

Volume 11
Published on September 2024Cancer encompasses a broad spectrum of diseases marked by abnormal cell growth that can potentially spread throughout the body. Common types include breast, lung, colon, rectal, and skin cancers, among others. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment of skin cancer, which ranks among the prevalent forms of cancer. However, traditional diagnostic methods are time-consuming and depend on the expertise of dermatologists. This research aims to investigate the application of machine learning (ML) for identifying skin cancer from images, aiming to improve early detection and diagnosis. Various image preprocessing techniques, feature extraction methods, and ML algorithms are applied to a dataset of skin lesion images. Various machine learning models are assessed and compared based on relevant metrics for their effectiveness in detecting skin cancer. Preliminary findings indicate that ML algorithms can achieve high accuracy in skin cancer identification, potentially improving diagnostic efficiency and accessibility. However, the research also highlights obstacles such as imbalanced data and the need for model interpretability, which must be addressed for practical implementation. This research contributes to the expanding knowledge on ML applications in healthcare, particularly in dermatology. It highlights the potential of ML in skin cancer identification and provides insights into the challenges and limitations that need to be overcome for successful implementation. The study emphasizes the necessity for future research to refine these techniques and enhance their clinical applicability.

 View pdf
View pdf


Facial scanning is becoming more common as the commercial use of facial recognition technology expands. Face recognition technology, can be widely used in public security, finance, subway, airport and other important fields of natural identification. Now, the technology has also been applied to the routine outbreak control and prevention, through the form of "face recognition" to bring more convenient, safer and more accurate experience. However, with the development of technology, the drawbacks of facial recognition are gradually revealed, and people's opinions on the technology are mixed. As facial recognition is widely used in the market, protecting users' privacy information and data is becoming an increasingly important issue. In this article, this paper will discuss the different factors contributing to the popularity of facial recognition among people from five aspects, respectively from the aspects of devices and people. This paper was covered a number of parts in this article to explore what factors influence the popularity of facial recognition, racially biased, Accuracy of identification, public acceptance, Personal experience with technology, public perception of face recognition technology and Alternatives to FRS. The conclusion is that the factors which most strongly impact on FR is accuracy.

 View pdf
View pdf


When SiC MOSFET power devices operate under radiation environment conditions, radiation induces trap charges in their gate oxide, which affects the device's short-circuit and avalanche characteristics. The short-circuit and avalanche characteristics are crucial for the reliable operation of devices under radiation environments. To ensure the efficient and stable operation of SiC MOSFET power devices under radiation environments, this paper focuses on studying the degradation patterns of the short-circuit and avalanche characteristics of SiC MOSFET power devices after being subjected to radiation, and analyzes the degradation mechanisms through theory and simulation.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, due to technological progress, the cost of solar power generation has decreased, and the Chinese government has supported renewable energy technology, solar photovoltaic technology has developed rapidly. This paper discusses the development prospect of solar power generation in China. By analyzing and comparing the advantages and disadvantages of solar power generation and coal power generation in environment, manufacturing, cost and policy, we explore whether solar power generation can replace coal power generation. It focuses on the advantages of solar power generation in terms of environmental impact, the development of solar power generation promoted by the Chinese government's vigorous implementation of sustainable development strategies, and the many limitations of coal in these aspects, reflecting the advantages of solar energy in today's power generation methods. At the same time, it also analyzes the technological progress of solar power generation, the decline of costs, and the challenges of solar panel recycling. Efficiency has always been the most concerned aspect of solar power generation. Studies have found that the use of different materials, the efficiency of photovoltaic power generation is also different. Increased efficiency is also affected by external temperature, humidity, dust, and light. Solar energy also faces many limitations in this regard. Based on these studies, solar energy has great potential as a renewable energy source and has the potential to replace coal power generation on a large scale by 2060. This essay looks at these studies and concludes that there is potential.

 View pdf
View pdf


The emergence of driverless cars, also known as autonomous vehicles (AVs), has generated a great deal of excitement and speculation regarding their potential to revolutionize transportation. With advanced sensors and sophisticated algorithms, driverless cars are capable of navigating roads and traffic without human intervention. There will be some help and wide use of driverless cars to reduce traffic accidents. The research will focus on the impact of driverless cars on reducing traffic accident rates in the future. After analyzing the current situation and summarizing some existing studies, the final conclusion is that driverless cars will indeed effectively reduce the traffic accident rate and it will be more widely used in the whole society in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf


This dissertation aims to research how quantum battery work and the comparisons between quantum battery and lithium-ion battery. Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable energy storage devices that have become widely used in various applications, ranging from portable electronics to electric vehicles. They are known for their high energy density, long cycle life, and relatively low self-discharge rate. Quantum batteries are a relatively new and emerging concept in the field of energy storage. Unlike traditional batteries, which rely on chemical reactions for energy storage, quantum batteries utilize principles from quantum physics to store and release energy. The dissertation uses the available literature review to illustrate the difference between quantum batteries and lithium-ion batteries for storing energy, and which one is better. In terms of current technology, lithium-ion batteries are the best choice for portable charging devices. But in the future, quantum batteries made with advanced technology may replace lithium-ion batteries.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the field of wildlife conservation, it is challenging to distinguish visually similar species, such as leopards, lions and tigers. This poses huge obstacles for automated detection systems. In this study, transfer learning uses YOLOv5 model from Ultralytics repository to enhance the accuracy of the detection. We pre-trained the model on datasets specific to each species and then applied transfer learning across different species pairs (e.g., leopard to lion, lion to tiger). Our results indicate that while models pre-trained on individual species achieved high detection accuracy (mAP@0.5 > 0.95), the effectiveness of transfer learning varied significantly depending on the visual similarity between species. For instance, transferring from leopard to lion demonstrated strong performance (peak mAP@0.5 of 0.91), while transferring from leopard to tiger resulted in lower accuracy (peak mAP@0.5 of 0.80), showing the limitations of transferring learned features between more visually distinct species. These findings indicate that transfer learning largely reduces training time and improves the adaptability of the models when applied to closely related species. However, further improvements are still needed for more distant species pairs and for too small datasets.

 View pdf
View pdf


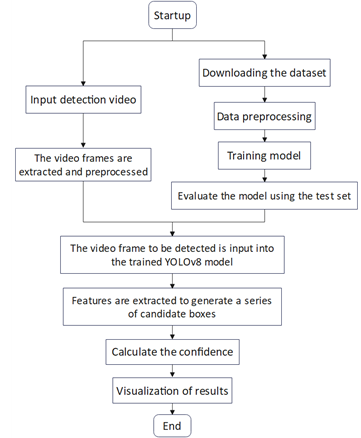
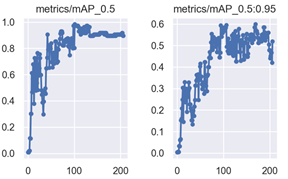
Intelligent video surveillance is a significant research area in computer vision, with the detection and tracking of abandoned objects in public spaces attracting considerable public attention. However, existing detection technologies still face challenges, including false alarms, missed detections, poor adaptability to environmental conditions, and an inability to monitor in real-time. This paper proposes a method for tracking abandoned objects in surveillance video by analyzing human trajectories. The method addresses three main challenges: detection, tracking, and identification of abandoned objects. First, the paper discusses the inter-frame comparison method and the YOLOv8-based object detection algorithm for identifying abandoned objects and determining their categories. Additionally, it explores person re-identification technology and its application in identifying the owner of an abandoned object. Finally, the movement trajectory of the object’s owner is analyzed to determine the intent of the person who placed it.

 View pdf
View pdf


According to data from the Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes in the Elderly, there are approximately 35.5 million elderly diabetic patients over the age of 65 in China, accounting for 1/4 of the total number of elderly diabetic patients worldwide, and this number is still on the rise. This article analyzes and studies the wearable glucose meters for the elderly from the characteristics and lifestyle features of elderly diabetic patients, starting from the perspective of user experience and combining with the Positive Experience Design theory. The design strategies for elderly wearable glucose meters based on the Positive Experience Design theory are concluded, aiming to enhance the blood sugar control experience of the elderly and promote their active participation in blood sugar management, in order to improve the diabetes management experience and health status of the elderly.

 View pdf
View pdf


In this study, we delve into the intersection of high-dimensional statistics and machine learning within the realm of sports analytics, with a particular focus on real-time prediction of NBA game outcomes. We harness cutting-edge data techniques and innovative AI models to boost our predictive capabilities and real-time performance. By combining advanced data processing with the latest in machine and deep learning, we're able to deliver more accurate and timely insights across a range of complex scenarios. Our approach integrates Bayesian statistical methods to quantify prediction uncertainty, ensuring robust and interpretable models. We utilize a combination of traditional machine learning models, such as Random Forest and Logistic Regression, alongside advanced deep learning architectures, including CNNs, RNNs, LSTMs, and Transformer networks. Our comprehensive preprocessing pipeline includes advanced statistical techniques for handling missing values and outliers, ensuring data consistency, and feature selection and dimensionality reduction methods like PCA and RFE. Implementing real-time data streaming technologies such as Apache Kafka and distributed databases like Apache Cassandra ensures high availability, scalability, and efficient handling of large volumes of data. This study highlights the significant potential of integrating high-dimensional statistics and deep learning in sports analytics, offering deeper insights, more accurate predictions, and real-time analysis capabilities, paving the way for future innovations and applications in the field.

 View pdf
View pdf




