

Volume 141
Published on October 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2025 Symposium: AI for Healthcare: Advanced Medical Data Analytics and Smart Rehabilitation
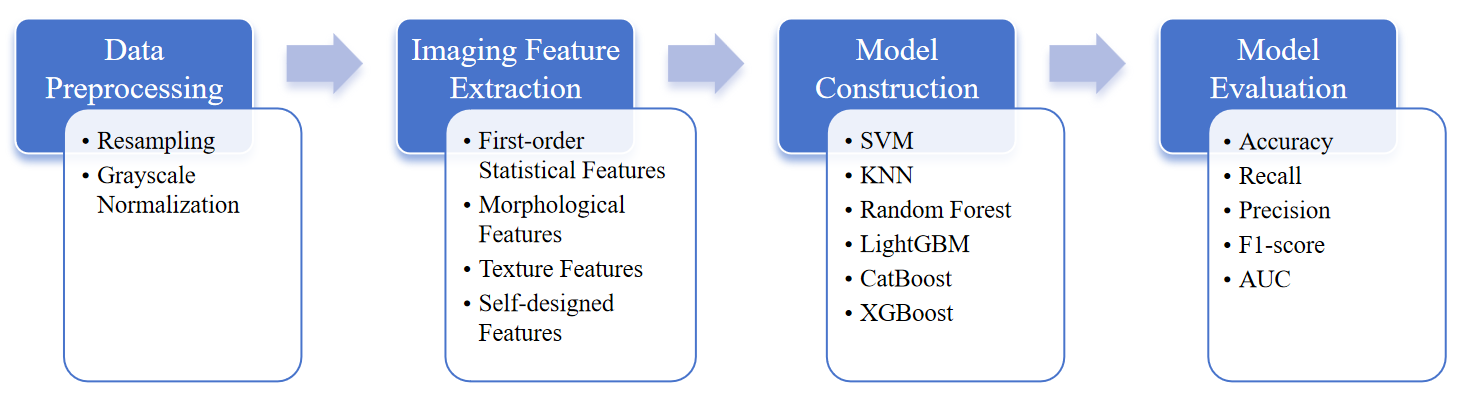
This study aims to improve the accuracy of breast cancer diagnosis by constructing a binary classification model through machine learning-based extraction of radiomic features from breast ultrasound images. A total of 780 breast ultrasound images from 600 female patients aged 25–75 years were selected and divided into "diseased" and "non-diseased" groups. Features including first-order statistics, morphological characteristics, texture parameters, and a self-created concentric grey-level fitting curve slope feature were extracted. Six classifiers, including SVM and KNN, were used to construct models, which were evaluated using ten-fold stratified cross-validation. Results showed that model performance improved across all approaches when incorporating the self-created feature. Notably, the LightGBM model exhibited enhanced discriminatory capability, with AUC increasing from 0.683 to 0.715. This indicates that machine learning-based radiomics feature extraction can effectively support breast cancer diagnosis.

 View pdf
View pdf


Central nervous system (CNS) disorders, particularly neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and Parkinson’s disease (PD), represent major challenges in contemporary medical research. The blood–brain barrier (BBB), an essential protective interface of the CNS, helps maintain brain homeostasis but also restricts the entry of most drugs and therapeutic molecules into the brain, severely limiting clinical efficacy. As nanoscale extracellular vesicles, exosomes possess an intrinsic capacity to traverse biological barriers—including the BBB—and can transport a wide range of bioactive cargos to modulate various physiological and pathological processes. Research indicates that exosomes play pivotal roles in the pathological progression of neurodegenerative diseases: they can mediate the spread of pathogenic proteins while also contributing protective effects such as the clearance of pathological aggregates and the attenuation of neuroinflammation. Moreover, engineering strategies (e.g., drug loading and targeted surface modification) expand the potential of exosomes as drug-delivery vehicles. Despite promising diagnostic and therapeutic prospects, challenges including exosomal heterogeneity, limited loading efficiency, imperfect targeting specificity, and stability in clinical settings remain significant bottlenecks. With further advances in exosome engineering, standardized characterization, and scalable production, exosomes hold promise as important tools for the early diagnosis and precision treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.

 View pdf
View pdf


Valvular heart disease (VHD), a category of diseases severely affecting circulatory system function caused by structural or functional abnormalities in heart valves, significantly reduces patients 'quality of life and life expectancy. Although pharmacological interventions and surgical procedures can alleviate clinical symptoms to some extent, achieving valve tissue regeneration and functional reconstruction remains challenging. In recent years, exosomes have gained widespread attention as an emerging therapeutic strategy. These nanoscale vesicles secreted by cells are rich in various bioactive components and play crucial roles in intercellular communication, inflammation regulation, tissue repair, and pathological process modulation. Studies indicate that during the development of cardiac valvular lesions, exosomes demonstrate significant therapeutic potential by regulating inflammatory responses, promoting tissue regeneration, and improving valve function. However, the specific mechanisms of exosomes in valvular disease treatment remain complex, with clinical translation facing multiple challenges including improvements in isolation and purification techniques, enhancement of in vivo stability, and systematic elucidation of action mechanisms. This systematic review examines the pathogenesis of valvular heart disease, discusses exosomes' biological characteristics and their potential as biomarkers and targeted therapies, while exploring current research progress and key scientific issues to provide theoretical foundations for further exploration and clinical application in this field.

 View pdf
View pdf


The incidence of depression has been on a continuous rise, which emerges as a major mental illness of concern in the global public health domain. As a primary intervention for moderate to severe depression, pharmacological treatment holds significant importance. Currently, commonly used clinical antidepressants include SSRIs, SNRIs and NaSSAs. However, notable differences exist among these drugs in terms of efficacy, safety, onset time, and patient compliance. How to scientifically select and optimize treatment regimens has thus become a key challenge in clinical practice. In recent years, evidence-based medical approaches like meta-analyses have been widely applied. Network meta-analysis enables indirect comparisons of different antidepressants by integrating data from multiple randomized controlled trials, which provides more comprehensive evidence for clinical medication choices. This article provides a review of depression’s pathological mechanisms, which include neural plasticity impairment, neurotrophic factor deficiency, the monoamine hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis axis dysfunction, and the monoamine neurotransmitter hypothesis. It also examines the efficacy, safety, and related research progress of three main classes of antidepressants such as SSRIs, SNRIs, and NaSSAs, to provide references for clinical medication selection.

 View pdf
View pdf


Forests in northeast China are critical for climate regulation and biodiversity conservation. Over the past few decades, climate change has become a strong stressor for these forests, resulting in changes in temperature, precipitation regimes, and ecological processes. Recent studies have begun to explore how these environmental changes affect forest structure and carbon processes. This paper explores the impacts of climate change on forest ecosystems in northeast China, especially biodiversity and carbon sinks. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and frequent extreme weather events have altered forest structure, species diversity, and ecosystem processes in the region. These climate changes are weakening forest stability and health, and reducing forests' ability to serve as carbon sinks. This study also explores how feedback mechanisms and regional heterogeneity enhance these impacts. Recommendations are proposed to strengthen adaptation measures, increase carbon sinks, and improve governance. This discussion not only provides policy-relevant information for regional forest management in China, but also contributes to a comprehensive understanding of climate-related issues facing temperate and boreal forests worldwide.

 View pdf
View pdf


This review focuses on the recent development of digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) in pathogen detection and cancer early screening. dPCR partitions samples into multiple independent units,enabling absolute quantification of target molecules. It surpasses traditional qPCR in sensitivity and accuracy. Nevertheless, it has limitations, such as the inability to distinguish between live and dead bacteria and relatively high costs. In virus detection, dPCR notably enhances the early diagnosis rate of COVID -19 and shortens the HIV detection window period. In cancer early screening, it demonstrates high sensitivity in detecting early-stage thyroid cancers. Despite existing drawbacks, with technological advancements, dPCR is expected to become a core molecular diagnostic tool, contributing significantly to public health and cancer prevention and control. Although there was still scope for improvement regarding cost and automation, digital PCR would develop more efficiently and cost-effectively through technological changes. it was anticipated that digital PCR would become a central tool for molecular diagnosis and play a bigger part in public health and in the prevention and treatment of cancer.

 View pdf
View pdf


Exercise-induced fatigue and sports injuries represent interconnected challenges for athletes: fatigue disrupts energy metabolism, redox balance, immune function, and endocrine homeostasis, elevating the risk of overuse injuries and delaying return to sport. Addressing this multisystem issue is crucial for safe and timely athlete rehabilitation. This paper explores traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) interventions for exercise-induced fatigue and sports-related injuries, focusing on five key approaches: herbal remedies, bioactive polysaccharides, Tuina, acupuncture, and integrated TCM-Western rehabilitation. Herbal interventions enhance glycogen storage, stabilize blood glucose, and reduce lactate, urea, and triglyceride levels; they also regulate redox balance (e.g., Danshen improves antioxidant enzyme activity), suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines to modulate immune function, and optimize the testosterone-cortisol balance for endocrine homeostasis. Bioactive polysaccharides like those from Cassia seed lower lactate levels, extending exercise endurance. Combinations of Astragalus, Codonopsis and jujube alter amino acid metabolism and gut microbiota composition. When paired with functional training, Tuina and acupuncture reduce pain, accelerate recovery, and enhance intervention efficacy. Integrated TCM-Western programs further boost functional improvements and athletes’ readiness to return to play. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that TCM serves as an effective complementary approach, alleviating fatigue, facilitating injury recovery, supporting personalized care, and aligning with modern sports rehabilitation practices.

 View pdf
View pdf


Alzheimer's disease (AD), the leading cause of dementia, poses a significant challenge in early detection. Research indicates that sleep disturbances may precede noticeable cognitive decline. Normal ageing makes sleep lighter and shorter, but the changes are much more substantial in AD. Patients usually have less slow-wave sleep (SWS), reduced rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, more awakenings at night, and a longer time to fall asleep. Electroencephalography (EEG) reveals slower rhythms, fewer spindles, and abnormal spindle-slow wave coupling. Some suggest impaired sleep accelerates AD by hindering amyloid clearance. Recent work shows that sleep measures, especially EEG features, might help predict who will decline and can be added to models with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) markers. There are also studies using machine learning with polysomnography (PSG) and EEG, which look promising. But there are problems too, since sleep varies a lot between people, and not every sleep problem means AD. Ethical considerations arise, such as the appropriateness of informing individuals of potential health risks based solely on sleep data. This paper will go over what is known about sleep in early AD, the brain mechanisms behind it, and how sleep might be used to predict disease.

 View pdf
View pdf


As a classic nanocarrier delivery system, liposomes significantly enhance drug stability and bioavailability. By prolonging in vivo circulation time and improving tumor-targeting capability, they exhibit unique advantages and considerable value in cancer treatment. This review outlines the basic composition and common preparation methods of liposomes, and systematically introduces their classifications and respective characteristics. It highlights recent advances in liposome applications for treating breast cancer, lung cancer, and glioma, discusses key challenges in clinical translation, and offers perspectives on improving therapeutic efficacy and safety through optimized preparation processes, novel materials, and innovative drug delivery strategies.

 View pdf
View pdf


Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) ranks among the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Recent epidemiological data demonstrate a rising incidence of HCC, which is further compounded by its insidious onset, poor prognosis, and limited therapeutic options. Elucidating its molecular pathogenesis and identifying viable therapeutic targets remain critical unmet needs. While prior studies have implicated members of the AP-1 (Activator Protein-1) transcription factor family (e.g., c-Fos and c-Jun) in hepatocarcinogenesis, the roles of Fos-related antigens (Fra-1 and Fra-2) remain poorly characterized. This study investigates the mechanistic interplay between c-Jun/Fra-2 heterodimers and the oncogenic driver c-Myc—a well-established molecular nexus in HCC pathogenesis—unraveling their collective impact on HCC proliferation, inflammatory cascades, and tumorigenesis. Through a systematic literature review, this study delineates the pro-tumorigenic role of the c-Jun/Fra-2-Myc axis in murine HCC models. This paper elucidates how c-Jun-Fra-2 heterodimers transcriptionally regulate c-Myc to orchestrate core oncogenic programs. Integrative analysis of the HCC tumor microenvironment (TME) further reveals that c-Jun-Fra-2 overexpression induces TME remodeling, characterized by low-grade inflammation, mild fibrosis, and dyslipidemia—key permissive factors for HCC progression. The findings underscore the pivotal role of c-Jun-Fra-2 heterodimers in HCC pathogenesis, wherein their upregulation of c-Myc drives tumor initiation and progression. Notably, the c-Jun-Fra-2/c-Myc axis exhibits both reversibility and dependency, suggesting a therapeutic vulnerability. In HCC patients with elevated c-Jun-Fra-2 expression, pharmacological inhibition using the BET inhibitor JQ-1 significantly attenuates tumor growth, highlighting its potential as a precision therapy target. This work advances the molecular understanding of HCC and provides a rationale for targeted intervention in defined subsets.

 View pdf
View pdf




