

Volume 77
Published on July 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Software Engineering and Machine Learning
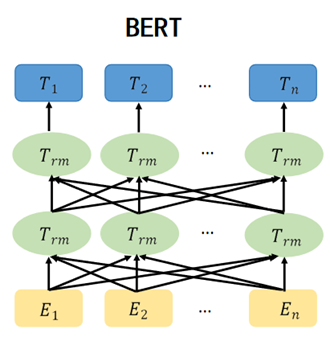
As of June 2023, China has witnessed a surge in internet users, reaching 1.079 billion, with an internet penetration rate of 76.4%. This rapid expansion of social media and online communication channels has not only enhanced the ease of information sharing but has also intensified the spread of rumors and misinformation. This trend poses substantial threats to social order and public safety. In response to this challenge, this work introduces an innovative approach to detect online rumors, utilizing the BERT-CNN methodology. By harnessing the contextual understanding capabilities of the BERT model and the efficient feature extraction prowess of CNN models, the study has crafted a framework that seamlessly integrates these technologies. This integrated approach proves effective in accurately identifying and categorizing rumors in online data. Through extensive experiments conducted on various real-world datasets, a comparative performance analysis had conducted against existing technologies. The results reveal significant enhancements in key metrics such as accuracy, recall, and F1 score when compared to traditional methods. This affirms the efficacy of the BERT-CNN approach in the domain of online rumor detection. This research not only introduces a fresh perspective to rumor detection technology but also furnishes a robust tool to tackle the challenges associated with the dissemination of rumors in the digital age.

 View pdf
View pdf


Since the first Neural Network computer was made by Marvin Minsky and his schoolmates in 1951, the development of artificial intelligence (AI)has undergone various and huge changes. It generally evolves into a field that has infinite possibilities and a major branch of computer science that can not be ignored. With the trend of computerization and the rapid evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT), gesture recognition emerged. Various prototypes are blossoming in the laboratories, and some of them have become certain products that have practical applications in later days. At the same time, more and more deep learning technology has been applied to gesture recognition systems that greatly improve the quality of the service. The purpose of this review is to summarize and analyze the existing algorithms of Dynamic Gesture Recognition systems, which have several different methods that are based on multiple signal extractors. This study focuses on the 3D Convolutional Neural Network(CNN), which plays an important role in the Dynamic Gesture Recognition optimization algorithm and data analysis algorithm. In this paper, we reviewed past papers in the gesture recognition field, which include the sEMG method, microwave method, and vision recognition method. During the process of data collecting and summarizing the past papers, we mainly focused on the accuracy differences between recognition methods and the efficiency differences in data processing algorithms. (CNN-based, LSTM based, etc.) Then, we analyzed the main difficulties and challenges of these methods, which are briefly listed in the Introduction part. Data processing algorithms are also being studied, and a horizontal comparison between CNN-based, LSTM-based, and transformer-based algorithms is also being made. Besides this, for those problems that already have a reliable solution, we also summarized the possible solutions and listed them out. We found that the gesture recognition system has already been systematically studied and is partly used in some fields. However, the algorithm and modeling methods can still be optimized and it also needs further study to be more widely used.

 View pdf
View pdf


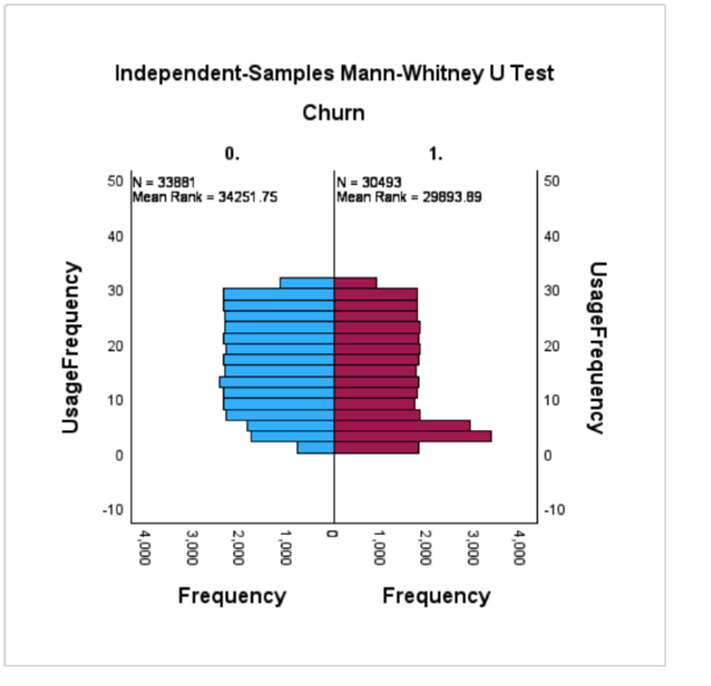
Churn is the phenomenon of a customer terminating their relationship or subscription with a company or service provider[1]. It represents the rate at which customers stop using a company's product or service during a specific period of time. Attrition rate is an important metric for businesses as it directly impacts revenue, growth and customer retention. In the context of the churn data set, the churn label indicates whether a customer has been churn. Lost customers are those who decide to stop buying the company's products. On the other hand, non-churn customers are those who continue to buy the company's products. Understanding customer churn is critical for businesses to identify the patterns, factors, and metrics that lead to customer churn. By analyzing churn behavior and its associated characteristics, companies can develop strategies to retain existing customers, improve customer satisfaction, and reduce customer churn. Predictive modeling techniques can also be applied to anticipate and proactively address potential customer churn, enabling companies to take proactive steps to retain at-risk customers[2].

 View pdf
View pdf


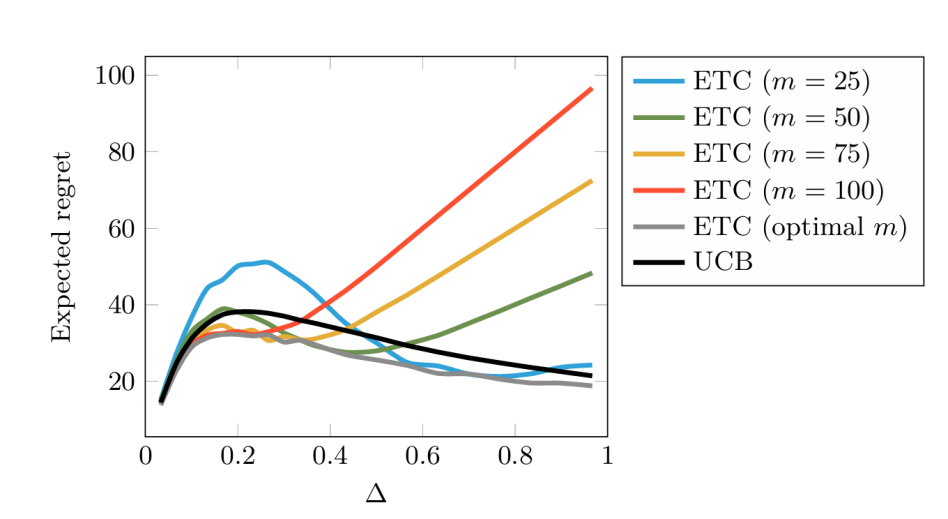
In recent years, the multi-armed bandit (MAB) model has been widely used and has shown excellent performance. This article provides an overview of the applications and technical improvements of the multi-armed bandit machine problem. First, an overview of the multi-armed bandit problem is presented, including the explanation of a general modeling approach and several existing common algorithms, such as ε-greedy, ETC, UCB, and Thompson sampling. Then, the real-life applications of the multi-armed bandit model are explored, covering the fields of recommender systems, healthcare, and finance. Then, some improved algorithms and models are summarized by addressing the problems encountered in different application domains, including the multi-armed bandit considering multiple objectives, the mortal multi-armed bandits, the multi-armed bandit considering contextual side information, combinatorial multi-armed bandits. Finally, the characteristics, trends of changes among different algorithms, and applicable scenarios are summarized and discussed.

 View pdf
View pdf


Artificial intelligence, also known as AI, has led the trend of evolution in the past and future decades, and the potential of consciousness artificial intelligence emerges as a renovative field to address. The computer machine aims to process repetitive and tedious tasks for humans since its concept was first developed. Whether AI is conscious does not raise unprecedented discussion before the appearance of the concept of machine learning. After it appears, the machine, instead of merely passing in input and generating output, is able to learn while processing the information, which resembles a human's learning process. Therefore, this paper delves into the complex terrain of AI to explore the theoretical possibility of endowing machines with consciousness and addresses the future concerns and potentials of AI. Illustrating through the aspects of ethical concerns, metaphysical perspectives on consciousness, and the latest advancements in AI, the study critically examines whether machines can possess a consciousness similar to human understanding.

 View pdf
View pdf


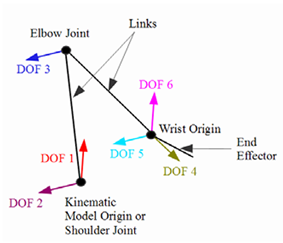
Massage robots, as innovative therapeutic devices, have garnered significant attention and application due to technological advancements and society's increasing focus on wellness. However, amidst this progress, gaps persist in fully understanding their capabilities and optimizing their functionalities, highlighting the need for further research in this domain. This paper focuses on exploring the intricate technical principles, mechanical structure, sensing technology, and intelligent control systems of massage robots, with the aim of providing both theoretical foundations and practical insights for researchers and practitioners in this field. Specific inquiries encompass the elucidation of working principles, emulation of human massage techniques, mechanical design considerations, applications of sensor technology, and implementations of intelligent control systems within massage robots. Employing a blend of literature review, comparative analysis, and experimental validation, this paper aims to not only deepen the understanding of massage robot functionality but also contribute to the advancement and refinement of this technology, fostering innovation and growth within the industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into macroeconomic models marks a significant evolution in the field of economic forecasting and analysis. Traditional macroeconomic models, often constrained by linear assumptions and a limited set of variables, struggle to accurately capture the complexities of the global economy. This paper explores how AI, particularly machine learning algorithms like Random Forests and Neural Networks, enhances these models by processing and interpreting vast and diverse datasets, including unstructured data such as social media sentiment and news analysis. AI's capability to adapt and learn from new data enables dynamic models that remain relevant and accurate amidst changing economic conditions. By addressing non-linearities and enhancing model robustness, AI provides a more nuanced understanding of economic dynamics, uncovering intricate patterns missed by traditional analyses. The implications of AI-enhanced macroeconomic models are profound, offering more reliable foundations for economic research and policy-making. This paper argues that the integration of AI into economic modeling not only improves the precision of economic forecasts but also enriches the field of economic research and the formulation of more effective policy interventions. Through examples such as inflation rate forecasting and the identification of complex, non-linear economic relationships, this study highlights the transformative potential of AI in macroeconomic analysis and policy formulation.

 View pdf
View pdf


The field of musical exploration grows rapidly with the rapid development of technology in the digital era. In this paper, the application of machine learning in music recommendation systems is mainly focused on and the existing data sets about Spotify are used to analyze and show how machine learning achieves musical personality recommendations. This paper mainly uses principal component analysis and the K-means clustering algorithm to realize the goal. Principal component analysis (PCA) helps people to reduce the dimensionality of the whole dataset, and this method helps people to retain key information and reduce the complexity of the data. The k-means clustering algorithm divides the songs into different clusters. These clusters show consistency in musical features, and the dots will cluster together. By visualization of the clusters, people can deeply interpret the relationship between distinct music genres and discover the areas of music and songs that users are interested in. This research not only explains how music exploration is implemented but also promotes the development of personalized music recommendation systems.

 View pdf
View pdf



The rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI), notably represented by ChatGPT, has greatly influenced User Interface (UI) design. ChatGPT, an advanced language model, aids designers by suggesting ideas, generating interface images, providing feedback, and simulating user interactions. Its integration into UI design processes has improved efficiency, allowing designers to explore more design options quickly. Additionally, ChatGPT facilitates user research by simulating conversations with potential users, gathering valuable feedback on user experience. However, there are also a lot of challenges, even risks, of using artificial intelligence to help designers, including maintaining design quality, protecting creativity, and ensuring designs remain user-centered. Moreover, a lot of people worry that with the rapid development of ChatGPT, many UI designers will be out of work in the future. This article discusses the influence of artificial intelligence represented by ChatGPT on UI design, including the advantages and challenges of AI in UI design. There is no doubt that as AI technology evolves, its role in UI design will expand rapidly, reshaping the digital experience in the future. But the question of whether AI will cause a lot of designers to lose jobs needs time to give us an answer.

 View pdf
View pdf


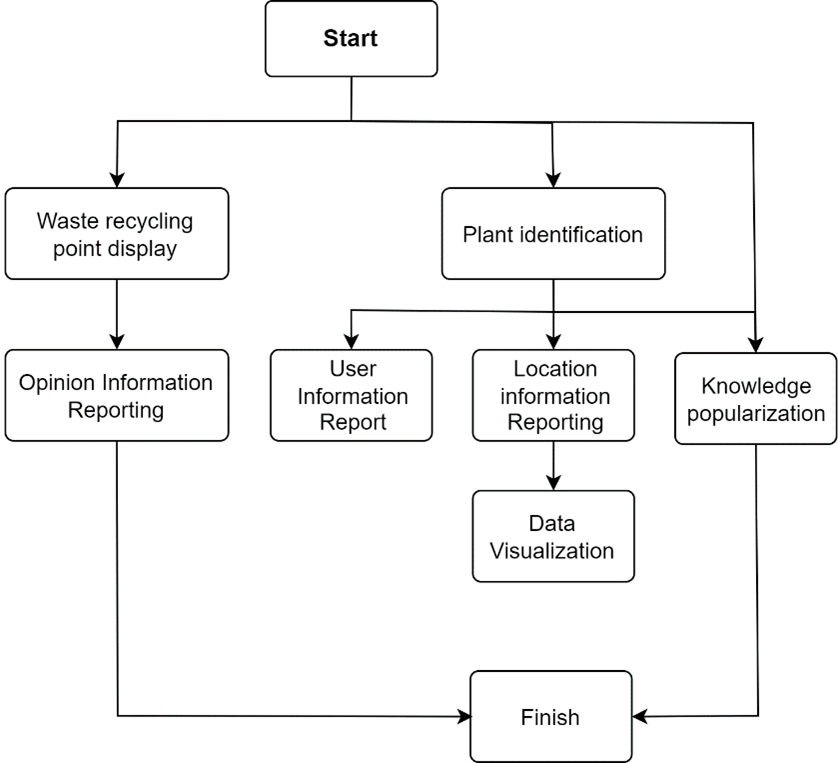
Forests are essential for ecological stability yet pose significant management challenges due to their expansive and remote nature. Despite advancements in data acquisition, there is a lack of tools that effectively combine image recognition with big data analytics for real-time monitoring. This study introduces a "Smart Forest Protection" mini program, developed using Spring Boot, which integrates these technologies to facilitate immediate and efficient forest management. The program features intelligent plant recognition, user-driven incident reporting, waste recycling point displays, and a platform for disseminating forest conservation knowledge. Additionally, a big data visualization platform illustrates the spatiotemporal distribution of forests in Zhuhai, aiding governmental and environmental agencies in making informed decisions that enhance forest conservation and promote sustainable practices.

 View pdf
View pdf




