

Volume 63
Published on December 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science
This research investigates the relationship between the consumption of ultra-processed foods (UPFs) and obesity by analyzing seven studies, including both cross-sectional and longitudinal designs. The NOVA classification framework is employed to distinguish foods based on their degree of processing, with particular attention given to the adverse health outcomes associated with UPFs, which are characterized by high sugar, fat, and salt content, and low nutritional value. This review also explores potential mechanisms by which UPFs contribute to obesity, including their nutrient composition, impact on satiety, and behavioral factors related to their consumption. The findings indicate that measures should be taken to reduce UPF consumption and encourage healthier dietary habits to combat the global obesity epidemic.

 View pdf
View pdf


Stem cell-based therapies are emerging as promising adjuncts to conventional cancer treatments, offering innovative strategies to target cancer cells and enhance patient recovery. This paper explores the potential of stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUCMCs), to improve cancer treatment outcomes through their regenerative and differentiation capabilities. MSCs exhibit significant promise due to their ability to inhibit tumor growth, support tissue regeneration, and modulate immune responses. Their unique features, including targeted homing to tumor sites and the secretion of bioactive molecules, present novel approaches to overcoming the limitations of traditional therapies. Despite these advancements, challenges such as immune rejection and tumorigenicity must be addressed. Current strategies to mitigate these issues involve immunosuppressive drugs, genetic engineering, and advanced technologies like CRISPR-Cas9. However, the reviewed studies often involve small sample sizes or remain in the laboratory phase, limiting the generalizability of findings. Future research should focus on larger-scale clinical trials to validate the effectiveness and safety of stem cell therapies, aiming to refine these treatments and integrate them into clinical practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


Depression seriously affects the overall well-being of patients, and it causes great suffering and pain. Around 5 to 10 percent of the population globally experience depression. Within this population, the prevalence of depression in women is approximately 1.5 to 2 times higher than men and about 50% of older adults above 65 years old suffer from depression than young adults. A creative form of psychotherapy — art therapy, specifically drawing and painting therapy, allows depressive patients to gain insights about their feelings, promoting healing in a harmless way. This article reviewed the benefits of art therapy in treating depressive patients based on past research. The review divides the patients into different age groups and sexes: elderly, children, adults, male, and female. It indicates that art therapy can be performed successfully across different age groups and sexes, bringing varieties of personalized benefits, especially for children, women, and elders. Some common benefits include increased self-esteem, change of perspective, and growth in mentalities.

 View pdf
View pdf


The maintenance of normal epigenetic growth and development is crucial for various biological processes, with DNA methylation playing a significant role. The UHRF1-DNMT1 complex regulates DNA methylation, particularly in mammalian cells. This review paper explores the relationship between UHRF1, DNMT1, and DNA methylation homeostasis in cancer cells. Studies have primarily focused on human colorectal cell lines HCT116 and DLD1, shedding light on the protein stabilization of UHRF1 and DNMT1 through methylation-mediated ubiquitination. The impact of UHRF1 on DNA methylation in cancer cells is evaluated by controlling growth hormones. Furthermore, the study reveals that UHRF1 down-regulation influences DNMT1-mediated methylation on DNA and highlights the non-canonical functions of UHRF1 that significantly contribute to DNA methylation homeostasis. This review paper delves into the intricate relationship between the UHRF1-DNMT1 complex and DNA methylation homeostasis, particularly in the context of cancer cells. By examining the protein stabilization mechanisms of UHRF1 and DNMT1, as well as the regulatory role of UHRF1 in DNA methylation, this study provides valuable insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying epigenetic regulation. The findings presented in this review contribute to a better understanding of the role of UHRF1 and DNMT1 in maintaining DNA methylation patterns and highlight their potential implications in cancer biology.

 View pdf
View pdf


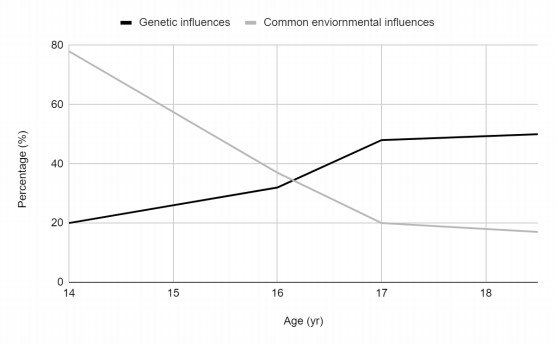
This review systematically summarized and discussed the impacts of genetics and geoscience on human behaviors, especially young people, and how human behaviors change the geographic environment. In the review, some basic methodologies of genetic epidemiology have been revisited. It also compared environmental influences with adaptive genetic influences across various adolescent behaviors as examples. Pathways for the occurrence of genetic risks arepresented in this review as well where issues not just in deviant behaviors but also in the health issues mentally and physically. While geographic environment has impacts on the behaviors of young people, human activities are one of the reasons for those changes as well. Summaries and insights exhibited in this review can not only shed light on future research of the impact of various human activity on the geographic environment, but also implies benevolent activities human can take for the environment that consequentially benefit the growth of our adolescents at both cognitive and body level.

 View pdf
View pdf


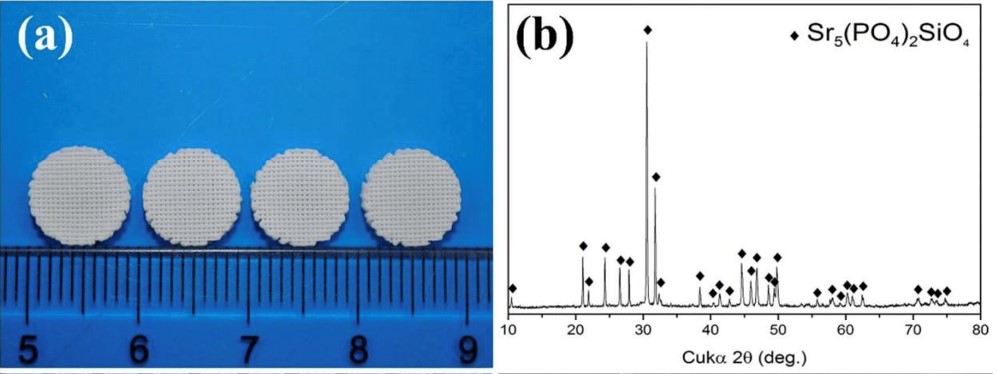
Bone repair has been a challenging issue for a long time. Some recent studies focused on the incorporation of metallic elements into scafffolds for improving the performance for bone regeneration. This review explores the use of metallic elements in bone repair scaffolds, focusing on strontium (Sr), silicon (Si), magnesium (Mg) and Titanium (Ti). These elements enhance scaffold properties, promoting bone regeneration. Sr5(PO4)2SiO4 (SPS) bioceramic scaffolds, fabricated through 3D plotting and sol-gel methods, exhibit superior mechanical strength and induce osteogenesis and angiogenesis in vitro. Sr and Si ions within the SPS scaffolds upregulate genes related to cell proliferation, osteogenesis, and angiogenesis. Porous magnesium (Mg) scaffolds, with their biodegradability and ability to stimulate bone formation, offer an alternative to traditional metal implants. Mg scaffolds demonstrate good biocompatibility, physical properties, and osteoinductive potential. Porous titanium (Ti) scaffolds, manufactured through powder metallurgy, address the issue of stress shielding associated with conventional Ti implants. The interconnected pore network and controlled porosity of these scaffolds mimic natural bone, leading to improved biocompatibility and cell interaction.

 View pdf
View pdf


Cardiac disease persists as one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide and therefore there is a critical need for the establishment of innovative treatment approaches. This review updates the innovations in 3D bioprinting technology and its applications in cardiac tissue engineering, a fast-developing field that aims to overcome the limitations of the current treatments of cardiac diseases. The 3D bioprinting technique enables the layer-by-layer construction of complex tissue structures emulating natural cardiac tissue in architecture and function using bio-inks composed of living cells, biocompatible materials, and growth factors. The paper reviews inkjet-based, extrusion, and laser-assisted bioprinting techniques, all having different advantages and challenges. It further identifies the need for proper biomaterials, namely natural and synthetic polymers, to facilitate cellular growth and differentiation, as well as the 4 main cell types utilized in the bioink. The 3D bioprinting applications will be reviewed in the fabrication of heart patches and prosthetic heart valves and their potential to improve cardiac repair and regeneration will be described. Although these developments are quite promising, challenges relating to scalability, cell viability, and regulatory considerations remain. The conclusion drawn is that further research in the refinement of bioprinting methodologies and integration with advanced technologies is required so that cardiac care can be revolutionized with personalized and effective therapeutic solutions.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the increasing trend of late childbearing and low childbearing, the incidence of breast cancer is increasing rapidly worldwide. At present, breast cancer has become one of the more frequent malignant tumor diseases in women and has aroused widespread concern in society. The cause of the disease is not completely clear, with the deepening of research, the relevant detection methods are constantly updated, as far as possible early diagnosis. At present, the main methods of breast cancer prevention are lifestyle adjustment, including reducing alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight and chemical prevention, but the methods are limited, so the research on breast cancer prevention is particularly important. At the same time, medical workers should educate the majority of women about disease prevention, so that women can establish a correct concept of prevention and treatment, so as in order to lower the prevalence of breast cancer and improve the women health.

 View pdf
View pdf


Neurorehabilitation is a very important area that aims at bettering lives of patients who have neurological disorders and have severely damaged motor functions and impaired communications abilities. Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) technology has emerged as one of the highly promising tools in the application of neurorehabilitation, having innovations in motor recovery, speech restoration, and independence for patients. This review presents the applications and efficiency of brain-computer interface technology in neurorehabilitation procedures related to high-incidence neurological disorders like stroke, traumatic brain injury, and spinal cord injury, and complex neurological disorders like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, and cerebral palsy. Among these, some BCI approaches, mostly based on electroencephalographic recordings, have shown promising potential for motor recovery, communication, and improvement of independence in patients. It discusses key modalities like motor imagery-based training, neurofeedback, and robotic assistance, together with the landmark studies proving their efficacy. Moreover, it pays attention to basic and clinical research and points out the challenges and future directions for the alleviation of limitations in BCI technology. Despite the fact that BCI technology still has some basic problems at this point in terms of signal acquisition, processing, and individual training, there is huge potential for application in developing neurorehabilitation and improving the quality of life of those patients who have undergone serious neurological injury.

 View pdf
View pdf


The hippocampus is one of the most well-studied areas in the brain. After the studies on Henry Molaison (H.M.) and rodent model confirming its role in memory formation and consolidation, its anatomical, physiological, and psychological characteristics in memory processing have been studied for a long time. The framework of its role in memory processing is continuously building up from the synapse level to the system level. Current studies are working on enriching the detail of the blueprint and confirming whether the framework can explain results recording from new techniques. This review will introduce the physiological, theoretical mechanism of memory formation and consolidation in the hippocampus with results from current studies. In addition, it will also discuss the current process of framework, suggest some limitations that these studies face, and give a comprehensive view of the role of hippocampus’ functions in memory processing after the study of H.M. Future studies should incorporate longitudinal designs to understand the developmental trajectory of hippocampus and its role in cognitive development.

 View pdf
View pdf




