

Volume 148
Published on April 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Smart Systems

This paper explores the movement mechanisms of microswimmers in low Reynolds number environments by analyzing key physical concepts, microbial swimming mechanisms, and methods of calculating swimming speed. The study is based on three significant documents: “Life at Low Reynolds Number,” “The Hydrodynamics of Swimming Microorganisms,” and “A Mathematical Explanation of an Increase in Bacterial Swimming Speed with Viscosity in Linear-Polymer Solutions.” The main focus is on understanding how microorganisms adapt to their environment. Methods for calculating swimming speed were translated into MATLAB code to simulate the effect of angle on swimming speed, and a model confirming microbial movement was designed through SOLIDWORKS and 3D printing. Two experiments using the model were conducted in two different fluid environments. The result demonstrated the influence of different fluid viscosity on swimming velocity and stability. Computational simulations and experiments offered valuable insights into the swimming mechanisms of microorganisms in surroundings with low Reynolds numbers.

 View pdf
View pdf


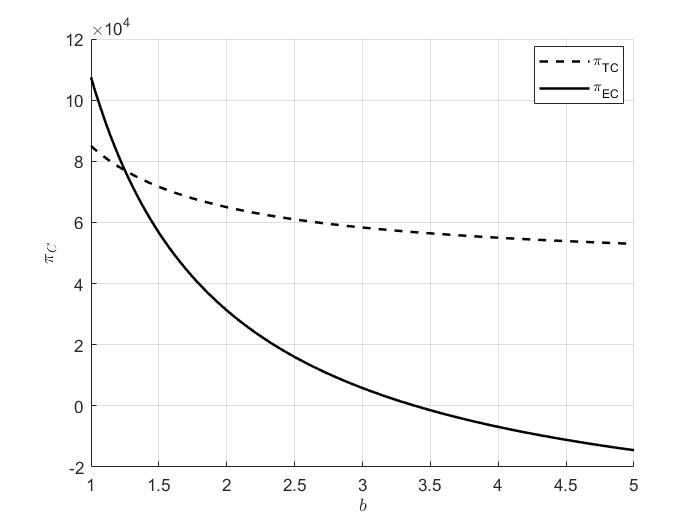
Against the background of the global emphasis on carbon emission reduction, the reform of the European Union's carbon emission trading system (EU ETS) will be incorporated into the shipping industry from 2024, which will have a significant impact on the operation of shipping enterprises. In this context, China's shipping enterprises urgently need to choose an appropriate carbon emissions trading model to effectively respond to the impact of the EU ETS, so as to accelerate the low-carbon transformation. Based on this, this paper constructs the Gounod competitive game model of two shipping companies under the baseline scenario and the cooperative strategy scenario, takes into full consideration the key factors of the shipping companies' market potential, cost, carbon emission quota and price in the model, and researches on the choice of carbon quota trading modes of the shipping companies under the EU ETS, such as purchasing emission allowances or cooperating with other companies to obtain allowances, etc. The equilibrium transportation of the shipping companies under different scenarios is also studied, and the impacts of different scenarios are also examined. The equilibrium volume, price and profit of shipping companies under different scenarios are solved, and MATLAB is applied to numerically analyze the decision-making variables of the model to further analyze the potential impact of EU ETS on the shipping industry. The results show that EU ETS policies always have a negative impact on traditional shipping companies, while sustainable shipping companies are affected.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid development of power electronics technology, DC-DC converters are increasingly applied in areas such as electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. This paper focuses on two common DC-DC converters—Buck (Step-Down Converter) and Boost (Step-Up Converter)—and elaborates on their operating principles. Through literature analysis and comparative studies, this paper explores the application of wide-bandgap semiconductor materials, strategies for suppressing electromagnetic interference (EMI), and optimization methods such as synchronous rectification and multiphase interleaving topologies. Additionally, the importance of these two converters is analyzed in practical applications like electric vehicle charging systems and solar power systems. The results show that adopting new materials such as gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) and intelligent control strategies can effectively improve converter efficiency, reduce losses, and address technical challenges in high-frequency operation. This research provides theoretical and practical references for the design and application of high-performance DC-DC converters, contributing significantly to technological advancements in the renewable energy field.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper investigates the critical impact of industrial robotic arms on the shift towards intelligent manufacturing, a transition defined by Industry 4.0. We explore the ways in which these arms, characterized by their growing flexibility and accuracy, are transforming smart manufacturing by boosting productivity, safety, and comfort in the workplace. Our research covers the historical development of robotic arm technology, its significant improvements, and its use in diverse fields such as factory automation, space missions, medical operations, and agriculture. We evaluate how robotic arms influence the intelligent transformation of businesses, emphasizing their role in economic growth, eco-friendly practices, and the move to digital operations. The paper points out areas where further research is needed, especially regarding precision agriculture and cross-disciplinary studies, and proposes solutions to bridge these gaps. We also discuss a successful example of heavy-duty robots in car manufacturing and how government policies can drive intelligent transformation. Our findings highlight the importance of robotic arms in the evolution of smart manufacturing and stress the importance of ongoing innovation and the adoption of these technologies.

 View pdf
View pdf




