1. Introduction
Across the globe, lung cancer is the highest percent of cause of death. There are many causes of lung cancer. Smoking is the main cause of it, due to smoking cancer patients account for about 85% of all lung cancer cases. Diagnosing at an advanced stage usually means many treatment options are not available. In order to detect cases early and improve the survival rate of patients with this disease, we need to screen high-risk groups [1]. In addition, the general population also needs primary prevention, which can reduce the incidence of lung cancer and save lives. At present, the targeted therapy of NSCLC has developed rapidly, and the understanding of molecular carcinogenic mechanisms and the determination of carcinogenic drivers in the biomedical industry have also greatly promoted its development. Therefore, with effective and advanced treatment, the survival period of lung cancer patients has been extended. In more than 2 million people who are newly diagnosed with lung cancer each year, there are more than 80% of lung cancer patients have a history of smoking [2]. In addition to smoking, heredity also has a high risk. There are also some other risks, such as age and unhealthy diet. Avoiding bad living habits can help to prevent lung cancer [2].
During a long period of research and experiments on lung cancer, scientists discovered the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the MET proto-oncogene (MET). They are able to promote cell growth, survival and proliferation, and the occurrence and development of cancer are stimulated and stimulated by them. Amivantamab is a bispecific antibody that recognizes EGFR and MET. Amivantamab, as a bispecific antibody, has the ability to recognize EGFR and MET. People use Amivantamab to treat NSCLC, by inserting in patients who have progressed after platinum-based chemotherapywith EGFR 20 exon [3].
This article reviews the mechanism of action, cell structure, therapeutic methods, and clinical trials of Amivantamab in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer.
2. Mechanism
2.1. EGFR in NSCLC
EGFR is the most important and main part of the growth factor receptor family, which has inherent tyrosine kinase activity; there is frequently high expression and internal deletions of EGFR in brain tumors, whereas in lung cancer. It is general that point mutations and small insertions. Due to these characteristics, EGFR and its common dimerization partner, HER2/ERBB2, the targets are usual to use in treatment of cancer. However, studies on EGFR often yield unexpected results, which will be discussed here. Upon activation by ligands, EGFR triggers a sequence of time-dependent molecular processes, including the downregulation of numerous microRNAs, a decrease in newly synthesized mRNA, and the regulation of protein function via covalent modification, all of which collectively influence genes that determine phenotype. Additionally, long non-coding RNAs and circular RNAs are also important on EGFR signaling. Beyond initiating cancer through driving mutations, EGFR also facilitates cancer metastasis through various mechanisms. The paracrine loop formed by tumor and stromal cells allows EGFR to assist tumor cells in traversing tissue barriers, ensuring the survival of circulating tumor cell populations, and aiding the colonization of distant organs [4].
2.2. MET in NSCLC
The MET receptor encoded by MET exon 14 contains a 47-amino acid near-membrane domain, which is a key region in the regulation of MET signaling. In METex14 mutant cancers, the transcriptional splicing process of the MET gene is disrupted due to changes in exon 14 and its surrounding introns, or the absence of exon 14. Beause of the block of ubiquitination and receptor internalization, it makes affection the degradation process of the MET protein receptor, resulting in overactive MET signaling that promotes cell proliferation and tumor growth. About 2% to 4% of advanced non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) have mutations or deletions of the METex14 site. Compared to other cancer driver genes, NSCLC patients with METex14 mutations are typically older (median age 70), and nearly half of them are smokers [5].
One patient with non-small cell lung cancer had a long history of smoking and reported a METex14 mutation. METex14 mutations occur primarily in the adenocarcinoma and pulmonary sarcomatoid subtypes of NSCLC, with the latter occurring in approximately 20% of cases. METex14 has also been seen in squamous non-small cell lung cancer, occurring in up to 9% of cases in recent trials. Although METex14 mutations do not usually co-exist with other carcinogenic drivers, recent studies have shown associations with 34%, 19%, and 11% of coamplifications and TP53 mutations.
Current technologies for detecting METex14 mutations include DNA Next generation sequencing (NGS) platforms, Sanger sequencing, and RNa-based analysis methods such as reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and RNa-based NGS. In the DNA NGS panel test, the sensitivity of NGS based on hybridization capture is higher. Rna-based methods may have higher sensitivity than DNA methods because DNA methods may have limitations in capturing the breadth of METex14 changes. However, the CDx DNA test developed by Foundation Medicine (Cambridge, MA) is highly consistent with RNA sequencing. With NanoString's nCounter system, METex14 can be recognized at the RNA level. Finally, recent studies using blood-based NGS report consistency between tissue and liquid biopsies, with similar covariant percentages. In addition, fewer METex14 alterations were detected in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), which may be associated with tumor shedding. Similar to other oncogenic driver genes, a positive result for METex14 in liquid biopsies is an important predictive biomarker for personalized therapy [5].
3. Structure and molecular basics of amivantamab
3.1. Structure of amivantamab
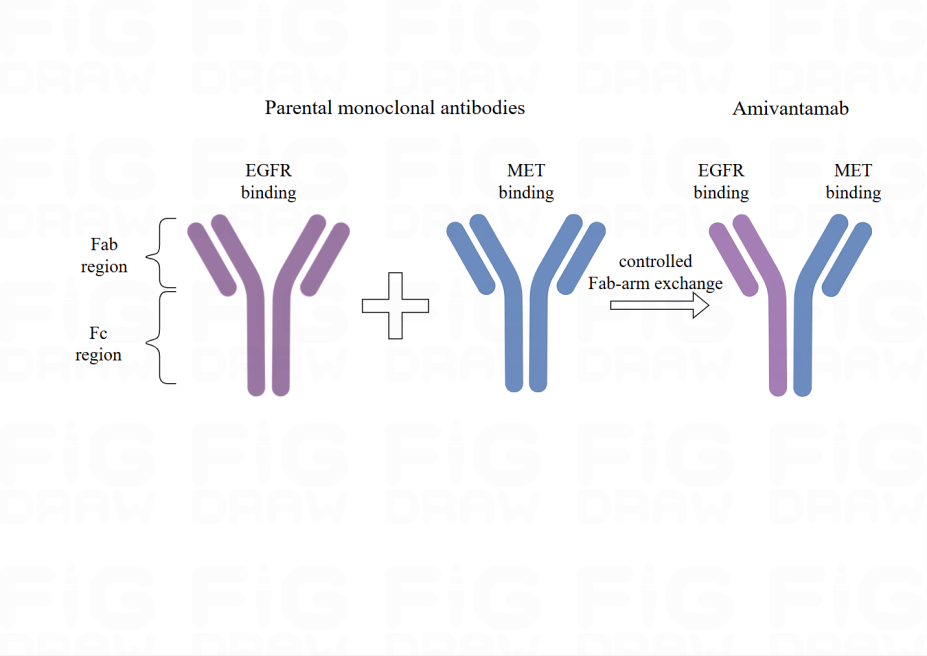
Two parent monoclonal antibodies, which are EGFR and MET create Amivantamab (Figure 1). There is the process of exchanging antigen-binding fragment (Fab) arm. These parent antibodies undergo the process and are managed by Genmab DuoBody technology, followed by creating bispecific antibodies with a single binding site (monovalent) for each antigen. Furthermore, the parent monoclonal antibodies are produced in an engineered cell line with low focus on the Fc region, which enhances the binding of antibodies to Fc receptors on immune effector cells, thus boosting the anti-tumor activity directed by immune cells [6].
|
Figure 1. The structure of Amivantamab. Amivantamab is derived from two parental monoclonal antibodies (Mabs), one against EGFR and the other against MET. Modified from [6]. Created from figdraw.com. |
3.2. Signaling pathways modulated by amivantamab
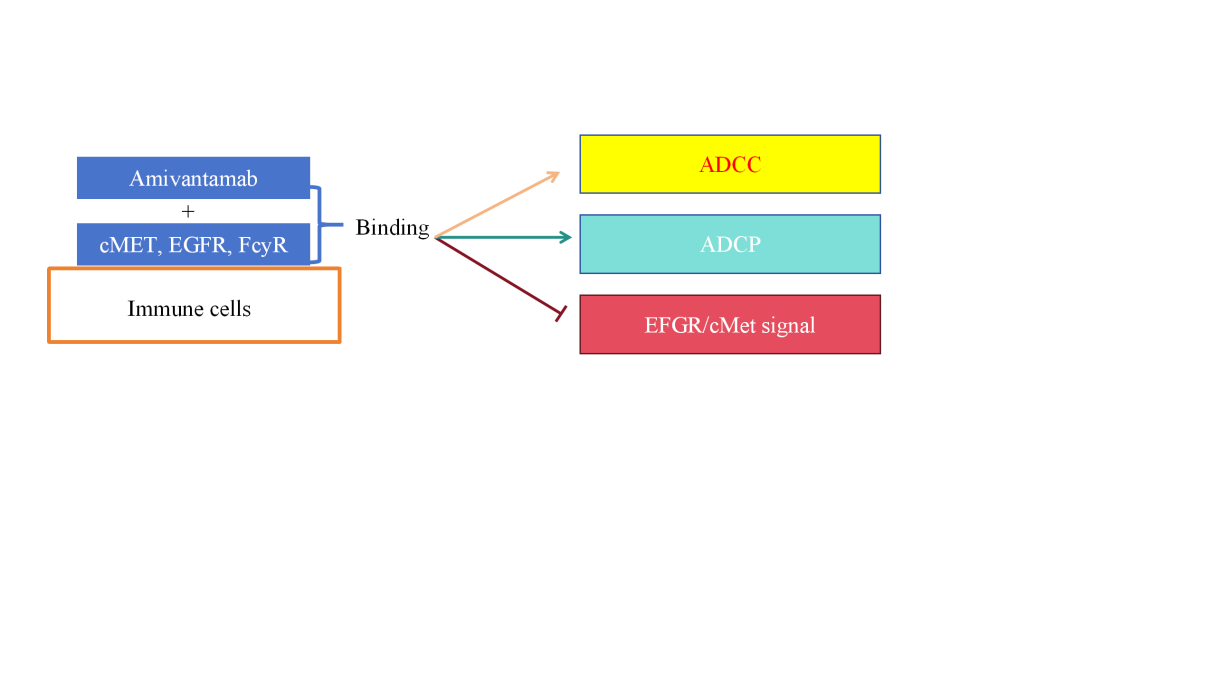
Amivantamab is produced in low concentrations of engineered CHO cell lines to improve the antibody's ability to bind to the Fc receptor (FcγR)-IIIa/CD16a on immune cells. By binding to FC-γRS, human IgG1 antibodies induce immune effector cells to clear target cells. When IgG1 antibodies bind to cell surface antigens, they can trigger ADCC and ADCP, and bind to FC-γRs on natural killer cells (NK cells) and macrophages, resulting in antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent cytophagocytosis (ADCP) (Figure 2). In addition, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) is activated by the interaction of complement component C1q with antibodies to binding target cells. Tumor-targeting antibodies such as rituximab (anti-CD20 antibody), cetuximab (anti-EGFR antibody), and trastuzumab (anti-HER2 antibody) are known to utilize these three FC-γ-mediated mechanisms (Figure 2) [7].
Macrophages increase tumor cell clearance through antibody-dependent cellular uptake (ADCT), a mechanism that is often underestimated. Tumor targeting antibodies work by binding ligands on tumor cell membranes and Fc receptors of effector cells. Previous studies have shown that amivantamab can not only inhibit EGFR and cMet signaling pathways in a non-FC-dependent manner, but also induce ADCC and ADCP. In vivo studies conducted in tumor models with EGFR mutations and cMet activation, the researchers found that the standard version of amivantamab showed higher tumor growth inhibition (TGI) compared to the IgG2Q version, suggesting that Fc interactions are critical to its anti-tumor effects. In addition, the IgG2Q version of amivantamab showed reduced downregulation of EGFR, cMet, and their respective signaling components in vivo, further suggesting that Fc interactions of amivantamab are necessary to downregulate receptor and signaling pathway activity [7].
|
Figure 2. Signaling pathway regulated by Amivantamab. Abbreviations: Antibody-Dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC), Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis (ADCP), Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR), Figure credit: Original |
4. Clinical trials
In a Phase IB/II clinical trial, amivantamab demonstrated encouraging outcomes in patients with tumors harboring EGFR exon 20 mutations. First- and second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) that target EGFR are ineffective for these tumors because exon 20 mutations create steric hindrance in the kinase domain, which prevents the drug from accessing the binding pocket. Consequently, targeting the extracellular domain of EGFR with antibodies has emerged as a compelling therapeutic approach. The toxicity levels of the drug fall within acceptable limits, and it has received FDA approval for treating advanced NSCLC with EGFR exon mutations that have progressed following platinum-based dual-agent first-line therapy. Amivantamab is currently undergoing Phase III clinical trials to assess its efficacy in combination with chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. Furthermore, ongoing studies are evaluating amivantamab as a monotherapy or in combination with Lazertinib for other EGFR and MET mutation types [3].
Mutations within the EGFR kinase domain can be categorized into classical mutations, Ex20 insertion mutations, T790m-like mutations, P-ring mutations, and αC-helix compression mutations. Amivantamab has received approval for use in patients with NSCLC featuring EGFR Ex20 mutations after their disease progressed post-platinum therapy. As a bispecific monoclonal antibody, amivantamab targets both EGFR and MET receptors on the cell surface, potentially showing effectiveness against other EGFR mutations as well. Ongoing clinical trials are assessing amivantamab in patients with non-Ex20 NSCLC , with preliminary findings available. According to the Mariposa study, osimertinib, a standard first-line treatment for NSCLC, was linked to longer progression-free survival. Additionally, the MARIPOSA2 study indicated that combining amivantamab with chemotherapy or adding Lazertinib resulted in a favorable therapeutic response in patients with classical EGFR mutant NSCLC whose disease advanced after osimertinib treatment [8].
5. Conclusion
Lung cancer, as the most common cause of death, is critical to treat on time. EGFR is the key to tumor treatment targets; the mutant form common in lung cancer, through the molecular switch, affects tumor phenotype, and MET exon 14 mutations in NSCLC accounted for about 2% to 4%, leading to excessive active MET signal. Amivantamab, a bispecific antibody that inhibits tumor growth by binding EGFR and MET, has shown efficacy in selected NSCLC patient populations in clinical trials,and more studies are underway to explore its potential in other mutation types. The research and application of amivantamab may further expand, including the wider to evaluate the curative effect of patients with EGFR mutations and MET and exploration of other treatments, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy combined, in order to improve treatment effect. In addition, it is expected that through precision medicine strategies, the use of amivantamab can be optimized according to the specific mutation characteristics of individual patients, reducing side effects and improving survival and quality of life. At the same time, further study of EGFR and MET signaling pathways, as well as their roles in tumor progression, may find new therapeutic targeting strategies, and treatment options for patients with NSCLC.
References
[1]. World Health Organization, Lung cancer (2024), Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lung-cancer.
[2]. Chen P, Liu Y, Wen Y and Zhou C 2022 Cancer Commun (Lond). 42 937-970
[3]. Petrini I and Giaccone G. 2022 Onco Targets Ther. 15 1197-1210.
[4]. Uribe ML, Marrocco I and Yarden Y. 2021 Cancers (Basel). 13 2748, ,
[5]. Remon J, Hendriks LEL, Mountzios G, García-Campelo R, Saw SPL, Uprety D, Recondo G and Villacampa G.J 2023 Thorac Oncol. 18 419-435
[6]. Cho BC, Simi A, Sabari J, Vijayaraghavan S, Moores S, Spira A. 2023 Clin Lung Cancer. 24 89-97.
[7]. Vijayaraghavan S, et al. 2020 Mol Cancer Ther. 19 2044-2056
[8]. Wang K, et al. 2024 J Thorac Oncol. 19 500-506
Cite this article
Huang,X. (2024). Therapeutic role of amivantamab on lung cancer: Mechanisms and applications. Theoretical and Natural Science,61,173-177.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. World Health Organization, Lung cancer (2024), Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lung-cancer.
[2]. Chen P, Liu Y, Wen Y and Zhou C 2022 Cancer Commun (Lond). 42 937-970
[3]. Petrini I and Giaccone G. 2022 Onco Targets Ther. 15 1197-1210.
[4]. Uribe ML, Marrocco I and Yarden Y. 2021 Cancers (Basel). 13 2748, ,
[5]. Remon J, Hendriks LEL, Mountzios G, García-Campelo R, Saw SPL, Uprety D, Recondo G and Villacampa G.J 2023 Thorac Oncol. 18 419-435
[6]. Cho BC, Simi A, Sabari J, Vijayaraghavan S, Moores S, Spira A. 2023 Clin Lung Cancer. 24 89-97.
[7]. Vijayaraghavan S, et al. 2020 Mol Cancer Ther. 19 2044-2056
[8]. Wang K, et al. 2024 J Thorac Oncol. 19 500-506