

Volume 123
Published on December 2024Volume title: Proceedings of ICEMGD 2024 Workshop: Policies to Enhance Sustainable Development through the Green Economy
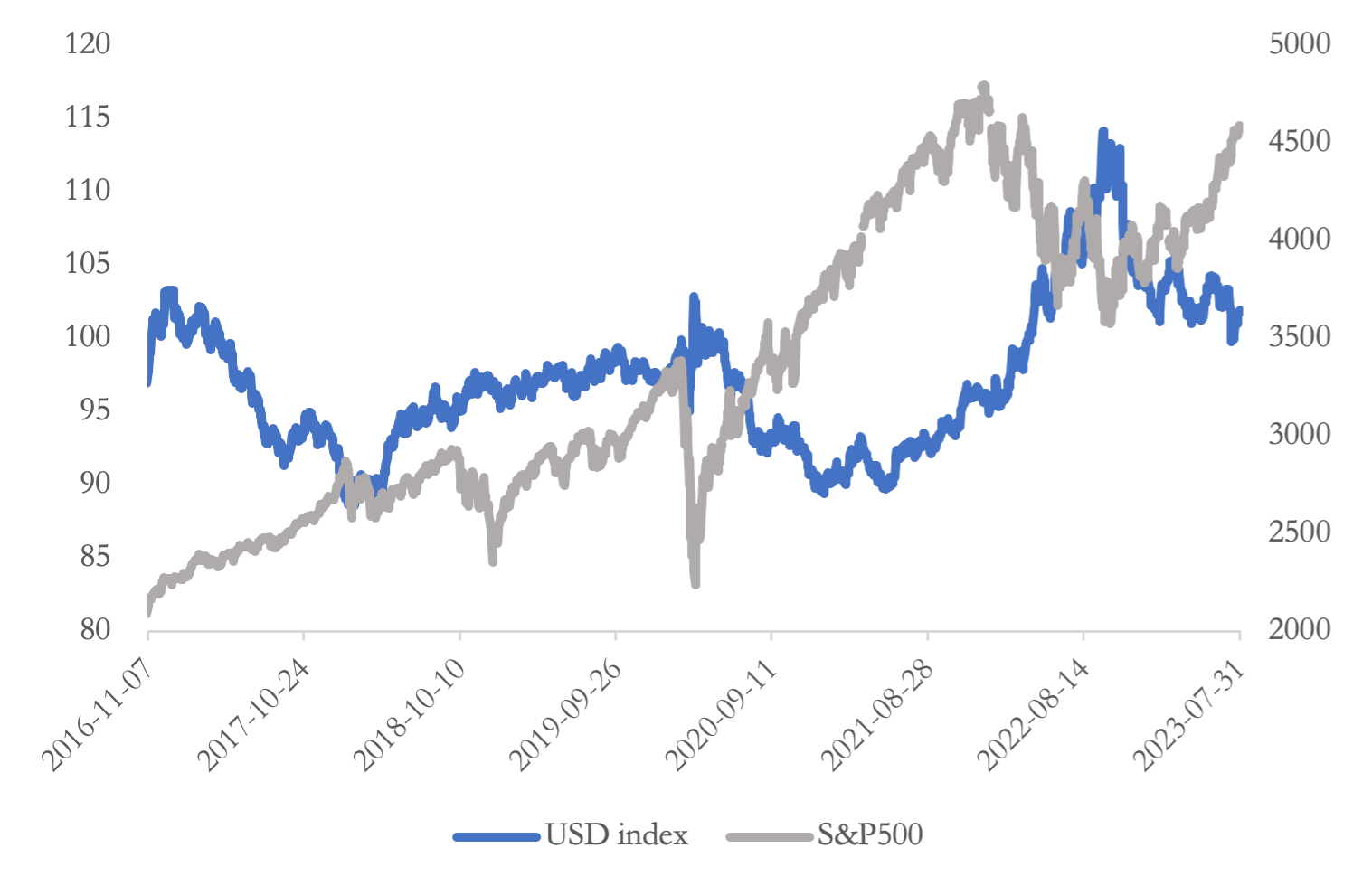
This paper investigates existence of equilibrium relationships among the USD index and S&P500 in the long term in the United States. By applying correlation matrix analysis to daily data for the 2016:07:30–2023:08:01 period, this paper finds that there was a slight negative correlation between the USD index and the S&P 500. Basing on the Augmented Dickey-Fuller test (ADF test), this paper shows that that the correlation between the USD index and the S&P 500 is stable while vector autoregressive model (VAR model) proving that changes in the USD index can cause changes in the S&P 500 index. Firstly, using ADF test and VAR model to investigate the relationships between the USD index and A&P500, this paper reveals not only judge the negative relationship between this two, but also studying the stability of this relationship, proving the validity to explain the changes of S&P500 by the changes of the USD index. This conclusion can act as a good judging basic for US leaders to make economic decisions such as raising or lowering interest rates.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study investigates how the new energy industry (NEI) contributes to the economy's growth. As time went on, more and more countries gradually accepted the concept of new energy development. Evidence shows that NEI helps economic growth and indicates significant benefits including job creation, technological advancements, and enhanced productivity. Besides make direct contributions to the economic growth, the application of NEI also have some positive indirect effect on the economy. NEI increases long-term profits by reducing health care costs and environmental maintenance caused by pollution. However, current research reveals gaps, particularly in the long-term economic impacts of cleaner energy, regional disparities, and the integration of social well-being metrics. Future studies are proposed to address these gaps, including detailed analyses of the impacts on small and medium enterprises, comparative policy effectiveness, and the effects on rural and remote areas. By advancing research in these areas, policymakers and stakeholders can better understand and leverage the economic benefits of the NEI to support sustainable development and global financial stability.

 View pdf
View pdf


In China, the College Entrance Examination weights great in both students' and parents' hearts, which is even recognized as the rare chance to change a people's fate. At this circumstances, heavy homework, countless tests, little break time, burning night oils and even extracurricular tutoring on the weekends have become the daily routine for Chinese high school students, which have hurt their health conditions and added great burden on their mental health. To curb this long-standing issue caused by this phenomenon, a new educational policy called Double Reduction was released by the Chinese government on 2021 and nine Chinese cities are selected as the national policy pilot areas to test the effect in advance. This paper aims to verify the impact of the Double Reduction Policy in some provinces in which lie the selected policy pilot areas. Through continuous difference-indifference method, this study found no significant correlation between the Double Reduction and the College Entrance Examination performance in these areas. Policy makers should make proper actions to implement this new policy, in order to lighten the physical and mental burden of students and the financial burden of parents while take students learning effectiveness into consideration meanwhile.

 View pdf
View pdf


Global climate change has increasingly posed a serious threat to coastal cities, rendering them particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of rising sea levels, more frequent and intense extreme weather events, and the shifting patterns of climate. Traditional urban planning methods, which had been the cornerstone of city development, were found to be inadequate in addressing these escalating challenges. The previous studies often failed to account for the critical importance of integrating climate factors into the planning process, leading to vulnerabilities in urban infrastructure and design. This study meticulously examined the limitations of these conventional urban planning approaches and explored the potential for adapting urban planning strategies in China’s coastal cities to better respond to the looming threat of climate change. By conducting a thorough analysis of the impacts of high temperatures, floods, and other climate-related events, the study proposed a comprehensive series of response measures tailored to the specific conditions of the time. These measures included the integration of green policies into urban planning to enhance environmental sustainability, the strategic selection of building materials aimed at mitigating urban heat, and the enhancement of water resource management systems to alleviate the urban heat island effect. Moreover, the study closely investigated existing climate response measures through detailed case studies in Xiamen and Dalian, two prominent coastal cities in China. The primary objective was to significantly enhance the resilience of these cities, effectively reduce the risks associated with climate change, and promote a path towards sustainable development. Ultimately, the goal was to create more livable, safer, and sustainable urban environments that would be better equipped to face the challenges posed by an unpredictable climate future.

 View pdf
View pdf


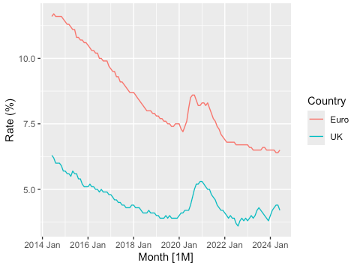
The objective of this study is to predict the unemployment rate in the UK and the Eurozone for the years 2014 to 2024 using the time series analysis model known as ARIMA. It is essential to be informed of changes to employment rates in order to address them and changes in the economic environment including historical occurrences such as Brexit, COVID-19, and shifts in the labor market. The ARIMA model was used because it fits non-stationary time series, which is a feature present in the employment rates of both time series. The monthly unemployment rates for each state were seasonally adjusted and the ARIMA parameters were estimated by the automatic method. The study observed that while the interior portion of the trading cycle was effectively predicted by the ARIMA model, it failed to do so for the short-term UK unemployment in the post-2023 period because of exogenous shocks. However, the model was equally successful in predicting a marginal contraction in unemployment rates in the Euro zone after 2023. By performing the Ljung-Box test, it was established that the residuals of the models were random and therefore, the models were fit. Accordingly, the results suggest that the estimates derived from the ARIMA model are beneficial in economic predictions, which helps governments to design better social security programs and other economic plans to address the changing employment landscape.

 View pdf
View pdf


As problems such as the increase in extreme weather, rising sea levels, and social inequality continue to sharpen with the intensifying climate change, changes are demanded. The cement and iron and steel industries are among the major spheres responsible for the rising global temperature. Carbon reduction methods cannot fully solve the problem and help these industries reach carbon-neutral emissions. Therefore, carbon capture (CC) technology is urgently needed. This article introduces the application of pre-combustion carbon capture (PreCCC), post-combustion carbon capture (PostCCC), and oxyfuel combustion carbon capture in the cement industry and the iron and steel industry. Research has shown that oxyfuel combustion is one of the most assuring pathways to reach carbon neutrality in cement plants since problems of temperature management can be solved by recycling part of the fuel gases, and its cost is relatively lower than the other methods. However, PostCCC is a better solution in the iron and steel industries. Although technological innovations in physical absorption and chemical absorption are still needed, PostCCC can mitigate a large portion of steel plants’ carbon footprint. Carbon capture intensity can be increased with further technological development in combining PostCCC and oxygen-rich combustion. The combination of different pathways may be a novel hypothesis, but it has a great possibility of alleviating the carbon emission of the industrial sector.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid increase in global demand for high-performance batteries, particularly driven by the growth of electric vehicles and large-scale clean energy storage systems, the need for effective battery recycling methods has become more pressing than ever. This paper provides a comprehensive examination of both traditional and innovative methods for battery recycling, which has become increasingly critical due to the growing environmental concerns associated with the disposal of batteries, particularly from electric vehicles and large-scale energy storage systems. The study analyzes three primary recycling methods: mechanical processing, chemical recovery, and direct reuse, detailing their underlying principles, advantages, and limitations. In addition, the paper introduces an innovative recycling approach that integrates bioremediation microorganisms and nanotechnology to enhance the efficiency of metal recovery and minimize environmental impact. This novel method offers a pollution-free, sustainable solution that addresses the inefficiencies and environmental risks associated with traditional recycling techniques. Through a comparative analysis, the study highlights the potential of this innovative approach to revolutionize battery recycling, contributing to more sustainable practices and the circular economy. The findings emphasize the importance of adopting advanced recycling technologies to meet the increasing demand for battery materials while ensuring environmental protection.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study examines the determinants of NBA group execution from 2018 to 2023. It investigates the relationship between key variables such as group finance, player productivity, harm status, and coaching encounter, employing a fixed-effects board relapse demonstrate. The point is to get it how these factors impact a team's winning rate, with a center on the interaction between monetary venture and on-court victory. The discoveries uncover that higher finance, effective players, and solid home-court execution essentially improve a team's winning rate. Moreover, the ponder highlights the antagonistic impacts of player wounds and the basic part of adjusted hostile and cautious methodologies. The comes about emphasize the require for NBA groups to embrace a multifaceted approach, combining monetary speculation with vital gameplay and group cohesion to realize maintained victory. This research offers important experiences for group directors and decision-makers within the NBA, giving a establishment for arrangement suggestions to optimize group execution in future seasons. The study's inventive utilize of comprehensive information and econometric modeling contributes to the writing on sports financial matters and group execution examination.

 View pdf
View pdf


Wind energy has a long history and has evolved into a crucial component of sustainable energy solutions. This paper introduces the development and distribution of wind energy, explaining the components and functionality of wind turbines, particularly Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT). It discusses their advantages, such as sustainability and low operational costs, as well as their disadvantages, including site selection challenges, noise, aesthetic concerns, and environmental impacts on wildlife. The paper also explores the significant global expansion of wind energy, highlighting the rapid increase in wind power capacity and its role in the global energy mix. Moreover, the study evaluates the efficiency of wind turbines, considering factors such as blade design, pitch control, and the Betz limit. It suggests advanced site assessment, noise reduction technologies, and environmental impact mitigation strategies to optimize wind energy efficiency and acceptance. These strategies are essential for maximizing the potential of wind energy as a key player in the transition to a sustainable energy future.

 View pdf
View pdf


This article explores the integration of truck platooning and clustering algorithms within logistics path planning. Clustering algorithms divide a specific area into several zones, each with a designated distribution center for further route planning. This approach ensures that the route planning process extends the distance that truck fleets can travel together in platoon formation, maximizing the benefits of truck platooning. The integration of clustering and platooning not only enhances environmental sustainability by reducing fuel consumption and emissions but also increases operational efficiency. The review examines key studies employing machine learning and real-time data integration to optimize these techniques, addressing implementation challenges, technological advancements, and future research opportunities. Additionally, it investigates various methodologies to combine these techniques, including multi-agent systems and hierarchical clustering, highlighting significant improvements in fuel efficiency, cost savings, and emissions reduction. Case studies demonstrate practical benefits such as fuel savings ranging from 10% to 20% and reduced delivery times. The article emphasizes the potential for these integrated systems to revolutionize logistics operations through improved efficiency and sustainability, outlining the challenges and future directions for research and implementation in this field.

 View pdf
View pdf




