1. Introduction
Gene annotation is a crucial step in genomics in that it determines the meaning of DNA sequences by recognizing the genes and their functions within a genome. The identification of genes, their function, and regulatory pathways enables the researcher to derive possible functions, regulatory pathways, and evolutionary relationships [1]. This is one of the fundamental steps in the fields of medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology, in which knowledge of genetics is the base upon which innovation is generated. While sequencing technologies have advanced, opening the way to a fast and efficient production of large amounts of data, the annotation of these sequences has not reached the same level, with most genes remaining poorly characterized or uncharacterized [2].
Traditional gene annotation tools, represented by BLAST, have formed the basis of genomic studies for many years. These tools rely on sequence homology, comparing new sequences to existing ones in reference databases such as UniProt or Ensembl[3]. They are well-trusted because they provide interpretable results: one understands how genes were annotated based on comparison scores or statistical metrics. To ensure the reliability of these traditional methods, manually reviewed databases are followed. They have some significant limitations. The tools struggle with novel sequences or species that have little or no homologous data in reference libraries. Moreover, traditional tools depend on linear analyses, which may miss complex relationships between sequences. This problem becomes especially acute for large datasets or genes showing little similarity to any known examples [4].
In the modern world, artificial intelligence has emerged as a potential alternative to traditional annotation methods. AI-powered tools, such as DeepGOPlus, rely on machine learning and deep learning algorithms to analyze DNA sequences without relying solely on reference databases [5]. This capability allows for the prediction of gene functions even for uncharacterized or newly identified sequences. Artificial intelligence models can incorporate different types of data, such as gene expression patterns and protein-protein interactions, making their predictions more reliable. Such tools prove to be highly effective at handling large datasets, thus becoming very important in the present era of high-throughput sequencing.
Despite its potential, AI is not without its challenges. A prevalent critique of artificial intelligence tools pertains to their insufficient transparency. Frequently referred to as "black boxes," these models yield outcomes without clarifying the underlying processes that informed their predictions. This deficiency in interpretability may pose a significant obstacle, particularly in domains such as healthcare, where comprehending the rationale behind a prediction is essential for informed decision-making. Moreover, the efficacy of AI is significantly contingent upon the availability of high-quality training data. In addition, if the training data are incomplete or biased, AI may have lower accuracy of prediction for the sequences, especially those coming from the underrepresented species. Moreover, training and running AI models requires enormous computational resources and could also become a heavy burden to bear for some smaller labs [5].
Moreover, it is impossible to overlook the many advantages that artificial intelligence brings to gene annotation. Advantages are speed, scalability, and the predictions of functions for previously uncharacterized genes offered by AI. With finer honing of such tools by researchers, it is possible that AI will continue to be more and more critical within genomics. This would be in improving AI model interpretability, standardizing the performance evaluations of such models, and developing hybrid approaches that incorporate the strengths of both AI and traditional methods. To better explore these ideas, this review takes Escherichia coli K-12 as a representative model organism. By contrasting traditional approaches, such as BLAST, with newer artificial intelligence-created tools such as DeepGOPlus, the advantages and disadvantages of each can be highlighted. While classical tools yield reliable and interpretable results, they are usually less able to deal with new sequences or very large datasets [6]. For example, the artificial intelligence tools are also very interesting opportunities, but they still need to be further developed to get closer to their full potential. Gene annotation has been probably one of the most central parts of genomics, and AI, with its advances in this field, can only promise better results. While scientists are still figuring out ways to embed AI technology into genomic processes, discovery and new avenues of innovation increase exponentially. Better gene annotation will probably result in significant changes in the trajectory of scientific progress regarding personalized medicine, synthetic biology, and evolutionary studies.
2. Literature review
In modern biological research, bioinformatics tools and databases have become essential resources for analyzing and interpreting large-scale sequence data. BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) and UniProt (Universal Protein Resource) are two of the most important bioinformatics tools, playing a significant role in sequence alignment, data storage, and annotation. This paper reviews the development history, characteristics, and impact of these tools on the field of bioinformatics based on classic literature.
In recent years, the application of deep learning has further advanced the development of bioinformatics, complementing the shortcomings of traditional tools. For instance, ProtTrans models large-scale protein sequences using self-supervised deep learning, "decoding" the language of life from a linguistic perspective, showcasing its strong protein function prediction capabilities [7]. Additionally, the groundbreaking results of AlphaFold provide high-precision protein structure predictions, solving the 50-year-old "folding problem" that has troubled the biological community, significantly improving the reliability of functional annotations [9]. In genomic research, the complete genome sequencing of Escherichia coli K-12 has provided valuable reference data for constructing and validating gene annotation tools [10]. Complementing this is the research on the programmable assembly of multicomponent protein nanoparticles, which achieves functional tunability through engineering design, providing the physical and chemical foundation for the development of new tools [11]. At the same time, the development of explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) methods has made AI model results more transparent, offering higher credibility and user trust in biological function prediction [8].
The article uses BLAST for preliminary computational analysis, comparing basic biological sequence information such as protein or nucleotide sequences. According to the BLAST algorithm, it can quickly search large biological databases to find sequences similar to the query sequence [1]. Further analysis is conducted using UniProt, which provides sequence data and supports protein-related research [3]. Additionally, protein prediction is based on deep learning methods applied to genetics and genomics [2].
From the perspective of tool performance comparison, traditional tools (such as BLAST and UniProt) excel in data reliability and interpretability. Their results are traceable and consistent. However, the limitations of these tools lie in the incompleteness of their databases, especially when dealing with genes that have fewer annotations or new sequences, leading to restricted coverage. For example, in the biological process (P category) annotations of certain genes, traditional tools only capture common functions and lack extended terms.
Artificial intelligence tools (such as DeepGOPlus) perform exceptionally well in new function prediction capabilities and coverage. For example, they can provide additional terms for the C category (cellular component), describing more complex cellular localizations [5]. However, their limitations include lower confidence in some prediction results. For example, predicting overly broad terms (such as “cellular anatomical entity”) may lack biological specificity, providing limited functional insights and involving a certain rate of false positives.
In P and F category annotations, AI tools and traditional tools show a high degree of consistency, but AI tools can supplement terms not covered by traditional tools. In terms of metabolic pathway prediction, traditional tools and AI tools also demonstrate high consistency. The main reason for this is that metabolic pathways are well-studied, and the literature on them is thorough. For example, the KEGG database provides high-quality annotations for traditional tools, which are also used to train AI algorithms, leading to overlapping prediction results.
This consistency validates the reliability of both types of tools in functional annotation and highlights the importance of mapping GO annotations to metabolic pathways as a method to verify functional annotation results.
3. Methodology
This study focused on the E. coli K12 genome and selected 30 well-characterized genes based on their functional diversity and representation in different Gene Ontology (GO) categories (P, F, and C). Two annotation tools were used in the comparison: traditional tools (including BLAST and UniProt) and the AI-based tool DeepGOPlus. BLAST was used for sequence comparison and functional annotation, while UniProt provided manually edited GO terms. deepGOPlus, a deep-learning model, can predict P, F, and C categories based on the protein sequence of GO terms and be therefore selected. Annotations were performed using both traditional and AI tools.
3.1. Traditional method
In traditional annotation, the authors first retrieved the gene sequences of selected E. coli K12 genes from the NCBI database in FASTA format and then analyzed these sequences using the gene prediction tool AUGUSTUS to identify coding regions, exons, and gene structures. The predicted coding sequences (CDS) were translated into protein sequences and further functionally annotated. Subsequently, the predicted protein sequences were subjected to sequence alignment with reference databases using BLAST. This step provided initial functional annotation by identifying homologous sequences. Finally, the annotations were refined and extended using UniProt, which retrieves curated Gene Ontology (GO) terms as well as functional descriptions associated with the aligned sequences.
3.2. AI method
The AI-based workflow also starts with the gene sequence of selected E. coli K12 genes in FASTA format retrieved from the NCBI database. The gene sequences were then translated into protein sequences using AUGUSTUS, followed by saving the protein sequences in FASTA format, and finally using DeepGOPlus to predict GO terms and their associated confidence scores. Evaluation metrics included annotation coverage for the three GO categories (P, F, and C), the proportion of consistent annotations (matches, partial matches, and mismatches), and the confidence scores of the AI-predicted terms. In addition, the authors analysed metabolic pathway predictions to assess the reliability of GO annotations.
4. Results
This study aimed to evaluate the annotation performance of traditional and AI-based methods across three Gene Ontology (GO) categories—Biological Process (P), Molecular Function (F), and Cellular Component (C)—and to analyze metabolic pathway matching.
4.1. Gene Annotation
Traditional methods demonstrated high coverage in annotating the selected 30 genes. For the Biological Process (P) and Molecular Function (F) categories, traditional methods successfully annotated all 30 genes, achieving a coverage rate of 100% in both categories. For the Cellular Component (C) category, 27 out of 30 genes were annotated, resulting in a coverage rate of 90%. Overall, traditional methods successfully annotated 87 out of 90 annotation instances across the three categories, yielding a total coverage rate of 96.7%. In comparison, AI-based methods yielded moderate annotation performance. For the Biological Process (P) category, AI-based methods annotated 22 out of 30 genes, achieving a coverage rate of 73.3%. In the Molecular Function (F) category, 25 out of 30 genes were annotated, corresponding to a coverage rate of 83.3%. In the Cellular Component (C) category, 26 out of 30 genes were successfully annotated, yielding a coverage rate of 86.7%. Overall, AI-based methods annotated 73 out of 90 annotation instances across the three categories, achieving a total coverage rate of 81.1%.
When comparing the two methods, traditional methods consistently outperformed AI-based methods in all categories, particularly in the Biological Process (P) category, where traditional methods achieved 100% coverage compared to 73.3% for AI-based methods. Similarly, traditional methods yielded higher overall annotation coverage (96.7%) compared to AI-based methods (81.1%), reflecting their superior annotation accuracy and consistency.
4.2. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
Although this study primarily focuses on gene annotation, metabolic pathway matching results provide additional insights. Of the analyzed cases, 52 (57.8%) were categorized as “Not Match,” primarily due to both traditional and AI-based methods failing to identify pathways. Additionally, 3 cases (3.3%) were classified as “Partially Match,” while 35 cases (38.9%) were successfully matched. The relatively high proportion of “Not Match” cases highlights the limitations of both traditional and AI-based methods in identifying metabolic pathways and suggests that further optimization is necessary to improve performance in this area.
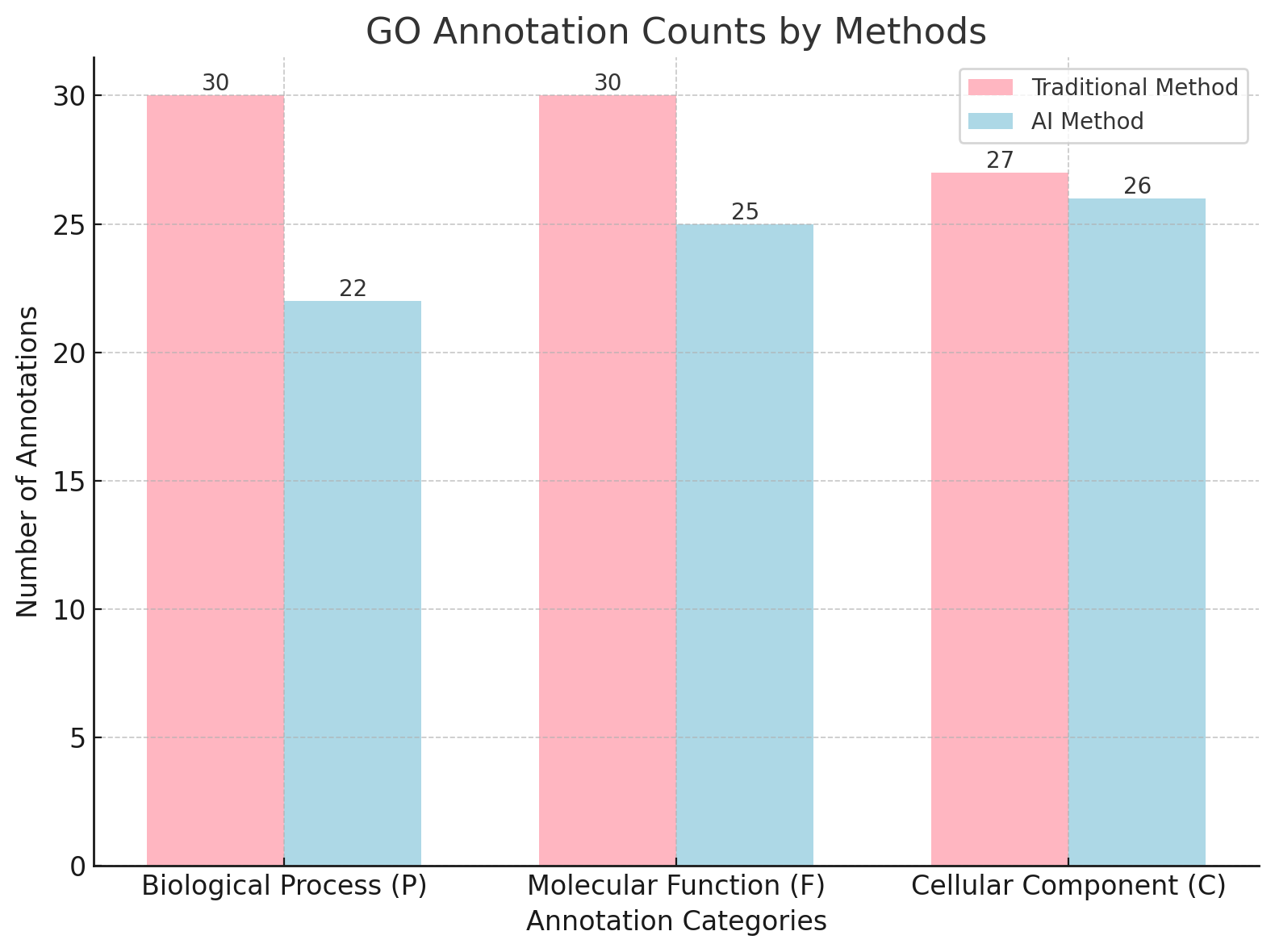
Figure 1: Traditional vs AI annotation counts for P, F, and C categories.
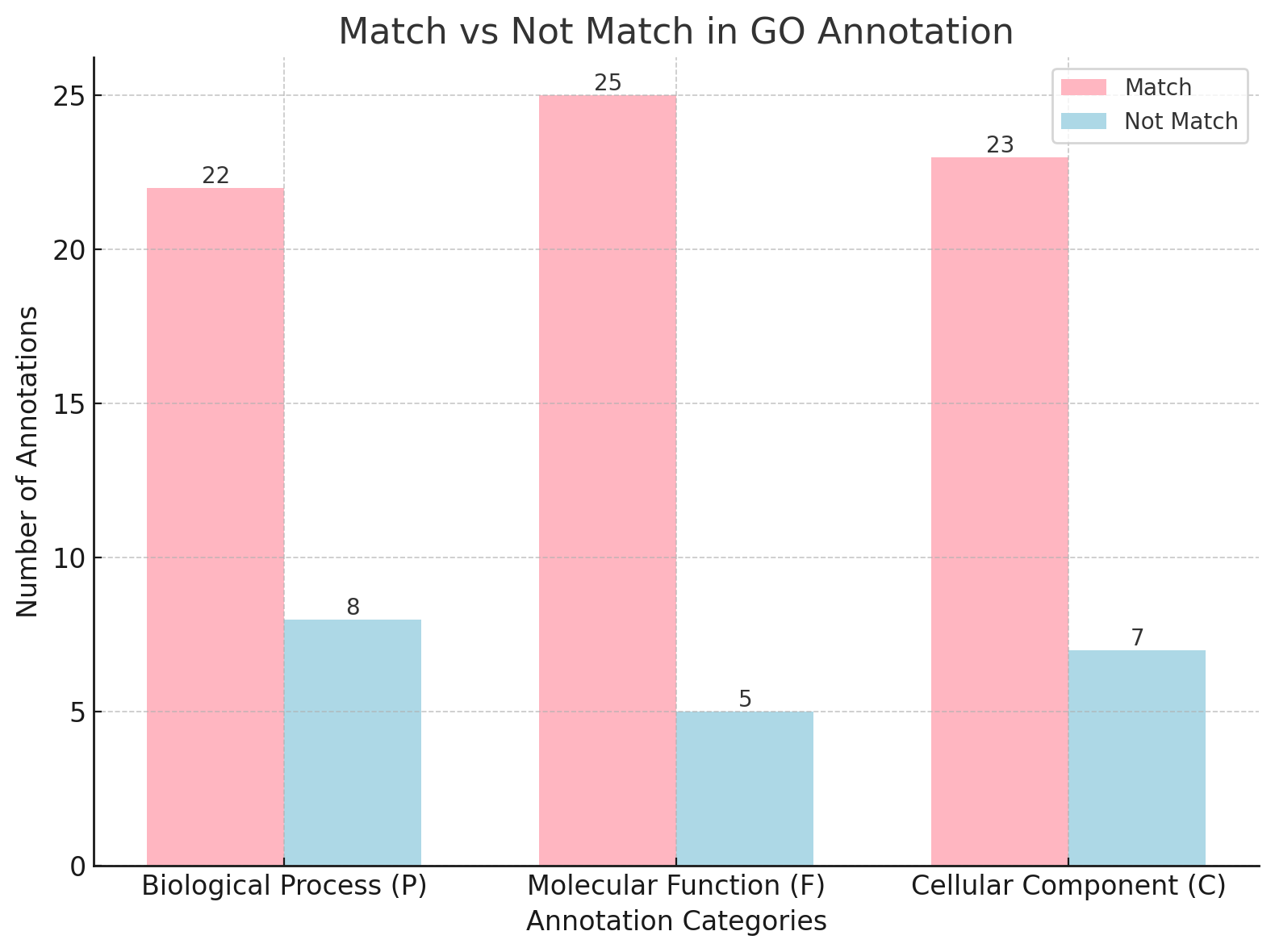
Figure 2: Matching performance in GO annotation for P, F, and C categories.
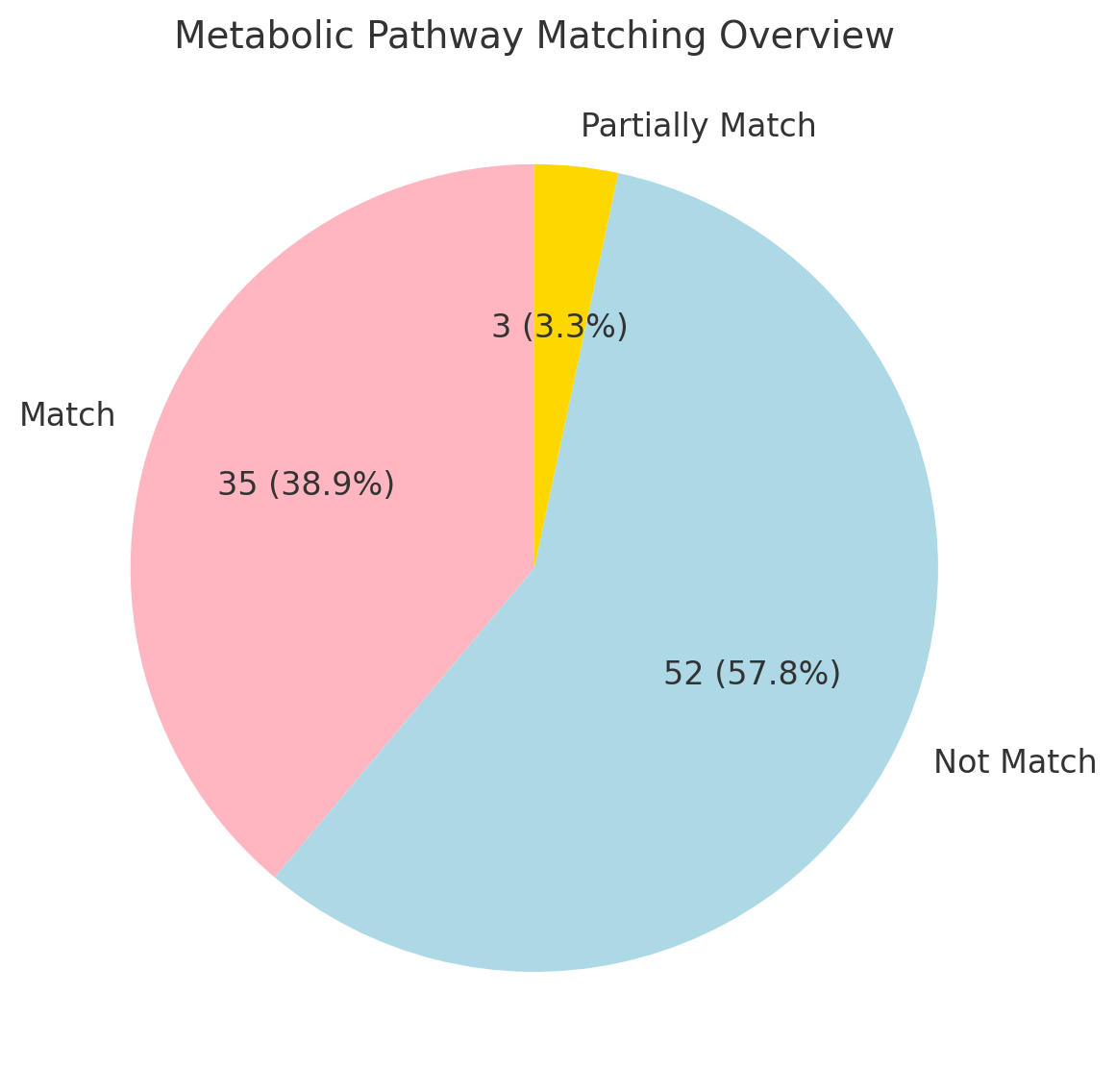
Figure 3: Proportion of metabolic pathway matching outcomes.
5. Discussion
This study systematically compared the performance of traditional tools (BLAST and UniProt) and the AI tool DeepGOPlus in annotating GO terms across Biological Process (P), Molecular Function (F), and Cellular Component (C) categories. Traditional tools demonstrated high reliability due to their standardized metrics, such as e-values, which make their outputs consistent and traceable. However, their performance is constrained by the completeness of reference databases, limiting coverage, particularly for genes with fewer annotations or newly discovered sequences. For example, traditional tools achieved 100% coverage in the P and F categories (30 annotations each) but fell slightly short in the C category with 27 annotations.
AI-based methods, such as DeepGOPlus, excelled in certain aspects, particularly in predicting novel or specific annotations. For instance, in the C category, DeepGOPlus annotated 26 genes, including more specific terms like “nuclear envelope” and “peroxisomal membrane.” However, the tool sometimes predicted overly broad terms, such as “cytoplasmic region,” which, while valid, lacked detailed biological insights. In the P and F categories, predictions from both tools were largely consistent, with relatively few mismatches, though DeepGOPlus occasionally introduced false positives, reducing confidence in its results. The differences in performance highlight the trade-offs between database-reliant traditional methods and AI tools trained on extensive datasets, with AI tools better suited for handling newer sequences.
Metabolic pathway associations underscore these differences. While traditional tools rely on curated databases to annotate C-category terms directly linked to pathways, such as the Beta-galactosidase complex (GO:0009341) in lactose metabolism, they often fail to identify indirect associations. Conversely, AI tools can infer pathway relevance by integrating C-category annotations with complementary P and F terms, although such predictions may still require experimental validation. For example, the mismatch rate in metabolic pathway associations was 58%, with AI tools showing the potential to bridge gaps in annotations but also emphasizing their limitations.
Ultimately, the integration of traditional and AI-based approaches offers the best potential for comprehensive annotation. Traditional tools provide robust, validated results, while AI tools enhance coverage by predicting missing annotations. This complementary use of both methods could maximize accuracy and depth in functional and localization analyses, advancing gene annotation efforts and improving pathway predictions.
6. Conclusion
The study summarizes how AI-based and classical approaches present themselves in all their strengths and weaknesses concerning gene ontology (GO) annotations. For instance, AI tools such as DeepGOPlus are very effective and scalable as they can predict annotations for new sequences and include multiple other datasets in the annotation process. However, there exists a drawback for them because of their black-box nature concerning training data dependency and somewhat limited cross-species generalizability. It may however be fast but lacks interpretability because its reliability comes mostly from created databases like UniProt and KEGG. Traditional tools are still essential as they are interpretable, significantly useful for small studies, and when the required annotation is of high confidence. Future advancements need to move towards making these AI tools more transparent and better generalizers, towards merging multi-omics data for contextual prediction improvements as well as combining the traditional and the AI tools to reduce false positives but increase coverage. Another important issue is to set up standardized benchmarks to evaluate annotation tools so that it can be possible to make consistent comparisons across sites, making it easier to compare. When issues of this nature are settled, it opens the door wider for the annotation of genomes to be tougher and more reliable, thereby paving the way for a great deal of advancement in personalized medicine, synthetic biology, and even evolutionary research.
References
[1]. Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215(3):403-10. Available from:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2231712/
[2]. Libbrecht MW, Noble WS. Machine learning applications in genetics and genomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16(6):321-32. Available from:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3920
[3]. Bairoch A, Apweiler R, Wu CH, Barker WC, Boeckmann B, Ferro S, et al. The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(Suppl_1):D115-9. Available from:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15608167/
[4]. The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D506-15. Available from:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30395287/
[5]. Kulmanov M, Khan MA, Hoehndorf R. DeepGO: predicting Gene Ontology terms with deep learning. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(4):660-7. Available from:https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/34/4/660/4265461?login=false
[6]. Zhou N, Jiang Y, Bergquist TR, Lee AJ, Zhi D, Lan M, et al. The CAFA challenge reports improved protein function prediction and new functional annotations for hundreds of genes through experimental screens. Genome Biol. 2019;20:244.Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13059-019-1835-8
[7]. Elnaggar A, Heinzinger M, Dallago C, Rehawi G, Yu W, Jones L, et al. ProtTrans: towards cracking the language of life's code through self-supervised deep learning and high performance computing. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1-19. Available from:https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.06225
[8]. Samek W, Wiegand T, Müller KR. Explainable artificial intelligence: interpreting, explaining and visualizing deep learning models. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2017;35(1):86-94. Available from https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-030-28954-6
[9]. Senior AW, Evans R, Jumper J, Kirkpatrick J, Sifre L, Green T, et al. AlphaFold: a solution to a 50-year-old grand challenge in biology. Nature. 2020;577(7792):706-10. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31942072/
[10]. Blattner FR, Plunkett G, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, et al. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. [accessed 2024 Dec 3];277(5331):1453-1474. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2907659/.
[11]. Bottcher S, Stephanopoulos N. 2023. Engineering multicomponent protein nanoparticles with programmable assembly and functionality. BioTechniques [accessed 2024 Dec 5];75(5):267-277. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2144/btn-2023-0023.
Cite this article
Xu,Y.;Cui,J. (2025). Artificial Intelligence in Gene Annotation: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Theoretical and Natural Science,98,8-15.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215(3):403-10. Available from:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2231712/
[2]. Libbrecht MW, Noble WS. Machine learning applications in genetics and genomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2015;16(6):321-32. Available from:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3920
[3]. Bairoch A, Apweiler R, Wu CH, Barker WC, Boeckmann B, Ferro S, et al. The Universal Protein Resource (UniProt). Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32(Suppl_1):D115-9. Available from:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15608167/
[4]. The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: a worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D506-15. Available from:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30395287/
[5]. Kulmanov M, Khan MA, Hoehndorf R. DeepGO: predicting Gene Ontology terms with deep learning. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(4):660-7. Available from:https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article/34/4/660/4265461?login=false
[6]. Zhou N, Jiang Y, Bergquist TR, Lee AJ, Zhi D, Lan M, et al. The CAFA challenge reports improved protein function prediction and new functional annotations for hundreds of genes through experimental screens. Genome Biol. 2019;20:244.Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13059-019-1835-8
[7]. Elnaggar A, Heinzinger M, Dallago C, Rehawi G, Yu W, Jones L, et al. ProtTrans: towards cracking the language of life's code through self-supervised deep learning and high performance computing. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):1-19. Available from:https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.06225
[8]. Samek W, Wiegand T, Müller KR. Explainable artificial intelligence: interpreting, explaining and visualizing deep learning models. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2017;35(1):86-94. Available from https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-030-28954-6
[9]. Senior AW, Evans R, Jumper J, Kirkpatrick J, Sifre L, Green T, et al. AlphaFold: a solution to a 50-year-old grand challenge in biology. Nature. 2020;577(7792):706-10. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31942072/
[10]. Blattner FR, Plunkett G, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, et al. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. [accessed 2024 Dec 3];277(5331):1453-1474. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2907659/.
[11]. Bottcher S, Stephanopoulos N. 2023. Engineering multicomponent protein nanoparticles with programmable assembly and functionality. BioTechniques [accessed 2024 Dec 5];75(5):267-277. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2144/btn-2023-0023.









