

Volume 54
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2024 Workshop: Workshop on Intelligent Medical Data Analysis for Precision Medicine
Pain, as one of the major clinical and social problems, still lacks effective objective evaluation indicators. At present, nearly one in five adults suffer from different types and different parts of pain. An important feature of clinical pain is persistent pain, in addition to sensory discrimination processes, it involves a range of brain regions involved in top-down cognitive and emotional processing. However, clinical pain is often affected by multiple factors and is difficult to assess objectively. Recently, blood, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, and biopsy tissue have been identified using novel, sensitive, and specific protein analysis methods in an attempt to detect changes in biological markers associated with different pain types. This paper will summarize the biological markers related to different parts of pain in the latest relevant studies at home and abroad and focus on the application prospect of such biological markers in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis evaluation of the pain.

 View pdf
View pdf


The elbow joint is one of the most complex joints in the human body, playing a crucial role in coordinating movements between the shoulder, forearm, and wrist, with functions including flexion, extension, and rotation. Elbow dislocation is a common yet serious injury, causing significant discomfort and increasing economic burden for patients in their normal work and daily life. With a deepening understanding of the condition, an increasing number of scholars recognize the importance of comprehensive management focused on prevention. This paper, integrating concepts and principles of tertiary prevention from preventive medicine, provides an overview of common causes, diagnostic methods, and preventive measures for this condition. Early diagnosis and intervention are emphasized to offer healthcare workers a theoretical basis for action. Through multi-dimensional, multi-system preventive measures, the occurrence rate of elbow dislocation can be reduced, improving clinical treatment outcomes and enhancing disease prognosis, so that to improve patients' quality of life.

 View pdf
View pdf


Pregnancy is one of the important life events in a woman's life, which in the face of pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding process, maternal psychology and physiology will have obvious changes, among which postpartum depression is more common. Postpartum depression (PPD) is a mental syndrome with obvious depressive symptoms or typical depressive episodes during the puerperal period. Its etiology is complex, with sleepiness, gloomy expression, crying and other symptoms in clinic, and even some patients will have suicidal tendencies, which seriously endangers maternal physical and mental health. In recent years, the adverse events caused by postpartum depression have attracted more and more social attention, and postpartum women's mental health has become a hot spot in clinical research. Clinical workers should improve the awareness of postpartum depression, and strengthen the maternal mental health screening, so as to detect psychological abnormalities as early as possible and give timely intervention measures. In view of the high incidence of postpartum depression, it is very important to establish a sound mental health service system for pregnant women. This paper will analyze the high risk factors of PPD summarized the targeted primary prevention and secondary prevention, and proposed prevention strategies before and after the onset of postpartum depression, respectively, to provide theoretical basis for effectively preventing the occurrence of postpartum depression or delaying the progression of postpartum depression.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the deepening of the aging of society, the management of serious diseases is becoming more and more important. Therefore, the need for hospice and palliative care is growing rapidly these years. As a kind of well-rounded way of caring, hospice and palliative care can not only relieve patients’ pain physically, but also support them psychologically and make them fit in society. Effective care can enhance the quality level of patients’ daily lives to ensure their dignity and respect their wishes at the last stage of their lives. Many countries are taking measures to develop hospice and palliative care to improve people’s life quality. Different strategies have been used to reduce patients’ pain and improve their life quality. However, dilemmas still exist at the level of patients, providers, and policy. This article comprehensively analyzes the current situation and dilemma of hospice and palliative care in the aging context and provides potential solutions.

 View pdf
View pdf


Context Fencing is an ancient sport that originated in medieval European wars and gradually developed into a regulated competitive sport. It is a combination of elegant movements and flexible tactics, requiring athletes to be highly focused mentally and well-coordinated physically. Such high demands on movements and reactions reflect the excellent skills and agility of fencers. In order to achieve excellent competition results, many aspects are often involved in the training, including the comprehensive training of technical, physical, tactical and psychological quality. Such high-demand training and high-intensity competition make the probability of sports injury in the process of sports greatly increased. These injuries not only affect the athletes' immediate performance, but also may have a negative impact on their long-term career and shorten the athletes' sports life and may also bring huge psychological pressure and anxiety to the athletes. How to effectively avoid athletes' sports injury and improve the quality of training have become the key reasons for fencers to achieve good results. By understanding the causes and influencing factors of knee joint injury of fencers, it can provide theoretical basis for injury protection of fencers. At the same time, individual prevention or intervention strategies are adopted.

 View pdf
View pdf


Aquatic exercise is an active exercise that make full use of the physical and hydrodynamic characteristics of water in a water environment to achieve a similar strength increase effect as land training, while avoiding the aggravation of joint stress and muscle microdamage caused by repetitive training. It has been widely studied in the field of sports rehabilitation and public fitness, while its form is basically presented in the form of aerobic exercise or interval training, the aquatic resistance exercises are often ignored by people. Due to the influence of the physical characteristics of water, the main form of muscle contraction of athletes performing resistance training in water is similar to isokinetic contraction, and the force used by practitioners is proportional to the resistance of water, which increases the centrifugal load of muscles and greatly reduces the risk of sports injury. In addition to the athletes, aquatic resistance exercises also have certain benefits for other clinical diseases. In this paper, the application of this training in swimming performance, rheumatoid arthritis, postmenopausal osteoporosis and knee osteoarthritis was reviewed in order to improve the clinical understanding and promote its rational application.

 View pdf
View pdf


Faced with the large number of patients with ischemic heart disease and high mortality rates, traditional drug treatments come with the risks of drug resistance and rebound effects after discontinuation, as well as the shortcomings of surgical treatments such as poor blood circulation and the inability to restore necrotic myocardium. This article starts from the perspective of stem cell regenerative medicine, focusing on the stem cell therapy for ischemic heart disease, and provides a comprehensive review of the types of stem cells and transplantation methods. It also includes further summaries and prospects, believing that more comprehensive and improved treatment methods will emerge in the future to benefit patients.

 View pdf
View pdf


Cancer is one of the most lethal chronic diseases in the world. In the United States alone, over 1.7 million diagnosed new cases of cancer cases was reported in 2022 and over half a million people died due to complication regarding cancer in that same year. The mutation that gives rise to cancer cells occurs in normal cells and causes them to proliferate uncontrollably, obstructing essential organs and making the body more vulnerable to deadly infectious infections. In modern society, the combination of a sedentary lifestyle and exposure to unsafe molecules around the public has drastically increased the mass’s probability of mutation within their genetics and for cancer cells to proliferate. Cryogenesis therapy is the usage of cryogenic substances such as liquid nitrogen or argon gas to freeze and destroy the cancer cell. Cryogenesis generally involves the repetition of two steps: the freezing process and the thawing process. The freezing process is performed under extremely low temperatures and allows for the formation of ice crystals both on the inside and outside of the cell membrane, which in terms causes the rupture of the cell membrane. The thawing process is performed after the freezing process and allows the target cell to thaw; the thawing process is performed to induce osmotic shock and further induce the damage caused by the freezing process. The two cryogenesis cycles are repeated to reinforce the damage caused to the cancer cells. Compared with traditional therapies, cryogenesis therapy, as a non-invasive treatment, has The advantages of using cryogenesis are the therapy’s non-invasive treatment methods, pinpoint precision and accuracy, reduced side effects after the therapy, and repeatability. Although the cryogenesis process is still new in under development, it has the potential to be effective against the most lethal cancer types, such as lung cancer and brain cancer. This review explores a new treatment for cancer, in cryogenesis, that have minimal side-effect and discusses its mechanism and application to different type of cancer and combination effect.

 View pdf
View pdf


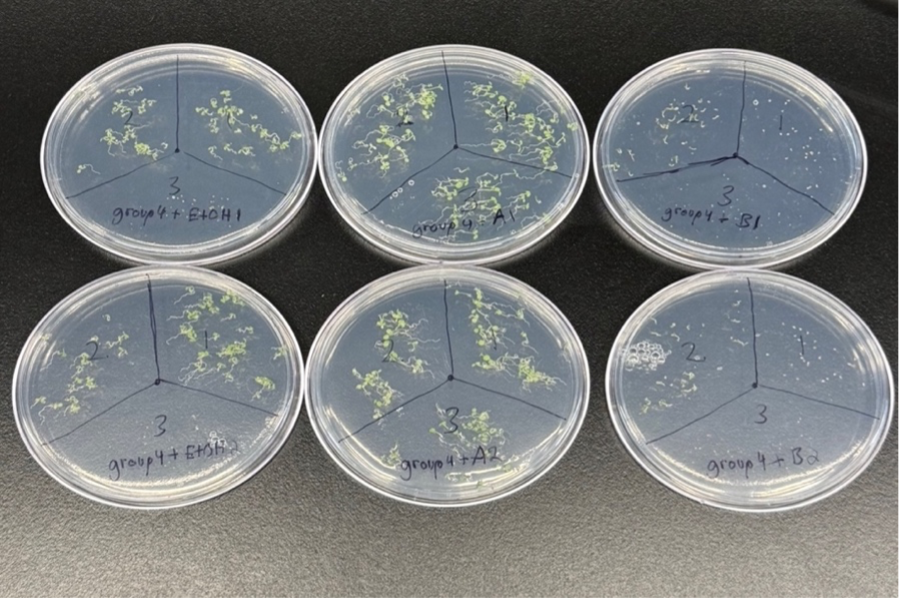
It is well known that plant growth depends on the interaction of auxin and hormones, but whether different hormones have different effects on seed growth in different varieties is not fully understood. This study used a controlled experimental setup in which seeds from three different genotypes (assumed to be wild-type, abscisic acid (ABA) insensitive, and gibberellic acid (GA) deficient) were exposed to treatments of these compounds (labeled compounds A and B), as well as a control treatment using ethanol. Our results confirm the identities of Compound A as gibberellic acid and Compound B as abscisic acid through their consistent effects on seed germination. Gibberellic acid (Compound A) significantly enhanced germination across all genotypes. With the help of Gibberellic acid, GA-deficient genotype also showed a dramatic increase in germination rates which suggested a compensatory effect. Conversely, abscisic acid (Compound B) markedly inhibited germination, with the most pronounced effect observed in the wild-type genotype. The ABA-insensitive genotype demonstrated reduced susceptibility to Compound B, supporting its phenotypic characterization. The study highlights the key antagonistic role of gibberellic acid and abscisic acid in seed germination, providing valuable insights into defining genotypic-phenotypic interactions in plant responses to environmental and chemical signals.

 View pdf
View pdf


Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a prevalent neurodegenerative disorder. It triggers metabolic disorders within the body due to genetic mutations, thus leading to irreversible damage to one's memory and brain. The primary pathogenic features of AD are intracellular neurofibrillary tangles caused by hyperphosphorylated Tau and extracellular amyloid plaques created by the buildup of β-amyloid β-protein (Aβ). However, up to now, there has been no effective treatment program for Alzheimer's disease. And after a long time of development, many gene editing technologies have been perfected and utilized in practice. Among them, CRISPR-Cas9 technology is the most efficient and practical. As a result, an increasing number of scientists have examined and debated the potential use of CRISPR-Cas9 technology in the management of Alzheimer's disease. This review addresses the use of the CRISPR/Cas9 system to treat Alzheimer's disease and presents the disease's pathophysiology, including the establishment of AD models, genetic screening for the cause of AD, and targeted therapy for AD.

 View pdf
View pdf




