

Volume 87
Published on June 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEIPI 2025 Symposium: Reimagining Society: AI's Role in Cultural Transformation and Learning Environments
China’s inclusive education, while progressive in policy discourse, is undermined in practice by a standardised assessment regime that structurally excludes students with special educational needs (SEN). This article conducts a critical analysis of how standardized assessments exacerbate the exclusion of students with SEN through policy analysis and current research, as well as through the perspective of critical disability theory. The research indicates that while policies advocate equity, standardized assessments marginalize students with SEN by emphasizing limited academic criteria, hence perpetuating stigma and epistemic injustice. The critical analysis highlights the paradox between China’s inclusive commitment and standardized assessment mechanism rooted in historical keju tradition. In order to bridge the gap, integrate formative assessment and reconstruct teacher training programs to improve the celebration of cognitive diversity. Otherwise, without systematic shifts towards equity-driven evaluation, the advocacy of inclusive education in China would remain a utopian vision. The article underscores the necessity for meaningful and inclusive structural reforms in primary education in China.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article critically evaluates the factors contributing to mental health inequalities through the lens of the social-ecological framework. By exploring interactions across individual, interpersonal, community, societal, and environmental levels, this research highlights how marginalized groups are disproportionately affected by mental health disparities. The study analyzes contemporary issues and trends, emphasizing the complex interplay among factors such as gender, race, socioeconomic status, interpersonal relationships, community cohesion, structural discrimination, cultural contexts, and environmental stressors. A case study examining the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic further demonstrates the significance of these interwoven factors. The study concludes by outlining implications for mental health research and practice, advocating for community-centered, culturally sensitive, strength-based approaches, and systemic transformations to dismantle underlying structures of inequality. Ultimately, the study aims to inform evidence-based interventions, policy changes, and equitable resource distribution, thus promoting both individual healing and broader social justice.

 View pdf
View pdf


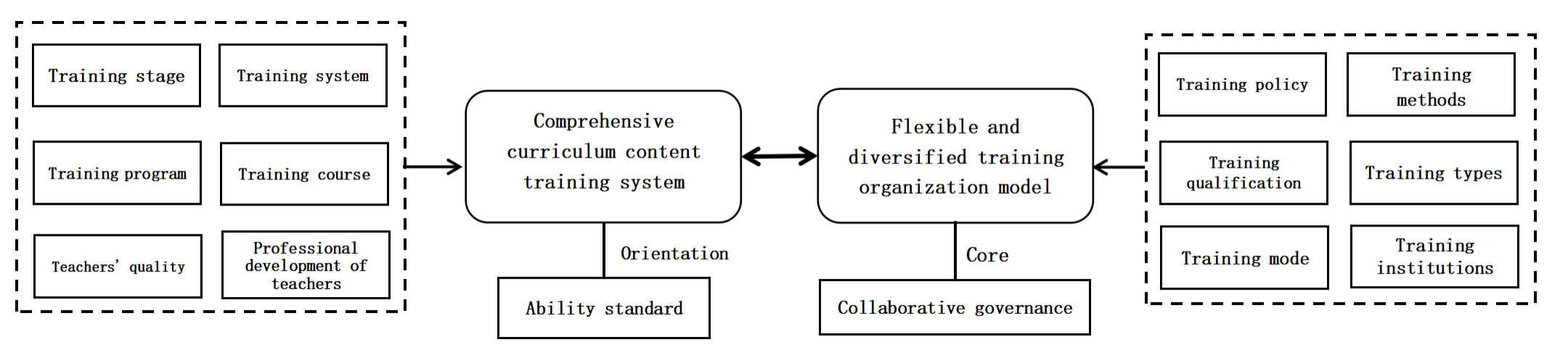
As a key component of educational modernization, the core of enhancing preschool education quality lies in the professional development of teachers. Although the current kindergarten teacher training system in China plays an important role in building the teaching workforce, its theoretical framework still lags behind practical exploration. In contrast, developed countries, with their mature education systems and advanced educational philosophies, have accumulated rich experience in kindergarten teacher training. Therefore, this study uses the United States, United Kingdom, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore as case studies and applies grounded theory methods along with Nvivo 11 Plus software to code and analyze literature, systematically deconstructing the content system and organizational models of kindergarten teacher training in developed countries. The study finds that the five countries generally construct curriculum frameworks oriented around core competencies, emphasizing the deep integration of practical skills and theoretical knowledge. Additionally, they adopt phased, multi-subject collaborative training models that effectively meet the professional development needs of teachers. Based on these findings, the study proposes four recommendations: (1) constructing a "competency-based" content system; (2) promoting a "multi-cooperative" organizational model; (3) improving the "dynamic closed-loop" quality assurance mechanism; and (4) focusing on "special groups" and "emerging fields," to provide theoretical and practical paths for the systematic reform of kindergarten teacher training in China.

 View pdf
View pdf


Nowadays, with the development of AI, an increasing number of college students in China have began to utilize it as a tool for English study, and AI has demonstrated its double-edged effect in many aspects of writing assistance. The propose of this study is to explore the impact of AI assist reading on five Female students of English major in an coastal university in Guangdong, China. This study also inquires about the room for improvement of college English teaching under the phenomenon of the popularity of AI tools. A qualitative research approach, leveraging literature review and qualitative interview as research design and approach were used and effectively facilitated the realization of the study purpose. This study finds that college students have a strong dependency on AI-assist reading. Both the students and researchers express a strong interest in integrating AI into the college English teaching process, and various suggestions are provided. On one hand, these young female college students point our the potential room for improving college English major’s education under the back ground of popularization of AI. On the other hand, they also set an alarm on the important of guiding students to distinguish the boundary between AI assistance and AI instead of themselves.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the continuous acceleration of urbanization, the differences between urban and rural areas in various aspects are gradually increasing. In terms of education, represented by English education, there are also significant differences in students' academic performance. Students' academic performance is related to their learning motivation, so this paper focuses on the differences in English learning motivation between urban and rural students. This paper will discuss the reasons for the differences in learning motivation among middle school students in non-English speaking countries and the corresponding solutions. When analyzing the reasons for the differences in motivation, the researchers divide the factors into personal factors and environmental factors, and find that individual factors are to some extent caused by environmental factors. If solutions are sought from these reasons for the differences in motivation, it will, to some extent, promote educational equity and social mobility. Future research should focus on this area, providing more evidence and direction for our educational methods and policies.

 View pdf
View pdf


Educational inequality remains a global issue, particularly in low-income communities, where limited resources, insufficient funding, and a shortage of qualified teachers severely impact students' learning opportunities. Government intervention plays a crucial role in addressing this challenge, yet the effectiveness of different policies varies depending on the socioeconomic context of each country or region. For example, Finland has successfully reduced educational disparities through an equitable funding distribution system and inclusive education policies. In contrast, many other countries continue to struggle with structural inequalities that hinder access to quality education. This study evaluates the impact of government policies in three key areas: education funding allocation, affirmative action initiatives, and digital education strategies, all of which aim to mitigate educational inequality. By conducting a comparative policy analysis, this research seeks to assess the effectiveness of these interventions in promoting educational equity. Additionally, it aims to provide insights and recommendations for future education reforms to create more inclusive and accessible learning opportunities for all students, regardless of their socioeconomic background.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study explored the effects of multicultural education on ethnic minority students', especailly Chosŏnjok (Korean-Chinese) elementary school students, learning experiences and academic performance. Based on interviews with teachers and analysis of standardized exam scores, the research compares two schools in a minority-concentrated region, one that implements multicultural practices and one that does not. In the multicultural school, students not only excelled in the primary-to-secondary school test (小升初) but also showed more motivation and confidence in class. Interviews with teachers pointed to the inclusiveness of our curricula and bilingual strategies that encourage deeper participation, while noting that the lack of cultural relevance in the control school consistently resulted in disengagement. By contrasting the assimilationist Chinese policy paradigm with the inclusive ones in many international contexts, this paper argues that culturally responsive pedagogy that focuses on equity is critical to achieving in diverse education settings. The findings indicate that ethnic minority pupils in mainstream Chinese schools could continue to struggle academically and emotionally without such fundamental reform.

 View pdf
View pdf


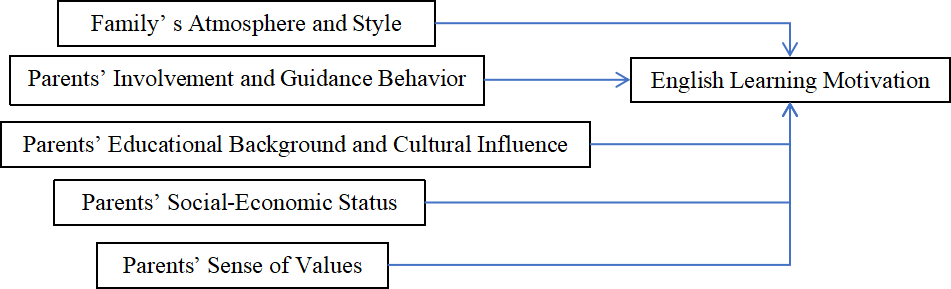
English learning motivation is a critical and common factor that exists in our daily learning life. Learners in two main environments while learning, the school environment and family environment, these environments are psychologically and physically affecting learning motivation. In college students in China, many researchers have focused on searching the school environment’s influence on English learning motivation, while the family environment is less studied in contrast. This research aims to provide a more comprehensive classification of family factors and expand the existing perspective on their influence on English learning motivation. Through the questionnaire method in mixed-method research, the results of this paper will provide insights into family factors on students’ English learning motivation in China and identify the correlation and the degree of influence. This paper will demonstrate that the family factors (i.e., parents’ sense of values, parents’ social-economic status, parents’ educational background and cultural influence, parents’ involvement and guidance behavior, family's atmosphere and style) is positively related to students’ English learning motivation, and further find the way to improve students’ English learning motivation through paying attention to strong influencing factors and providing appropriate family support.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article reviews determinant literature on Bourdieu’s cultural capital theory in relation to studies on immigrant children. Based on the analysis of the existing literature, the paper looks into the applicability of Bourdieu’s cultural capital in figuring out the outcome of education among immigrant children and their social integration in the new society and asserts that the cultural capital, such as language proficiency, and social habitus, has a significant impact on the educational experiences and social adjustment of immigrant children. Moreover, the paper also demonstrates how immigrant children’s family strategies can be combined with the rewards of the educational system, which, to a certain extent, can help children bypass the obstacles imposed by the school. By analysing the relevant literature using the PRISMA framework, the article summarises the main research questions, research findings and research gaps in the present literature in this article. Thus, in addition to enhancing the understanding of the experience of immigrant children in the education system of the host country, the article also provides a reference for future research, especially about how the cultural capital affects the generational development of immigrant children.

 View pdf
View pdf


Under the background of globalisation, multilingual learning has evolved from personal development options to a necessary literacy for survival in modern society. In the process of language learning, people will be more or less influenced by their mastered language, which is the effect of language transfer. Therefore, language transfer has always been an important topic in the field of second language acquisition. When the positive transfer phenomenon occurs, the mother tongue (L1) or the mastered language plays a role in promoting the learning of the target language (L2); on the contrary, when L1 plays a negative role on L2, the negative migration of the language occurs. In order to better reflect the impact of language transfer in the field of second language acquisition and promote the improvement of teaching methods, this article will briefly describe the theories and hypotheses that have far-reaching significance in the field of linguistics so far, and take native Japanese speakers who learn Chinese as an example to explain the performance of positive transfer and negative transfer in grammar, phonetics, etc. The research results will also be analysed, and suggestions will be made for future Chinese learning and textbook preparation.

 View pdf
View pdf




