

Volume 18
Published on October 2023Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and Data Science
The lack of access to extensive and varied datasets remains one of the major issues facing the field of machine learning, despite recent advancements. This is especially true in the healthcare sector, where it can be challenging to gather and use patient data for research because it is frequently compartmentalized across many healthcare providers. By enabling secure and privacy-preserving access to distributed data, blockchain technology, and federated learning have the potential to overcome these difficulties. In this article, we'll look at how federated learning and blockchain are used in the healthcare industry and talk about their benefits and drawbacks. We will also examine the Hedera platform, which makes use of blockchain technology and a new algorithm called Gossip Degree to provide a revolutionary method of federated learning. We will also go over the potential effects of federated learning on the healthcare sector and what it means for future research.

 View pdf
View pdf


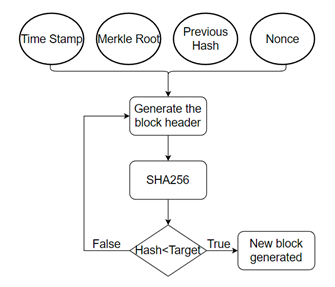
As a distributed ledger technology, blockchain has found widespread use in a variety of industries, including finance, the Internet of Things (IoT), healthcare, and manufacturing. This technology addresses the trust issue by converting a low-trust centralized ledger into a highly trusted distributed ledger maintained by various entities. Consensus algorithms are one of the fundamental building blocks of the blockchain, controlling how nodes cooperate and synchronize data to perform secure and reliable activities in a decentralized setting. This paper examines the extant mainstream consensus algorithms, introduces six representative consensus algorithms, analyses their benefits and drawbacks, and discusses the application scenarios and suitability of each consensus algorithm in various blockchain platforms.

 View pdf
View pdf


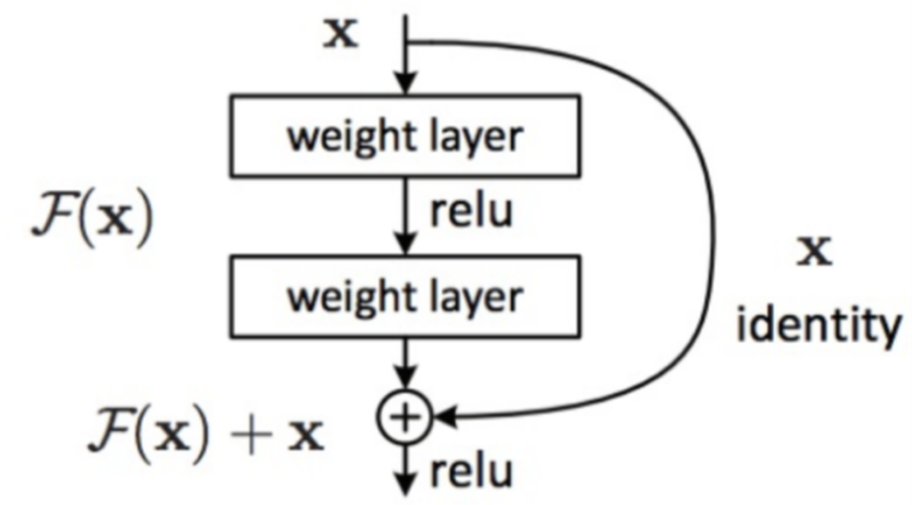
The task of handwritten digit recognition is to recognizing the handwritten digits from pictures. Applying machine learning based models to automatically perform handwritten digit recognition task can significantly improve efficiency. This paper applies two machine learning based models, including multi-layer perceptron and residual neural network, for such a task. Firstly, this paper introduces the basic concept of the simple multi-layer perceptron model and then presents the structure of the residual neural network model. Subsequently, such two models are trained on the MNIST corpus, one of the classical dataset for the handwritten digit recognition task. The data pre-processing, like the splitting of training and test set, is described. Also, the processes of testing and training of the two models are presented. According to the experiments on the test set of MNIST, it is observed that the residual neural network can achieve better performance where the accuracy score is 99.240%, while the accuracy score of the multi-layer perceptron model is 97.260%.

 View pdf
View pdf


Currently, advanced technologies such as big data, artificial intelligence and machine learning are undergoing rapid development. However, the emergence of cybersecurity and privacy leakage problems has resulted in serious implications. This paper discusses the current state of privacy security issues in the field of machine learning in a comprehensive manner. During machine training, training models often unconsciously extract and record private information from raw data, and in addition, third-party attackers are interested in maliciously extracting private information from raw data. This paper first provides a quick introduction to the validation criterion in privacy-preserving strategies, based on which algorithms can account for and validate the privacy leakage problem during machine learning. The paper then describes different privacy-preserving strategies based mainly on federation learning that focus on Differentially Private Federated Averaging and Privacy-Preserving Asynchronous Federated Learning Mechanism and provides an analysis and discussion of their advantages and disadvantages. By improving the original machine learning methods, such as improving the parameter values and limiting the range of features, the possibility of privacy leakage during machine learning is successfully reduced. However, the different privacy-preserving strategies are mainly limited to changing the parameters of the original model training method, which leads to limitations in the training method, such as reduced efficiency or difficulty in training under certain conditions.

 View pdf
View pdf


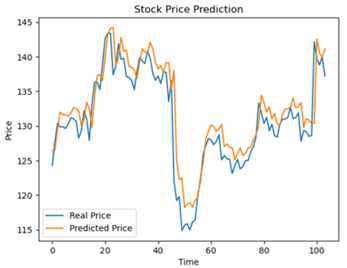
Stock analysis is a challenging task that involves modelling complex and nonlinear dynamics of stock prices and volumes. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) is a type of recurrent neural network that can capture long-term dependencies and temporal patterns in time series data. In this paper, a stock analysis method based on LSTM is proposed that can predict future stock prices and transactions using historical data. Yfinance is used to obtain stock data of four technology companies (i.e. Apple, Google, Microsoft, and Amazon) and apply LSTM to extract features and forecast trends. Various techniques are also used such as moving average, correlation analysis, and risk assessment to evaluate the performance and risk of different stocks. When compare the method in this paper with other neural network models such as RNN and GRU, the result show that LSTM achieves better accuracy and stability in stock prediction. This paper demonstrates the effectiveness and applicability of LSTM method through experiments on real-world data sets.

 View pdf
View pdf


Heart failure is a complex medical condition that arises due to the heart's inability to adequately circulate blood throughout the body, which is challenging to predict. This research aims to investigate three distinct models, namely logistic regression, random forest and decision tree generation algorithms. Logistic regression is essentially a logistic function applied to linear regression, and the loss function associated with linear regression is similar to the mean square error-like loss. In contrast, the loss function for logistic regression follows cross-entropy loss. while cross-entropy loss is often used in practice, it differs from mean square error loss. The derivative of cross-entropy loss is a difference that updates rapidly when the error is significant and slowly when the error is small, which is a desirable trait for the purposes. Decision tree generation algorithms utilize tree structures in which internal nodes represent judgments on attributes, branches represent outputs of judgments, and leaf nodes represent classification results. Random forest is an integrated learning algorithm that employs decision trees as the base learner. In classification models, multiple decision trees are processed for voting, while multiple decision tree results are processed for averaging in regression models. Experimental results indicate that random forest outperforms the other two models, albeit with a marginal difference. Further studies should incorporate additional models to identify a more suitable model for predicting heart failure.

 View pdf
View pdf


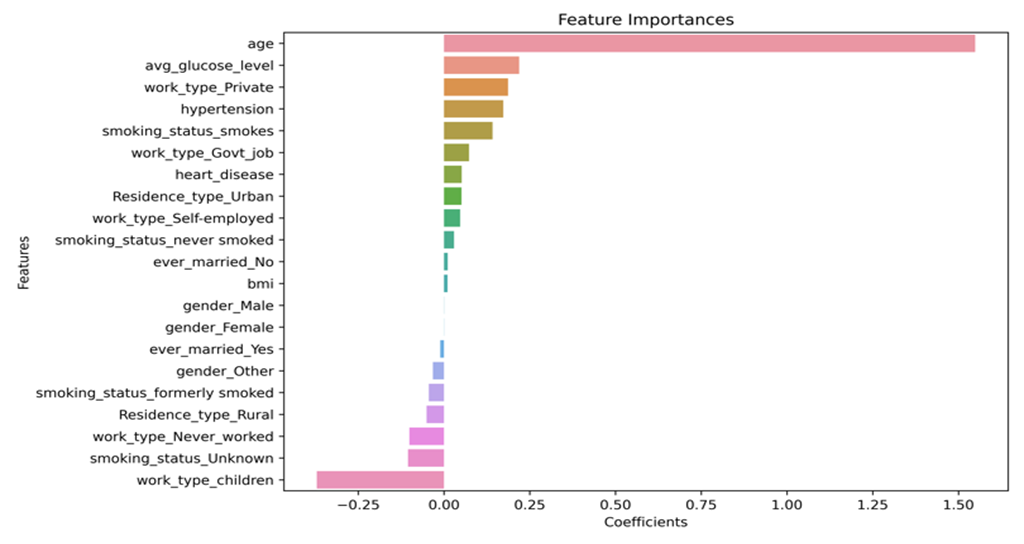
Stroke is a leading cause of death and disability worldwide, which requires the accurate and timely diagnosis for effective stroke management. Based on the Kaggle dataset, data preprocessing, which included addressing missing values, encoding categorical variables, and normalising numerical features, was done first in the study. Next, this paper implemented three commonly used machine learning models: logistic regression, decision tree, and random forest. To assess the performance of the models, the paper applied accuracy as the evaluation metric, which measures the proportion of correct predictions out of all predictions. This study also identified the most important features affecting stroke risk using feature importance analysis provided by the machine learning. All three models achieved accuracy rates, according to the experimental findings, albeit random forest outperformed the other two models. The reliability of the models for random forest, decision tree, and logistic regression were 0.963, 0.925, and 0.961, respectively. Feature importance analysis revealed that age, average glucose level, and work type were the most important predictors of stroke risk. Findings in this study suggest that machine learning algorithms, particularly the Logistic Regression model, can effectively predict the likelihood of stroke using the Stroke Prediction Dataset. These findings are in line with other research that also showed how machine learning has the potential to enhance stroke diagnosis. The identification of important features affecting stroke risk can provide valuable insights for clinicians and researchers in developing targeted interventions for stroke prevention and management.

 View pdf
View pdf


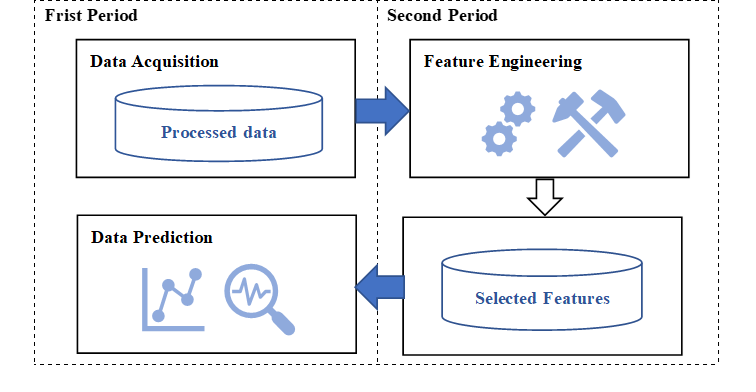
Artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science, an intelligent system that can simulate human thinking, recognize complex situations, acquire learning abilities and knowledge, and solve problems. With the continuous development of information technology, artificial intelligence techniques are increasingly being improved and applied to large-scale genetics research, image detection and classification in medicine. Predictive models for medical data can be built using a wide range of machine learning algorithms: decision trees, multilayer perceptrons, plain Bayes, random forests, and support vector machines, etc., thus processing massive, high-dimensional data and conducting medical research. This paper addresses the specific applications of artificial intelligence in medical practice.

 View pdf
View pdf



The article focuses on the application and development of the Stable Diffusion module in the field of artificial intelligence image generation. The article presents a comprehensive description, analysis and discussion of the module's overview, operating environment, usage methods and its instructions, and points out the corresponding advantages and disadvantages.

 View pdf
View pdf


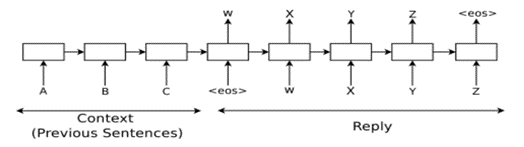
In the 21st century, there has been a growing importance placed on the "body" of artificial intelligence, particularly as it relates to language processing. Researchers have developed various machine learning models with a focus on language understanding, including Large Language Model (LLM), Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformers (BERT), and Natural Language Processing (NLP). These models have led to the development of numerous applications, such as ChatGPT-3.5, which has recently gained widespread attention. In addition to ChatGPT, other applications have also benefited from these language processing models, including Question Answering Systems (QAS). This paper will examine three QAS that have been enhanced by the context of ChatGPT, discuss the relevant applications, and analyze these different applications in order to predict future trends in this field. One notable QAS is OpenAI's GPT-3-powered AI that can answer questions about any topic. This application leverages the capabilities of GPT-3 to provide accurate and informative responses to a wide range of questions. Another QAS is IBM's Watson, which utilizes natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to understand and respond to user queries. Watson has been used in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and retail. A third QAS is Google's BERT-based system, which uses pre-trained language models to improve its responses to user queries. This system has been integrated into Google Search and other products, allowing users to receive more precise and relevant search results. Overall, the development of these QAS and other language processing applications marks an exciting period of progress in the field of artificial intelligence. As researchers continue to refine these models and explore new applications, we can expect to see even more advanced and sophisticated language processing systems emerge in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf




