

Volume 239
Published on November 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICFTBA 2025 Symposium: Data-Driven Decision Making in Business and Economics
Against the backdrop of expanding retail participation, rising passive ownership, and evolving market microstructure, understanding the links between trading, pricing, and the real economy has renewed importance. This review examines how equity markets function, what determines stock prices, and how those prices shape macroeconomic outcomes. The study’s theme is integrative: it synthesizes theory and evidence on four core market functions (price discovery, risk sharing, capital formation and governance, and liquidity provision), organizes pricing determinants across present-value logic, risk-based factor models, and demand- or constraint-driven mechanisms, and traces macroeconomic transmission through household wealth, firm investment, credit conditions, and monetary policy. This study connects canonical models with recent empirical findings and institutional observations, highlighting points of agreement and contention. The significance of this study lies in providing an integrated framework for researchers and policymakers: it clarifies when prices primarily reflect cash-flow news versus pressures driven by discount rates or order flows; it highlights how ownership composition and intermediation capacity shape price impacts; and it identifies practical implications for estimating the cost of capital, designing markets, and monitoring financial stability.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper looks at how investing in artificial intelligence (AI) affects company agency costs. Using data from non-financial firms listed in Shanghai and Shenzhen A-shares in China between 2012 and 2024, it carries out a real-world study with a fixed-effects model. The results show that corporate AI investment significantly increases both Type I and Type II agency costs, specifically the management expense ratio between shareholders and management, and the proportion of other receivables between major stockholders and minority stockholders. This worsens the conflicts of interest between company owners and managers, and also between large owners and small owners. Based on these conclusions, this paper proposes that a corporate governance system adapted to AI investment should be improved, and enterprises should focus on enhancing investment efficiency and building transparency to ensure that AI investment truly serves sustainable development and long-term value enhancement of enterprises.

 View pdf
View pdf


The explosive growth of China’s express delivery industry has driven economic development while also posing severe environmental challenges, such as packaging waste pollution and consistently high carbon emissions. Existing research is mostly limited to the optimization of partial links, lacking discussions on systematic ness and regional applicability. Taking JD Logistics as an example, this paper adopts case analysis and the SWOT method to study the implementation paths and effects of its green logistics system. The study finds that multi-link collaboration can significantly improve emission reduction efficiency; the extended producer responsibility system and deposit-return mechanism can effectively promote the use and recycling of circular packaging; and the differentiated implementation of circular packaging and biodegradable materials, along with the construction of a cross-platform carbon incentive ecosystem, are key paths to solve the "green premium" problem. This study demonstrates that enterprises can convert environmental pressure into sustainable competitiveness through technology output, transparent carbon accounting, and material R&D cooperation, providing a practical basis and strategic reference for the green transformation of the logistics industry in the context of emerging markets.

 View pdf
View pdf


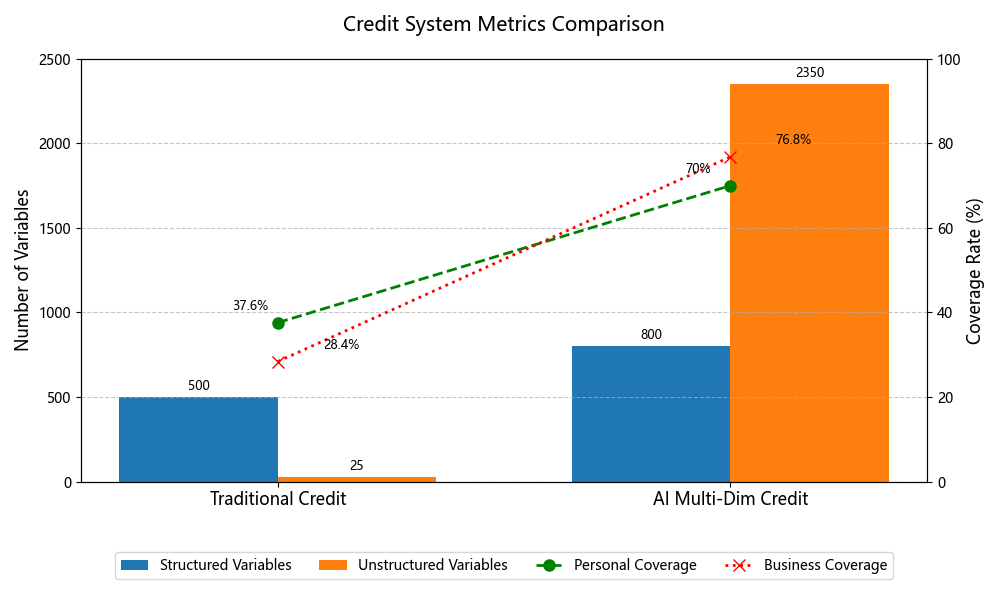
Against the background of a traditional credit system that can no longer meet today’s needs, this paper systematically analyzes its structural shortcomings, including one-dimensional data sources, outdated information updates, and severe data fragmentation, which explains the reason that it hampers inclusive-finance development. On this basis, it then explores how artificial intelligence and big-data technologies can be applied to credit reporting through three key relationship-network construction, including the use of relationship networks, full-dimension credit profiling, and dynamic risk alerts to improve both assessment accuracy and real-time timeliness. The study further highlights multiple risks in AI-driven credit systems, such as legal compliance challenges, privacy leakage, and model explainability risks inherent in AI-driven credit scoring. Accordingly, it proposes optimizing and governing a multi-level governance framework through the three layers: relationship networks, full-dimension profiling, and dynamic alerts, to push the industry toward greater precision, inclusiveness, and a secure development path for the credit industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


By the end of 2023, there were 21,625 private investment fund managers in mainland China, with 153,032 private equity funds on record, the scale of private equity funds reaching 20.32 trillion yuan. The development of private equity funds is rapid. Numerous studies indicate that private equity funds are emerging as a key vehicle for innovative capital formation. At the same time, the Yangtze River Delta economy achieves remarkable results. It accounts for 4% of China's land area, contributing approximately 30% of the country's national economic growth, and the private equity fund management scale accounts for around 40% of the country's total. As a result, the regional agglomeration of private equity funds examines the factors contributing to this phenomenon and its associated impacts. In this regard, this study selects data based on four driving factors: economy, innovation, finance, and foreign trade, and combines them with empirical analyses to assess the impact of regional factors on private equity in the Yangtze River Delta. Finally comes to the following conclusions: credit expansion, innovation, and foreign trade are the key driving forces that promote the establishment of funds and active investment. The stability of the macroeconomic conditions is the key to ensuring effective collection and smooth launch of private equity.

 View pdf
View pdf


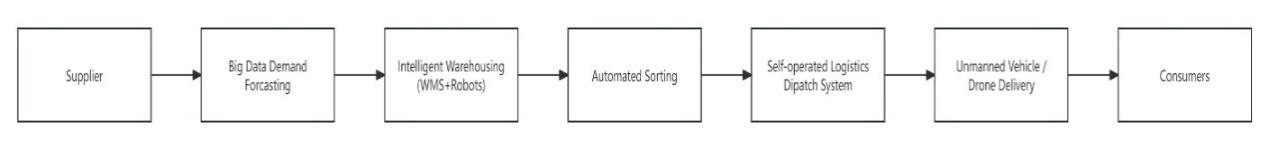
With the development of the retail industry and digital technologies, enterprise supply chains are facing demands for improved efficiency, faster response, and optimized user experience. This paper analyzes the application of digital intelligence and model innovation in retail supply chains, using JD Convenience Store and Hema Fresh as examples. The study found that big data-driven demand forecasting, intelligent warehousing, forward warehouse layout, and instant delivery are key means to improve efficiency and service. JD Convenience Store achieves integrated online and offline management through regional warehouses and high-frequency, small-batch replenishment, while Hema Fresh builds an agile supply chain based on forward warehouses and community instant delivery, demonstrating differentiated practices. Digital transformation can optimize inventory turnover, reduce out-of-stock rates, improve delivery efficiency, and enhance user satisfaction, but challenges remain, such as high costs, regional adaptability, and insufficient flexibility. Future retail supply chain development should focus on full-chain digitalization, enhanced flexibility and resilience, green sustainability, omni-channel integration, and personalized customization.

 View pdf
View pdf


Big data presents previously unheard-of difficulties for traditional statistical inference techniques created in the 20th century, endangering both their underlying presumptions and their usefulness in real-world scenarios. Three interconnected core challenges are methodically examined in this paper: (1) The out-of-control error discovery rate caused by multiple tests in a high-dimensional environment; (2) Dimensionality disasters and sparsity challenges in high-dimensional data analysis; (3) Computational complexity - Statistical accuracy dilemma. These problems are systemic in nature and call for all-encompassing solutions rather than existing in isolation. The corresponding countermeasures, such as the FDR control strategy, regularization-based high-dimensional modeling techniques, and distributed computing techniques, were reviewed and examined in this paper. As demonstrated in this paper, an innovative method framework that integrates regularization techniques, multiple test corrections, and effective computing strategies offers a workable solution to the significant limitations that traditional statistical methods face in the big data environment. These advancements offer a new path for statistical practice in the digital age by reorienting the paradigm from one that prioritizes accuracy to one that is computationally feasible.

 View pdf
View pdf


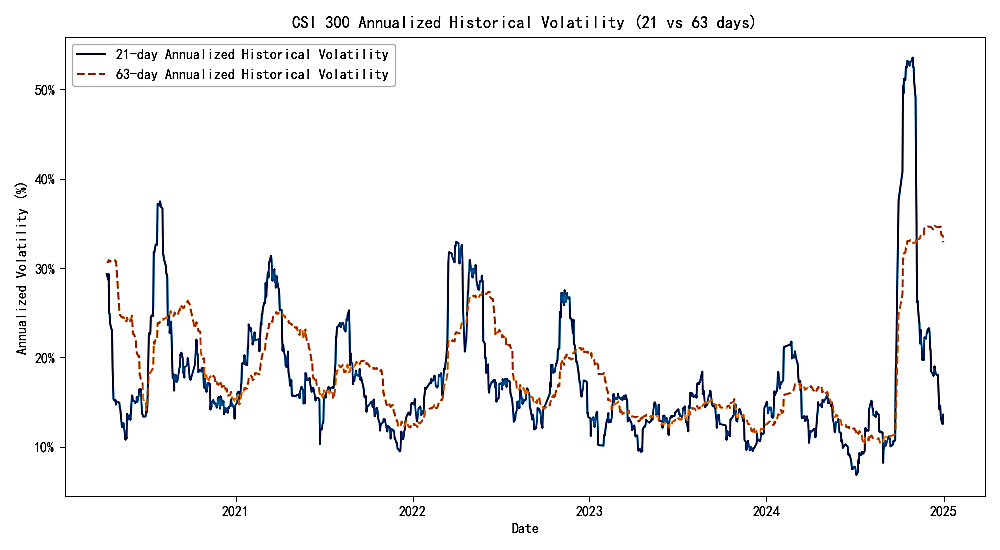
This paper conducts a systematic review around the characteristics, measurement methods and forecasting models of financial market volatility, and conducts an empirical verification with the sample data of the Shanghai and Shenzhen 300 Index from 2020 to 2024. First of all, at the theoretical and literature levels, this paper combs several stylistic facts of volatility, including the characteristics of fat tail and peak of return distribution, volatility aggregation, leverage effect and asymmetric response, as well as long memory and roughness, and reviews the latest progress of relevant domestic and foreign research. Secondly, at the methodological level, this paper compares the unconditional measurement model represented by historical volatility, the conditional heteroscedasticity model represented by the GARCH family, the HAR-RS model based on high-frequency interval volatility, and the rough volatility model emerging in recent years, and discusses their theoretical basis, applicable scenarios, advantages and disadvantages respectively. Finally, in the empirical analysis, this paper compares the rolling forecasts based on the daily data of the Shanghai and Shenzhen 300 Index. The results show that GARCH (1, 1) - t and HAR-RS models are competitive in short-term forecasting, while RSV Lite has more advantages in overall forecasting efficiency; However, in the Value-at-Risk (VaR) backtest, all models have the problem of tail risk underestimation under extreme market scenarios. The results of this study provide important model selection basis and decision-making reference for financial institutions to carry out risk management and portfolio optimization.

 View pdf
View pdf


Based on the sample of Chinas Shanghai and Shenzhen A-share listed companies from 2010 to 2023, this study employs multiple regression analysis to explore the impact and mechanism of corporate digital transformation on dual innovation, with a focus on analyzing the moderating effect of corporate ESG performance. The research findings indicate that digital transformation has a significant positive promoting effect on dual innovation (including exploratory innovation and exploitative innovation), and corporate ESG performance positively moderates this relationship. Specifically, companies with superior ESG performance demonstrate stronger empowerment effects of digital transformation on dual innovation. Heterogeneity analysis reveals that this positive effect is more pronounced in state-owned enterprises, companies listed on the main boards (Shanghai and Shenzhen Stock Exchanges), and larger firms.

 View pdf
View pdf


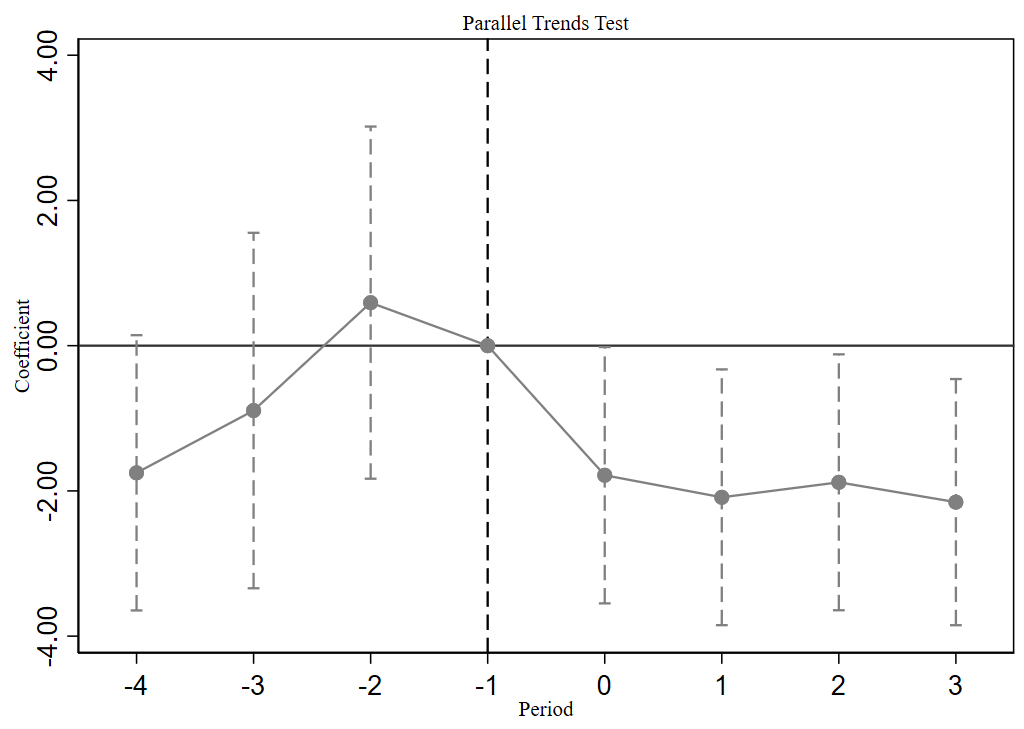
Against the backdrop of global energy transition and green development, academics and policymakers are widely interested in how government energy policies influence corporate sustainability practices. This article focuses on China's New Energy Demonstration City policy (NEDC). It conducts an empirical study, employing a difference-in-differences (DID) design to examine its effects on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) outcomes. Empirical research indicates that the NEDC has significantly enhanced the ESG ratings of companies in pilot cities, with this impact exhibiting a consistent positive trend across all three dimensions: environmental, social, and governance. Mechanism analysis reveals that the NEDC improves ESG metrics through three pathways: enhancing total factor productivity, stimulating green innovation, and promoting digital transformation. This conclusion validates previously established hypotheses, contributes to ESG economics theory, and provides empirical evidence for government policymaking on green transitions. Overall, the findings highlight the crucial role of targeted energy policies in fostering corporate sustainability and offer insights for advancing global low-carbon transformation.

 View pdf
View pdf




