

Volume 15
Published on October 2023Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
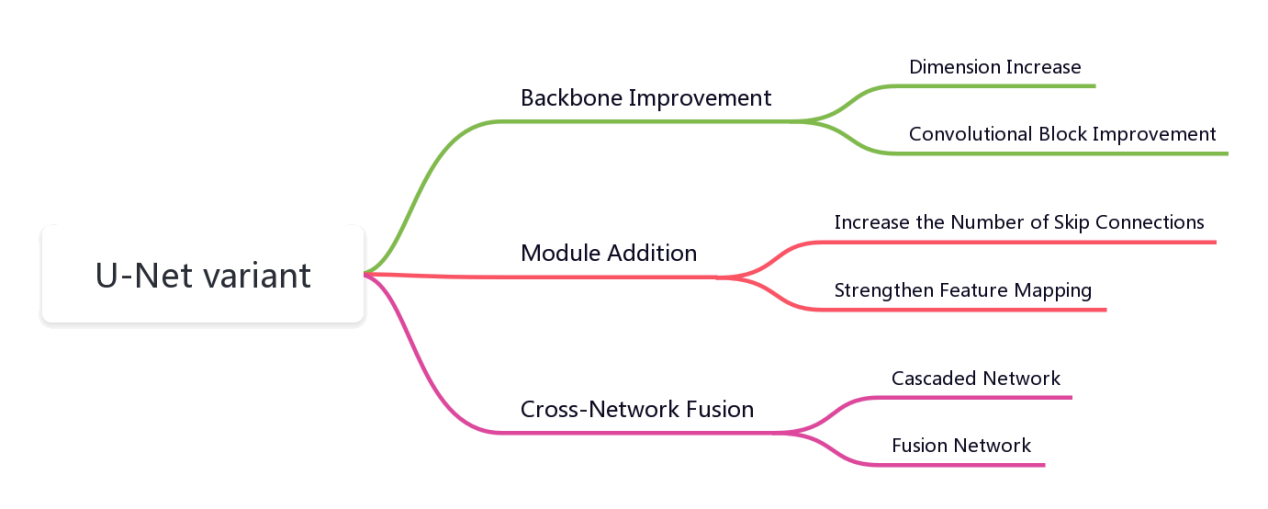
Medical image segmentation can provide valuable information for doctors, it has important research value in the medical field. Meanwhile, U-Net, as the fundamental networks for such tasks, brings a substantial improvement in the segmentation performance of traditional medical images. With the increasingly widespread use of U-Net, researchers have designed various U-Net variants according to different task requirements. However, most of the current summaries of U-Net variants are divided according to the direction of network applications, and the structural relationship between the variant networks and U-Net is not elaborated. Therefore, this paper classifies U-Net variants according to their network framework by elaborating the principles of U-Net structure. According to the U-Net network structure, it is divided into three main categories: backbone improvement, module addition and cross-network fusion. Further, the characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of different categories of variants are introduced, and the directions of the variants for U-Net optimization are analyzed. Finally, the article summarizes the current development direction of U-Net variants and provides an outlook on the future directions that can continue to be optimized.

 View pdf
View pdf


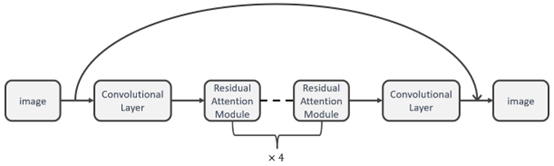
Cat species recognition holds significant potential in many fields. The primary objective of this research is to develop an automated algorithm for recognizing the presence of cats in images. The application prospects of this algorithm are diverse and include security, image search, and social media. Hence, this research has considerable practical value in various domains. In this study, we propose a cat image recognition algorithm based on the PyTorch, with ResNet50 as the foundational network architecture, and an attention mechanism (Efficient Channel Attention) integrated into the model for improved performance. We first introduced the Resnet network, and then introduced the combination of attention mechanism and Resnet in detail The proposed model achieved a 92.37% accuracy rate in classifying the 12 cat species, demonstrating its efficacy in accurately classifying and recognizing the collected images. The research conclusion of this paper has certain reference value.

 View pdf
View pdf


The protection of user data interests is of utmost significance in this day and age, when everyone's private life details and possessions are being digitised and stored in the cloud. Data now rules the world. This paper reviews the relevant literature in order to study the balance of rights in the protection of user data interests in the era of big data. It then suggests various countermeasures for the problem that it identifies. According to the findings of this study, the key factors contributing to the imbalance in the protection of user data rights are the progression of science and technology, the increase in the value of user data, and a lack of awareness regarding the protection of user personal data rights.

 View pdf
View pdf


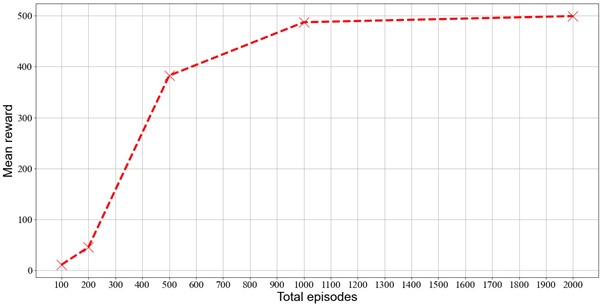
Deep Q-learning Network (DQN) is an algorithm that combines Q-learning and deep neural network, its model can adopt high-dimensional input and low-dimensional output. As a deep reinforcement learning algorithm proposed ten years ago, its performance on some Atari games has surpassed all previous algorithms, even some human experts, which fully reflects DQN’s high research value. The tuning of hyperparameters is crucial for any algorithm, especially for those with strong performance. The same algorithm can produce completely different results when using different sets of hyperparameters, and suitable values can considerably improve the algorithm. Based on the DQN we implement, we test on number of episodes, size of replay buffer, gamma, learning rate and batch size with different values. In each round of experiments, except for the target hyperparameter, all others use default values, and we recorded the impact of these changes on training performance. The result indicates that as the number of episodes continues to increase, the performance improves steadily and degressively. The same conclusion is also applicable to the size of replay buffer, while other hyperparameters need to be given values to have optimal performance.

 View pdf
View pdf


Mobile robots are used extensively across a variety of industries and fields. How to discover a start-to-end path without colliding has become a hot topic in recent years due to the complexity and uncertainty of the workplace. In various environments, a path planning technique should demonstrate high efficiency and speed. And this can reduce the energy consumption of the robots and greatly increase their working efficiency. This paper will conclude the presently popular path planning algorithm. Based on the different features of these algorithms, they are divided into three types: traditional path planning algorithm, neural-work-based algorithm, and sampling-based algorithm. Based on the new papers in these years, detailed introduction of the algorithms and their variants will be given. At the end of the paper, the thesis is summarized and the future research trend is prospected.

 View pdf
View pdf



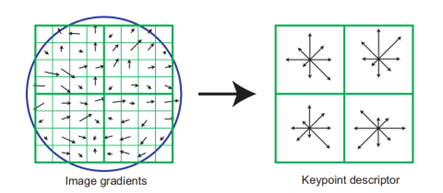
Image stitching is the process of combining numerous photos to make a panorama. The technique of image stitching has rapidly advanced and grown to be a significant area of digital image processing. Many image stitching methods have been proposed and studied in prior study. In this paper, the image stitching process is implemented using different algorithms. For keypoints detection, the algorithms of Harris corner detection, SIFT(Scale-Invariant Feature Transform), SURF(Speeded Up Robust Feature) and ORB(Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF) algorithms are applied, then use different methods (i.e., Brute Force, etc.) for feature matching. The RANSAC(Random Sample Consensus) method is used to calculate a homography matrix from matched feature vectors and use it to warp the images. Image blending and cropping methods are proposed to enhance the image quality. Given groups of the self-captured images, experiments have been down to shown the performance of different techniques.

 View pdf
View pdf


Channel coding plays a crucial role in enhancing the reliability and efficiency of communication systems, particularly when transmission channels are disrupted by noise and interference. This paper presents an in-depth review of various channel coding techniques, their applications, and future research directions. Key topics discussed include prevalent channel coding methods, such as repetition codes, convolutional codes, LDPC codes, turbo codes, and polar codes. The paper also delves into the selection of suitable channel coding parameters and their applications in digital TV, mobile and satellite communications, unmanned aerial vehicle data links, speech communication, and underwater acoustic channels. Moreover, the paper explores the performance analysis and comparison of different channel coding techniques, shedding light on their strengths and weaknesses. Lastly, the paper identifies emerging trends and challenges in channel coding research, providing valuable insights for researchers and practitioners in the field of communication systems. By examining these techniques and future directions, this comprehensive overview aims to contribute to the development of more robust and efficient channel coding schemes for a wide range of communication applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the continuous improvement of the manufacturing process of mobile phone cameras, the demand for panoramic photos by the industry and the public is not limited to ordinary cylindrical panoramic images, so a series of accurate panoramic image stitching technologies have been derived. However, these techniques often fail to take into account the stitching effect and speed, and there is still a technical gap in current multi-image panoramic stitching techniques. This article mainly compares the accuracy and efficiency of various feature extraction algorithms to select the most suitable algorithm for obtaining feature point pairs and estimating the homography matrix. Finally, a dual band hybrid algorithm is used to distort and fuse multiple images into panoramic photos. The results show that the panoramic images generated with multiple images using the algorithm provided in this paper are very good, even though there is a little bit of light and dark interlacing and ghosting.

 View pdf
View pdf


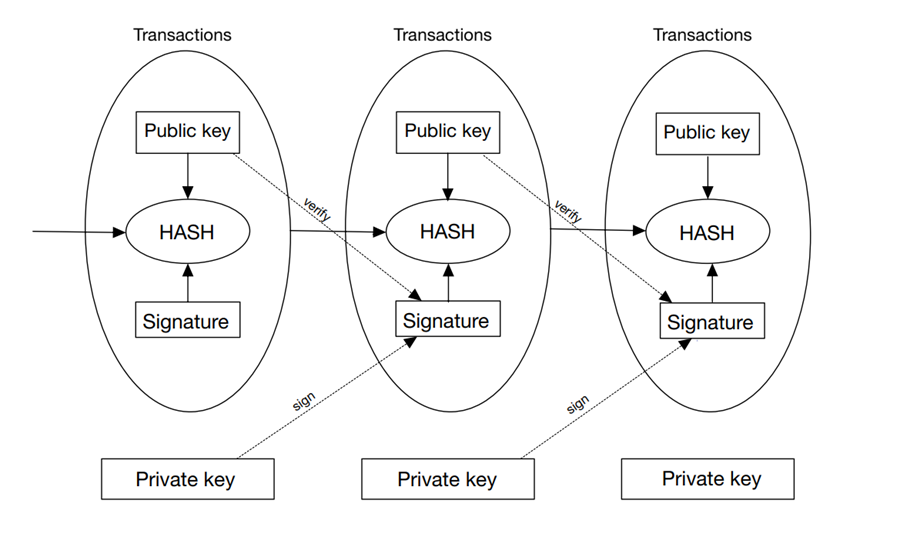
Digital currencies have become an increasingly popular topic of discussion in recent years. Digital currencies are virtual forms of currency that operate outside the traditional banking system. They are based on cryptographic technologies and are often decentralized, meaning they are not controlled by a central authority. The most well-known digital currency is Bitcoin, but there are many other types of digital currencies in existence. Digital currencies can be used to purchase goods and services online or transferred between users directly without intermediaries like banks. They have gained popularity due to their potential for increased security, transparency, and efficiency in financial transactions. In today's digital currency, a variety of digital currencies emerge in an endless stream, and crypto technology is also constantly developing to improve the security of digital currency payments. In section 2, this paper briefly introduces several common digital currencies and encryption algorithms, and in section 3, this paper introduces these typical digital currencies in detail through the analysis of representative literature. Bitcoin is mainly encrypted based on blockchain technology, and its encryption principle is mainly divided into three parts: public key encryption, hash function, and proof of work. Ethereum is a distributed blockchain platform with encryption principles similar to Bitcoin, including public key encryption and hashing algorithms. Ripple is a distributed cryptocurrency. Its encryption principle mainly adopts the public-private key encryption system. In terms of encryption technology, blockchain technology, the Hash algorithm and symmetric and asymmetric encryption are also popular encryption algorithms in digital currencies.

 View pdf
View pdf


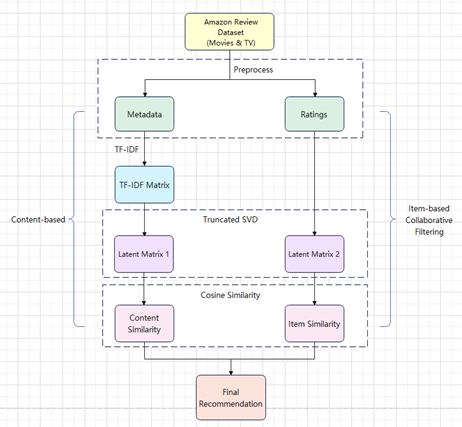
With the rapid development of multimedia technology and the constant upgrading of film and television libraries, users' demand for movies and television is increasing. How to accurately and timely find favorite movies from massive movie and television resources according to user's preferences and needs has become a great challenge. In recent years, the recommendation of movies and TVs has attracted a lot of research interest from academia and industry. The existing recommendation algorithms mainly include content based and collaborative filtering. The former recommends projects through collaborative learning of others' interests, while the content-based method examines the rich context of the project. In this paper, to further improve the performance of recommendations, a content based collaborative filtering method is proposed to provide recommendations for movies and television. Specifically, we extract and vectorize feature and category information from movies based on TF-IDF and apply truncated SVD to reduce the dimensions of the rating and TF-IDF matrix to retain the most representative information. We calculate the cosine similarity between the vectors from these two matrices. The final recommendation is to list 10 movies based on the average similarity of content and ratings. Extensive experiments on Amazon review data have proven the effectiveness of this method.

 View pdf
View pdf




