

Volume 128
Published on September 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2025 Symposium: AI for Healthcare: Advanced Medical Data Analytics and Smart Rehabilitation
The use and conditions of different treatment methods vary, so choosing the appropriate treatment method for adolescent scoliosis is crucial. This article explores the main treatment methods for scoliosis, including stent therapy, exercise therapy, surgical treatment, and hand therapy. Stent therapy involves various types, such as cervical thoracolumbar sacral stents (such as Milwaukee stents) and thoracolumbar sacral braces (such as Boston stents), with different applicability and efficacy, but compliance and curve characteristics can affect the results. Schröder therapy, core muscle exercises, and SEAS exercise therapies focus on self correction and functional recovery, showing effectiveness in preventing progression, but have limitations in duration and applicability. Surgical treatment (posterior, anterior, combined, minimally invasive) is suitable for severe cases (usually Cobb angle>50°), but it can cause trauma and complications. Hand therapy (acupuncture and moxibustion, massage, chiropractic) is effective for mild cases with high efficacy, but needs long-term application. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on factors such as the severity of the curve, patient age, and compliance.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the continuous improvement of living standards and changes in diet and other lifestyles, obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2DM) caused by obesity are on the rise, and they are gradually getting younger. Plant-based diet (PBD) is considered to have a positive effect on the prevention and control of T2DM because it reduces animal fat and unsaturated fatty acids and increases the intake of dietary fiber. By studying the concept of PBD and the mechanism of T2DM caused by obesity, this paper analyzed the relationship between PBD pattern and T2DM mellitus in depth. So as to explore whether a healthy vegetarian model can help reduce blood sugar, increase cellular resistance to insulin, reduce cellular oxidative stress response, and thereby reduce the risk of diabetes and related complications. Studies have shown that an overall PBD significantly increases the risk of T2DM. Future research should promote high-quality PBDs through society, deeply explore the preventive effect in different groups of people, as well as the compliance of the masses, formulate personalized prevention strategies, promote the popularization of health models, and reduce the incidence of T2DM.

 View pdf
View pdf


The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and 3D magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is transforming orthopedic practice by overcoming traditional diagnostic limitations. This review synthesizes current advancements and future directions of AI-assisted 3D MRI analysis in orthopedics. Through critical evaluation of technical frameworks and clinical literature, we examine AI algorithms (including 3D CNNs and transformers), accelerated MRI acquisition techniques, and solutions for data heterogeneity and computational efficiency. Our analysis confirms that AI significantly enhances fracture classification accuracy, achieves exceptional segmentation precision for bone and cartilage structures, and reduces surgical complications through personalized planning and real-time navigation. Emerging strategies like federated learning address privacy concerns, while lightweight architectures optimize clinical deployment. Persistent challenges include data scarcity, model interpretability, and integration into healthcare systems. Future progress hinges on standardized multi-center validation, biomechanical simulation integration ("digital twins"), and regulatory alignment. AI-assisted 3D MRI promises to advance precision orthopedics but requires concerted collaboration across computational, engineering, and clinical domains to realize its full translational potential.

 View pdf
View pdf


Glioblastoma (GBM) is one of the most aggressive malignant brain tumors. The Stupp protocol is associated with a short median survival and high recurrence rate, referring to limited effective therapeutic alternatives. Various immunotherapies are therefore under active investigation. However, to date, their clinical application has been hindered by an unfavorable risk-benefit profile, with drug resistance posing a major barrier to therapeutic success. This review focuses on an immune checkpoint PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors, which have shown limited efficacy as monotherapy. Key mechanisms of resistance include the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, aberrant genetic and epigenetic regulation, and impaired T-cell function and infiltration. To address these challenges, combination strategies targeting these resistance mechanisms have been developed, including combination of dual or triple drug regimens, targeting multiple pathways to reverse the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment or correct underlying genetic abnormalities, along with the optimization of drug delivery routes to fundamentally enhance the drug efficacy. These approaches offer a promising theoretical framework for enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in GBM.

 View pdf
View pdf


Teens between the ages of 10 and 18 are affected by the spinal issue known as adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. The global prevalence rate is 2%-3%, which is relatively high considering the global adolescent population base. If left untreated, it may cause physical pain, psychological distress, and functional impairment. This paper focuses on the three main treatment methods for AIS - physical therapy, brace therapy, and surgical treatment, analyzing their advantages and disadvantages, mechanisms of action, and applicable scenarios. The results show that physical therapy is effective in preventing progression and improving muscle balance for mild cases, but its effectiveness in clinical treatment still requires further experiments to confirm. Brace therapy can reduce the risk of severe progression for moderate cases, but there are challenges related to compliance. Surgical treatment has a relatively high correction rate for severe cases, but it also has corresponding risks and may lead to limited mobility and neurological complications. This paper provides evidence-based guidance for personalized treatment options, emphasizing the need to develop targeted intervention plans based on the severity of the disease and the specific scoliosis condition of the individual.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the improvement of sports technology and the increase in competition intensity, the complexity of sports injuries is becoming increasingly prominent, which puts higher demands on the accuracy of their diagnosis and treatment. This paper focuses on the special issue of ankle anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) injury, and conducts a systematic study from three dimensions: diagnosis, treatment and subsequent efficacy, aiming to sort out and summarize effective treatment processes. The results of this paper indicate that arthroscopy remains the most accurate method in the diagnostic stage, while ultrasound examination can serve as an effective alternative, providing reliable evidence for clinical diagnosis. In terms of treatment, if conservative treatment is adopted, elastic bandaging is the preferred way to fix the ankle joint. In contrast, the combined reconstruction of the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) and calcaneofibular ligament (CFL) has more advantages - in the long run, this procedure can minimize the risk of patients developing chronic ankle instability, allowing athletes to almost 100% recover to pre-injury exercise levels. This paper analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of various diagnosis and treatment methods, constructs a comprehensive and systematic treatment process, and provides scientific reference for both doctors and patients to choose the most suitable rehabilitation plan. It helps to promote the standardization and personalization of sports injury diagnosis and treatment, and ultimately promotes the efficient rehabilitation of athletes.

 View pdf
View pdf


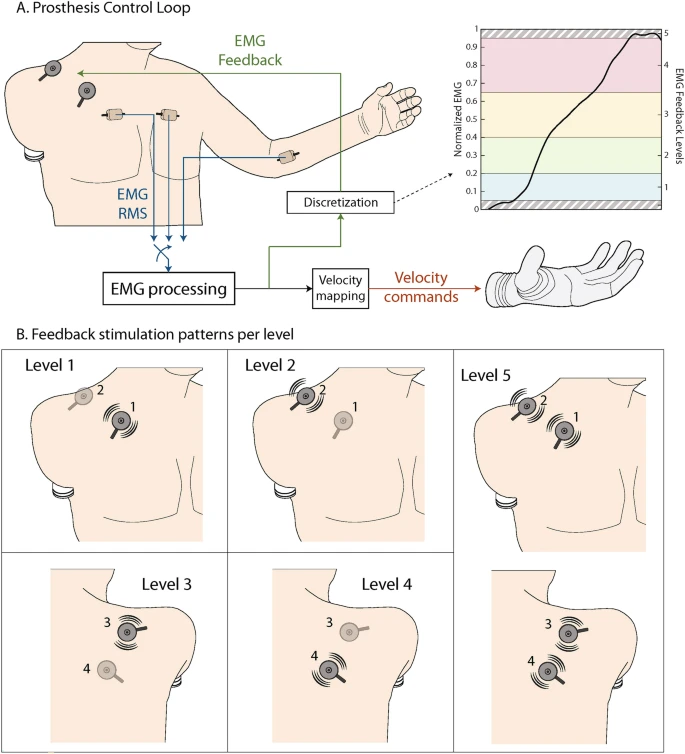
Wearable devices have become more advanced in recent years, with scientists and engineers creating smart limbs, sensors, brain-computer interfaces (BCIs), and exoskeletons to help amputees move better. These tools are also used in hospitals and rehab centers for muscle training, motion analysis, and making therapy more engaging. While they have already helped many people walk again, hold objects, and even play rehab games, research is still working to improve their performance outside the lab by focusing on accuracy, battery life, comfort, and affordability. However, many devices remain expensive and hard to access, and some cannot yet work well in daily life, especially in busy or outdoor environments. This essay reviewed four main types of wearable devices, their real-life and rehab uses, and three cases where they restored movement and independence. These findings prove that wearable devices can change lives, and future research should make them smaller, stronger, and more affordable, with designs that work well at home so more people can benefit.

 View pdf
View pdf




