

Volume 112
Published on May 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICEGEE 2025 Symposium: Sensor Technology and Multimodal Data Analysis
Circadian rhythm disorder is one of the main symptoms of bipolar disorder. The circadian rhythm disorder in bipolar disorders is caused by the combined effects of genes, neurotransmitters, hormones, etc. It can manifest as a gene expression disorder, a sleep-wake cycle disorder, and other metabolic disorders of the body. Its influencing factors include season, light intensity, working mechanism, and social pressure. Treatment of bipolar disorder often begins with addressing circadian rhythm disorders, thus giving rise to various therapies, ranging from drugs to psychological and behavioral therapies. This article mainly summarizes the information regarding the introduction of circadian rhythm, the interplay between bidirectional regulation and circadian rhythm, and the association between circadian rhythm disorders and their respective treatment strategies. Moreover, this review aims to generate insights for future research on novel therapeutic approaches and drug development for the bipolar disorder treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


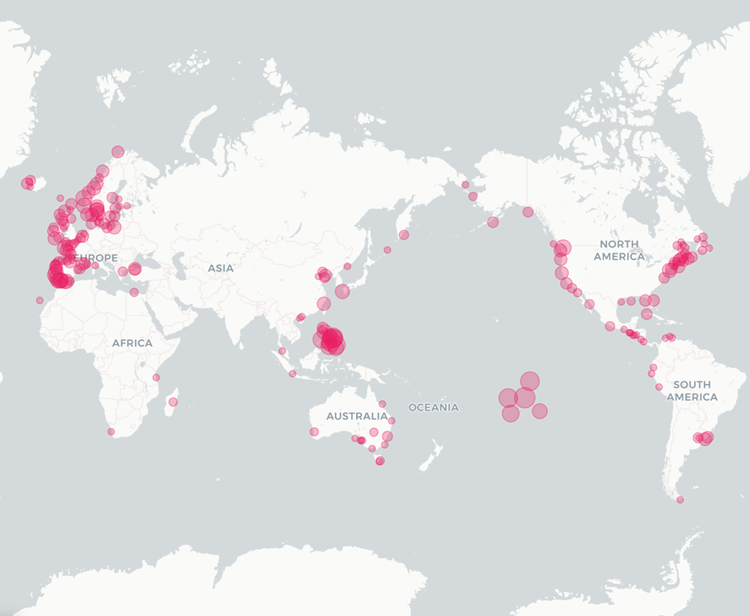
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) are increasingly recognized as a critical global environmental challenge, particularly in the context of climate change. This paper synthesizes the current understanding of HABs’ global distribution, key environmental drivers, ecological and economic impacts, and advancements in monitoring technologies. Recent data indicate significant regional clustering of HAB events, especially in coastal regions of Europe, Asia, and North America. The study highlights how climate change exacerbates HABs through rising ocean temperatures, increased precipitation leading to nutrient runoff, and ocean acidification caused by elevated CO₂ levels, which enhance the growth and toxicity of harmful algal species. The consequences of HABs are severe and multifaceted, including mass marine organism mortality, bioaccumulation of toxins, threats to public health via contaminated seafood, and substantial economic losses in fisheries and tourism. The paper also explores evolving monitoring methods, such as molecular diagnostics, AI-assisted remote sensing, and IoT-integrated water quality sensors. It highlights the importance of international cooperation, standardized data collection, and proactive policy development to mitigate future impacts. Overall, the study provides a comprehensive perspective on HABs in the background of growing climate change and calls for approaches to effectively manage their ecological and societal risks.

 View pdf
View pdf


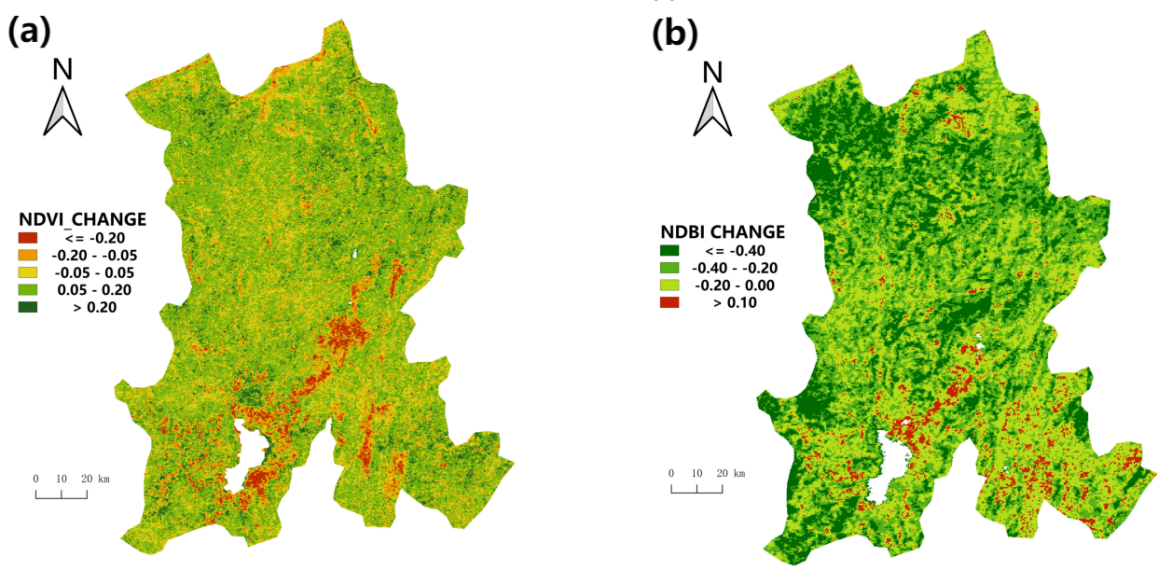
Reduced vegetation cover due to accelerated urbanization can lead to many ecological problems, and whether ecological conservation measures can effectively mitigate this effect remains to be assessed. This paper explores the influence of urbanization on vegetation cover and the performance of related ecological protection measures in Kunming. This paper reveals the significant negative correlation between NDVI and NDBI data during the period of 2000-2022 through linear regression analysis and Pearson correlation analysis, and combines spatial analyses to demonstrate the changes of vegetation cover in Kunming during the urbanization process. The study results indicated that the NDVI in Kunming City as a whole had a slow increasing trend, with 0.0020 per year, and NDBI had a slow decreasing trend with 0.0014 per year. And they are significantly negatively correlated with a Pearson correlation coefficient of -0.6168. In addition, the vegetation cover in non-urban areas and the area around Dianchi Lake has increased considerably, indicating that the ecological protection measures in the region are effective, but the vegetation cover in urban areas has still declined. The study provides an important scientific basis for ecological protection policies and sustainable urban planning in similar cities, and promotes urban ecological protection and green development.

 View pdf
View pdf


The accelerating process of urbanization has had an impact on the living environment of birds and other wildlife; hence, many wild animals and plants have been forced to become urban settler. Birds, as an important indicator of the ecosystem, and analyzing the impacts and changes of the urban environment on bird populations can enable researchers to better understand the state of the ecosystem. Therefore, the purpose of this paper is to explore the effects of urban environments on bird populations and summarize how urbanization has changed the bird’s survival in various aspects. The paper finds that disturbances in urban environments cause birds to develop corresponding adaptive changes through behavioral changes to avoid the effects of environmental disturbances; meanwhile, urban birds also use some features of urban environments to reduce the consumption of their survival. The analysis in this paper briefly summarizes the impact of urbanization on the survival of birds in various aspects.

 View pdf
View pdf


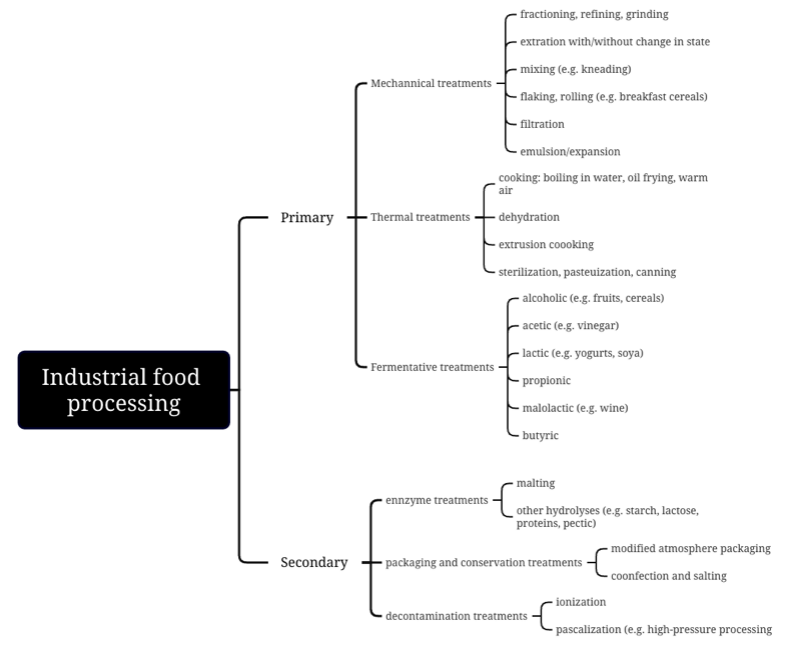
Micronutrient deficiency, commonly known as Hidden Hunger, has raised significant discussion in recent years, affecting more than 2 billion people worldwide. This review examines how Ultra-processed Foods (UPFs) amplify such deficiencies in modern diets. Characterized by industrial formulations and complex processing methods, UPFs are rich in additives but poor in essential vitamins and minerals. Their growing dominance in contemporary food systems can be associated with their convenience, affordability, and palatability. However, the extensive processing methods used in their production strip them of their natural nutritional values while integrating excessive processed sugars, fats, and sodium, contributing to the global burden of nutritional imbalances. Epidemiological studies have highlighted a distinct association between a high UPF-composed diet and increased risk of obesity, cardiovascular diseases, metabolic syndromes, and micronutrient deficiencies, posing threats, particularly among vulnerable populations. Mainstream methods currently used to tackle hidden hunger include fortification and supplementation, yet these measures fail to replicate the synergistic benefits of the consumption of whole foods. This review underscores the urgent need for multifaceted interventions through national and global policies, including taxation, market restriction, and promotion of educational programs, ultimately in hopes of reducing UPF reliance and promoting dietary diversity and equality. To align with Sustainable Development Goals, global cooperation is needed to address Hidden Hunger and ensure equitable access to unprocessed or minimally processed food.

 View pdf
View pdf


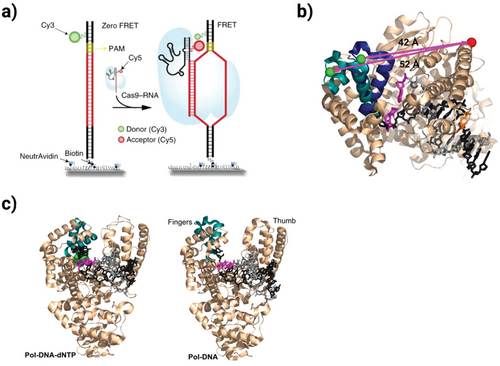
Conventional diagnostic methods for pathogen identification face significant limitations in clinical practice. These include inadequate sensitivity for low microbial loads, prolonged processing times, and susceptibility to sample matrix interference. As a result, this review focuses on recent progress in polymerase chain reaction technology, with particular emphasis on digital PCR platforms. Digital PCR represents a substantial improvement over quantitative PCR methodology. It provides three key advantages: direct absolute quantification without standard curves, enhanced detection capability for rare targets (sensitivity to 1 copy/μL), and superior performance in inhibitor-containing samples. These characteristics address many limitations observed in traditional diagnostic approaches. Emerging PCR-CRISPR integrations (e.g., PCR-Cas13a for H. pylori) are also discussed in this review. Current limitations include equipment complexity and sample interference, but portable devices, multiplex platforms, and AI-assisted analysis show promise for overcoming these challenges and improving diagnostics. These advancements are expanding PCR's applications in precision medicine and infectious disease management.

 View pdf
View pdf


Barnacles are a sessile crustacean that attaches to the outer surface of sea turtles. Sea turtles are key species in marine ecosystems, and studying the impact of barnacles on sea turtles can indirectly reflect the health status of marine ecosystems. This paper aims to investigate the ecological impact of barnacle infestation on sea turtles, to discover the trend of barnacle load levels and their relationship with turtle health, and further explore how barnacle infestation affects the survival and behavior of sea turtles. The research findings show that light barnacle attachment does not cause harm. The severity of barnacle infection determines its impact on turtle movement while causing skin injuries and making them more vulnerable to infections. Barnacles sometimes function as health indicators instead of being direct threats to turtles. Our knowledge about turtle ecology has expanded through the analysis of research data from various geographic areas and periods. Barnacles' population changes are indicators of invasive species movements, while their distribution patterns invasively correlate with the water temperature and salinity levels. The study thus brings out the importance of separating epiphytes from overgrowth in the context of marine ecosystems. Marine biologists and ecologists who work on monitoring the health of turtles will be able to grasp the significance of distinguishing between epiphytes and overgrowth, as well as to develop assessment protocols.

 View pdf
View pdf


Fruits are a cornerstone of human nutrition, providing essential nutrients and bioactive compounds that play a critical role in preventing malnutrition, metabolic disorders, and chronic diseases. This paper examines the systemic impact of dietary fruit intake on human health, focusing on their molecular mechanisms, physiological benefits, and epidemiological evidence. The results of this study indicate that fruits rich in flavonoids (e.g., berries, citrus) and carotenoids (e.g., mangoes, pineapples) neutralize oxidative stress by scavenging ROS and suppressing inflammation via NF-κB/NLRP3 pathways. Dietary fibers from fruits, such as pectin, remodel gut microbiota, enhancing short-chain fatty acid production (e.g., butyrate) and improving metabolic health. Epidemiological studies demonstrate that daily consumption of 200g of fruit reduces cardiovascular disease risk by 12% and type 2 diabetes risk by 7%, with berries showing the strongest protective effects. Additionally, short-term interventions (3–7 days) with specific fruits, like papaya and kiwifruit, rapidly improve digestive and immune functions. These findings underscore the importance of diversified fruit intake tailored to individual health needs, offering actionable strategies for chronic disease prevention and promoting overall well-being.

 View pdf
View pdf


Circadian rhythms, which are intrinsic 24-hour biological cycles, regulate essential physiological processes that significantly impact health and are intricately associated with cancer development. Modern lifestyle disruptions can disturb circadian rhythms, affecting key tumorigenesis pathways like cell cycle regulation, DNA damage response, and metabolic processes. Core circadian proteins BMAL1 and CLOCK significantly influence cancer progression. Specifically, BMAL1 has been shown to activate oncogenic signaling pathways. Chronotherapy is a novel treatment that synchronizes the delivery of treatment with circadian biology. It shows outstanding promise in enhancing cancer treatment efficacy while reducing side effects. Clinical trials indicate that optimal temporal administration of chemotherapeutic and immunotherapeutic agents can significantly reduce drug toxicity and improve treatment outcomes. Despite implementation challenges, recent technological advances and deeper circadian insights are enabling personalized treatment development. This study highlights the therapeutic potential of synchronizing cancer therapies with circadian rhythms to improve outcomes.

 View pdf
View pdf


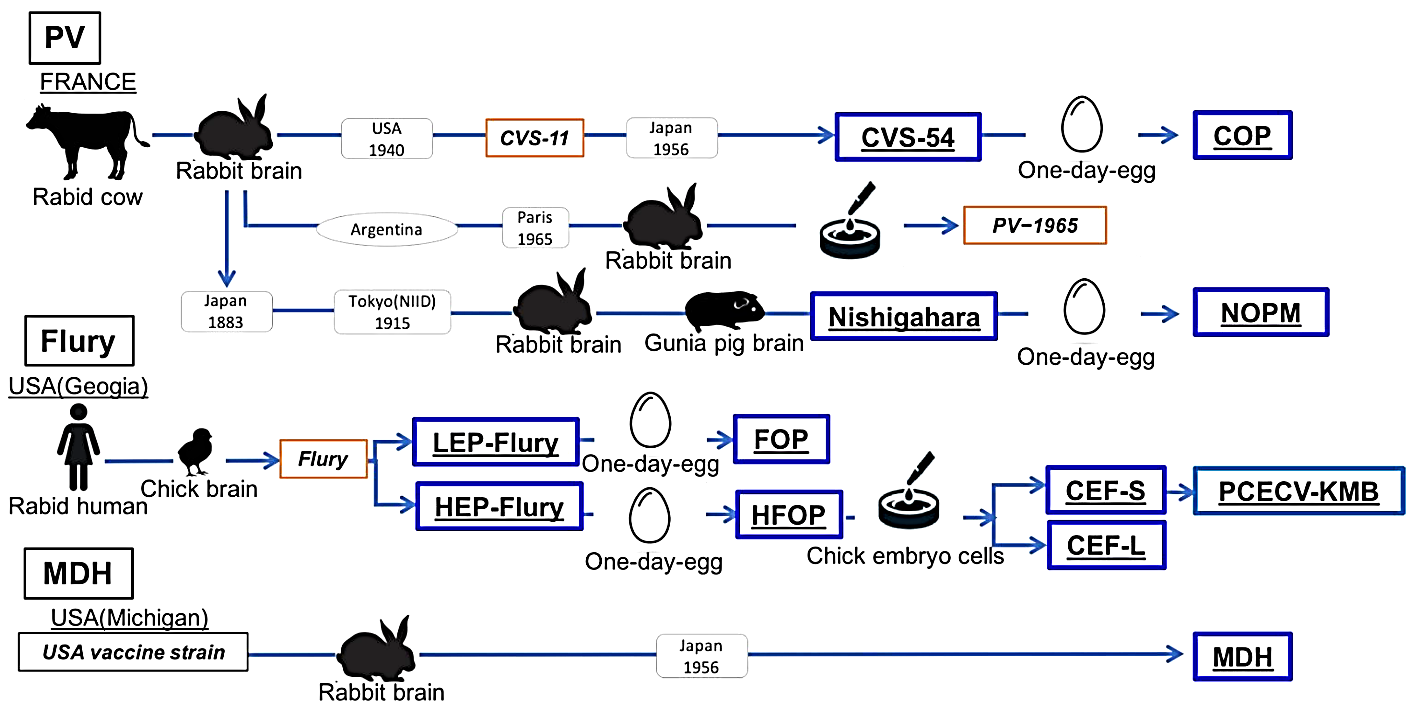
Rabies is an acute zoonotic infectious disease with a fatality rate of 100%. At present, there is no effective treatment methods and the specific therapeutic effect still needs further analysis. This research will discuss different types of rabies treatment methods and their therapeutic effects. After the onset of rabies, rabies patients and rabid animals may even exhibit aggressive behavior towards others, which is extremely dangerous. RABV is the pathogen that causes rabies. Through continuous exploration, potential drugs against RABV have been discovered. The main drugs known to have inhibitory activity against RABV are ribavirin, amantadine and interferon IFN-α. RNA vaccines are a new type of vaccine that has emerged in recent years. They are the new generation of nucleic acid vaccines. RNA vaccines have the advantages of good safety, high effectiveness and short research and development cycle. The development of new rabies virus vaccine adjuvants that are efficient, low-toxic, safe and inexpensive has become an important field in the current research of rabies vaccines.

 View pdf
View pdf




