1. Introduction
In today's world, where global trade is becoming ever more crucial, the US dollar plays a pivotal role as the settlement currency for numerous international transactions. The exchange rates between United States dollar (USD) and the currencies of other nations, as other other nations' monetary policies, interact with one another [1]. For the European Economic Community, the dollar and the euro influence each other, and European economic and monetary policies are often affected by changes in the dollar-euro exchange rate. Government bond yields, particularly the 10-year benchmark yield, serve as important tools for adjusting the impact of euro-dollar exchange rate fluctuations, reflecting long-term interest rates and economic expectations [2, 3]. Although changes in bond yields are influenced by various factors such as economic expectations and price trends, exchange rates are also a significant factor [4]. Additionally, the international trade growth rate, which represents the growth of international trade, is directly affected by exchange rates, and there is a reciprocal influence between international trade growth rates and government bond yields [5]. In this context, studying the relationships among European and American exchange rates, European government bond yields, and European international trade growth rates has become a hot topic of research.
Researching the changes in exchange rates that lead to changes in government bond yields holds significant value for both investors and government departments. It helps investors achieve higher returns and allocate investment funds more reasonably, and it assists government departments in preparing measures to respond to exchange rate changes or understanding potential changes in government bond yields through exchange rate movements [6]. Additionally, understanding how exchange rates affect international trade growth rates can directly aid both sides of the trade in formulating trade plans and determining trade partners.
Existing research usually primarily the method of the individual effects of exchange rates on either bond yields or trade growth rates, often neglecting the comprehensive interactions among these variables. These studies have shown that while exchange rates can influence economic indicators, the degree and nature of these impacts varies greatly depending on the economic context with policy context [7, 8]. However, a significant limitation in past research is the insufficient exploration of the combined effects of exchange rates, bond yields, and trade growth rates. This gap in the literature highlights the need for a more integrated approach to understand the multifaceted relationships among these critical economic variables.
Moreover, the interplay between these economic variables can offer insights into broader economic conditions and trends. For instance, fluctuations in exchange rates may signal underlying shifts in economic strength, influencing investor confidence and market stability [9]. Similarly, variations in government bond yields can reflect changes in monetary policy or economic outlook, impacting fiscal strategies and investment decisions [10]. This multifaceted relationship underscores the complexity of global economic interactions and the importance of comprehensive analysis in understanding these dynamics.
This study aims to analyze the relationship among the monthly exchange rates of EUR/USD, the 10-year government bond yields with international trade growth rates of 20 European countries from January 1991 to December 2016. It also explores the correlation coefficients among the three variables and the pairwise correlation coefficients between each pair of variables. By utilizing descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, regression modeling, and time series analysis, this research seeks to uncover the underlying dependencies and predictive insights among these financial variables. This comprehensive approach is intended to address the gaps in current research and offer a more profound insight into the interconnectedness of these economic elements.
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
In this research, used data includes the monthly exchange rates of EUR/USD (settlement data on the first of each month), average European government bond yields, and the international trade growth rates of 20 European countries from January 1, 1991, to December 1, 2015. The data of EUR/USD exchange rate is sourced from the Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED), European government bond yield data is from the European Central Bank, and European international trade growth rate data is from Eurostat.
2.2. Variable Selection
The original data covers different time periods, ranging from January 1970 to June 2024. To specifically examine the relationship between the euro and the dollar exchange rates, European government bond yields, and international trade growth rates after the formation of the European Community, data from January 1991 to December 2015 was extracted using Python. Further, Python tools were used to isolate the columns representing time and the three research factors from the three datasets, forming a new file with four columns: Time, Exchange Rate, Bond Yield, and Growth Rate. Instead of fixing the dependent variable, this paper sets different dependent and independent variables sequentially and compares the resulting R-values to identify the most influential two or three factors.
2.3. Method Introduction
This paper uses time series combined with multiple linear regression equations for the study. To achieve the research objectives, time series were used to visualize the three datasets, followed by multiple linear regression analysis of the three research factors. The formulas used are:
\( Exchange Rate= {β_{0 }}+{ β_{1}} ∙Bond Yield+ {β_{2}} ∙ Growth Rate + ε \) (1)
\( Exchange Rate= {β_{0 }}+{ β_{1}} ∙ Bond Yield + ε \) (2)
\( Exchange Rate= {β_{0 }}+{ β_{1}} ∙ Growth Rate + ε \) (3)
The analysis aims to explore the mutual influence coefficients among the three factors and determine whether the mutual influence among the three factors is stronger than the influence between any two factors alone.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Analysis
First, time series of Exchange Rate, Bond Yield, and Growth Rate data were visualized (Figure 1), showing different trends among the three. The Exchange Rate fluctuated continuously but with a small overall amplitude; the Bond Yield declined amid fluctuations; the Growth Rate rose amid fluctuations, with a high growth proportion.
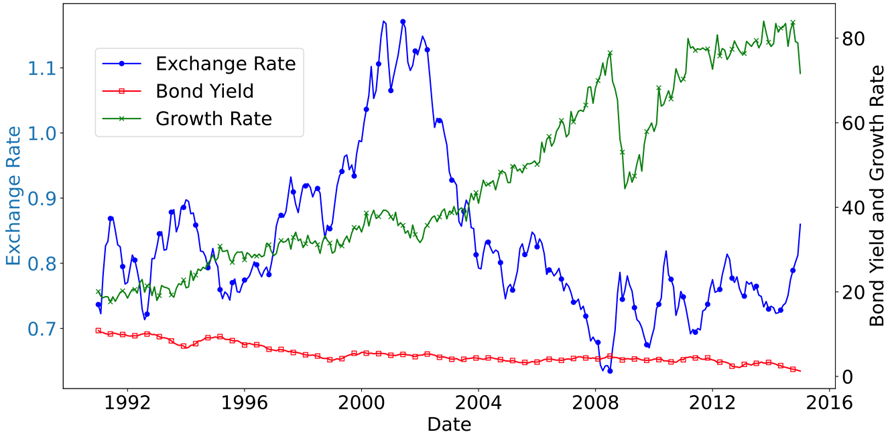
Figure 1. Time Series of Exchange Rate, Bond Yield, and Growth Rate
From Figures 2 and 3, there are correlations between the Exchange Rate and Bond Yield and Growth Rate, though the correlations are weak and negative. A detailed look at Figure 2 reveals a dense scatter plot of Exchange Rate and Bond Yield, but it does not exhibit a clear correlation. In contrast, Figure 3 shows a more dispersed scatter plot of Exchange Rate and Growth Rate, indicating a more evident negative correlation.
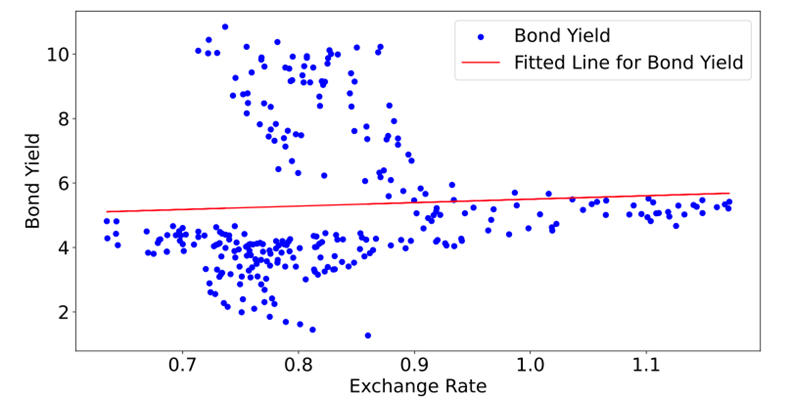
Figure 2. Regression Analysis: Exchange Rate Influencing Bond Yield
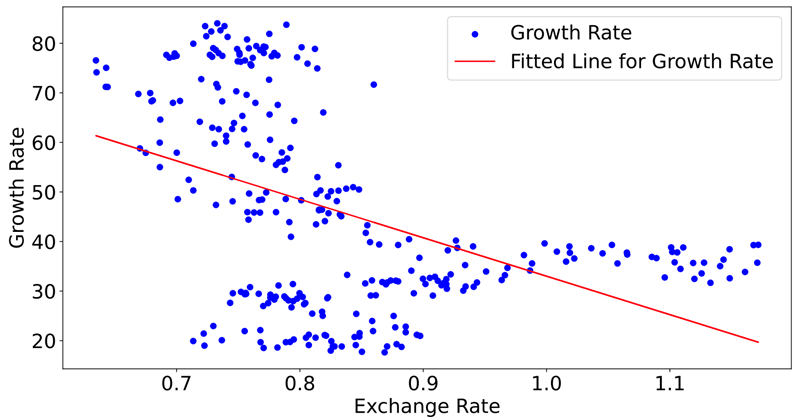
Figure 3. Regression Analysis: Exchange Rate Influencing Growth Rate
3.2. Model Results
The interaction of the Exchange Rate on two key variables: Bond Yield and Growth Rate, followed by understanding how Bond Yield and Growth Rate influence the Exchange Rate through multivariate regression analysis, is the main propose for this paper. The summary of the results is as follows: Multiple regression analysis reveals several key insights into the connection of Exchange Rate, Bond Yield, and Growth Rate. It shows that the interdependencies among these variables are complex and multifaceted. The results highlight the significance of considering multiple factors simultaneously rather than in isolation, as previous studies have often done. By incorporating both Bond Yield and Growth Rate into the analysis, this study provides a more holistic view of how these economic indicators interact and influence each other. This approach helps to uncover the underlying dynamics that drive exchange rate fluctuations and their broader economic implications. Moreover, the findings suggest that policy measures aimed at stabilizing exchange rates should take into account their potential impact on both bond yields and trade growth rates to achieve more effective economic outcomes.
Exchange Rate and Bond Yield (Table 1): The extremely low R-squared value (0.003) and insignificant coefficients indicate a fact: the interaction of Exchange Rate on Bond Yield is negligible. This suggests that other factors, such as monetary policy, inflation expectations, and market liquidity, have a greater influence in shaping bond yields. The bond market dynamics are intricate and can be affected by a range of economic indicators, both domestic and international.
Table 1. Linear Regression for Exchange Rate and Bond Yield
Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | p | Collinearity Diagnostics | B | SE | Beta | VIF | Tolerance | Constant | 0.817 | 0.018 | - | 45.107 | 0.000** | - | - | Bond Yield | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.057 | 0.963 | 0.336 | 1.000 | 1.000 | R2 | 0.003 | Adj R2 | -0.000 | F | F (1,287)=0.927,p=0.336 | D-W value | 0.030 | Dependent Variable: Exchange Rate | * p<0.05 ** p<0.01 |
Exchange Rate and Growth Rate (Table 2): The analysis shows a more significant relationship between Exchange Rate and Growth Rate, with an R-squared value of 0.210. The negative coefficient indicates that a higher exchange rate (implying a depreciated currency) is associated with a lower growth rate. This is consistent with economic theory, where a weaker currency makes imports more expensive, reducing consumer purchasing power and inhibiting economic growth. The significant influence from exchange rate to growth rate underscores the importance of maintaining currency stability for economic stability and growth.
Table 2. Linear Regression for Exchange Rate and Growth Rate
Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | p | Collinearity Diagnostics | B | SE | Beta | VIF | Tolerance | Constant | 0.957 | 0.016 | - | 61.659 | 0.000** | - | - | Growth Rate | -0.003 | 0.000 | -0.458 | -8.730 | 0.000** | 1.000 | 1.000 | R2 | 0.210 | Adj R2 | 0.207 | F | F (1,287)=76.209,p=0.000 | D-W value | 0.036 | Dependent Variable: Exchange Rate | * p<0.05 ** p<0.01 |
Multivariate Regression Analysis (Table 3): The multivariate regression model indicates that Bond Yield and Growth Rate collectively explain 44.5% of the variance in the Exchange Rate. Both factors have negative and significant coefficients, suggesting that higher bond yields and growth rates are associated with a stronger currency (lower exchange rate). This result highlights the interconnections among these economic variables. Higher bond yields can attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the domestic currency and thus enhancing its value. Similarly, robust economic growth can boost investor confidence and capital inflows, further supporting the currency's value.
Table 3. Linear Regression for Exchange Rate, Growth Rate, Bond Yield
Unstandardized Coefficients | Standardized Coefficients | t | p | Collinearity Diagnostics | B | Std. Error | Beta | VIF | Tolerance | Constant | 1.344 | 0.037 | - | 35.889 | 0.000** | - | - | Bond Yield | -0.042 | 0.004 | -0.779 | -11.011 | 0.000** | 2.582 | 0.387 | Growth Rate | -0.006 | 0.000 | -1.068 | -15.090 | 0.000** | 2.582 | 0.387 | R 2 | 0.445 | Adj R 2 | 0.441 | F | F (2,286)=114.690,p=0.000 | D-W valuer | 0.070 | Dependent Variable: Exchange Rate | * p<0.05 ** p<0.01 |
4. Conclusion
This research offers important understanding of the connections between three factors: Exchange Rate, Growth Rate, and Bond Yield. To summarize, the influence of Exchange Rate on Bond Yield is minimal, whereas its effect on Growth Rate is notably negative. When Growth Rate and Bond Yield act together on Exchange Rate, the negative effect is very significant and much greater than the sum of their individual effects on Exchange Rate. The output implies when the Exchange Rate falls, the Growth Rate rises; when both the Growth Rate and Bond Yield decline, the Exchange Rate increases significantly. Therefore, comparing univariate linear regression and multivariate linear regression analysis, the multivariate regression clearly provides better explanatory power, indicating that for models concerning Exchange Rate, Bond Yield, and Growth Rate, multivariate regression is more closely aligned with real data and has practical significance. These findings underscore the importance for policymakers to take these interconnected factors into account when devising economic and monetary policies to achieve stable and sustainable economic growth.
References
[1]. Joscha, B. and Robert. C. (2017) Exchange rate expectations and economic policy uncertainty. European Journal of Political Economy, 47, 148-162.
[2]. Degasperi, R., Hong. S. and Ricco, G. (2020) The Global Transmission of U.S. Monetary Policy. CEPR Discussion Paper, 14533.
[3]. Riccardo, D., Seokki, Hong. and Giovanni, R. (2020) The Global Transmission of U.S. Monetary Policy. CEPR Discussion Paper, 14533.
[4]. Valchev, R. (2020) Bond Convenience Yields and Exchange Rate Dynamics. American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics, 12(2), 124-66.
[5]. Morina, F., Eglantina, H., Uğur, E., Mirela, P. and Marian, C.V. (2020) The Effect of Exchange Rate Volatility on Economic Growth: Case of the CEE Countries. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 13, 177.
[6]. Akalpler, E. and Duhok, D. (2018) Does monetary policy affect economic growth: evidence from Malaysia. Journal of Economic and Administrative Sciences, 34, 2-20.
[7]. Suhadak and Dwi Suciany, A. (2020) Brief technical note: The influence of exchange rates on inflation, interest rates and the composite stock price index: Indonesia 2015 - 2018. Australasian Accounting, Business and Finance Journal, 14.
[8]. Maganioti, Y. and Han, J. (2020) The Impact of Exchange Rate Fluctuation on Economic Growth – Empirical Studies Based on Different Countries. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Business Corporation and Development in South-East and South Asia under B&R Initiative, Atlantis Press, 29-33.
[9]. Bhargava, V. and Konku, D. (2023) Impact of exchange rate fluctuations on US stock market returns. Managerial Finance, 49(10), 1535-1557.
[10]. Akram, T. (2021) A Note Concerning the Dynamics of Government Bond Yields. The American Economist, 66(2), 323-339.
Cite this article
Zhang,Y. (2024). Time Series Analysis of the Connection between Exchange Rate of EUR/USD, Bond Yields, and Trade Growth. Theoretical and Natural Science,52,207-213.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MPCS 2024 Workshop: Quantum Machine Learning: Bridging Quantum Physics and Computational Simulations
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Joscha, B. and Robert. C. (2017) Exchange rate expectations and economic policy uncertainty. European Journal of Political Economy, 47, 148-162.
[2]. Degasperi, R., Hong. S. and Ricco, G. (2020) The Global Transmission of U.S. Monetary Policy. CEPR Discussion Paper, 14533.
[3]. Riccardo, D., Seokki, Hong. and Giovanni, R. (2020) The Global Transmission of U.S. Monetary Policy. CEPR Discussion Paper, 14533.
[4]. Valchev, R. (2020) Bond Convenience Yields and Exchange Rate Dynamics. American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics, 12(2), 124-66.
[5]. Morina, F., Eglantina, H., Uğur, E., Mirela, P. and Marian, C.V. (2020) The Effect of Exchange Rate Volatility on Economic Growth: Case of the CEE Countries. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 13, 177.
[6]. Akalpler, E. and Duhok, D. (2018) Does monetary policy affect economic growth: evidence from Malaysia. Journal of Economic and Administrative Sciences, 34, 2-20.
[7]. Suhadak and Dwi Suciany, A. (2020) Brief technical note: The influence of exchange rates on inflation, interest rates and the composite stock price index: Indonesia 2015 - 2018. Australasian Accounting, Business and Finance Journal, 14.
[8]. Maganioti, Y. and Han, J. (2020) The Impact of Exchange Rate Fluctuation on Economic Growth – Empirical Studies Based on Different Countries. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Business Corporation and Development in South-East and South Asia under B&R Initiative, Atlantis Press, 29-33.
[9]. Bhargava, V. and Konku, D. (2023) Impact of exchange rate fluctuations on US stock market returns. Managerial Finance, 49(10), 1535-1557.
[10]. Akram, T. (2021) A Note Concerning the Dynamics of Government Bond Yields. The American Economist, 66(2), 323-339.









