

Volume 3 Issue 2
Published on August 2025This study aims to construct a quantitative evaluation model for the incidence of cardiovascular disease based on plaque characteristics in patients with coronary atherosclerosis, with the goal of providing robust scientific support for risk prediction and personalized prevention and treatment strategies. Patients with coronary atherosclerosis were selected as research subjects. Imaging characteristics of coronary plaques, including plaque volume, lipid core size, and fibrous cap thickness, were assessed. Clinical data such as age, sex, medical history, and lifestyle habits were also collected. Additionally, the occurrence of cardiovascular disease—including disease types and time of onset—was recorded. Based on these data, a quantitative evaluation model was developed using machine learning algorithms to predict the risk of cardiovascular disease. A quantitative evaluation model for cardiovascular disease incidence was successfully constructed based on plaque characteristics in patients with coronary atherosclerosis. The model integrated imaging features such as plaque volume, lipid core size, and fibrous cap thickness, along with clinical variables, and was built using a random forest algorithm. On the test set, the model achieved an AUC of 0.85, an accuracy of 78.5%, a recall rate of 75.0%, and an F1 score of 76.7%. Among these variables, plaque volume and lipid plaque ratio were identified as the most important predictors. The model can effectively identify high-risk patients, providing strong support for early clinical intervention.

 View pdf
View pdf


Primary liver cancer is a refractory tumor with a high recurrence rate and low quality of life. Traditional Chinese medicine, especially Chinese patent medicines, has shown positive therapeutic prospects in improving symptoms and quality of life. This study summarizes the potential efficacy of various Chinese patent medicines for primary liver cancer through a literature review, and describes their mechanism of action through multiple pathways, such as regulating the tumor immune microenvironment, modulating metabolic patterns, and inhibiting tumor cell growth and proliferation. Despite considerable advancements in the clinical utilization of Chinese patent medicines, existing research exhibits limitations, including the necessity to enhance the comprehensiveness of clinical data and the profundity of mechanistic investigations. Future research trajectories should encompass broadening the scope of clinical studies, intensifying the exploration of the mechanisms underlying Chinese patent medicines, and fostering the standardization and personalization of treatment protocols.

 View pdf
View pdf


Hyperlipidemia, a significant contributor to cardiovascular ailments, have a close association with obesity, is closely linked to obesity. Traditional anthropometric indices (BMI, WHR, WHtR) are widely used to assess obesity, but their nonlinear relationships with hyperlipidemia and gender-specific risk thresholds remain poorly understood. Leveraging data from 2,739 participants in the NHANES 2007–2020, this research utilized multivariable logistic regression analysis along with restricted cubic splines (RCS) to investigate both linear and nonlinear relationships between various obesity indices and the presence of hyperlipidemia. Nonlinear dose-response relationships were observed for BMI, WHR, and WHtR with hyperlipidemia (P for nonlinear < 0.001). Gender-specific risk thresholds were identified: males: WHR > 0.94, WHtR > 0.76, BMI >28.0; Females: WHR 0.91–0.99, WHtR 0.61–0.69, BMI 29.4–34.39. Gender differences in effect sizes were significant (e.g., WHR β: males 6.986, P<0.001 vs. females 5.666, P=0.023). Subgroup analysis showed stronger associations in younger individuals (≤50 years) without hypertension or diabetes. WHR remained an independent predictor in metabolic comorbidities, while BMI and WHtR were confounded by metabolic disturbances. This study highlights the importance of gender-specific risk thresholds for obesity indices, particularly WHR, in predicting hyperlipidemia. The results demonstrate that WHR serves as a more reliable predictor for metabolic disorder risks compared to other anthropometric indices, particularly highlighting the importance of implementing preventive measures in populations under 50 years of age. Future research should focus on developing precision stratification models to optimize obesity management.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study aims to evaluate the causal relationship between tea consumption and esophageal cancer using a bidirectional Mendelian Randomization (MR) approach. Methodologically, genetic instruments for tea intake were derived from a Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) involving 447,485 participants in the UK Biobank. Thirty-nine tea-associated Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) were selected and analyzed using two-sample MR to examine causality. The esophageal cancer data were obtained from the NA consortium’s publicly available GWAS, which includes 998 cases and 475,308 controls. A reverse MR analysis was also conducted to explore potential reverse causality. The results demonstrate a causal link between tea consumption and esophageal cancer. Specifically, using the inverse-variance weighted (IVW) method, a one standard deviation increase in tea intake was associated with a 194.5% increase in esophageal cancer risk (OR = 2.945, 95% CI: 1.794–4.833). Similar results were observed using the weighted mode (OR = 5.590, 95% CI: 2.713–11.519) and weighted median (OR = 4.446, 95% CI: 2.260–8.748) methods. The IVW method again showed a consistent result (OR = 2.945, 95% CI: 1.551–5.592). However, there was no evidence supporting reverse causality (IVW: P > 0.05). Overall, genetic evidence from bidirectional MR analyses indicates that increased tea consumption raises the risk of esophageal cancer, although no reverse causal relationship was found.

 View pdf
View pdf


Prostate cancer, as an epithelial malignant tumor occurring in the prostate, has already become one of the most common malignant tumors among the male population globally. Traditional diagnostic methods, such as PSA testing and biopsy, have certain limitations in practical application and are difficult to provide relatively intuitive and comprehensive diagnostic results. This article mainly reviews the current application status of multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging (mpMRI) technology in the diagnosis and staging of prostate cancer. The study has found that, relying on its unique advantages, the mpMRI technology can not only conduct a detailed and comprehensive diagnosis of prostate cancer but also demonstrate extremely high accuracy in tumor staging. With the research results of this study, medical staff can implement the diagnostic process for prostate cancer patients from a more refined dimension, thereby significantly improving the diagnostic efficiency and minimizing the adverse impacts caused to patients due to misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis. These results will contribute to reducing the burden on the healthcare system and promoting the improvement of the public's health level.

 View pdf
View pdf


Chronic Atrophic Gastritis (CAG) is recognized as a precancerous condition of gastric cancer, characterized by a prolonged course and complex pathogenesis. Increasing evidence suggests that gastric mucosal barrier dysfunction plays a central role in the onset and progression of CAG, typically manifested by thinning of the mucus layer, destruction of epithelial cell junctions, increased microvascular permeability, and sustained mucosal inflammation. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has shown unique advantages in the prevention and treatment of CAG through its multi-target, multi-level regulatory actions, particularly in restoring gastric mucosal barrier integrity. Recent studies have demonstrated that TCM formulations exert protective effects by promoting mucin secretion, enhancing the expression of tight and adherens junction proteins, suppressing inflammatory signaling pathways, and improving microvascular circulation. These interventions contribute to the repair and maintenance of gastric mucosal structure and function, thereby reducing the risk of further pathological progression. This review summarizes recent research progress on the role of TCM in modulating gastric mucosal barrier function in CAG, thereby providing new insights and a theoretical foundation for future research and clinical application of TCM in the management of this disease.

 View pdf
View pdf


Dental Fear and Anxiety (DFA) manifests as anxiety and fear symptoms specifically associated with dental treatment. This review article conducts a comprehensive analysis of the etiological factors and clinical implications of DFA, dissects the underlying vicious cycle mechanism, identifies limitations in existing theoretical models, and proposes a revised framework. The review demonstrates that patients with DFA tend to avoid dental care, leading to prolonged delays in treatment that exacerbate oral health deterioration. This progressive decline often culminates in unavoidable coercive interventions, while simultaneously generating psychological distress such as social embarrassment and perceived incompetence, thereby reinforcing the original fear response. Furthermore, this study innovatively integrates direct and indirect intervention strategies within a modified vicious cycle model. This comprehensive strategy aims to disrupt the negative feedback loop through simultaneous targeting of psychological and practical barriers.

 View pdf
View pdf


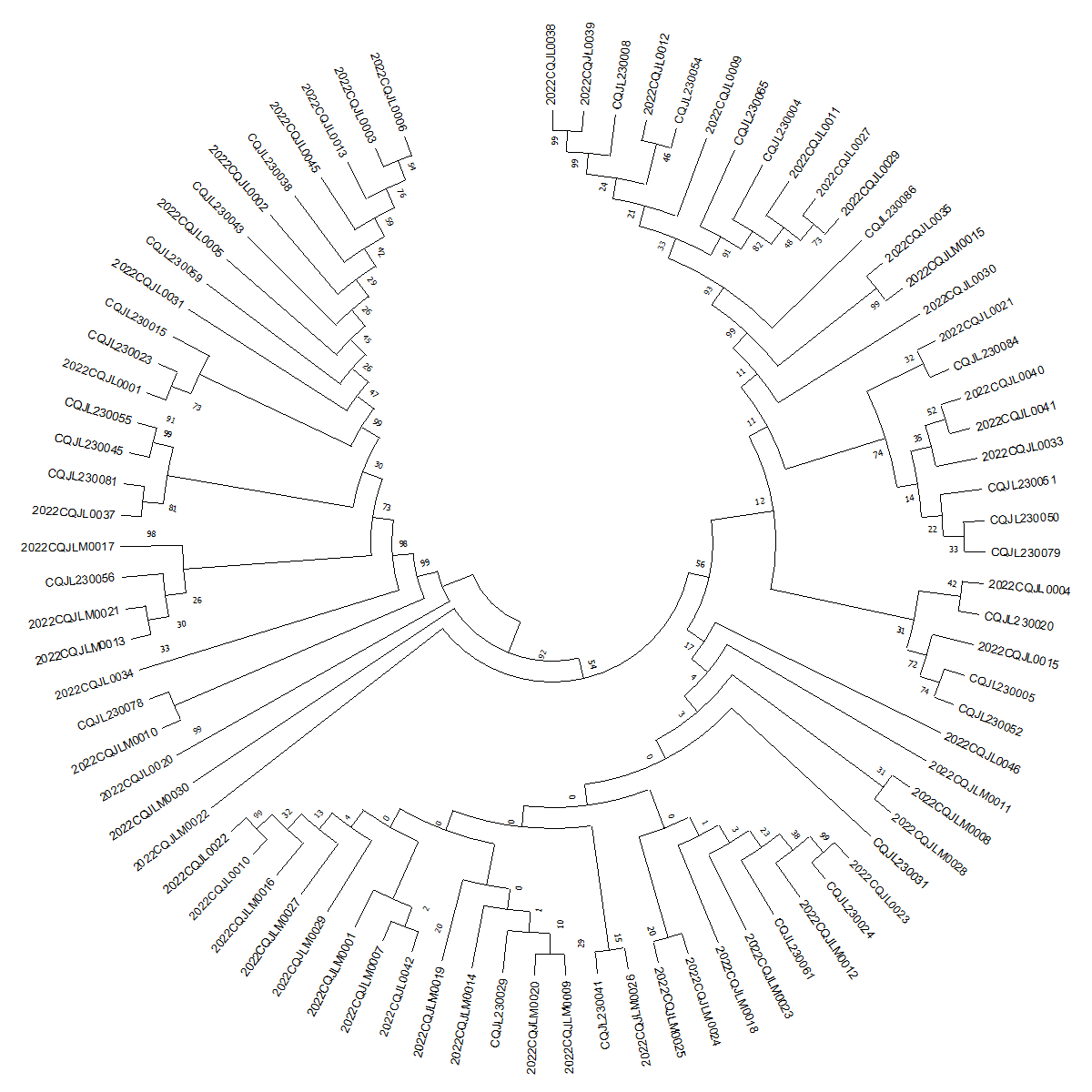
Objective: To understand the transmission characteristics of newly reported HIV/AIDS (Human Immunodeficiency Virus/Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) patients in key sub-districts and towns of Jiulongpo District, Chongqing through constructing the HIV molecular transmission network, so as to provide a reference for the precise intervention of AIDS in this district. Methods: Blood samples were collected from newly reported HIV/AIDS patients in these sub-districts and towns before treatment from 2021 to 2023. After extraction, amplification of the pol region, sequencing, and sequence collation, the HIV - TRACE tool was used to construct the molecular transmission network. Results: A total of 83 valid gene sequences were obtained. Most of the patients were male (89.16%), and the majority of them were aged 50 and above (59.04%). The highest proportion had an educational level of junior high school or below (65.06%). All infections were sexually transmitted, with heterosexual transmission being the main mode (65.06%). In terms of marital status, the married or in a spousal relationship and the unmarried accounted for 45.78% and 38.55% respectively. Occupations were mainly housework and unemployment and commercial services, accounting for 36.14% and 34.94% respectively. Gene subtype analysis showed that CRF07_BC and CRF01_AE were the predominant subtypes. Analysis of the HIV molecular transmission network showed that at a 1.5% genetic distance, the network entry rate was 21.69% (18/83), and a total of 6 molecular clusters were formed. The largest molecular cluster was CRF01_AE. The total number of links for all nodes in the network was 38, and the highest number of links for a single node was 6. Conclusion: In the key sub-districts and towns of Jiulongpo District, the viral gene types of the infected are diverse. The infected patients are characterized by older age, lower educational level, and mainly sexual transmission. Middle-aged and elderly groups and the spouses of positive patients are the key populations to be concerned about, and targeted interventions are needed.

 View pdf
View pdf


Western Blot (WB) and Quantitative Real-time PCR (qPCR) are cornerstone technologies in molecular biology, indispensable for protein and nucleic acid analysis. However, traditional WB and qPCR methods face challenges like limited throughput, specificity constraints, and high time consumption The advent of innovative technologies helps overcome these hurdles. Spatially resolved WB leverages tissue chips and single-cell subcellular analysis to bolster detection efficiency. Highly sensitive WB techniques have pushed the detection threshold down to femtograms, further enhancing sensitivity. High-throughput microfluidic WB and qPCR systems drastically cut down detection time and sample consumption through automation and multiplexing capabilities. Ultra-multiplex qPCR facilitates the simultaneous detection of numerous targets by utilizing multi-color fluorescent probes. Moreover, digital qPCR (dPCR) harnesses droplet partitioning technology for absolute quantification, showcasing remarkable precision in viral load monitoring and transgene analysis. Looking ahead, the integration of these technologies and the advent of spatial omics will be pivotal in facilitating their widespread clinical application. Nevertheless, the implementation of these novel technologies is not devoid of limitations and shortcomings. Through multidisciplinary collaboration and rigorous clinical validation, these advancements are poised to propel the advancement of precision medicine.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper examines the transformative potential of artificial intelligence (AI) companions in supporting posttraumatic growth (PTG). Considering rising global trauma and the persistent limitations of traditional mental health care, such as high costs, limited access, and constrained human resources, AI emerges as a scalable, accessible, and nonjudgmental alternative for healing. Grounded in psychological science and informed by positive psychology, humanistic, and transpersonal theories, this study reframes AI not merely as a technological tool but as an expert companion capable of nurturing resilience, facilitating emotional processing, and guiding meaning-making and identity reconstruction. Using a qualitative case study approach, the paper analyses FASSLING’s key features, including adaptive empathy, narrative reframing, and culturally inclusive support, and evaluates their alignment with established PTG frameworks. The findings suggest that AI companions can serve as ethically grounded co-creators in trauma recovery, particularly in low-resource or marginalized settings. The paper concludes with a call for increased investment in compassionate AI, ethical development practices, and long-term research to deepen our understanding of AI’s role in fostering human flourishing after trauma.

 View pdf
View pdf




