

Volume 133
Published on February 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning
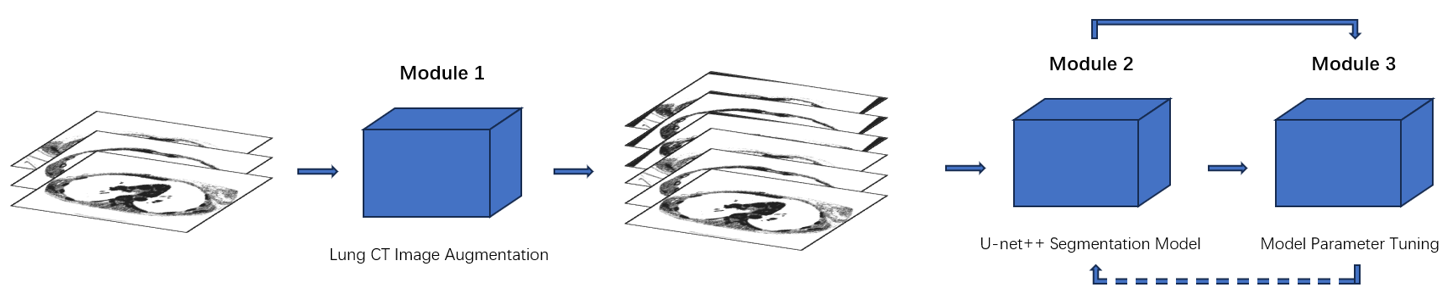
Recently, the state-of-art models for medical image segmentation is U-Net and their variants. These networks, though succeeding in deriving notable results, ignore the practical problem hanging over the medical segmentation field: overfitting and small dataset. The over- complicated deep neural networks unnecessarily extract meaningless information, and a majority of them are not suitable for lung slice CT image segmentation task. To overcome the two limitations, we proposed a new whole-process network merging advanced UNet++ model. The network comprises three main modules: data augmentation, optimized neural network, parameter fine-tuning. By incorporating diverse methods, the training results demonstrate a significant advantage over similar works, achieving leading accuracy of 98.03% with the lowest overfitting. potential. Our network is remarkable as one of the first to target on lung slice CT images.

 View pdf
View pdf


Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as transformative tools in Artificial Intelligence (AI), fueled by advancements in deep learning. Notably, OpenAI's Generative Pretrained Transformer (GPT) series has showcased their capacity to comprehend and generate human-like text, making them indispensable across various domains. This paper provides a comprehensive exploration of LLMs, encompassing their foundational principles, technical advantages, and multifaceted applications spanning agriculture, medicine, and information security. By elucidating how LLMs revolutionize these sectors through heightened efficiency, accuracy, and innovation, this work unveils their potential to reshape industries and drive technological progress. Additionally, this work delves into forthcoming prospects and potential challenges in LLM development and deployment, concluding with a synopsis of pivotal insights. As LLMs continue to evolve, their integration into diverse fields promises profound implications for human-computer interaction and societal advancement. This paper illuminates the trajectory of LLMs, from their inception to their current prominence, underscoring their pivotal role in shaping the future of AI and fostering responsible innovation.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid advancement of the Internet of Things (IoT), Ultra Wideband (UWB) Radio Frequency (RF) technology has emerged as a key communication method, providing distinct benefits for short-range, high-speed wireless connectivity. Thus, the paper explores the application and challenges of UWB RF technology with the aim of investigating how UWB technology, characterized by its high-precision positioning, high-speed data transmission, and low-power consumption, can be used in various IoT domains. By examining the fundamentals of UWB technology, specific applications such as smart homes, industrial automation, and health monitoring are examined. The analysis highlights the potential of UWB in enhancing positioning accuracy in smart homes, improving production efficiency and safety in industrial settings, and enabling real-time health monitoring with low latency. Through a detailed review of existing literature and case studies, it assesses the performance and potential of UWB in these areas, and identifies challenges facing UWB technology, including multipath interference, signal fading, spectrum sharing, and device interoperability and standardization. The results demonstrate that while UWB has great potential in the IoT, it requires further technological advancements and standardization to overcome its current limitations.

 View pdf
View pdf


Disinformation has become a major challenge in the digital age, with significant consequences for public opinion, social cohesion, and the democratic process. This paper aims to explore the mechanisms of misinformation propagation within social networks, focusing on the role of key influencers, platform accountability, and policy interventions. By examining previous literature, this research seeks to identify strategies that influence the spread of misinformation. The research examines theoretical models such as the Attraction-Introduction Model to understand the dynamics of misinformation spread and the influence of key individuals in either amplifying or suppressing its dissemination. The study highlights that individuals with high network centrality, such as influencers, play a pivotal role in spreading and containing false information. Social media platforms are found to bear significant responsibility for managing information flow, primarily through algorithmic design and content moderation. Policy interventions, including regulation and public education, are necessary, but their impact is limited without international cooperation and platform transparency. The study requires a comprehensive approach to counter misinformation. Social media platforms must strengthen their accountability, algorithms must be reconfigured to prioritize accuracy over engagement, and governments should implement legislative and educational strategies. Collaboration between platforms, policymakers, and the public is critical for creating more resilient and credible social networks.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid popularization of the Industrial Internet, the connection between industrial control systems and enterprise networks has become increasingly tight, making them primary targets for cyberattacks. This trend not only intensifies the security risks of industrial control systems but also presents new challenges for cybersecurity protection. Deep learning technology in artificial intelligence, with its capability to learn complex problems from unsupervised data, is a powerful tool for protecting the cybersecurity of industrial control systems. This paper explores the foundational theories of Industrial Internet security and intrusion detection, covering basic concepts, major characteristics, and various security threats and risks faced by the Industrial Internet. It further analyzes the limitations of traditional security technologies in the context of the Industrial Internet, including their inadequacies in responding to new threats, particularly their vulnerability to system vulnerabilities and virus attacks. Moreover, the paper introduces the specific applications of three deep learning algorithms—Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)—in the security of the Industrial Internet. Through systematic analysis and research, the paper reveals specific cybersecurity issues present in the Industrial Internet and proposes effective methods to address these issues using deep learning algorithms. These findings not only provide new ideas and technical support for contemporary Industrial Internet security protection but also offer valuable insights and a theoretical foundation for future research directions.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the growing demand for IoT devices, developing low-power AI models on embedded systems has become increasingly important. However, the efficient implementation of AI models within the computational and battery limitations of these devices remains a significant challenge. This study addresses how model pruning and quantization compression techniques can reduce power consumption without significantly compromising model accuracy. The research method optimizes the performance of the three-color recognition model, organizes a dataset consisting of red, yellow, and green classification images, and pre-processes them to standardize the resolution and format. The research object is to use pruning and quantization techniques in combination to optimize memory and computational efficiency further. Experimental evaluation was performed on an Arduino Nano 32 with a camera model, TensorFlow Lite for Microcontrollers for deployment, and a power measurement tool to record energy consumption. The results demonstrate that these methods significantly reduce energy consumption while maintaining acceptable accuracy for real-time applications. This study provides practical optimization strategies for deploying TinyML on resource-constrained devices, offering valuable insights for low-power AI development in IoT and edge computing applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), the backbone of internet communication, ensures reliable, connection-oriented data transmission. Despite its widespread use in areas such as email, web browsing, and file transfer, TCP faces significant security vulnerabilities stemming from its design era, which prioritized functionality over security. Common threats include TCP sequence number prediction, session hijacking, SYN flood attacks, and TCP Reset attacks. Existing mitigation strategies, such as TCP-AO, SSL/TLS encryption, and network-based security measures like IDS/IPS, have reduced risks but face challenges like performance overhead and compatibility issues. This study reviews the root causes of TCP vulnerabilities, evaluates existing solutions, and highlights gaps in addressing threats within modern network architectures. While current measures are effective to an extent, future research must explore advanced technologies such as quantum cryptography, blockchain-based authentication, and AI-driven anomaly detection to enhance TCP security and adaptability. This work underscores the urgent need for interdisciplinary collaboration and innovation to secure TCP in evolving digital ecosystems.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the accelerated aging of the population and the improvement of health awareness, the recreation industry is experiencing a booming development. Smart sensors, as the core component of recreation monitoring systems, play a key role in multi-scenario applications. This paper reviews the current research status of a multi-scenario recreation smart sensor monitoring system and analyzes its application in different scenarios such as family, community, and hospital. Firstly, the technological progress of smart sensors in physiological parameter monitoring, behavior analysis, and environment sensing is described. Second, the overall architecture design and data fusion method of a multi-scenario recreation monitoring system are discussed. Secondly, the characteristics and application requirements of smart sensors in different scenarios are compared and analyzed. Finally, the current technical challenges, including data security and privacy, system reliability, and intelligence level, are pointed out, and the future development trend is also prospected. The study shows that the introduction of emerging technologies such as multimodal sensing fusion, edge computing, and artificial intelligence will further enhance the performance of the recreation monitoring system. In the future, the construction of an intelligent and personalized recreation monitoring system covering the whole life cycle is of great significance in promoting the high-quality development of the recreation industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


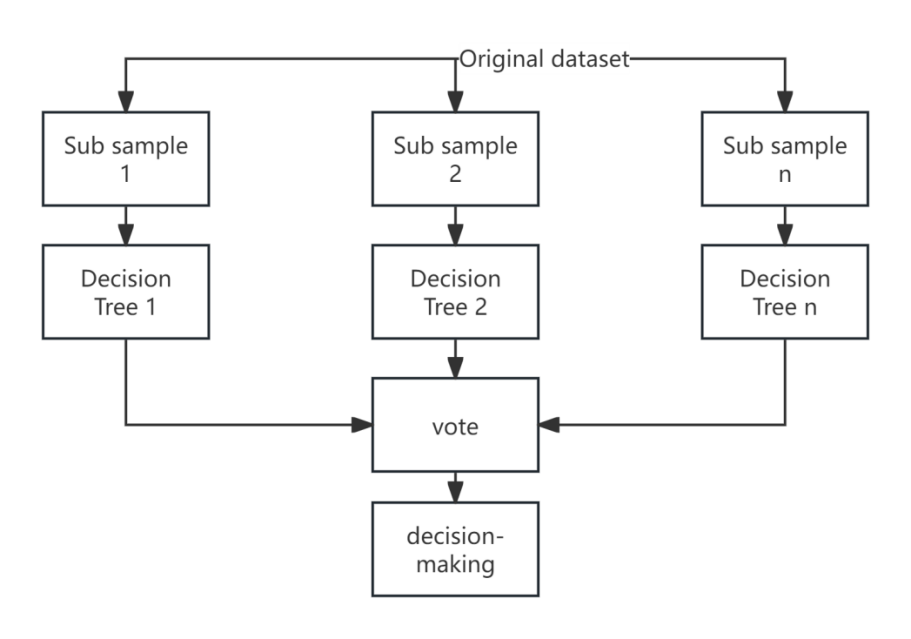
Random forest algorithm is an effective machine learning algorithm in stock return classification prediction, with high accuracy, but it has problems such as parameter optimization defects and difficulty in feature selection. To this end, based on the traditional random forest algorithm, a new algorithm is proposed by combining the feature selection particle swarm algorithm with the parameter grid search algorithm - the particle swarm parameter grid search random forest algorithm. Using particle swarm optimization algorithm for feature selection of input data, reducing the dimensionality of input data by removing redundant features, and introducing grid search algorithm to optimize some parameters of random forest, not only reduces the computational complexity of random forest algorithm, but also improves the classification and prediction accuracy of random forest. The experimental results were compared with the original random forest, decision tree, and support vector machine classification models, confirming that the parameter optimized random forest stock prediction model has higher accuracy and AUC values in model evaluation than other models.

 View pdf
View pdf


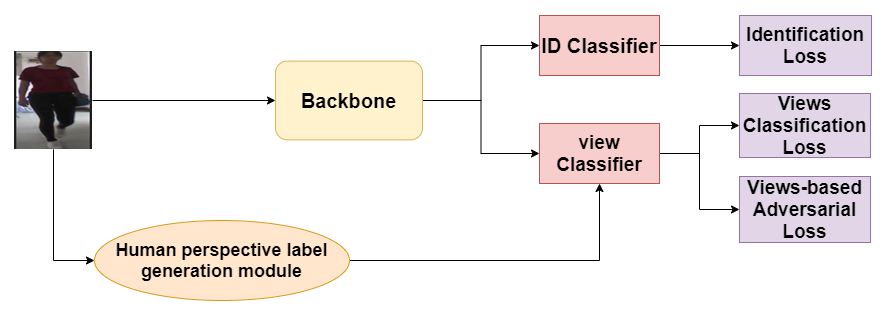
Address clothes-changing person recognition of other key is to extract the characteristics associated with human nature, for example, face, hair, body size and gait. At present, most of the research work mainly focuses on processing multi-modal information and fails to make full use of the information related to human nature in the original RGB images. In this paper, a viewpoint-based adversarial loss algorithm is proposed to mine visually relevant features from the original RGB images by punishing the predictive ability of the ReID model. A lot of experiments show that our model has achieved good results.

 View pdf
View pdf




