

Volume 3 Issue 3
Published on October 2025Autoimmune encephalitis (AE) is a group of inflammatory disorders of the central nervous system caused by abnormal activation of the immune system, often presenting with psychiatric symptoms, seizures, cognitive impairment, and consciousness disturbances. Traditional treatments primarily include glucocorticoids, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), plasma exchange (PLEX), and second-line immunosuppressants. While most patients show improvement, some cases progress to "refractory AE." In recent years, advances in immunology and molecular therapy research have led to the emergence of various novel therapeutic strategies, such as B-cell and precursor-targeted therapies, plasma cell and bone marrow suppression, FcRn inhibitors, cytokine pathway interventions, localized central immune modulation, and stem cell or cellular therapies. These innovative approaches provide new perspectives and options for treating refractory AE. However, current evidence is largely derived from case reports or small-scale studies, and there remains a lack of large-scale randomized controlled trials to validate their efficacy and safety. In the future, precision medicine and biomarker-guided individualized treatments, along with optimized combination and sequential strategies, hold promise for improving long-term patient outcomes.

 View pdf
View pdf


Objective: To explore factors influencing the occurrence of hypothyroidism and how collaboration among physicians, pharmacists, and nurses can reduce related complications. Methods: A clinical pharmacist analyzed and summarized the chemotherapy regimen and treatment course of one lung cancer patient who developed thyroid dysfunction during immunotherapy. Results: The occurrence of thyroid dysfunction was associated with multiple factors, including the immunotherapy regimen, drug toxicity, treatment duration, and patient adherence. Through appropriate and precise pharmacotherapy, the patient’s hypothyroidism was brought under control. Conclusion: By carrying out pharmacotherapy monitoring, clinical pharmacists can provide rational medication recommendations, assist physicians in formulating an optimal pharmacotherapeutic plan, help patients manage immunotherapy-induced thyroid dysfunction, and improve quality of life.

 View pdf
View pdf


Esketamine, a novel N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, has demonstrated notable advantages in the perioperative management of pediatric limb fracture surgery. Its rapid onset, strong analgesic effect, significant antidepressant properties, and relatively low incidence of adverse reactions contribute to favorable clinical outcomes for preoperative sedation, intraoperative anesthesia, and postoperative analgesia. With deeper understanding of esketamine’s mechanisms of action and optimized clinical use in the future, it is expected to become an important tool in pediatric perioperative management, offering children safer and more effective anesthesia and pain-control solutions.

 View pdf
View pdf


Peptic ulcer is a common disease of the digestive system, referring to a defect in the gastrointestinal mucosa that usually extends beyond the mucosal muscular layer. Globally, both its incidence and recurrence rates are relatively high, severely affecting patients’ quality of life. The typical symptom of peptic ulcer is upper abdominal pain, which belongs to the category of “stomach pain” in traditional Chinese medicine. Long-term use of therapeutic drugs such as proton pump inhibitors and H₂ receptor antagonists brings drawbacks. The emergence of Helicobacter pylori resistant strains and the increasing elderly population, together with more frequent use of anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antithrombotic drugs, make the prevention and treatment of PU more difficult. At present, traditional Chinese medicine has definite efficacy in treating gastrointestinal ulcers. Among them, cuttlefish bone has a clear therapeutic effect on peptic ulcers, with the functions of astringing to stop bleeding, consolidating essence to stop leucorrhea, neutralizing gastric acid to relieve pain, and absorbing dampness to heal sores. This paper analyzes the reliability of cuttlefish bone in treating peptic ulcers from the perspectives of clinical application, clinical trials, and laboratory research, aiming to provide a reference for the clinical use of medications in peptic ulcer treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


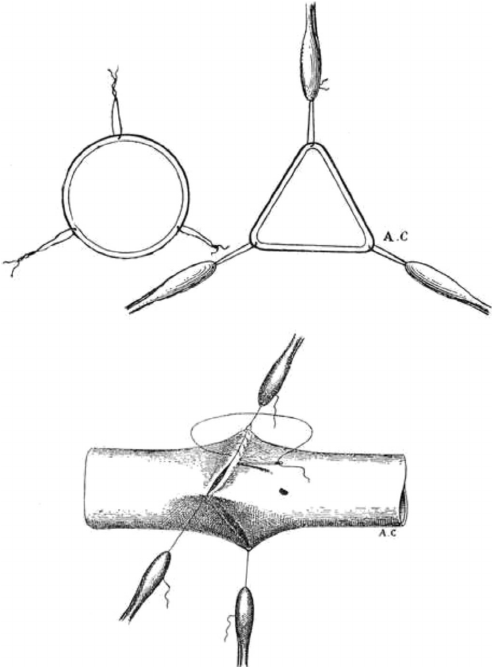
This topic was chosen during the research process for EPQ subjects. Although head transplantation surgery seems difficult to achieve, given the limitations of current medical technology, as well as the ethical and moral issues it raises. However, it is recognized that high risk is often associated with high reward, and the successful realization of this surgery in the future could lead to numerous possibilities for modern medicine. Therefore, further investigation into the possibility of success for this procedure and the existing obstacles is deemed important. From the first trial performed on a dog by surgeons in the early 20th century to the full rehearsal of a Cephalosomatic anastomosis (CSA) on two recently deceased human cadavers at Medical University in China, this review makes a brief conclusion of the past trials and the improvements made in head transplanting. These experiments have confirmed the surgical feasibility of human CSA, representing a significant step toward achieving human CSA in the coming years. And the innovations invented and developed for this surgery can be utilized to refine the surgical procedures currently employed in modern surgery. While the development of such experiments is seen as a major advance in the medical world and will change human life, it also brings major challenges in the field of public health, such as psychological and ethical challenges. This review also focuses on the ethical implications and challenges of head transplantation surgery and the aspects that require anticipation and control before the procedure can be standardized are also examined. Given the potential impact of these surgical experiments, and the various technical barriers that have been encountered and those that have been overcome, this review also discusses whether these studies are technically accessible to human use today or in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf


Parkinson's disease is a common nervous system degenerative disease in the middle-aged and elderly. Its core characteristics include motor symptoms (bradykinesia, resting tremor, muscle rigidity, postural balance disorder) and non-motor symptoms (cognitive impairment, autonomic dysfunction, etc.), which seriously affect the quality of life and health of patients. At present, the main treatment methods of Parkinson's disease include drug therapy, surgical treatment, cell therapy, and gene therapy. This paper summarizes the research results of the last five years of research into the treatment of Parkinson's disease, including ABBV-951, optimized DBS technology, induced pluripotent stem cells, and FAM171A2, with thje aim of providing a comprehensive and effective strategy for its treatment. Through the analysis of the mechanisms and advantages of different treatment methods, it is believed that the stable administration of ABBV-951 and the precise treatment of Deep Brain Stimulation are more advantageous, and may become the main treatment methods in the future. In addition, the treatment of Parkinson's disease is constantly improving and developing towards non-invasive, precise and personalized. Utilising findings from the literature, this paper discusses the improvements in pharmacological and surgical therapies compared to traditional therapies, as well as describing the therapeutic mechanisms of two new therapies, cellular therapy and gene therapy.

 View pdf
View pdf


Melanoma, originating from melanocytes, is an extremely aggressive and globally relevant public health problem with increasing incidence. Although surgical resection is still the gold standard in early-stage melanoma, numerous advances in the field of oncology have expanded the therapeutic armamentarium, especially for advanced or metastatic disease. Current management of melanoma now encompasses a combination of immunotherapy, targeted therapy, radiotherapy and novelx series of the method of new experimental medical therapy. Immunotherapeutic agents (immune checpoint inhibitors): Anti-PD1 and Anti-CTLA-4 inhibitors have changed the survival curve, providing long-term remissions in a subgroup of patients. The targeted therapies to BRAF and MEK mutations are also known to present quick clinical responses, as well as the development of resistance, which is a significant limitation. Radiotherapy remains essentially palliative, and chemotherapy significantly less effective. In addition, emerging interventions; oncolytic viruses therapy, microRNA therapeutics and epigenetic modulators are being actively studied. Ancillary therapies, such as TCM, are also adjunctive and require cautious combination with Western medicine. In this review, we review current melanoma therapies considering them for clinical advantage (pros) and disadvantage (cons). The aim is to provide clinicians, researchers, and patients with a tool to help them to build knowledge about the new therapies for melanoma, to help make informed, personalized treatment decisions based on the most up-to-date scientific data and clinical practice.

 View pdf
View pdf


The periodontal ligament’s viscoelastic collagen mesh anchors teeth to alveolar bone yet is irreversibly destroyed by periodontitis or trauma; conventional grafts restore neither Sharpey’s fibers nor vascularity. We therefore surveyed recent progress in rebuilding this interface by coupling dental-pulp mesenchymal stem cells with 3D-bioprinted scaffolds. A systematic literature search (PubMed/Web of Science, 2019–2024) yielded 58 eligible articles that were narratively analysed. Low-temperature extrusion, digital-light-processing and micro-valve jetting each preserved >90 % DP-MSC viability, with micro-valve patterning achieving 25 µm resolution critical for fiber alignment. Gradient GelMA-collagen/PCL bioinks (20 MPa → 50 MPa) matched native modulus, while co-printing DP-MSCs with VEGF- or TGF-β3-laden microspheres doubled vessel density and elevated COL1A1/Periostin five-fold through synergistic Smad2/3-β-catenin signalling. In 5-mm periodontal defects of beagles, these constructs achieved 78% bone volume regeneration, a density of 42 Sharpey’s fibers per square millimeter, and 80% recovery of mechanical strength at the 12-week time point. Remaining hurdles—donor heterogeneity, scaffold degradation mismatch and M1/M2 imbalance—were mitigated by HLA-typed iPSC-DP-MSCs, enzyme-responsive PCL (t½ 10 weeks) and IL-10 liposomes. Thus, standardised stem-cell banks integrated with dynamic, immunomodulatory 3D printing constitute a clinically translatable platform for personalised periodontal regeneration.

 View pdf
View pdf


Objective: To analyze the relationship between VTCN1 and brain low-grade glioma (LGG) using bioinformatics methods, and to explore the potential prognostic value and underlying therapeutic mechanisms of VTCN1 in LGG. Methods: Forest plots and Kaplan-Meier curves were used to examine the relationship between VTCN1 expression and patient prognosis in various cancers. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis, univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were employed for survival analysis. Based on the results of multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis, a nomogram and a calibration plot were constructed to predict the X-year overall recurrence rate. The TIMER database was used to analyze the expression profile of VTCN1 and the abundance of immune infiltration in pan-cancer. Mutation analysis and ferroptosis-related gene analysis were performed using data from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. The UALCAN database was used to analyze VTCN1 expression levels. The GEPIA2 database was used to analyze gene correlations. Spearman correlation analysis was applied to explore the relationship between VTCN1 and signaling pathways. The CCLE database was used to investigate VTCN1 expression in different cell lines. Results: High VTCN1 expression affects the cell cycle, apoptosis, and oxidative stress through DNAJC12 and TEF, and influences iron homeostasis through NCOA4, thereby participating in the occurrence and development of LGG. In addition, high tumor mutational burden (TMB) and infiltration of relevant immune cells may also play important roles. Conclusion: VTCN1 may serve as a potential target for survival prediction and treatment in brain low-grade glioma.

 View pdf
View pdf




