

About AEIAdvances in Engineering Innovation (AEI) is a peer-reviewed, fast-indexing open access journal hosted by Tianjin University Research Centre on Data Intelligence and Cloud-Edge-Client Service Engineering and published by EWA Publishing. AEI is published monthly, and it is a comprehensive journal focusing on multidisciplinary areas of engineering and at the interface of related subjects, including, but not limited to, Artificial Intelligence, Biomedical Engineering, Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Materials Engineering, Traffic and Transportation Engineering, etc.For the details about the AEI scope, please refer to the Aims and Scope page. For more information about the journal, please refer to the FAQ page or contact info@ewapublishing.org. |
| Aims & scope of AEI are: · Artificial Intelligence · Computer Sciences · Aerospace Engineering · Architecture & Civil Engineering · Biomedical Engineering · Electrical and Electronic Engineering · Energy and Power Engineering · Materials Engineering · Mechanical Engineering · Traffic and Transportation Engineering |
Article processing charge
A one-time Article Processing Charge (APC) of 450 USD (US Dollars) applies to papers accepted after peer review. excluding taxes.
Open access policy
This is an open access journal which means that all content is freely available without charge to the user or his/her institution. (CC BY 4.0 license).
Your rights
These licenses afford authors copyright while enabling the public to reuse and adapt the content.
Peer-review process
Our blind and multi-reviewer process ensures that all articles are rigorously evaluated based on their intellectual merit and contribution to the field.
Editors View full editorial board

Chicago, US
momar3@iit.edu

New York, United States

Quanzhou, China

Eskişehir, Turkey
Latest articles View all articles
With the rapid growth of the Internet economy and the rising rate of urbanization, urban residents' travel modes have become increasingly diversified, with taxis featuring online booking becoming a common choice for daily commuting. Taxis meet the residents' "door-to-door" travel needs, but their travel modes exhibit significant randomness and uncertainty. Moreover, there are often imbalances in supply and demand, such as "difficult to hail a taxi" and "long-distance orders". Therefore, accurate and rapid prediction of taxi demand is crucial for improving regional transport capacity and achieving a "win-win" situation for platforms, drivers, and passengers. This paper uses the "New York City Taxi and Limousine Commission (TLC) Green Taxi Trip Data for April 2015" dataset, applying data mining techniques based on the LSTM taxi demand prediction model to forecast single-region taxi demand and regional OD matrix. The paper selects real network car order data to validate the model’s effectiveness. Additionally, different prediction models are compared to determine the optimal forecasting model.

 View pdf
View pdf


Somatosensory interaction technology is an important pathway driving the development of artificial intelligence that meets societal needs, and the application of robots in human society is becoming increasingly widespread. This study aims to systematically review and evaluate the current state of artificial intelligence research based on somatosensory interaction technology, particularly its applications in the field of automated robotics. Using a literature review methodology, this paper elaborates on how automated robotics technology integrates somatosensory interaction to achieve natural human-machine interaction. It provides a comparative analysis of the progress made in current applications, existing limitations, and potential future development directions, followed by a comprehensive summary. The research indicates that somatosensory interaction technology offers a more intuitive and natural means of interaction for automated robots, achieving significant results across various fields. However, challenges remain in terms of technical precision, environmental adaptability, and cost. It is hoped that this study will provide valuable insights for the development of related technologies in China.

 View pdf
View pdf


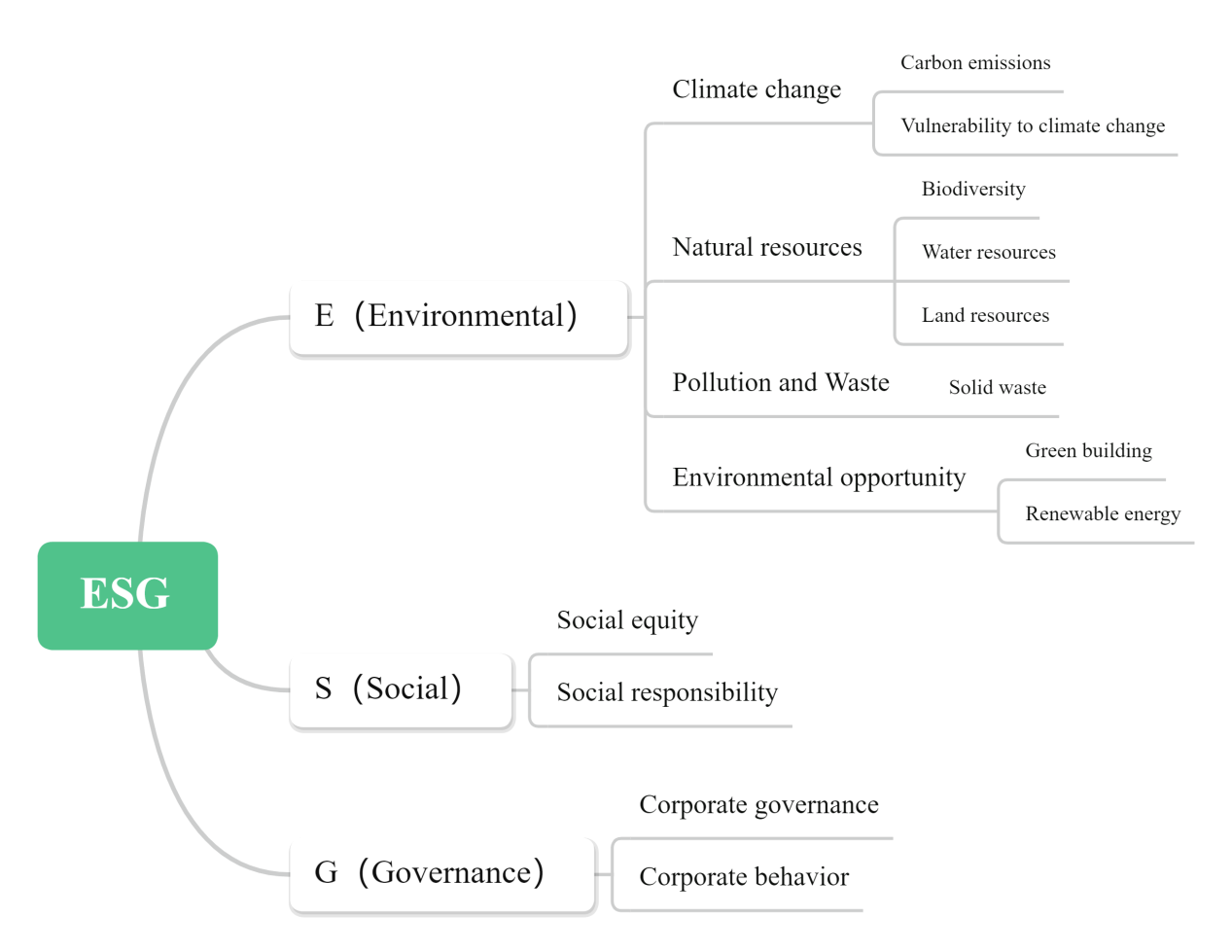
This paper systematically reviews the evolution of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) model construction and traces the development of ESG disclosure and supervision, highlighting regional differences. It further unpacks the core components of the three ESG dimensions and, on this basis, examines their nonlinear interactions. The paper argues that environment, society, and governance do not operate in isolation; rather, through a “boundary–baseline–mechanism” closed loop, they jointly constitute the core framework for corporate sustainable development. Finally, the paper summarizes the opportunities and challenges facing ESG and points out that ESG is poised to become a powerful engine driving the next generation of global growth.

 View pdf
View pdf


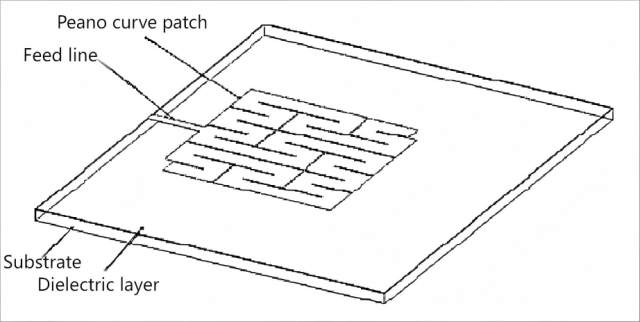
With the development of millimeter-wave technology, the miniaturization and integration of antennas have become key requirements. This paper presents a millimeter-wave second-order fractal antenna, including its structural design, fabrication method, and application in a silicon-based three-dimensional integrated structure. This antenna realizes a miniaturized structure with a Peano fractal curve on the substrate, featuring a novel structure, small size, and compatibility with other devices and chip processes. Meanwhile, a large-thickness BCB dielectric layer is adopted, which contributes to the miniaturization and integrated integration of the system. By elaborating on the design principle, fabrication steps, and performance of the antenna in the three-dimensional integrated structure, this paper provides a valuable reference for the development of millimeter-wave three-dimensional integration technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


Volumes View all volumes
2025
Volume 16April 2025
Find articlesVolume 16March 2025
Find articlesVolume 16September 2025
Find articles2024
Volume 14December 2024
Find articlesVolume 13November 2024
Find articlesVolume 12October 2024
Find articlesAnnouncements View all announcements
Advances in Engineering Innovation
We pledge to our journal community:
We're committed: we put diversity and inclusion at the heart of our activities...
Advances in Engineering Innovation
The statements, opinions and data contained in the journal Advances in Engineering Innovation (AEI) are solely those of the individual authors and contributors...
Indexing
The published articles will be submitted to following databases below:





