision)); TS=(construction OR architecture); TS=(safety management OR risk management); #3 AND #2 AND #1” . Ultimately, 164 articles—including articles, proceeding papers, review articles, and early access—that were pertinent to the research content were acquired. The time range of the articles was from 1997 to 2023, and no additional time filtering was done due to the small number of articles.
2.2. Literature analysis
2.2.1. Analysis based WOS. WOS has statistical analysis of these articles. From a temporal standpoint, Figure 1 illustrates the annual growth in the quantity of articles on CV in construction safety. Figure 1 shows how the engineering industry’s use of CV technology for safety management increased significantly after 2018. This roughly corresponds with the rise in popularity of tools like neural networks and deep learning, suggesting that advancements in computer algorithms have paved the way for CV applications and advancements.
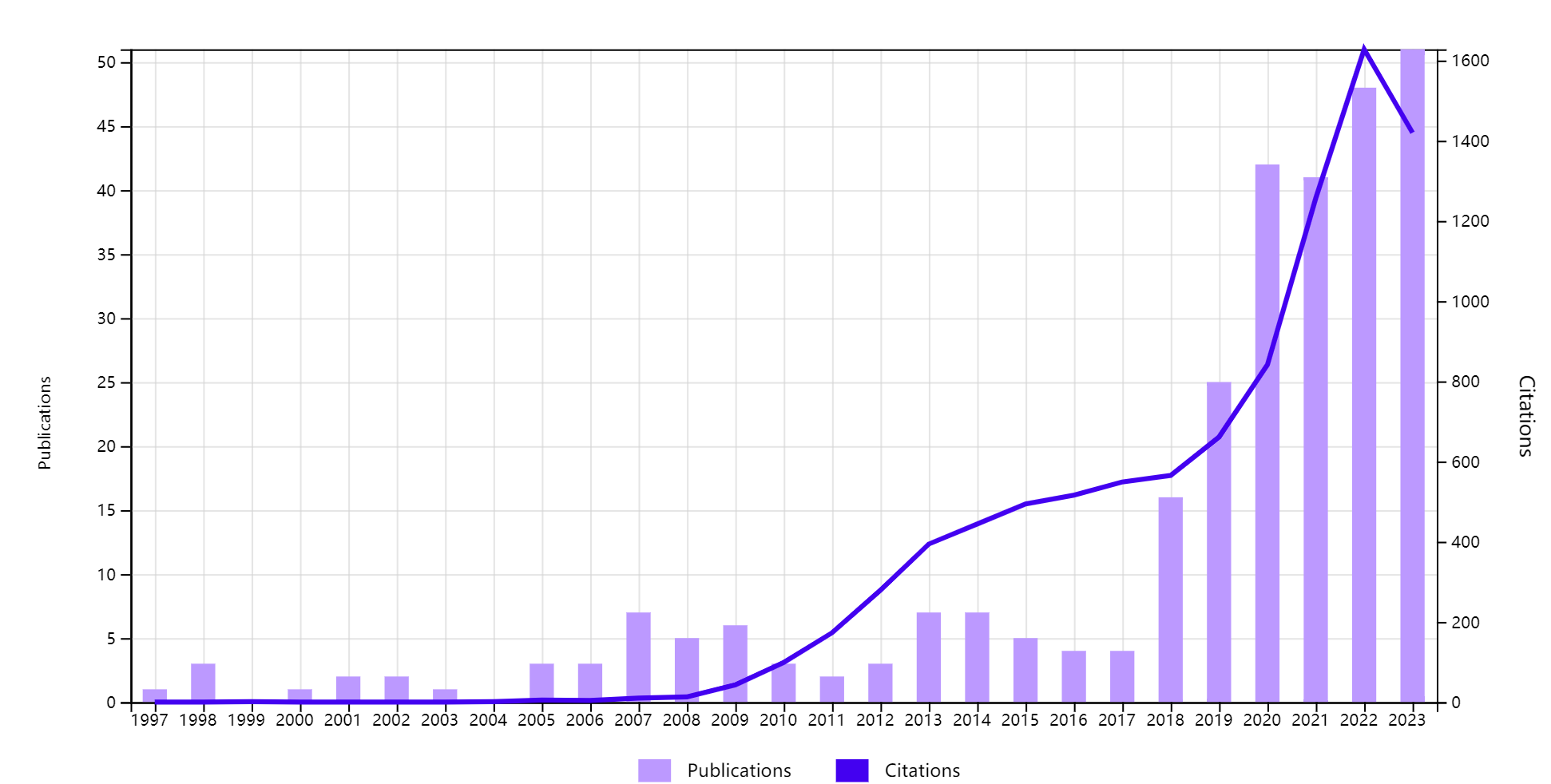
Figure 1. Times cited and publications over time.
Figure 2 illustrates the surprising total of 71 articles on China in terms of research regions. Due to the two articles on Taiwan Province not being counted, the number of articles on China in Figure 2 is displayed as 69, and the adjusted number is 71. The nearly 50% share demonstrates how much attention Chinese academics have recently given worker safety. China saw 734 construction-related accidents and 840 fatalities in 2018, and by 2020, there would be 689 accidents and 794 fatalities.
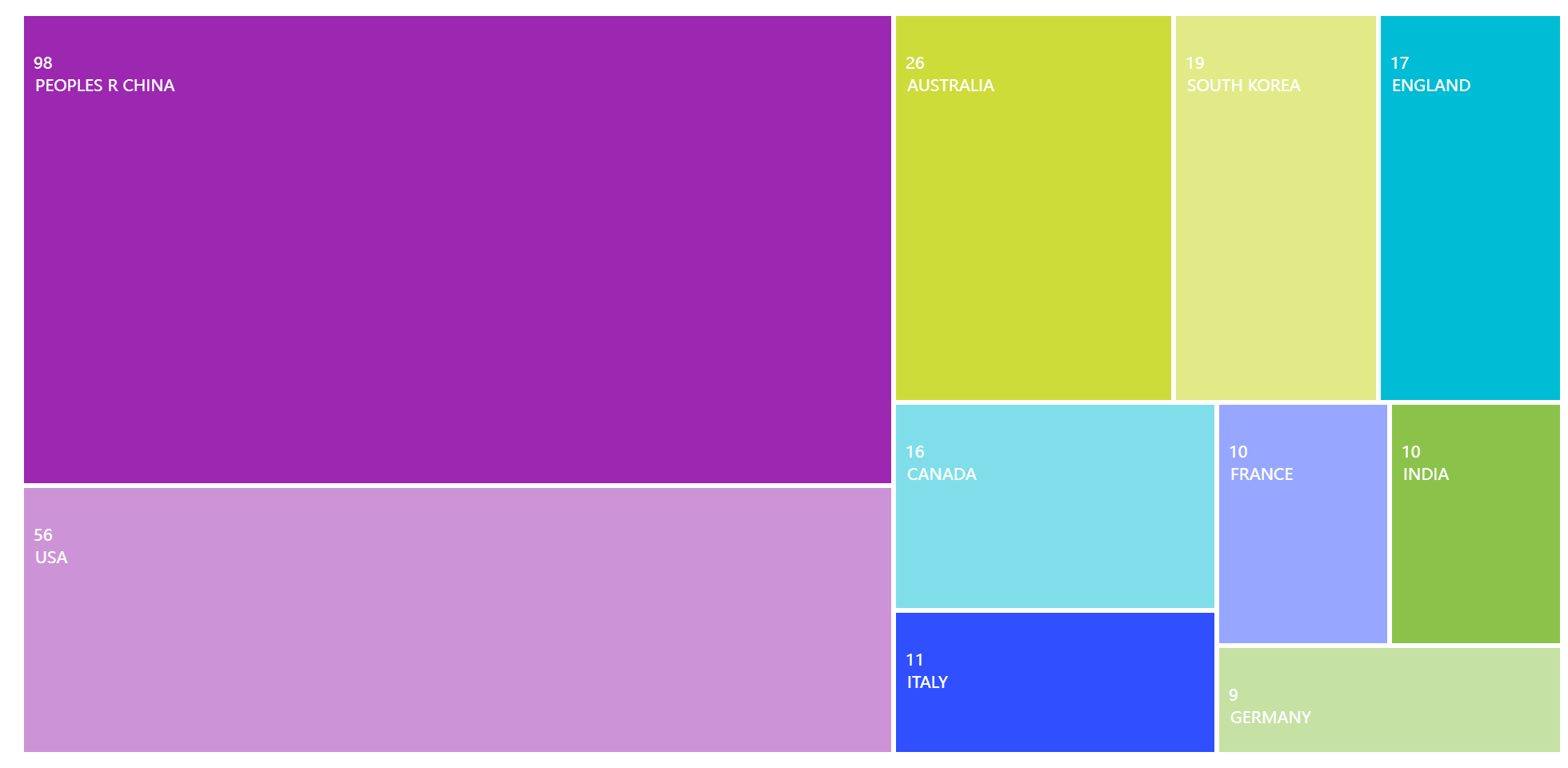
Figure 2. Region or country of papers.
2.2.2. Analysis based CiteSpace. Furthermore, this study conducted a keyword co-occurrence network analysis of 164 articles using CiteSpace, a visual literature analysis tool. The results, which can represent current research hotspots in the field, are displayed in figure 3. Since CiteSpace is based on the graph theory-based spectral clustering algorithm, it naturally has an advantage over co-reference networks, which cluster nodes based on linking relationships rather than attributes. It has an inherent benefit. According to CiteSpace’s working procedure, the credibility of the clustering results is generally assessed based on two key values: Silhouette, or the S-value, which is the average profile of the clusters. It is generally accepted that S>0.5 indicates that clustering is reasonable and S>0.7 indicates that clustering is pleasant. The first value is Modularity, or the value of the clustering module (Q-value). A clustering of 0.7 is deemed convincing. As can be observed from figure 3, the clustering result for Q in this paper is 0.5117, and for S, it is 0.7899. The outcome is trustworthy.
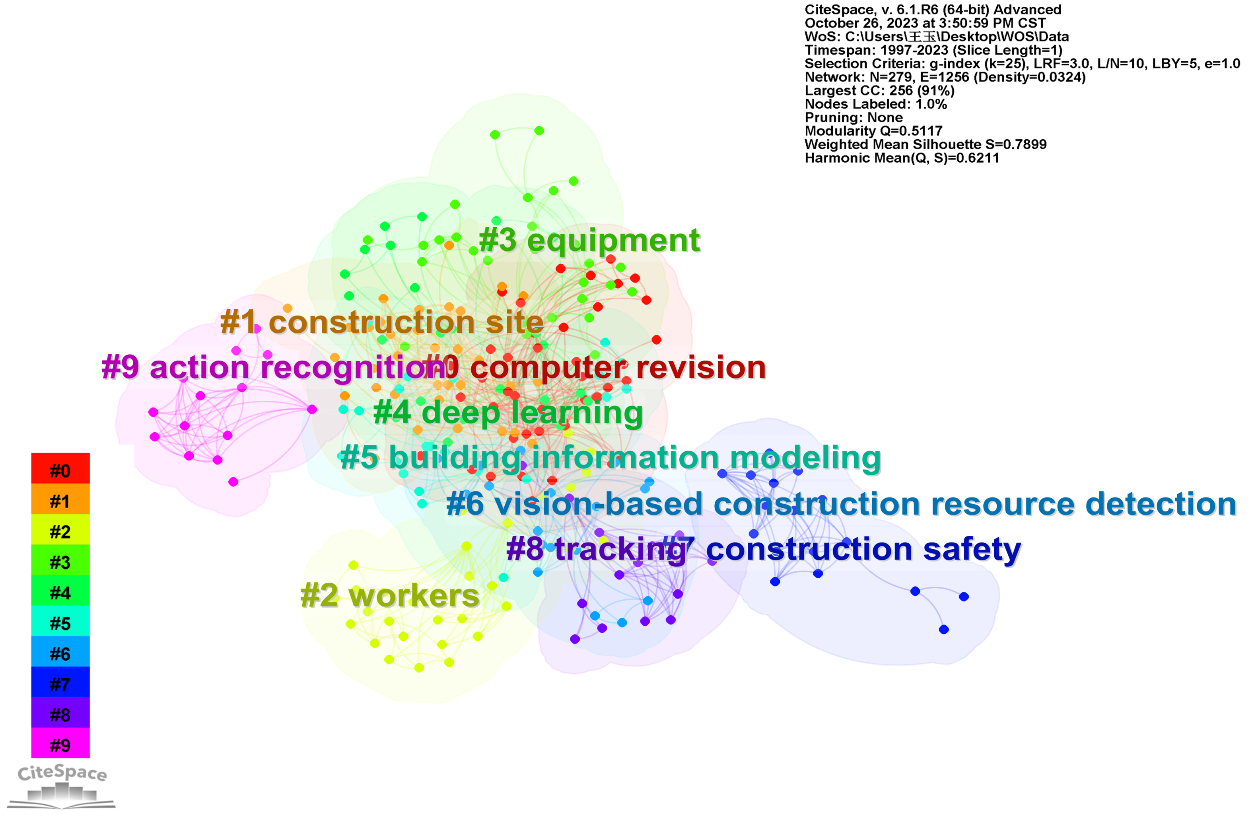
Figure 3. Keyword co-occurrence network based CiteSpace.
Figure 3 shows the results of 10 keyword cluster analyses. The keywords are numbered from 0 to 9, with smaller numbers indicating more keywords included in the clusters. Each cluster is made up of several closely related words. The construction site, workers, equipment, and materials are the four categories into which this research divides the objects of CV in engineering safety management based on an analysis of these ten words. This outcome serves as the foundation for the discussion in this study’s following section.
The timing of the appearance of some of the topics closely related to the research theme is shown by the co-occurrence network in figure 4, where it is evident that terms like neural networks, deep learning, convolutional neural networks, etc. appeared in 2018.Without a doubt, 2018 was a turning point in history because most of the keywords began to surface one after another, supporting each other’s findings and the conclusions of the earlier analysis based WOS.
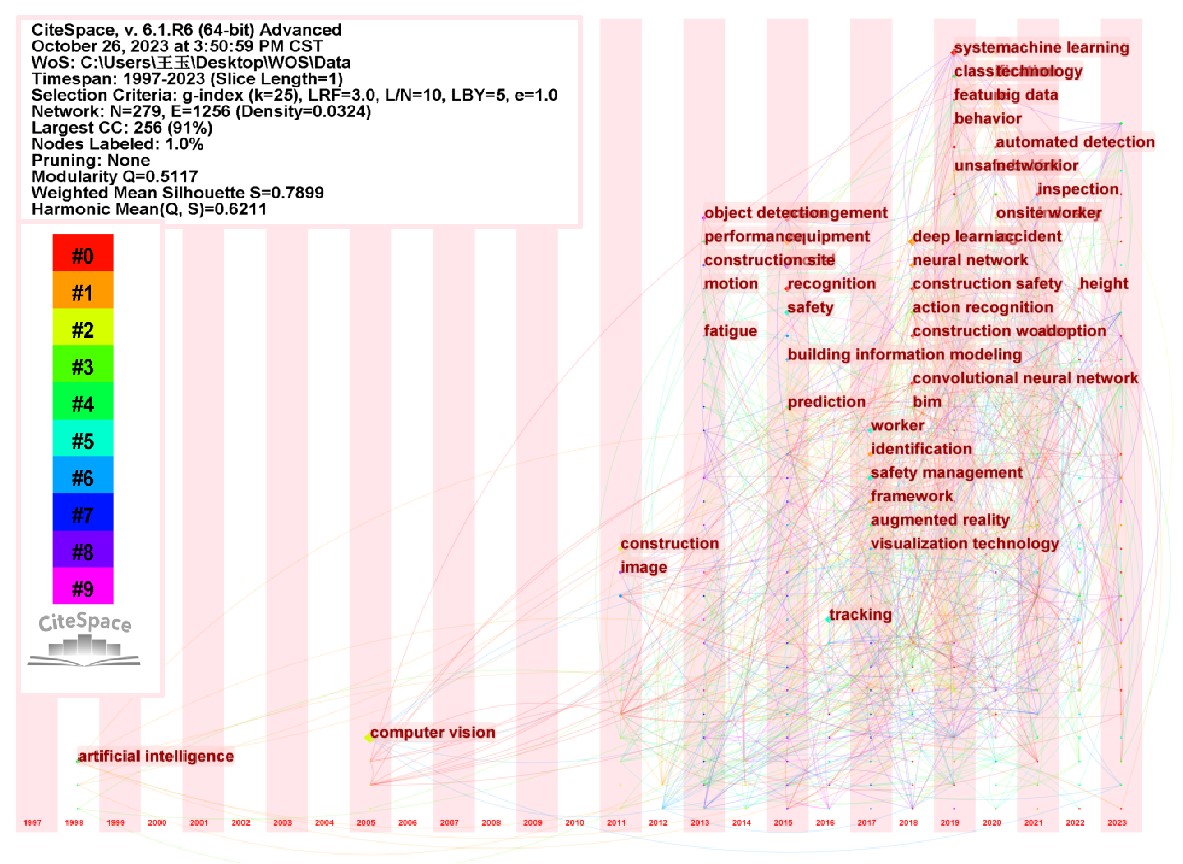
Figure 4. Timeline of typical keyword appearances based CiteSpace.
3. Contend-based Literature review
3.1. Construction site monitoring
One application of CV for construction site management is safety monitoring. This involves using the technology to continuously observe the work site and identify possible dangers like fire, smoke, or building collapse. This allows the emergency response plan to be triggered promptly. (2) Hazardous area identification: It can be used to designate high-risk or locations containing hazardous materials on a construction site so that workers are aware of them and can take extra precautions. (3) Traffic monitoring: In order to maintain traffic safety, particularly for the roads and bridges inside and close to project sites, machines monitor traffic flow and usage on construction sites.
Yan et al. [9] developed a comprehensive conceptual framework for the management of construction accidents in a recent study on safety monitoring. By employing CV technology and other methods, the severity of the building collapse incident in Shanghai was effectively managed, as evidenced by the provision of comprehensive scenario information. Ahn et al. [10] proposed a novel methodology for enhancing fire detection and reducing the occurrence of accidents and property damage. Their approach involved the development of a CV system integrated with indoor closed-circuit television (CCTV) technology. The model achieved an impressive accuracy rate of 91% and demonstrated the ability to detect fires within 1 second in indoor settings.
The dangers present at a construction site exhibit variability contingent upon the specific location under consideration. However, it is possible to mitigate the occurrence of accidents by employing a technological approach to identify and assess the most perilous areas of the site. According to Pushkar et al. [10], the utilisation of image-based 3D reconstruction of the site was proposed as a means to identify the most hazardous areas include locations where employees are exposed to potential hazards, such as machinery and equipment operation zones, as well as areas designated for the storage of materials. The area’s safety is monitored through the utilisation of real-time image processing employing many cameras and CV techniques. The authors Luo et al. [12] developed an intelligent video surveillance system that utilises CV to distinguish between stationary and moving personnel in different hazardous areas with variable levels of risk.
The management of traffic accidents holds significant importance in enhancing safety management on construction sites, as they frequently include the use of numerous heavy transport vehicles and mechanical equipment. Zhu et al. [13] devised a CV-based early warning system for real-time monitoring of traffic situations at crossings within construction sites. This system is capable of effectively handling complex traffic scenarios involving buses, transport vehicles, workers, and pedestrians, while maintaining a cost-effective approach.
In summary, the utilisation of CV for tasks such as construction site safety monitoring, identification of hazardous areas, and traffic management has the potential to enhance construction safety, mitigate accidents, and enhance project quality. Consequently, these advancements play a crucial role in the successful completion of construction projects and the preservation of workers’ well-being.
3.2. Worker identification and tracking
The utilization of CV technology in safeguarding construction workers can be categorized into three key domains: (1) Training and education programs aimed at enhancing worker safety. (2) Identification of hazardous worker conduct. (3) The identification and tracking of workers’ locations.
Research has indicated that a significant correlation exists between the prevalence of accidents and two key variables: insufficient training and low comprehension among construction workers [14]. Numerous research endeavors have been dedicated to enhancing the efficacy of training by means of technological advancements, among which augmented reality (AR) has emerged as a prominent technology. The fundamental aspect involves the implementation of CV [14]. Kivrak et al. [15] developed an innovative safety education methodology that employed augmented reality glasses to facilitate an engaging and immersive learning experience, allowing users to view safety animations. In a study done in 2018, Eiris et al. developed a platform for a safety training system that incorporated the use of augmented 360-degree panoramic reality (PARS) [16]. A cohort of 30 individuals underwent testing, which revealed a notable improvement in their capacity to identify all four designated samples of hazards. The findings from each of these research indicate that the utilization of CV technology is anticipated to enable the development of advanced training platforms. These platforms possess the capacity to enhance safety education and training, hence enhancing workers’ proficiency in identifying and addressing potential dangers. The forthcoming worker training initiative aims to incorporate cutting-edge technologies in order to enhance engagement through immersive experiences.
The identification and monitoring of construction workers’ behavior is a crucial approach for mitigating safety mishaps. However, the comprehensive execution of this duty has been deficient due to the demanding and intricate nature associated with it. The occupation of working at elevated levels has long been recognized as a hazardous endeavor. In practical application, a significant proportion of workers demonstrate a lack of concern or intentional disrespect for the utilization of essential safety apparatus, such as helmets and safety ropes. In order to tackle these concerns, Fang et al. [17] put out a safety management approach that combines convolutional neural networks and CV. Interventions and preventive measures can be promptly applied upon the identification of certain behaviors, leading to a significant reduction in fall incidents within the working-at-height setting. In their study, Hayat et al. [18] presented a new framework that utilizes CV technology to automatically check safety helmets. The architectural design demonstrates the ability to identify unfavorable circumstances, such as inadequate lighting or the existence of diminutive entities, while yet upholding a commendable level of precision, quantified at 92.44%. The hybrid deep learning model introduced by Ding et al. [19] integrates Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) to autonomously classify the actions of individuals across various body positions. In their work, Alateeq et al. [20] developed a methodology that employs closed-circuit television (CCTV) video records for the purpose of recognition. The proposed approach integrates deep learning and CV methodologies to enhance the identification and categorization of construction workers’ actions and their adherence to safety protocols. Based on the aforementioned findings, it is evident that CV techniques are undergoing rapid advancements in the realm of worker behavior monitoring. These techniques can be effectively integrated with various wearable devices to enhance convenience. Additionally, the incorporation of intelligent methodologies like deep learning, as well as the utilization of advanced depth cameras, binocular cameras, optical camera and similar technologies, can contribute to a more precise and autonomous approach towards the management of worker behavior [21].
Safety management frameworks or systems for worker location on construction sites are frequently implemented, nevertheless a significant portion of these frameworks rely on Internet of Things (IoT) systems and sensor devices like Radio Frequency Identification (RFID). These technologies facilitate the representation of worker location information within a virtual system. The implementation of CV technology not only enhances the stability and convenience of worker positioning, but also enables real-time tracking and observation of specific workers’ locations in real-world scenarios. Park et al. have done a great deal of work in this field. Park et al. [22] introduced a computer-based visual system designed to identify and track construction workers inside video frames. This system not only enables the detection of worker positions, but also facilitates the determination of spatial coordinates for various elements such as materials, buildings, and mechanical equipment present at the construction site. In their study, Park et al. [23] introduced a strategy that enables the tracking of workers in densely populated outdoor environments. This approach combines camera technology with CV methods. In their study, Park et al. [24] integrated CV with other technologies, such as virtual reality and human-computer interaction, to design an approach that combines the tracking and worker localization processes. In a recent study conducted by Lin et al. [25], an online visual tracking approach utilizing Multi-Domain Convolutional Neural Networks (MD-CNN) was proposed. The study demonstrated that this system achieved satisfactory tracking performance even in construction settings with intricate backdrops.
In a nutshell the conventional understanding posits that the process of ensuring worker safety at a given site has historically been a laborious and monotonous task, necessitating the physical presence of managers and engineers who must traverse the site in order to detect potential risks. In contrast, CV is a viable option to address the inefficiency of manual labor by enabling automated worker position tracking and behavioral monitoring using image analysis.
3.3. Equipment monitoring
Machinery-related accidents typically rate high in construction site risk statistics, especially for large vehicles such as cranes and excavators. The task of monitoring the location of machinery on a construction site, detecting its movements, and providing guidance during certain operations using vision-based techniques has long been a central concern in the realm of construction automation. Extensive research has been conducted in this area to address this challenge.
Azar et al. [26] proposed a novel CV methodology that use an active zoom camera to effectively monitor the operations of excavators and dump trucks. The technique utilises a target identification algorithm, resulting in a recognition accuracy ranging from 80% to 90%. This study highlights the advantages of employing an active camera system for such monitoring purposes. In their study, Xiao et al. [27] proposed a tracking methodology for monitoring multiple machinery and equipment units. The approach involved utilising hash features extracted from images as an appearance model. By employing a combination of CV and deep learning techniques, the researchers were able to effectively track multiple machinery and equipment units operating concurrently in challenging conditions, such as poor lighting and occlusion.
A plethora of research has been undertaken to investigate the identification of attitudes in construction machinery, utilizing several methodologies including the utilization of IMU sensors. Within the scope of these inquiries, the realm of machinery collision avoidance arises as a noteworthy facet of safety administration. In their study, Zhang et al. [28] devised an assessment framework for enhancing collision avoidance safety. This framework employed CV and fuzzy reasoning techniques. The authors identified proximity and crowding of machinery and workers as the primary contributors to collision accidents. To enhance the efficiency of the system, the authors incorporated a more rapid R-CNN algorithm to establish a quantitative relationship in identifying these factors. In their study, Zhang et al. [29] examined a safety warning mechanism for lifting equipment utilised in work processes. This mechanism, which incorporates vision technology, aims to extract and forecast various parameters such as worker and cargo trajectory, movement speed, and other relevant factors. By establishing proximity-based safety protocols for lifting equipment, this comprehensive system serves to effectively provide real-time warnings and ensure safety.
The successful implementation of earthworks often requires the proficient utilization of large machinery by trained workers. Furthermore, the complex and dynamic geological conditions present potential hazards by exacerbating the difficulties related to the conveyance of various substances, such as rock, soil, sand, and gravel. Therefore, the field of engineering is primarily focused on guaranteeing the optimal functioning of such endeavors. Tsuchiya et al. [30] introduced a novel vision technique in their work, which employs two depth cameras to precisely assess the spatio-temporal deformation of soil during earthmoving excavation. Furthermore, the researchers made revisions to the preexisting model used for forecasting the resistance of buckets during excavation, incorporating the aforementioned measurements into the new version. Nevertheless, it is crucial to acknowledge that the precision of the method can be augmented by means of algorithmic advancements. However, this study has substantial ramifications for the utilization of vision technology in accurate assessments. In their publication, Naghshbandi et al. [31] conducted a study that examined the application of computer vision (CV) technology in enhancing safety measures during earthmoving activities. The main emphasis was placed on the establishment of automated safety monitoring and target monitoring. The utilization of various techniques, including multi-camera calibration, data fusion, and attitude estimation, contributes to the improvement of detection accuracy and the reduction of processing complexity in this approach.
The incorporation of CV technology into the regulatory process of construction machinery and vehicles holds significant potential for mitigating hazards associated with unsafe areas and blind spots, as well as enhancing operational management in challenging conditions such as earthworks.
3.4. Materials and resources management
The utilization of computer vision (CV) in the realm of safety management for construction materials or resources, such as temporary scaffolding and formwork, predominantly emerges through the processes of identifying, classifying, and tracking these materials or resources. The subject of discourse concerns the monitoring of material quality. The presence of high quality standards is a must for ensuring safety. The building site has a labor-intensive and extensive nature, necessitating a significant workforce, machinery, materials, and temporary provisions. Insufficient management and coordination of these components can result in negative consequences for both the schedule of construction and safety protocols [32].
In their investigation, Dimitrov et al. [33] proposed a methodology for classifying materials using CV and support vector machine classifiers The researchers collected a dataset consisting of over 20 commonly used construction materials, with 150 images obtained for each category. Notably, the images were carefully conditioned to ensure optimal lighting conditions at the site, resulting in enhanced accuracy of the classification process. Hence, Mahami et al. [34] developed and presented a visual material classification approach based on deep learning. A total of 1231 images from diverse construction sites were gathered to train a substantial dataset. The study successfully attained a detection accuracy of 97.35% for various building materials, even in intricate surroundings.
The field of vision-based inspection for assessing the quality of building materials and structural integrity, with a particular focus on crack detection, has experienced significant advancements in recent years. In their study, Dinh et al. [35] integrated inspection robots and CV techniques to facilitate the automatic extraction of visible cracks from photo. This was achieved by the utilisation of image binarisation thresholding, employing non-parametric peak detection algorithms. According to Koch et al. [36], CV has made significant advancements in automating the detection of cracks, joint damage, and cavities in various infrastructural elements such as tunnels, asphalt pavements, and pipelines. The authors emphasise the significance of this visual quantification approach in ensuring the safety and quality assurance of these materials. In their recent review, Deng et al. [37] have showcased the application of CV in crack detection, along with the integration of artificial intelligence techniques. These techniques have witnessed significant advancements, transitioning from manual image processing techniques (IPTs) that relied on low-level features, to more sophisticated feature learning methods. As a result, the current approaches offer comprehensive and precise quantification outcomes.
4. Conclusion
CV technology has been widely used in various fields of construction safety management, showing its extensive research applications. Using CiteSpace as a bibliometric analysis method, this paper summarizes the application of CV technology in the field of construction safety management. The analysis was carried out from four different dimensions, namely site environment, workers, machinery and materials. The importance of CV as a cutting-edge technology in improving the effectiveness of safety management is emphasized. The subject matter can be condensed into the following dimensions:
(1) CV technology is convenient for real-time continuous monitoring of complex construction sites. Cameras have the capability to gather real-time data pertaining to multiple aspects of the construction site, such as worker behavior, machinery operation, material quantity and quality, overall site safety monitoring, and more. When combined with intelligent algorithms, sensors, LIDAR, and other equipment, a comprehensive and precise understanding of the real-time construction site conditions can be achieved. This enables timely identification of risk factors and implementation of corrective measures.
(2) CV technology can realize risk prevention and intelligent decision-making. The utilization of CV for the accumulation of a substantial volume of image data can lead to the creation of an extensive database. By employing this data in conjunction with intelligent algorithms, it becomes possible to generate strategies or systems for risk identification, risk assessment, and risk decision-making. This enables the prediction and intelligent control of unknown risks, while also enhancing the efficiency of construction safety management.
In addition, this paper summarises several key trends regarding the application of CV in various aspects of construction safety management:
(1) Greater intelligence and automation: this means that systems will be able to automatically identify and respond to unsafe behaviours, hazardous areas and equipment failures, thereby reducing the need for human intervention and increasing the efficiency and accuracy of safety monitoring.
(2) Deep combined with AI technology: machines will continue to benefit from developments in deep learning and AI technology. These technologies can help systems better understand complex construction scenarios and behaviours, thereby improving the ability to identify and predict safety issues.
(3) Multi-sensor fusion: future CV systems may integrate multiple sensors, such as depth cameras, optical cameras, radar, etc., to monitor construction sites more comprehensively. Multi-sensor fusion can provide additional information to better understand the construction environment and risks.
(4) CV systems are expected to increasingly employ cloud computing and big data analytics for the purpose of processing and storing substantial quantities of image and video data. The utilization of this tool enables the undertaking of long-term data analysis, detection of trends, and provision of decision assistance within the realm of safety management.
(5) Combined with smart personal protective equipment (PPE): CV can be combined with smart PPE, such as smart helmets or goggles, to provide additional safety for workers. These PPE can monitor workers’ physiological status, provide real-time alerts and enhance control of unsafe behaviours.
References
[1]. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China General Office of the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development on Production Safety Accidents in Housing and Municipal Engineering in 2020. 21 May 2021, Retrieved on November 13, 2023, Retrieved from: https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/ gongkai/zhengce/zhengcefilelib/202210/20221026_768565.html
[2]. International Labour Office 2005 Facts about safety at work iRetrieved on November 13, 2023, Retrieved from: https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---asia/---ro-bangkok/---ilo-beijing/documents/publication/wcms_142901.pdf
[3]. Wang M, Wong P, Luo H, Kumar S, Delhi V and Cheng J 2019 Proc. Inter. Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction 36 399-406
[4]. Guo B H, Zou Y, Fang Y, Goh Y M and Zou P X 2021 Safety Sci. 135 105130
[5]. Arshad S, Akinade O, Bilal M and Bello S 2023 J. Build. Eng. 107049
[6]. Xu S, Wang J, Shou W, Ngo T, Sadick A M and Wang X 2021 Archi. Comput. Methods Eng. 28 3383-3397
[7]. Fang W, Love P E, Luo H and Ding L 2020 J. Advanced Engineering Informatics 43 100980
[8]. Liu W, Meng Q, Li Z and Hu X 2021 Build. 11(9) 409
[9]. Yan X and Kim Y C 2018 A conceptual framework of ITSMCA for a building collapse accident Eng. Constr. Archit. Ma. 25(6) 721-737
[10]. Ahn Y, Choi H and Kim B.S 2023 Development of early fire detection model for buildings using computer vision-based CCTV J. Build. Eng. 65 105647
[11]. Pushkar A, Senthilvel M and Varghese K 2018 Automated progress monitoring of masonry activity using photogrammetric point cloud ISARC 35 1-7
[12]. Luo H, Wang M, Wong P K Y and Cheng J C 2020 Full body pose estimation of construction equipment using computer vision and deep learning techniques AUTCON 110 103016.
[13]. Zhu D, Wen H and Deng Y 2020 Pro-active warning system for the crossroads at construction sites based on computer vision Eng. Constr. Archit. Ma. 27(5) 1145-1168
[14]. Wilkins J R 2011 Construction workers’ perceptions of health and safety training programmes Constr. Ma. Econom. 29(10) 1017-1026
[15]. Jeelani I, Albert A and Han K 2020 Improving Safety Performance in Construction Using Eye-Tracking, Visual Data Analytics, and Virtual Reality In Construction Research Congress 2020 American Society Civil Eng pp 395-404
[16]. Eiris R, Gheisari M and Esmaeili B 2018 PARS: Using augmented 360-degree panoramas of reality for construction safety training Int. J. Environ. Health. Res. 15(11) 2452
[17]. Fang W, Ding L, Luo H and Love P E 2018 AUTCON 91 53-61
[18]. Hayat A and Morgado-Dias F 2022 J. Deep learning-based automatic safety helmet detection system for construction safety. Applied Sciences. 12(16) 8268
[19]. Ding L, Fang W, Luo H, Love P E, Zhong B and Ouyang X 2018 J. A deep hybrid learning model to detect unsafe behavior: Integrating convolution neural networks and long short-term memory. AUTCON. 86 118-124
[20]. Alateeq M M, Fathimathul Rajeena P P and Ali M A 2023 Construction Site Hazards Identification Using Deep Learning and Computer Vision Sustainability 15(3) 2358
[21]. Yan X and Kim Y C 2018 A conceptual framework of ITSMCA for a building collapse accident Eng. Constr. Archit. Ma. 25(6) 721-737
[22]. Park M W and Brilakis I 2012 AUTCON 28 15-25
[23]. Park M.W, Palinginis E and Brilakis I 2012 Detection of construction workers in video frames for automatic initialization of vision trackers In Construction Research Congress 2012: Construction Challenges in a Flat World pp 940-949
[24]. Park M W and Brilakis I 2016 AUTCON 72 129-142.
[25]. Liu W, Shao Y, Zhai S, Yang Z and Chen P 2023 IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems 106(5) 653-661.
[26]. Azar E.R 2016 Construction equipment identification using marker-based recognition and an active zoom camera J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 30(3) 04015033
[27]. Xiao B and Kang S C 2021 Vision-based method integrating deep learning detection for tracking multiple construction machines J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 35(2) 04020071
[28]. Zhang M, Cao Z, Yang Z and Zhao X 2020 J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 146(6) 04020051
[29]. Zhang M and Ge S 2022 Vision and trajectory–Based dynamic collision prewarning mechanism for tower cranes J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 148(7) 04022057
[30]. Tsuchiya K and Ishigami G 2020 Vision-based measurement of spatio-temporal deformation of excavated soil for the estimation of bucket resistive force J. Terramechanics 90 11-21
[31]. Naghshbandi S N, Varga L and Hu Y 2021 J. Technologies for safe and resilient earthmoving operations: A systematic literature review AUTCON 125 103632
[32]. Goodrum P M, Zhai D and Yasin M F 2009 J. Relationship between changes in material technology and construction productivity J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 135(4) 278-287
[33]. Dimitrov A and Golparvar-Fard M 2014 J. Adv. Eng. Inform. 28(1) 37-49
[34]. Mahami H, Ghassemi N, Darbandy M T, Shoeibi A, Hussain S, Nasirzadeh F, Alizadehsani R, Nahavandi D, Khosravi A and Nahavandi S 2020 J. arXiv preprint arXiv 16344
[35]. Dinh T H, Ha Q P and La H M 2016 Computer vision-based method for concrete crack detection. Int. Control Automation Robotics & Vision (ICARCV) 1-6
[36]. Koch C, Georgieva K, Kasireddy V, Akinci B and Fieguth P 2015. Adv. Eng. Inform. 29(2) 196-210
[37]. Deng J, Singh A, Zhou Y, Lu Y and Lee V C S 2022 Constr Build Mater. 356 129238
Cite this article
Wang,Y. (2024). Research on computer vision application for safety management in construction. Theoretical and Natural Science,30,232-242.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China General Office of the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development on Production Safety Accidents in Housing and Municipal Engineering in 2020. 21 May 2021, Retrieved on November 13, 2023, Retrieved from: https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/ gongkai/zhengce/zhengcefilelib/202210/20221026_768565.html
[2]. International Labour Office 2005 Facts about safety at work iRetrieved on November 13, 2023, Retrieved from: https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---asia/---ro-bangkok/---ilo-beijing/documents/publication/wcms_142901.pdf
[3]. Wang M, Wong P, Luo H, Kumar S, Delhi V and Cheng J 2019 Proc. Inter. Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction 36 399-406
[4]. Guo B H, Zou Y, Fang Y, Goh Y M and Zou P X 2021 Safety Sci. 135 105130
[5]. Arshad S, Akinade O, Bilal M and Bello S 2023 J. Build. Eng. 107049
[6]. Xu S, Wang J, Shou W, Ngo T, Sadick A M and Wang X 2021 Archi. Comput. Methods Eng. 28 3383-3397
[7]. Fang W, Love P E, Luo H and Ding L 2020 J. Advanced Engineering Informatics 43 100980
[8]. Liu W, Meng Q, Li Z and Hu X 2021 Build. 11(9) 409
[9]. Yan X and Kim Y C 2018 A conceptual framework of ITSMCA for a building collapse accident Eng. Constr. Archit. Ma. 25(6) 721-737
[10]. Ahn Y, Choi H and Kim B.S 2023 Development of early fire detection model for buildings using computer vision-based CCTV J. Build. Eng. 65 105647
[11]. Pushkar A, Senthilvel M and Varghese K 2018 Automated progress monitoring of masonry activity using photogrammetric point cloud ISARC 35 1-7
[12]. Luo H, Wang M, Wong P K Y and Cheng J C 2020 Full body pose estimation of construction equipment using computer vision and deep learning techniques AUTCON 110 103016.
[13]. Zhu D, Wen H and Deng Y 2020 Pro-active warning system for the crossroads at construction sites based on computer vision Eng. Constr. Archit. Ma. 27(5) 1145-1168
[14]. Wilkins J R 2011 Construction workers’ perceptions of health and safety training programmes Constr. Ma. Econom. 29(10) 1017-1026
[15]. Jeelani I, Albert A and Han K 2020 Improving Safety Performance in Construction Using Eye-Tracking, Visual Data Analytics, and Virtual Reality In Construction Research Congress 2020 American Society Civil Eng pp 395-404
[16]. Eiris R, Gheisari M and Esmaeili B 2018 PARS: Using augmented 360-degree panoramas of reality for construction safety training Int. J. Environ. Health. Res. 15(11) 2452
[17]. Fang W, Ding L, Luo H and Love P E 2018 AUTCON 91 53-61
[18]. Hayat A and Morgado-Dias F 2022 J. Deep learning-based automatic safety helmet detection system for construction safety. Applied Sciences. 12(16) 8268
[19]. Ding L, Fang W, Luo H, Love P E, Zhong B and Ouyang X 2018 J. A deep hybrid learning model to detect unsafe behavior: Integrating convolution neural networks and long short-term memory. AUTCON. 86 118-124
[20]. Alateeq M M, Fathimathul Rajeena P P and Ali M A 2023 Construction Site Hazards Identification Using Deep Learning and Computer Vision Sustainability 15(3) 2358
[21]. Yan X and Kim Y C 2018 A conceptual framework of ITSMCA for a building collapse accident Eng. Constr. Archit. Ma. 25(6) 721-737
[22]. Park M W and Brilakis I 2012 AUTCON 28 15-25
[23]. Park M.W, Palinginis E and Brilakis I 2012 Detection of construction workers in video frames for automatic initialization of vision trackers In Construction Research Congress 2012: Construction Challenges in a Flat World pp 940-949
[24]. Park M W and Brilakis I 2016 AUTCON 72 129-142.
[25]. Liu W, Shao Y, Zhai S, Yang Z and Chen P 2023 IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems 106(5) 653-661.
[26]. Azar E.R 2016 Construction equipment identification using marker-based recognition and an active zoom camera J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 30(3) 04015033
[27]. Xiao B and Kang S C 2021 Vision-based method integrating deep learning detection for tracking multiple construction machines J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 35(2) 04020071
[28]. Zhang M, Cao Z, Yang Z and Zhao X 2020 J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 146(6) 04020051
[29]. Zhang M and Ge S 2022 Vision and trajectory–Based dynamic collision prewarning mechanism for tower cranes J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 148(7) 04022057
[30]. Tsuchiya K and Ishigami G 2020 Vision-based measurement of spatio-temporal deformation of excavated soil for the estimation of bucket resistive force J. Terramechanics 90 11-21
[31]. Naghshbandi S N, Varga L and Hu Y 2021 J. Technologies for safe and resilient earthmoving operations: A systematic literature review AUTCON 125 103632
[32]. Goodrum P M, Zhai D and Yasin M F 2009 J. Relationship between changes in material technology and construction productivity J. Constr. Eng. Ma. 135(4) 278-287
[33]. Dimitrov A and Golparvar-Fard M 2014 J. Adv. Eng. Inform. 28(1) 37-49
[34]. Mahami H, Ghassemi N, Darbandy M T, Shoeibi A, Hussain S, Nasirzadeh F, Alizadehsani R, Nahavandi D, Khosravi A and Nahavandi S 2020 J. arXiv preprint arXiv 16344
[35]. Dinh T H, Ha Q P and La H M 2016 Computer vision-based method for concrete crack detection. Int. Control Automation Robotics & Vision (ICARCV) 1-6
[36]. Koch C, Georgieva K, Kasireddy V, Akinci B and Fieguth P 2015. Adv. Eng. Inform. 29(2) 196-210
[37]. Deng J, Singh A, Zhou Y, Lu Y and Lee V C S 2022 Constr Build Mater. 356 129238









