1. Introduction
With the rapid development of technology, online shopping has gradually become the primary method for individuals to purchase all kinds of products. Thus, reviews on shopping websites become a significant reference for customers to decide which products to buy and for sellers to make improvements on their products. There are many reviews to help consumers to choose different commodities of good quality. Nevertheless, some reviews are too long and have too many things to cover, which makes them difficult to read. Hence, I studied the Women's E-Commerce Clothing Reviews dataset in this project to make a recommendation and sentiment classification on reviews. The work on recommendation classification will help the shopping websites classify reviews and at the same time, help customers find reviews that are useful for them quickly; the work on sentiment classification can help sellers better understand their consumers [10].
There are some similar works by machine learning experts which offer instructive guidance for text processing techniques and methodology used in this study. For instance, Xie’s work on sentiment analysis of clothing reviews utilized Random Forest for classification, which enlightened me to try and improve this model to accomplish my work [4]. Besides, Agarap’s study on Statistical Analysis of E-Commerce Reviews encouraged me to utilize a sentiment intensity analyzer to classify sentiment from review text [5]. This project used similar patterns to hers, but the models and algorithms are totally different.
2. Exploratory Data Analysis
2.1. Data Description
In this project, I collected data from a dataset named Women's E-Commerce Clothing Reviews (https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/nicapotato/womens-ecommerce-clothing-reviews), which is a dataset revolving around the reviews written by consumers and contains some information of reviewers [1]. This dataset contains 23486 rows and ten columns. The columns “Review Text”, “Title”, and “Recommend IND” were used in this project. After dropping duplicates and rows without review text, 22641 rows were left, and I added a column called “Review Length” for classification.
2.2. Exploratory Data Analysis
2.2.1. Word Cloud. Word Cloud is a tool to realize visual representation of words that offers greater prominence to words which occur with higher frequency [7]. Figure 1 reveals the words appearing most frequently in the review text.
|
Figure 1. Word Cloud for text reviews. |
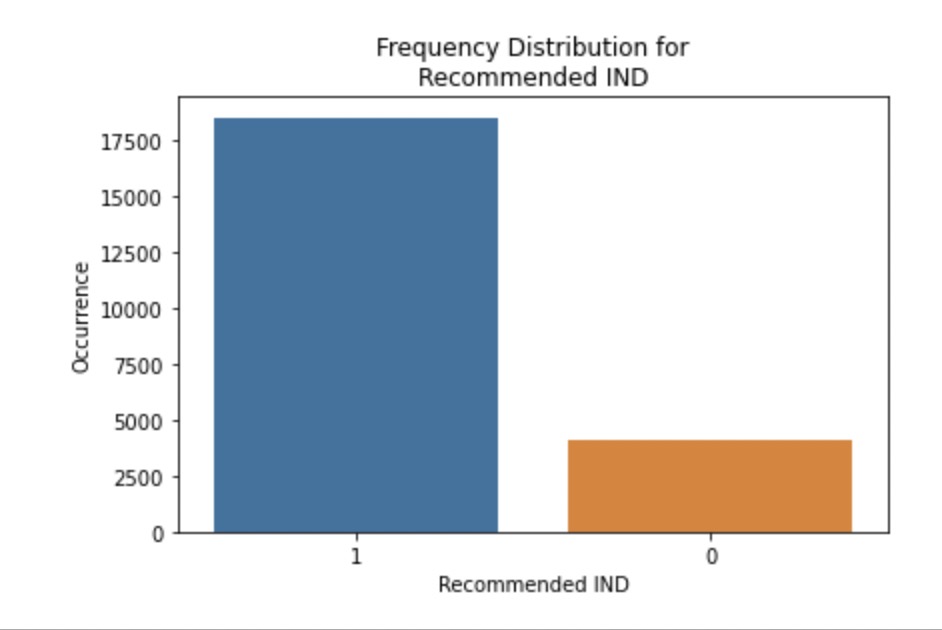
2.2.2 Frequency Distribution for Recommended Index. Figure 2 indicates that much more reviewers recommend reviewed clothing products.
|
Figure 2. Frequency Distribution for Recommended Index. |
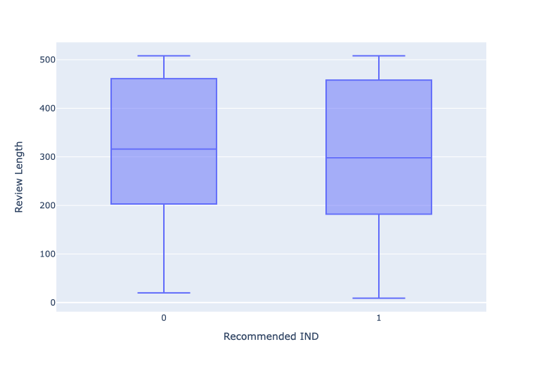
2.2.3. Relationship between Review Length and Recommend Index. Figure 3 demonstrates that the reviews that do not recommend the clothing products are longer than those that recommend the products.
|
Figure 3. Relationship between Review Length and Recommend Index. |
2.2.4. Data Distribution for Sentiment Classification. Figure 4 shows that the data for sentiment classification is hugely imbalanced, while reviews with positive sentiment are much more than those with neutral or negative sentiment. Model selection is essential to make the results of sentiment classification more accurate.
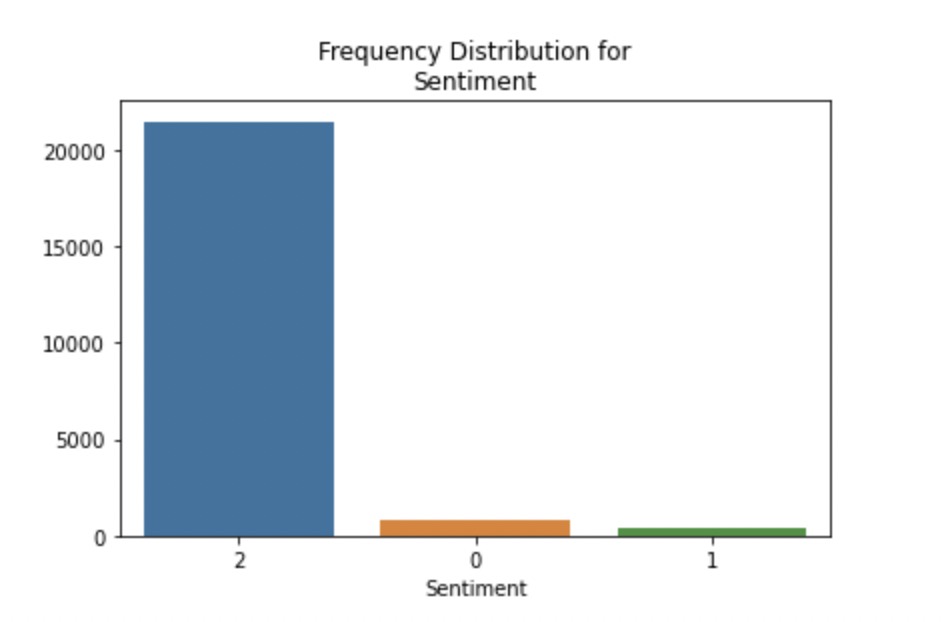
Figure 4. Frequency Distribution for Sentiment.
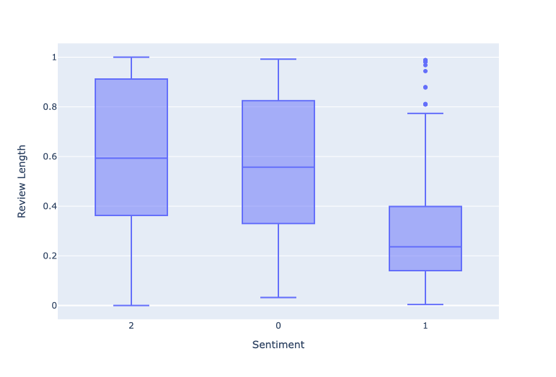
2.2.5. Relationship between Review Length and Sentiment. Figure 5 shows that the reviews with neutral sentiment are much shorter than others, while the positive reviews are the longest.
|
Figure 5. Relationship between Review Length and Sentiment. |
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Preprocessing
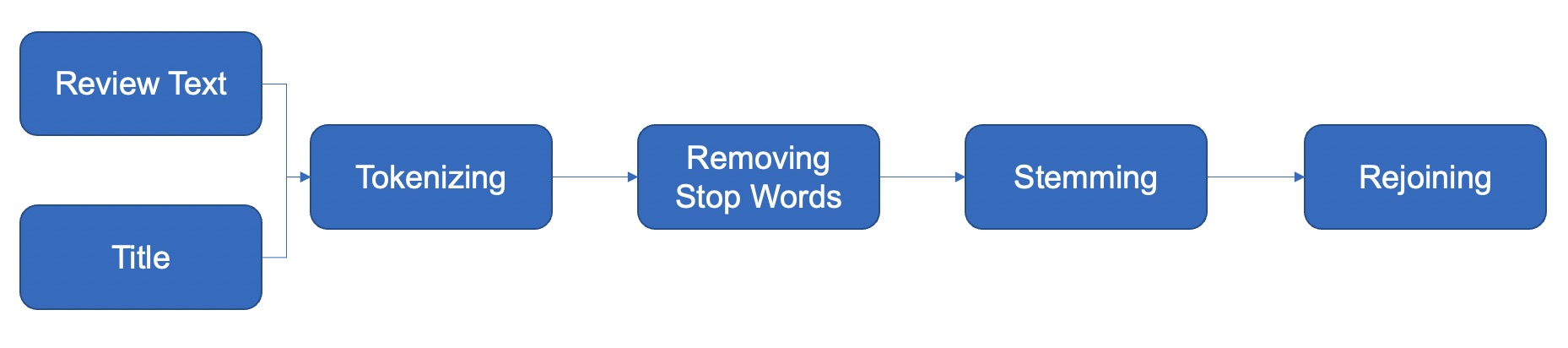
3.1.1 Text Preprocessing. Since my data mainly consists of text, text preprocessing is significant for me. Figure 6 shows the whole process of text preprocessing. First, I combined Review Text and Title to be my text data; then tokenizer was used to divide strings into lists of substrings for the following steps. Then, stop words were removed, which are not very meaningful and will affect the classification relying on my text data. After that, words were reduced to their stem without affixes and suffixes, which is convenient for document classification. Then, the words were rejoined to strings.
|
Figure 6. Text Preprocessing. |
After this process, I used Countvectorizer, the tool to convert a collection of text documents to a matrix of token counts. With the help of Countvectorizer, I selected 500 features for the text reviews, which are the occurrence of 500 words that appear most frequently in reviews.
3.1.2 Normalization. Since there are both numerical and text data of my data for classification, I used min-max feature scaling to normalize the review length, making it in the range of [0, 1]. As is shown in the following formula, the input is x, while the output is x’.
\( {x^{ \prime }}=\frac{x-min(x)}{max{(x)}-min(x)} \) (1)
3.1.3. Sentiment Analysis. Sentiment Intensity Analyzer from NLTK python package was used to analyze and classify reviewers' sentiment [2]. For sentiment classification, I used this tool to calculate polarity score for each review. If the polarity score of the review text is greater than 0, it is considered positive; if the score is 0, it is treated as neutral, and if the score is less than 0, it is negative.
3.2. Classification Models.
The modelling process is accomplished in Python with the help of the scikit-learn package, which offers users commonly used algorithms of machine learning. Besides, for both recommendation and sentiment classification, I set 80% of the data for training and 20% of the data as testing set with “train_test_split”.
3.2.1. Naïve Bayes Classifier. Naive Bayes is a conditional probability model based on Bayes' theorem, and it strongly assumes independence between the features. It works extremely fast and is also suitable for dealing with high-dimensional data. The following equation simply explains the principle of Naive Bayes, while x stands for different features, and \( {C_{k}} \) stands for different categories.
\( p({C_{k }}| x)=\frac{p({C_{k }})p(x|{C_{k}})}{p(x)} \) (2)
In my study on recommendation classification, I chose to use Multinomial naive Bayes, which models the data distribution with a best-fit multinomial distribution. The multinomial distribution describes the likelihood of observing counts among a few classes. Therefore, multinomial naive Bayes is commonly used in text classification, with events representing the appearance of a word in a single text. And the following formula explains this model.
\( p(x|{C_{k}})=\frac{(\sum _{i=1}^{n}{x_{i}})!}{\prod _{i=1}^{n}{x_{i}}!}\prod _{i=1}^{n}{{p_{{k_{i}}}}^{{x_{i}}}} \) (3)
3.2.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Principal Component Analysis (PCA) is a fast and flexible model to reduce dimensionality. Although 500 features were chosen for my text data, the dimensionality of my data is still very high, and the speed of the Support Vector Machine is not very fast; thus, I utilized PCA to find more meaningful and useful features in my study on recommendation classification before using SVM. After applying PCA, the remaining features can explain 90% of the total variance of my data.
3.2.3. Support Vector Machine (SVM). Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a robust supervised learning methodology whose input is vector space, and the output is positive or negative [9]. I tried to select different kernels for SVM and finally decided to use the radial basis function kernel, as it provides the best results. Then it is packed into pipes for recommendation classification with the preprocessor PCA as mentioned above. After that, GridSearchCV was applied to find best parameters for SVM.
3.2.4. Random Forest. The random forest model combines randomized decision trees, which classify data by asking a series of questions. It is a very powerful, fast, and flexible model [3].
Since it randomly chooses the features, random forest is suitable for high dimensional data, it is selected for sentiment classification of my project. Because the data for sentiment classification is highly imbalanced, I utilized Balanced Random Forest Classifier for my work, which is an improved Random Forest Classifier for unbalanced data [6]. It is a useful method in which each forest tree will be offered a balanced bootstrap sample by randomly under-sampling [8].
4. Evaluation
For the algorithms used in this project, confusion matrix, accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score are used to evaluate the results.
Please note that the data for both recommendation classification and sentiment classification is imbalanced; the amount of review that recommends the clothing product is much more than the ones not recommending the products; the number of reviews with positive sentiment is more than the ones with neutral and negative sentiment.
4.1. Multinomial Naive Bayes
Table 1. Results for Naïve Bayes model on recommendation classification.
Precision | Recall | F1-score | Support | |
1 (Recommended) | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 3557 |
0 (Not recommended) | 0.73 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 972 |
Weighted Average | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 4529 |
From table 1, we can tell that the accuracy for predicting reviews that recommend the products is higher than that for predicting the other category, which can be attributed to the limitation of my dataset as the data for reviews that recommend products is much more.
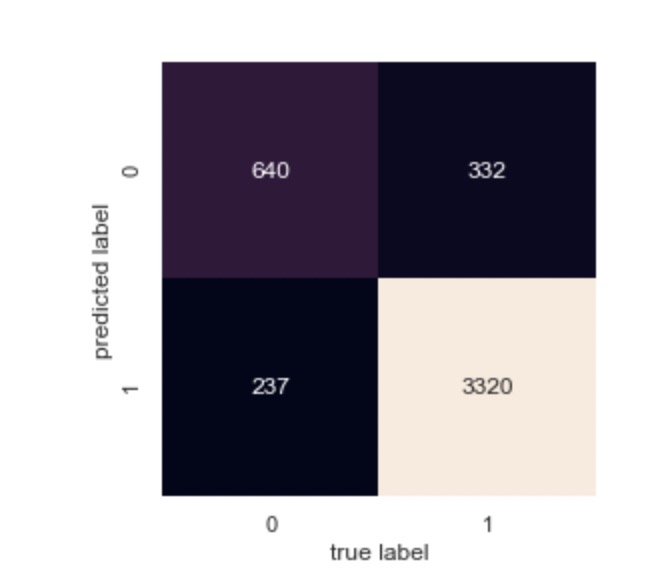
Figure 7 is the confusion matrix for Naïve Bayes model on recommendation classification, where 0 stands for not recommended class while 1 represents recommended class, we can also draw the conclusion that the accuracy for classifying recommended reviews is higher.
|
Figure 7. Confusion matrix for Naïve Bayes model on recommendation classification. |
4.2. Support Vector Machine
According to table 2, the precision for the Support Vector Machine on recommendation classification is almost the same as that for Naïve Bayes Model.
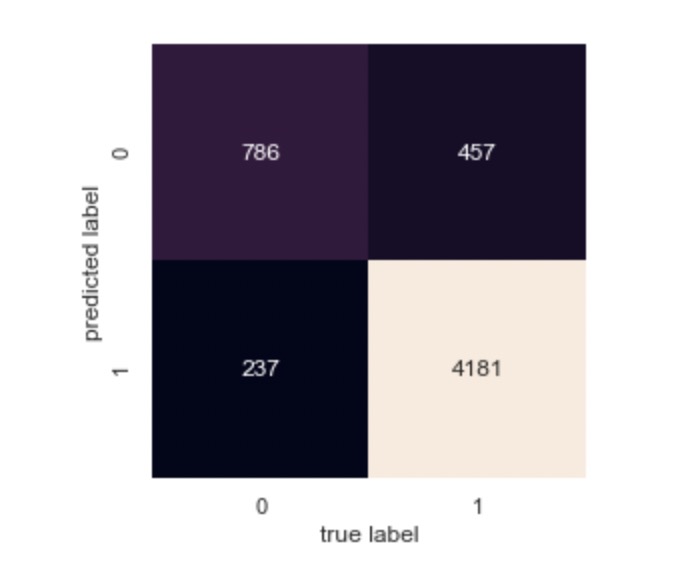
Besides, figure 8 is the confusion matrix for Support Vector Machine on recommendation classification, where 0 stands for not recommended class while 1 represents recommended class. According to this figure, we can tell that most of the recommended reviews were classifies correctly.
|
Figure 8. Confusion matrix for Support Vector Machine on recommendation classification. |
4.3. Random Forest
From table 3, it is clear that although the precision to predict negative reviews is relatively lower, the improvement for the random forest model really works for unbalanced data.
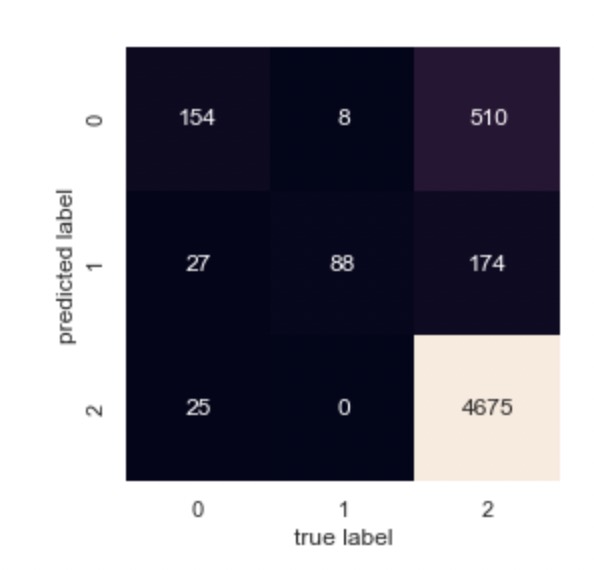
Figure 9 is the confusion matrix for Random Forest on sentiment classification, in which 2 represents positive sentiment, 1 stands for neutral sentiment, and 0 represents negative sentiment. As it can be seen in this figure, most of the reviews with positive sentiment were predicted correctly, while some of the negative reviews were mistaken.
|
Figure 9. Confusion matrix for Random Forest on sentiment classification. |
In conclusion, despite the data imbalance, the results of recommendation classification and sentiment classification given by the three models are good.
5. Conclusion
As seen from the evaluation, the Naïve Bayes model and Support Vector Machine perform well on recommendation classification, while Naïve Bayes model works much faster. For sentiment classification, the Balanced Random Forest Classifier works well in dealing with unbalanced data. Thus, this study can be a reference for the natural language processing of customers' reviews.
Moreover, this study has many rooms to be improved:
1. If I have more time to study neutral network, I will construct a deep learning model to classify the data, which will probably give more accurate results.
2. I have utilized Balanced Random Forest Classifier, and the results proved that it really works for unbalanced data. However, there are still many methods to improve the classification results for imbalanced data, and I want to try and compare them. Besides, I intend to learn the technique of visualizing decision trees to study how Balanced Random Forest Classifier classifies text data.
References
[1]. Brooks, Nick. (2018). Women’s E-Commerce Clothing Reviews. Kaggle. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/nicapotato/womens-ecommerce-clothing-reviews.
[2]. Jagdale, R. S., Shirsat, V. S. and Deshmukh, S. N. (2019). Sentiment analysis on product reviews using machine learning techniques, Cognitive Informatics and Soft Computing, Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing 768 pp. 639–647.
[3]. Vanderplas, J. (2017). Python Data Science Handbook. O’Reilly Media, Inc.
[4]. Xie, S. (2019). Sentiment Analysis Using Machine Learning Algorithms: Online Women Clothing Reviews.
[5]. Agarap, A. F. m. (2020). Statistical Analysis on E-Commerce Reviews, with Sentiment Classification Using Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network.
[6]. Alrehili, A. and Albalawi, K. (2019). Sentiment analysis of customer reviews using ensemble method, 2019 International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCIS).
[7]. Kumar, G. R. (2020). NLP with Women Clothing Reviews. Kaggle. https://www.kaggle.com/code/granjithkumar/nlp-with-women-clothing-reviews
[8]. Lemaitre, G. (2014, August). 5. Ensemble of Samplers. Imbalanced Learn. https://imbalanced-learn.org/stable/ensemble.html#forest
[9]. Boisberranger, J. D. (2007). 1.4. Support Vector Machines. Scikit-Learn. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/svm.html
[10]. Yang, P., Wang, D., Du, X.-L. and Wang, M. (2018). Evolutionary dbn for the customers’ sentiment classification with incremental rules, Industrial Conference on Data Mining ICDM 2018: Advances in Data Mining. Applications and Theoretical Aspects pp. 119–134.
Cite this article
Lin,T. (2023). Recommendation and sentiment classification on E-Commerce reviews. Theoretical and Natural Science,19,161-168.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study will be available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Disclaimer/Publisher's Note
The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s). EWA Publishing and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
About volume
Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computing Innovation and Applied Physics
© 2024 by the author(s). Licensee EWA Publishing, Oxford, UK. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and
conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license. Authors who
publish this series agree to the following terms:
1. Authors retain copyright and grant the series right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this
series.
2. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the series's published
version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial
publication in this series.
3. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and
during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See
Open access policy for details).
References
[1]. Brooks, Nick. (2018). Women’s E-Commerce Clothing Reviews. Kaggle. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/nicapotato/womens-ecommerce-clothing-reviews.
[2]. Jagdale, R. S., Shirsat, V. S. and Deshmukh, S. N. (2019). Sentiment analysis on product reviews using machine learning techniques, Cognitive Informatics and Soft Computing, Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing 768 pp. 639–647.
[3]. Vanderplas, J. (2017). Python Data Science Handbook. O’Reilly Media, Inc.
[4]. Xie, S. (2019). Sentiment Analysis Using Machine Learning Algorithms: Online Women Clothing Reviews.
[5]. Agarap, A. F. m. (2020). Statistical Analysis on E-Commerce Reviews, with Sentiment Classification Using Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Network.
[6]. Alrehili, A. and Albalawi, K. (2019). Sentiment analysis of customer reviews using ensemble method, 2019 International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCIS).
[7]. Kumar, G. R. (2020). NLP with Women Clothing Reviews. Kaggle. https://www.kaggle.com/code/granjithkumar/nlp-with-women-clothing-reviews
[8]. Lemaitre, G. (2014, August). 5. Ensemble of Samplers. Imbalanced Learn. https://imbalanced-learn.org/stable/ensemble.html#forest
[9]. Boisberranger, J. D. (2007). 1.4. Support Vector Machines. Scikit-Learn. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/svm.html
[10]. Yang, P., Wang, D., Du, X.-L. and Wang, M. (2018). Evolutionary dbn for the customers’ sentiment classification with incremental rules, Industrial Conference on Data Mining ICDM 2018: Advances in Data Mining. Applications and Theoretical Aspects pp. 119–134.