

Volume 160
Published on June 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-SEML 2025 Symposium: Machine Learning Theory and Applications
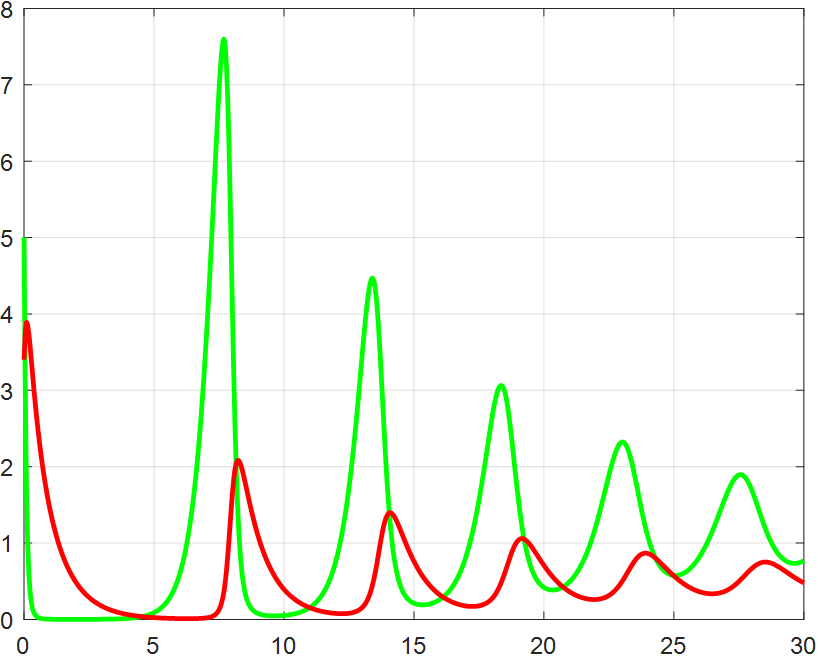
The invasive sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus poses a significant threat to aquatic ecosystems, particularly in the North American Great Lakes, due to its density-dependent sex determination mechanism. While traditional models have addressed population dynamics, they often overlook the nonlinear impacts of sex ratio variation on reproduction efficiency and ecosystem stability. This study develops a sex ratio-integrated multispecies Lotka-Volterra model to quantify how adaptive sex ratio dynamics in sea lampreys influence host-parasite interactions and energy flow. By incorporating a sex ratio factor into a tri-trophic system, we coupled nonlinear differential equations solved via the fourth-order Runge-Kutta method, with genetic algorithms optimizing parameters such as environmental carrying capacity and parasitic efficiency. Sensitivity analyses revealed threshold effects of sex ratio imbalance on genetic diversity, host resistance, and ecosystem oscillations. Results demonstrated that male-biased populations (η≥ 0.7) exhibit suppressed growth due to intra-sex competition and reduced female fecundity, aligning with logistic saturation. Conversely, female-biased ratios (η = 0.1) amplified host-parasite synchronization, increasing parasitic efficiency by 40% and destabilizing ecosystem equilibrium. Furthermore, parameter α modulated oscillation damping, while β regulated cycle periodicity, highlighting the nonlinear coupling between sex ratio dynamics and ecosystem resilience. These findings provide a mechanistic understanding of sex ratio adaptability in invasive species management and underscore the importance of integrating sex-specific traits into ecological models to predict ecosystem stability under anthropogenic and environmental stressors.

 View pdf
View pdf


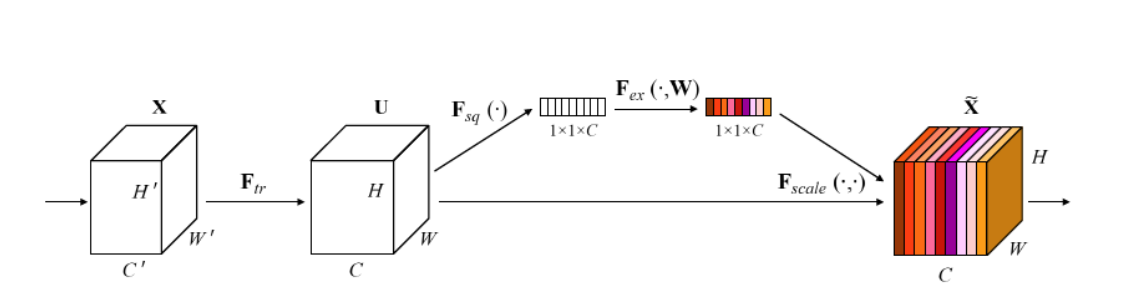
In response to the problem that most current automatic modulation recognition models cannot achieve high recognition rates while maintaining a certain training speed, this study proposes a neural network model based on depthwise separable convolution, residual connection, and channel attention mechanism. By using residual structures and Swish activation to alleviate gradient problems to support deep network training, dynamically optimizing feature channels using SE modules, and significantly reducing computational costs through depthwise separable convolution and global pooling, the model not only achieves lightweighting and ensures a certain training speed, but also has certain feature extraction capabilities, which can achieve high recognition rates. This study conducted comparative experiments to train different models in five SNR environments on the DeepSig RadioML 2018.01A dataset. The CNN_ResNet model can achieve a recognition rate of 92.67% in a 10dB environment, which is 20.07% higher than the basic CNN model. The results of the experiments demonstrate that the improved model exhibits a significantly higher recognition rate compared to other models, while maintaining a certain training speed.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the continuous advancement of infrastructure development, ensuring the health and safety of existing structures has become increasingly critical. Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) plays a vital role in assessing the integrity and longevity of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructures. However, traditional monitoring methods often face challenges related to efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. The rapid development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has opened new opportunities for SHM, offering intelligent, automated, and highly precise monitoring solutions. By integrating AI with SHM, it is possible to enhance detection accuracy, improve predictive maintenance, and significantly reduce operational costs. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive summary of AI technologies that have been successfully applied in the field of SHM. By reviewing current advancements, we seek to contribute to the ongoing development of intelligent monitoring systems and offer new perspectives on the future integration of AI in SHM.

 View pdf
View pdf


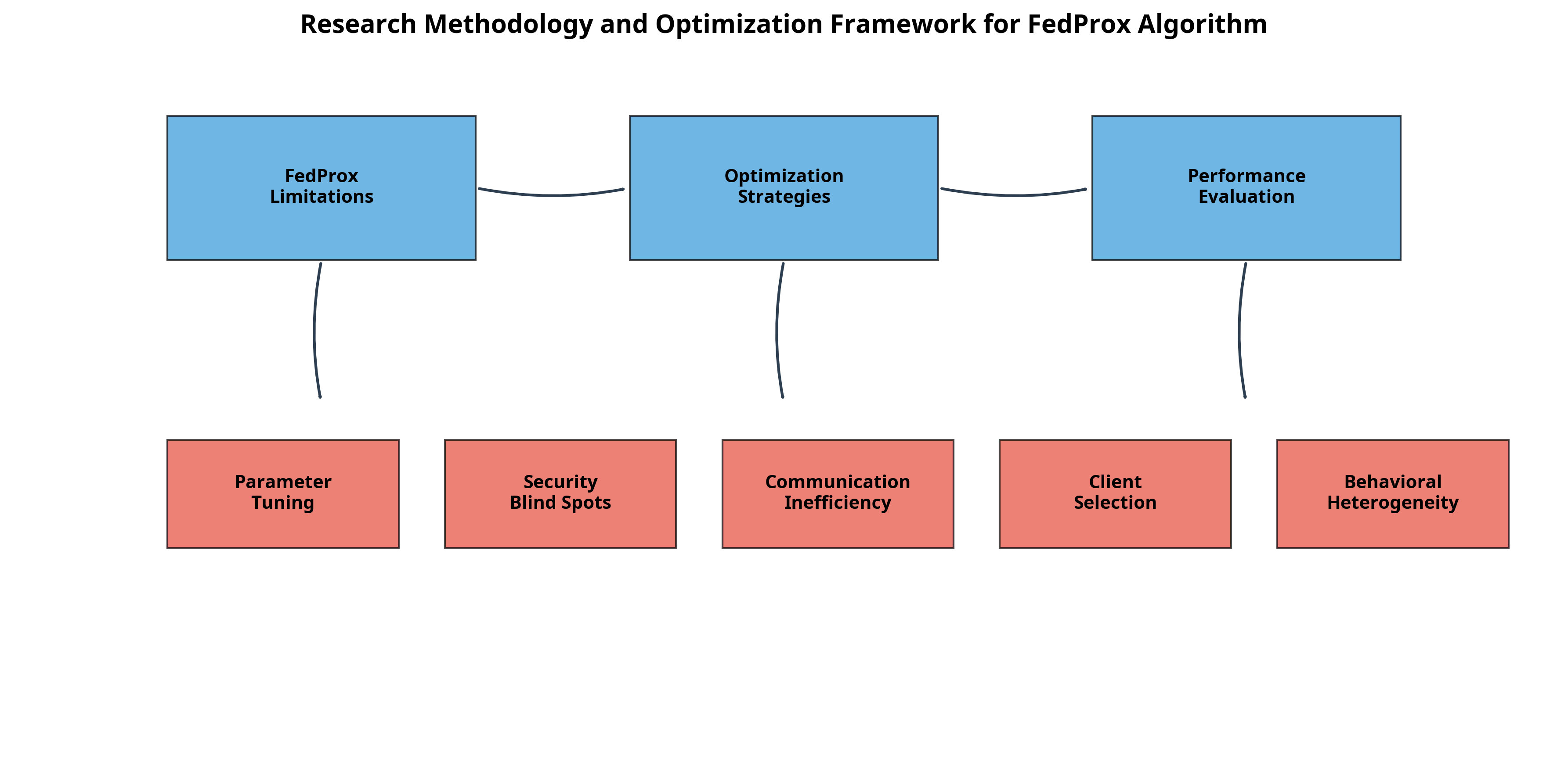
Federated Learning (FL) has to decentralize the model training but maintains users’ data privacy, hence it is potentially essential in critical applications such as healthcare, finance, etc. For FL, the main obstacles remain the client heterogeneity and the sensitivity to any security attacks, which severely hinder its application to real scenarios. In this paper, the thesis studies the edge cases of the Federated Proximal (FedProx) algorithm that incur this phenomenon and suggests six ways for mitigating them. More precisely, the thesis considers adaptive regularization, knowledge distillation and transfer, optimization on efficiency, security defenses, client selection strategies, and approaches dealing with behavioural heterogeneity. Experiments conducted on benchmark datasets such as Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR)-10 and Federated Extended Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology (FEMNIST) demonstrate that these strategies can improve FedProx accuracy by up to 7.2% and reduce communication rounds by up to 30%. The thesis’s findings enhance the robustness, scalability, and personalization of FedProx in heterogeneous and adversarial settings. Such enhancements have a practical benefit for implementing FL systems over various real-world settings.

 View pdf
View pdf


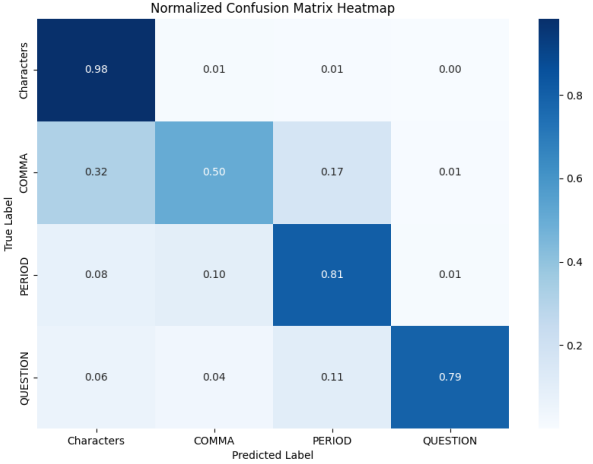
This paper explores the application of Chinese punctuation restoration technology utilizing the pretrained Transformer model XLM-RoBERTa-Base. With the increasing use of digital communication and development of automatic speech recognition, the absence of punctuation can lead to problems like misunderstandings, thus highlighting the importance of effective punctuation restoration technology. This paper focuses on Chinese punctuation restoration with data collected from the IWSLT2012 dataset, where punctuation signs are replaced with designated labels for preprocessing. The Transformer model is fine-tuned on this dataset, focusing on restoring punctuation tasks. After the training, the model's performance is evaluated using metrics including loss, accuracy, PR curves, and confusion matrices. The results indicate that, compared to existing models, the model outperforms in restoring Period and Question. However, the capacity of restoring Comma fails to be enhanced and remains at a moderate level. Also, the punctuation restoration of Chinese faces a performance drop compared to English but improvement compared to Bangla, with same model architecture. Over all, our findings demonstrate the applicability of pretrained Transformer models in Chinese punctuation restoration and suggest avenues for future improvements, particularly in enhancing comma restoration.

 View pdf
View pdf


In recent years, the development of music composition software has revolutionized the way music is created and produced, making it more accessible and efficient. This essay compares three prominent music creation platforms, i.e., Sibelius, Cubase, and GarageBand, highlighting their unique features and societal benefits. Sibelius, renowned for its robust music notation tools, caters primarily to composers, educators, and students focusing on score-based music. Cubase, a professional digital audio workstation (DAW), offers advanced editing, mixing, and production capabilities, making it ideal for both studios and educational environments. GarageBand, with its intuitive interface and integration across Apple devices, serves as an excellent entry point for beginners and an effective educational tool. Together, these software programs showcase how technological advancements are shaping the music industry, making creation, learning, and production more accessible to a wider audience. The significance of this research lies in understanding how different music software platforms serve varying needs, enriching the creative process and contributing to the democratization of music education.

 View pdf
View pdf


Algorithmic composition, the usage of computational processes to create musical works, has evolved significantly with advances in technology, offering composers new creative possibilities. This study presents a comparative analysis of three distinct approaches to algorithmic music composition, i.e., translational models, mathematical models, and AI tools. Translational models establish mappings between non-musical domains and musical parameters, creating compositions that reflect patterns from diverse sources. Mathematical models leverage formal structures like stochastic processes, fractals, and combinatorial techniques to generate music with distinctive organizational principles. AI tools, particularly neural networks and transformer models, learn patterns directly from musical data to generate compositions that capture nuanced stylistic elements. Through detailed examination of each method's principles, technical implementation, and applications, this research reveals their complementary nature rather than competing alternatives. Each approach offers unique advantages while facing specific limitations in areas such as control, accessibility, and aesthetic flexibility. It is concluded that the most promising direction for algorithmic composition lies in the integration of these different approaches, combining the cross-domain connections of translational models, the structural elegance of mathematical approaches, and the pattern-learning capabilities of AI tools. Such hybrid systems could leverage the strengths of each method while mitigating their individual limitations, expanding the creative possibilities available to composers and enriching the understanding of computational creativity.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the widespread adoption of IoT devices, firmware vulnerabilities have emerged as a significant cybersecurity threat. These vulnerabilities can lead to devices being controlled, data breaches, and even physical damage, severely impacting personal privacy and the security of critical infrastructure. This paper aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the formation, detection, assessment, management, and prevention of IoT firmware vulnerabilities, exploring their significance and role. Through a literature review and case studies, combined with techniques such as static analysis, fuzz testing, and deep learning, this study systematically investigates the causes of firmware vulnerabilities and their preventive measures. The research reveals that the causes of IoT firmware vulnerabilities primarily include design flaws, errors during the development process, and supply chain issues. This paper proposes various detection methods, including static analysis, fuzzing, and deep learning-based detection techniques, and discusses vulnerability management and prevention measures from technical, management, and policy/regulatory perspectives. The research findings indicate that the prevention of IoT firmware vulnerabilities requires a multi-faceted approach, integrating artificial intelligence and big data technologies to build a comprehensive security protection system.

 View pdf
View pdf


The high-speed rail communication network has significant characteristics such as high mobility, large signal penetration loss, and sudden traffic volume, and it faces challenges such as the Doppler effect, frequent switching, complex interference, and network capacity bottlenecks. This paper mainly focuses on the communication network in the high-speed rail scenario, comprehensively expounds its characteristics, challenges, optimization and signal enhancement technologies, and conducts an analysis in combination with cases from multiple regions. Through means such as scientific site selection, reasonable layout, algorithm improvement, interference suppression and signal enhancement, many projects have achieved remarkable results. For example, after the optimization of a 500-kilometer high-speed railway line, the signal coverage rate in mountainous areas has been significantly increased, the switching success rate has been significantly improved, and the data rate and traffic processing capacity have been enhanced. The optimization of the Changzhou section of the Beijing-Shanghai High-Speed Railway by China Telecom Changzhou Branch has increased the success rate of parallel section switching, enhanced the network speed and reduced the complaint rate. In the future, high-speed rail communication will develop in the direction of multi-technology integration, intelligent management, green and low-carbon development, and standardized cross-industry collaboration.

 View pdf
View pdf


Contemporarily, various composing software is developed. This study explores the application of two popular music production software programs, GarageBand and FL Studio, in educational settings. The primary goal of the research is to compare and contrast the features, ease of use, and suitability of these software programs for music education, while also offering a perspective on future developments in the field. Through a review of existing literature, the study highlights that while the use of computer music composition software has become increasingly widespread, its application in K-12 education remains limited. The findings suggest that while both GarageBand and FL Studio offer valuable tools for music creation, there is still a need for specially designed software to meet the developmental needs and learning preferences of students of different ages in K-12This research emphasizes the potential to enhance the integration of computer music into education by developing more age-appropriate software, ultimately fostering creativity and music skills at an earlier age and encouraging greater emphasis on music technology in future educational frameworks.

 View pdf
View pdf




