1. Introduction
Although strep throat has similar symptoms to other types of common throat disorders, it is uncommon in adults and usually accounts for a small percentage of sore throats. Streptococcal strep throat is most likely observed in children, but it affects people of all ages. If left untreated, the disease can cause complications such as kidney inflammation or rheumatic fever, to be general, that is to include most systematic infections. Throat pains due to bacteria infection is hardly a comfortable experience. Patients could undergo the following symptoms: Sore throat which usually comes quickly, pain when swallowing, tonsils’ strut and redness, in some cases, accompanied by white plagues or purulent, small spots at the back top areas of the mouth (soft or hard palate), swollen lymph nodes in the neck, tenderness, fever, headache, rash, nausea or vomiting, especially in young children, and body aches[1].
Streptococcal strep throat is typically caused by a bacterium called Streptococcus pyogenes, a bacterial pathogen specific to humans, can cause a wide range of disorders in the infected, consisting of both slight localized infection and fatal invasive infection[2]. Streptococcal gram-positive cocci grow in forms of pairs or chains. These cocci are categorized into mainly three types according to the type of blood agar hemolysis: beta-hemolysis (complete lysis of red blood cells), hemolysis (green hemolysis), and gama-hemolysis (no hemolysis). beta-streptococcus hemolytic is characterized by group A streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes) and group B streptococci (Streptococcus agalactis).
The negative impact of strep throat in a worldwide scale is tremendous, considering an average number of around 600 million people (mostly children) a year[3] contracting such disease.With some children, they will still have to have their tonsils removed even after the treatment with antibiotics. To conclude, streptococcal pharyngitis has greatly affected the lives of people around the world.
Streptococcal pharyngitis, as a bacterial led disease, can be treated with antibiotics designed to cure infections. There are two specific kinds of them are found to be very useful: one is amoxicillin, and the other is azithromycin. The two kinds of drugs, though both being effective, share little similarities. With the former being a beta-lactam antibiotics synthetic and the latter being a macrolide-type antibiotics, they have different structures, properties, as well as different mechanisms of curbing and killing bacteria.
2. Descriptions of chemical characteristics of both drugs
2.1. amoxicillin
Amoxicillin, a widely used antibiotic belonging to the genre of beta-lactam antibiotics, mainly attacks bacteria’s cell walls, forcing their cell walls to break and thus reaching its aim of killing the invaders. Diseases that could be treated with such drug are numerous both localized ones and systemic ones, including tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, and infections of the ear, nose, throat, skin, or urinary tract[4].
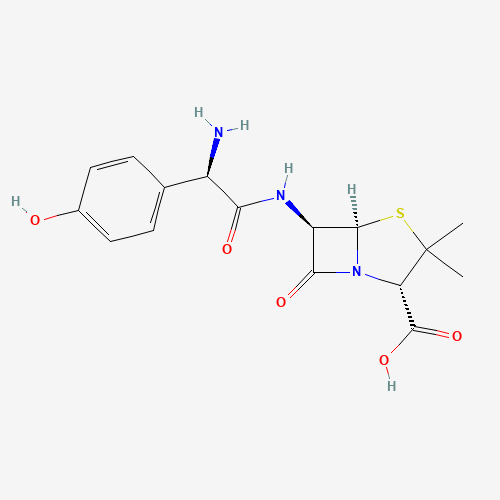
Figure 1. chemical structure of amoxillin
The biological features of amoxicillin is largely due to its chemical structures. Owning a molecular weight of 365.4 gram/mol ,the amoxicillin (C16H19N3O5S) is not a big molecule, as shown in figure 1. Its formal description is a penicillin in which the substituent at position 6 of the penam ring is a 2-amino-2- (4-hydroxyphenyl) acetamido group[5].
The mechanism of amoxicillin, as well as other beta-lactam antibiotics and semi synthetics, are to target on the penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) that can build the bacteria’s cell wall and thus can disrupt peptidoglycan synthesis, which causes death of bacteria. As a result, this kind of synthetics are only effective when facing rapidly multiplying organisms. Once these β-lactam antibiotic binds covalently and irreversibly to PBP, the cell walls of the bacteria would be destroyed and dissolved. The difference in lineage and activity of β-lactam antibiotics is largely related to their relative affinity for different PBPs. To bind with PBP, β-lactam antibiotics must first spread through the outer shells of the bacteria. Gram-negative bacteria are all equipped with an extra lipopolysaccharide layer that reduces the permeability of antibiotics. As a result, bacteria that are gram-positive are generally more sensitive to β-lactam than gram-negative bacteria. Due to the poor cytopathy of penetration in mammals, β-lactam antibiotics are normally not a good choice when facing intracellular pathogens.
Amoxicillin administration is also frequently used together with β-lactamase inhibitors, such as clavulanate and sulbactam. These inhibitors act through binding irreversibly with the organism's β-lactamase, resulting in the original β-lactam amoxicillin ring’s resistance. These drugs do not have inherent bactericidal activity; However, when combined with amoxicillin, they may expand the spectrum of amoxicillin to organisms that produce β-lactamase[6].
2.2. azithromycin
Another antibiotic that is utilized to treat strep throat is azithromycin. It is a broad-spectrum macrolide antibiotics with a long half life. This is due to its stable chemical structure. Azithromycin is also capable of penetrating tissues.
This drug, which has a molecular weight of 749.0 g/mol, is more sophisticated in structure compared to amoxicillin. Similar to erythromycin in structure, azithromycin [9-deoxo-9a-aza-9a-methyl-9a-homoerythromycin] belongs to macrolide azalactone subclass and contains a 15-membered ring with methyl-substituted nitrogen instead of carbonyl at position 9a on the glycosidone ring, thus preventing its metabolism. [7]
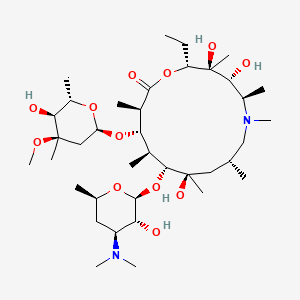
Figure 2. chemical structure of azithromycin
Azithromycin (see figure 2) inhibits the growth of microorganisms by cutting the pathway of protein synthesis. Similar to other macrolide antimicrobials, azithromycin binds to the 50S fraction of the 23S bacterial ribosome subunit. This suppresses the protein synthesis of bacteria by blocking the transport of aminoacyl-tRNA and the passage of proteins from growth through ribosomes. Compared with erythromycin, azithromycin is less likely to dissociate with gram-negative ribosomes, resulting in higher effects against pathogens that are gram-negative. Acting as a bacteriostatic agent, azithromycin undergoes similar processes like other macrolides and protein synthesis inhibitors, they all stop the growth of certain bacteria rather than killing them directly. Nevertheless, usually at high usage amounts, azithromycin will likely show bactericidal effects against certain bacteria, such as streptococcus and Haemophilus influenzae[8].
3. Side effects and possible negative outcomes of treatments
Although the two mentioned drugs prove to be very effective when facing diseases like strep throat, some patients that are allergic to these medicines may experience unpleasant side effects.
Amoxicillin:
General adverse effects: Amoxicillin is generally a well-tolerated synthetic drug, but patients may still undergo symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Hepatotoxicity: specific hepatic impairment has been reported in patients receiving amoxicillin. The pattern of serum enzymes associated with liver injury is hepatocyte with markedly elevated AST and ALT. Alkaline phosphatase elevation is small. Most patients recover quickly after discontinuation of amoxicillin and quickly after discontinuation of the drug. The cause of liver damage associated with the use of amoxicillin. Rare cases of acute liver failure and vanishing bile duct syndrome have been reported. Corticosteroids are commonly used to treat allergic manifestations of penicillin-associated immunoallergic hepatitis. Likelihood score: B (clinically obvious cause of liver damage is highly likely but rare).[9]
Other adverse effects may include disorders in nervous system, skin, gastrointestinal tract, and circulation system.
Azithromycin:
Azithromycin is actually considered as one of the safest macrolides and cause only very few patients having adverse effects. It is also occasionally linked with hepatotoxicity and mainly includes hepatocyte damage within 1 to 3 weeks of drug use. Clinical features of hepatotoxicity include cholestatic jaundice and elevated aminotransferase concentrations.
As with other macrolides, gastrointestinal adverse effects such as nausea and diarrhea are the most commonly reported adverse effects of azithromycin. All macrolides exhibit dose-dependent activation of enterodylinkin receptors, which stimulates gastric motility. (Because of this mechanism, erythromycin is widely prescribed by clinicians for gastroparesis.)[10]
4. Conclusion
In the context above, the author mainly introduced a bacteria intrigued disease called the strep throat, caused by streptococcus pyogenes. Streptococcal pharyngitis can greatly affect an individual’s daily routine, causing uncomfortable symptoms like a sore throat. This disease also owns a worldwide influence due to its large infection number. Antibiotics and drugs treating strep throat are also included, to be more specific, amoxicillin and azithromycin. These two drugs’ chemical characteristics and structures are being described, as well as their mechanisms of actions. The last parts of the passage mainly focused on the two medicines’ possible adverse effects on patients, with azithromycin being safer than amoxicillin.
References
[1]. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/strep-throat/symptoms-causes/syc-20350338
[2]. Ibrahim J, Eisen JA, Jospin G, Coil DA, Khazen G, Tokajian S. Genome Analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes Associated with Pharyngitis and Skin Infections. PLoS One. 2016;11(12): e0168177
[3]. https://www.lji.org/ “considering an average number of around 600 million people a year contracting such disease”
[4]. https://www.drugs.com/ “tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, and infections of the ear, nose, throat, skin, or urinary tract”
[5]. National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 33613, Amoxicillin. Retrieved July 25, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Amoxicillin.
[6]. Weber DJ, Tolkoff-Rubin NE, Rubin RH. Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate: an antibiotic combination. Mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, antimicrobial spectrum, clinical efficacy and adverse effects. Pharmacotherapy. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):122-36.
[7]. National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 447043, Azithromycin. Retrieved July 30, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Azithromycin.
[8]. Jelić D, Antolović R. From Erythromycin to Azithromycin and New Potential Ribosome-Binding Antimicrobials. Antibiotics (Basel). 2016 Sep 01;5(3)
[9]. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda (MD): Oct 20, 2020. Amoxicillin.
[10]. Barboza JL, Okun MS, Moshiree B. The treatment of gastroparesis, constipation and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth syndrome in patients with Parkinson's disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16(16):2449-64.
Cite this article
Gao,C. (2024). Introducing amoxicillin and azithromycin in treating streptococcal pharyngitis. Theoretical and Natural Science,47,97-101.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Environmental Geoscience and Earth Ecology
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/strep-throat/symptoms-causes/syc-20350338
[2]. Ibrahim J, Eisen JA, Jospin G, Coil DA, Khazen G, Tokajian S. Genome Analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes Associated with Pharyngitis and Skin Infections. PLoS One. 2016;11(12): e0168177
[3]. https://www.lji.org/ “considering an average number of around 600 million people a year contracting such disease”
[4]. https://www.drugs.com/ “tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, and infections of the ear, nose, throat, skin, or urinary tract”
[5]. National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 33613, Amoxicillin. Retrieved July 25, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Amoxicillin.
[6]. Weber DJ, Tolkoff-Rubin NE, Rubin RH. Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate: an antibiotic combination. Mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, antimicrobial spectrum, clinical efficacy and adverse effects. Pharmacotherapy. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):122-36.
[7]. National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 447043, Azithromycin. Retrieved July 30, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Azithromycin.
[8]. Jelić D, Antolović R. From Erythromycin to Azithromycin and New Potential Ribosome-Binding Antimicrobials. Antibiotics (Basel). 2016 Sep 01;5(3)
[9]. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda (MD): Oct 20, 2020. Amoxicillin.
[10]. Barboza JL, Okun MS, Moshiree B. The treatment of gastroparesis, constipation and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth syndrome in patients with Parkinson's disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16(16):2449-64.









