1. History
Nowadays, Ibuprofen is widely recognized as one of the most common household drugs. The story of ibuprofen starts when two Boots Pure Drug Company Ltd. employees, pharmacist and pharmacologist Stewart Adams and scientist John Nicholson, file a patent application for the chemical 2-(4-isobutylphenyl) propionic acid. It was granted in 1962, as mentioned in the Pharmaceutical Journal.[1]. Later, Ibuprofen first brought into the UK market in 1969 under the brand name Brufen, a prescription medication.
Since then, ibuprofen was popularized and remains a drug inside every home. Various studies have come out about additional effects of the drug. Some include trials conducted in 1995 that demonstrate how high ibuprofen dosages slow down the progression of lung disease in cystic fibrosis patients by preventing the release of lysosomal enzymes and the migration, adhesion, swelling, and aggregation of neutrophils. Later in 2005, Journal of the National Cancer Institute showed that long-term daily ibuprofen use is linked to a 51% increased risk of breast cancer [2] and Ann Neurol proposed that ibuprofen usage on a daily basis may reduce the incidence of Parkinson's disease, according to an epidemiological study [3]. In 2006, the European Medicines Agency concluded that A slight increase in the absolute risk of thrombotic events may be linked to NSAIDS. Two years later, Neurology discovered that using ibuprofen for longer than five years lowers the risk of Alzheimer's disease by 44% [4]. Most recently, European Heart Journal-Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy have come out with results showing ibuprofen increases the risk of heart disease. [5] More research remains to be done on the drug and new information is found with every passing year.
2. Structure & composition
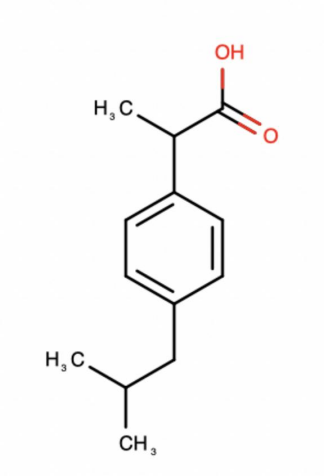
Figure 1: Structure of ibuprofen [6]
Ibuprofen is a useful and important chemical compound since it is used to moderate pain, fevers, headaches, and inflammation. NSAIDs (including ibuprofen), which is a class of drugs used to inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX) to reduce inflammation. The structure of ibuprofen is shown in figure 1. In the compound, are C-C covalent bonds.O-H bond and C-O bond. It contains three different functional groups, which are alkanes, carboxylic acid and benzene. In the benzene, each C-C bond has the same bond length, bond angle and bond enthalpy, so it is a stable structure. Benzene and an isobutyl group ( (CH3)2CHCH2 ) are linked to a propanoic acid, which makes ibuprofen stable and bioactive. The structure of ibuprofen enables it to block COX which can produce prostaglandins, the chemicals that lead to inflammation and pain.
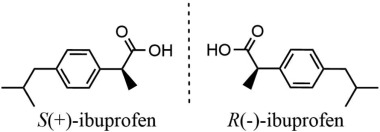
Figure 2: Enantiomers of ibuprofen [7]
There exists a chiral center with an ibuprofen molecule meaning that 2 enantiomers exist, the (R)-enantiomer and the (S)-enantiomer, which are shown in figure 2. The most typical form of ibuprofen is a racemic mixture which consists of an equi-molar combination of the two enantiomers. Obvious differences exist between the 2 isomers, when it comes to prostaglandin inhibition, the (S) isomer is 160 times more active than the (R) enantiomer. Other studies have shown that the (S)-enantiomer has the ability to inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 while the (R)-enantiomer can inhibit COX-1, albeit to a lesser extent, and it has no effect on COX-2. For this reason, the (S)-enantiomer has been available in recent years as a separate drug.
3. Mechanism
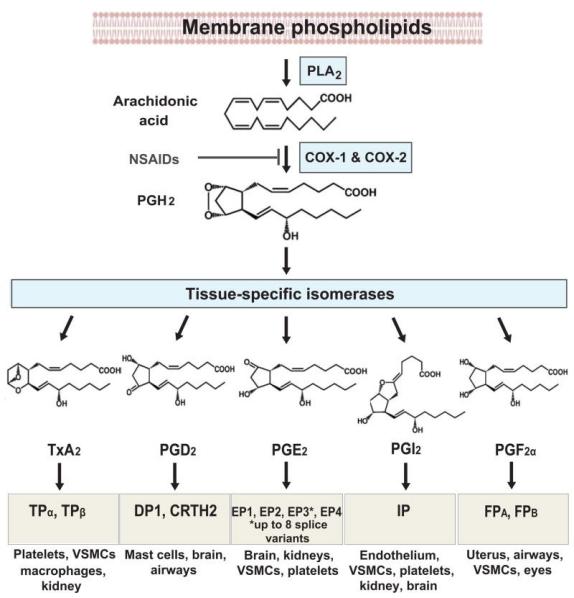
Figure 3: Process of prostaglandin synthesis [8]
Ibuprofen works by decreasing the synthesis of prostaglandins. Prostaglandin is a group of physiologically active substances that can affect hormones in animals, as mentioned by Encyclopedia Britannica. [9] As shown in figure 3, the phospholipids of the cell membrane are first hydrolyzed to arachidonic acid (AA) with the reaction of phospholipase A, (PLA). When AA is formed, it is metabolized through COX-1 and COX-2 and thus prostaglandin H (PGH,) is formed. After that, different synthases can then lead to other productions of prostaglandins. For example, the prostacyclin synthase will produce PGl2, prostaglandin F synthase, prostaglandin E Synthase and prostaglandin D synthase can produce PGF2α, PGE2, PGD2, respectively, and thromboxane synthase generates TXA2. Hence, many different forms of prostaglandins are formed.
Different prostaglandins are responsible for distinct functions. For example, PGl2 regulates cardiovascular health. It prevents platelet aggregation and relaxes the vascular smooth muscle in blood arteries. Also, it has immunosuppressive capability, which is suggested by Mediators of Inflammation. [10] BMC Veterinary Research proposed that PGF2α, on the other hand, regulates physiology of female reproductive processes. It impacts embryo quality and morula stage development. [11] Another prostaglandin, PGE2, is abundant in the kidney and it is important to renal function. It is responsible for renal hemodynamics, water and sodium metabolism, and blood pressure, as stated in Prostaglandins & Other Lipid Mediators. [12] TXA2, changes vascular tone and mediates platelet aggregation. The action of TXA2 impacts pulmonary hypertension, kidney and hepatic injury and angiogenesis. The increase in TXA2 activity affects stroke and bronchial asthma, which is shown by PubMed. [13] Mediators of Inflammation indicates that PGD2 regulates neurophysiological functions such as regulations of body temperature, hormone release, pain responses, and the sleep-wake cycle in mammals. [14]
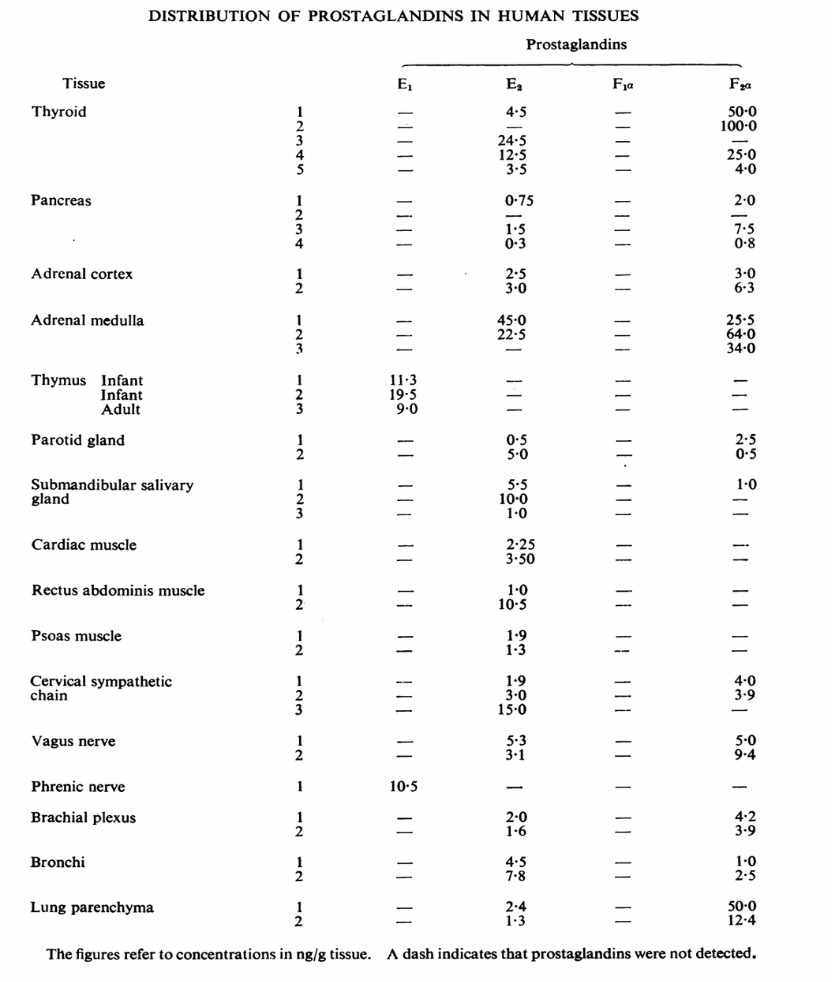
Figure 4: Distribution of prostaglandins in different human tissues [15]
Figure 4 indicates that prostaglandins are distributed in many tissues in the human body. Thus, in order to moderate inflammation, it is necessary to reduce formations of prostaglandins by inhibiting COX, the factor that leads to more being produced. COX contains two isoforms. which are COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 regulates cellular processes, it produces prostaglandins which have homeostatic functions, such a gastric cytoprotection and platelet function. On the other hand, COX 2 produces prostaglandins which have physiological functions, such as inflammation, cell proliferation, and functions in brain, kidney, and cardiovascular systems. Ibuprofen is a NSAID, so it inhibits both COX-1 and COX-2. It is anti-inflammatory and analgesic, but since it inhibits COX-1, it blocks platelet production of thromboxane, which increases bleeding to the stomach. As a result, some damage can be done to the gut. This is one of the side-effects of ibuprofen showing that ibuprofen can be harmful to the human body. There is another class of drugs called COX-2 selective inhibitors. They do not inhibit COX-1 so that it does not inhibit TXA2 leading to an impact on platelet aggregation. Therefore, patients may have an increased possibility of heart attacks and strokes.
4. Binding
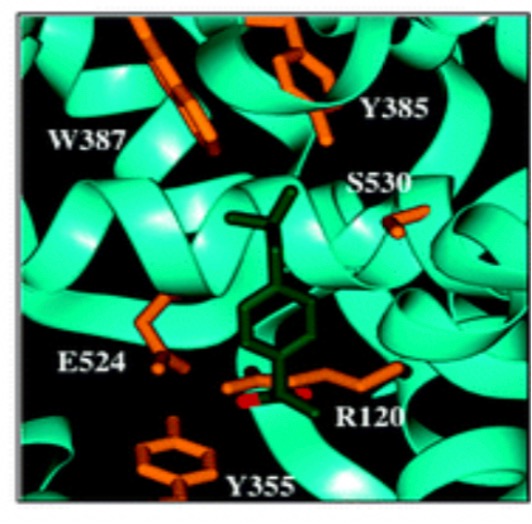
Figure 5: The binding of COX [16]
In figure 5, with carboxylate-coordinated Arg-120 and Tyr-355 at the constriction site, ibuprofen is bound in the COX-1 active site. Ibuprofen establishes a hydrogen bond with Tyr-355 as well as an ion pairing with Arg-120.
5. Metabolism
Ibuprofen can be almost fully metabolized. There is trace to non-existent amounts of the original drug in human urine and the most frequently occurring chemicals are 2-hydroxy-ibuprofen and carboxy-ibuprofen, together with the acyl glucuronides that correlate to each, which is stated in Pharmacogenetics and Genomics. [17] Once within the body, the enzyme α-methylacyl-coenzyme converts 50–65% of R-ibuprofen to the S enantiomer via an acyl-CoA thioester. Then, primary metabolism occurs through oxidative metabolism using CYP enzymes. CYP2C9 is the main CYP in charge of metabolism. It catalyzes the synthesis of 2-hydroxy- and 3-hydroxy-ibuprofen, which can subsequently be transformed by cytosolic dehydrogenases into carboxy-ibuprofen. 2C9 is shown to catalyze both enantiomers in the human body. Other CYPs such as CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 play a minor role in first pass metabolism. Ibuprofen that goes through second pass metabolism is directly glucuronidated to ibuprofen-acyl glucuronide. This can be produced with many uridine 5′diphosphoglucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) including UGT1A3, UGT1A9, and UGT2B4. This makes up around 10–15% of an ibuprofen dose.
6. Conclusion
From its initial development to the modern day, ibuprofen has proven again and again that it deserves to be recognized as a widely used drug. The NSAID’s inner workings are incredibly intricate but the researchers hope that this paper has been a informative guide to its structure, composition, history, and mechanism. Further research remains to be done on every aspect of the drug.
Acknowledgement
Both authors contributed equally and should be considered co-first authors.
References
[1]. The Pharmaceutical Journal. (2017) A brief history of ibuprofen. https://pharmaceutical-journal.com/article/infographics/a-brief-history-of-ibuprofen
[2]. Marshall, S. F., Bernstein, L., Anton-Culver, H., Deapen, D., Horn-Ross, P. L., Mohrenweiser, H., Peel, D., Pinder, R., Purdie, D. M., Reynolds, P., Stram, D., West, D., Wright, W. E., Ziogas, A., & Ross, R. K. (2005). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and breast cancer risk by stage and hormone receptor status. Journal of the National Cancer Institute., 97: 805–812.
[3]. Chen H, Jacobs E, Schwarzschild M et al. (2005) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use and the risk for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol ;58:963–967.
[4]. Vlad, S. C., Miller, D. R., Kowall, N. W., & Felson, D. T. (2008) Protective effects of NSAIDs on the development of Alzheimer disease. Neurology., 70: 1672–1677.
[5]. Sondergaard, K. B., Weeke, P., Wissenberg, M., Olsen, A. S., Fosbol, E. L., Lippert, F. K., Torp-Pedersen, C., Gislason, G. H., & Folke, F. (2016) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use is associated with increased risk of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a nationwide case-time-control study. European Heart Journal-Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy., 356:100–107.
[6]. DrugBank Online. Ibuprofen: Uses, interactions, mechanism of action. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01050
[7]. Zeng, Y., Wang, Y., Liang, Z., & Jiao, Z. (2020) The study of chiral recognition on ibuprofen enantiomers by a fluorescent probe based on β-cyclodextrin modified ZnS: Mn quantum dots. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.119002
[8]. Ricciotti, E, & FitzGerald, G. A. (2011) Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology., 31: 986–1000.
[9]. Encyclopedia Britannica. (2024) Prostaglandin | Definition, Function, Synthesis, & Facts. https://www.britannica.com/science/prostaglandin
[10]. Mediators of Inflammation. (2012) PGI2 as a regulator of inflammatory diseases. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22851816/
[11]. BMC Veterinary Research. (2019). Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) production possibility and its receptors expression in the early- and late cleavedpreimplantation bovine embryos. https://bmcvetres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12917-019-1939-0
[12]. Wang, J, Liu, M, Zhang, X, Yang, G, & Chen, L.(2018) Physiological and pathophysiological implications of PGE2 and the PGE2 synthases in the kidney. Prostaglandins & Other Lipid Mediators., 134: 1- 6.
[13]. PubMed. (2024) Physiology, Thromboxane A2. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30969639/
[14]. Mediators of Inflammation. (2012) PGD synthase and PGD2 in immune response. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/503128
[15]. Karim, S. M. M., Sandler, M., & Williams, E. D. (1967) Distribution of prostaglandins in human tissues. British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy., 31: 340–344
[16]. Blobaum, A. L., & Marnett, L. J. (2007) Structural and functional basis of cyclooxygenase inhibition. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry., 50: 1425–1441.
[17]. Mazaleuskaya, L. L., Theken, K. N., Gong, L., Thorn, C. F., FitzGerald, G. A., Altman, R. B., & Klein, T. E. (2014) PharmGKB summary. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics., 23: 96–106.
Cite this article
Jiang,Z.;Liu,Z. (2025). Comprehensive Overview: The History, Structure, Composition, and Mechanism of Ibuprofen. Theoretical and Natural Science,115,137-142.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. The Pharmaceutical Journal. (2017) A brief history of ibuprofen. https://pharmaceutical-journal.com/article/infographics/a-brief-history-of-ibuprofen
[2]. Marshall, S. F., Bernstein, L., Anton-Culver, H., Deapen, D., Horn-Ross, P. L., Mohrenweiser, H., Peel, D., Pinder, R., Purdie, D. M., Reynolds, P., Stram, D., West, D., Wright, W. E., Ziogas, A., & Ross, R. K. (2005). Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and breast cancer risk by stage and hormone receptor status. Journal of the National Cancer Institute., 97: 805–812.
[3]. Chen H, Jacobs E, Schwarzschild M et al. (2005) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use and the risk for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol ;58:963–967.
[4]. Vlad, S. C., Miller, D. R., Kowall, N. W., & Felson, D. T. (2008) Protective effects of NSAIDs on the development of Alzheimer disease. Neurology., 70: 1672–1677.
[5]. Sondergaard, K. B., Weeke, P., Wissenberg, M., Olsen, A. S., Fosbol, E. L., Lippert, F. K., Torp-Pedersen, C., Gislason, G. H., & Folke, F. (2016) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use is associated with increased risk of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a nationwide case-time-control study. European Heart Journal-Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy., 356:100–107.
[6]. DrugBank Online. Ibuprofen: Uses, interactions, mechanism of action. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01050
[7]. Zeng, Y., Wang, Y., Liang, Z., & Jiao, Z. (2020) The study of chiral recognition on ibuprofen enantiomers by a fluorescent probe based on β-cyclodextrin modified ZnS: Mn quantum dots. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.119002
[8]. Ricciotti, E, & FitzGerald, G. A. (2011) Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology., 31: 986–1000.
[9]. Encyclopedia Britannica. (2024) Prostaglandin | Definition, Function, Synthesis, & Facts. https://www.britannica.com/science/prostaglandin
[10]. Mediators of Inflammation. (2012) PGI2 as a regulator of inflammatory diseases. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22851816/
[11]. BMC Veterinary Research. (2019). Prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) production possibility and its receptors expression in the early- and late cleavedpreimplantation bovine embryos. https://bmcvetres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12917-019-1939-0
[12]. Wang, J, Liu, M, Zhang, X, Yang, G, & Chen, L.(2018) Physiological and pathophysiological implications of PGE2 and the PGE2 synthases in the kidney. Prostaglandins & Other Lipid Mediators., 134: 1- 6.
[13]. PubMed. (2024) Physiology, Thromboxane A2. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30969639/
[14]. Mediators of Inflammation. (2012) PGD synthase and PGD2 in immune response. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/503128
[15]. Karim, S. M. M., Sandler, M., & Williams, E. D. (1967) Distribution of prostaglandins in human tissues. British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy., 31: 340–344
[16]. Blobaum, A. L., & Marnett, L. J. (2007) Structural and functional basis of cyclooxygenase inhibition. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry., 50: 1425–1441.
[17]. Mazaleuskaya, L. L., Theken, K. N., Gong, L., Thorn, C. F., FitzGerald, G. A., Altman, R. B., & Klein, T. E. (2014) PharmGKB summary. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics., 23: 96–106.









