

Volume 144
Published on October 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2025 Symposium: AI for Healthcare: Advanced Medical Data Analytics and Smart Rehabilitation
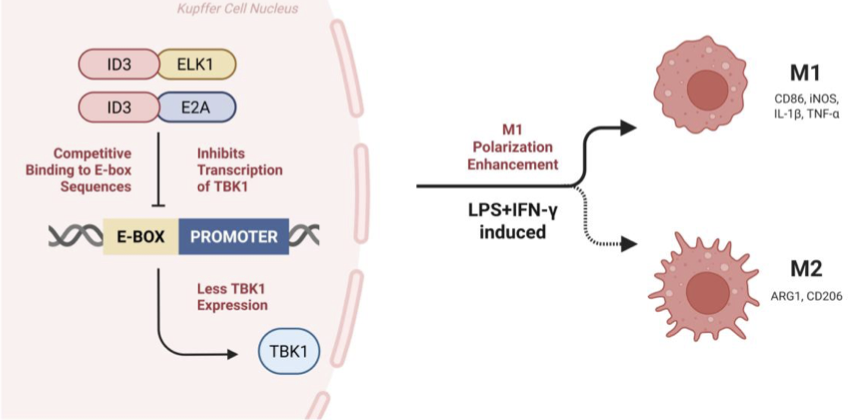
Cancer is a globally significant disease, which caused 9.7 million related deaths worldwide in 2022 alone. The tumor microenvironment (TME) represents a major barrier to effective cancer treatment, as it can promote tumor immune evasion and reduce the efficacy of anticancer therapies. Macrophage polarization is also a key determinant of tumor progression: by modulating the shift of macrophages between the M1 and M2 phenotypes, the body can modulate anti-tumor functions. This study aims to elucidate how the ID3–E2A/ELK1 complex modulates TBK1 expression to drive M1 macrophage polarization. We propose that this complex binds the TBK1 promoter, repressing its expression and subsequently promoting IRF5 activation, which shifts macrophages toward an M1 phenotype. Through genetic and functional assays, we propose to further explore how ID3-mediated TBK1 inhibition enhances phagocytosis and antitumor immunity. These insights may guide future development of macrophage-targeted immunotherapies for cancer treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


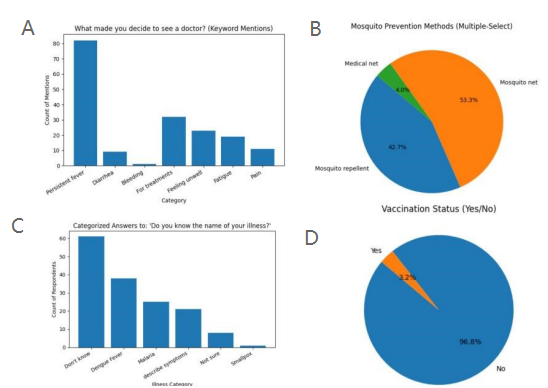
Rural Laos faces persistent infectious disease burdens driven by weak infrastructure, low health literacy, and environmental risks. In ten Savannakhet villages, community surveys showed care-seeking was mostly for persistent fever, with little ability to identify diseases; vaccination coverage was minimal and mosquito net use inconsistent. Provider surveys confirmed dengue and malaria as leading illnesses with seasonal peaks, while diagnosis relied on symptoms and treatment remained largely supportive due to shortages of diagnostics, drugs, and staff. Infection control was limited to heat and alcohol sterilization. Field observations highlighted stagnant water, unsafe drinking sources, and close livestock proximity as additional risks. These findings underscore how knowledge gaps, resource-constrained clinics, and environmental exposures jointly hinder rural healthcare, pointing to the need for stronger health literacy, diagnostic capacity, and environmental management.

 View pdf
View pdf


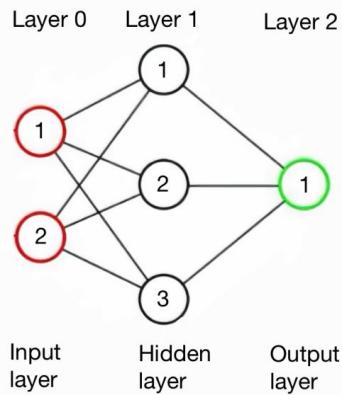
To develop a model that establishes if a patient's breast cancer is benign or malignant, it uses them in the patient data set. The issue discussed in this article is part of a larger problem that is classified as supervised learning. Python is employed for coding. This study makes use of Keras, which is linked to TensorFlow and serves as one of the most widely used free modules. It's a categorization problem that is binary, and neurons are employed to create the model. The sigmoid function is employed in the output layer as a means of activation. The article attempts to create different models with different numbers of hidden layers. A set for verification (25%) and the training data (75%), respectively, are created from the collected data. The validation set is used to assess each model's success after it has been first trained on the set that was used for training. The article's conclusion states that the model with no additional layer is the most effective.

 View pdf
View pdf


This is a review of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT). Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a widely used therapeutic treatment for treating psychological disorders by therapists, which is supported by a large body of clinical evidence. It is a structured approach used to help patients identify and analyze their own misconceptions about reality and change their irrational cognitive problems, thereby alleviating some of the symptoms of psychological disorders. In order to systematically summarize the basic principles of cognitive-behavioral therapy, its therapeutic measures for psychological disorders, and its application effects, this paper analyzed the existing literature related to cognitive behavioral therapy, summarized the core theories and application effects of CBT, and concluded that it has significant therapeutic effects on depressive disorders, generalized anxiety disorder and eating disorders. Also, a follow-up of the post-treatment showed that CBT was also effective in preventing the recurrence of these psychological disorder symptoms. For patients with severe symptoms, treatment should be administered in combination with other clinical approaches, such as medication.

 View pdf
View pdf


Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) usually occurs due to an overexpression of BCL6 protein. However, the indirect inhibition of BCL6 remains challenging. This work mainly aims to investigate the impact of BCL6-targeted PROTAC medicine--CFT7455 on degrading BCL6 and removing DLBCL tumour cells. By using SU-DHL-4 cell line and treating these cells with CFT7455 in different concentrations with different treatment durations, CFT7455’ function could be tested. MTT assay is used to test cell viability. And Western Blot is used to detect BCL6 protein level. TUNNEL assay and Annexin V/PI assay are used to validate apoptosis. The results could show that CFT7455 might induce potent, dose-and time-dependent BCL6 degradation. This degradation would lead to a significant decrease in cell activities and an increase in apoptosis at the same time. These findings may suggest the potential of CFT7455 as a treatment of BCL6-driven DLBCL, promoting the further development of it.

 View pdf
View pdf


We present a fully in silico pipeline for the de novo design of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP- 4) inhibitors that integrates data-driven curation, transfer learning, and reinforcement learning (RL) within the REINVENT architecture. Activity records for human DPP-4 (CHEMBL284) were programmatically retrieved from ChEMBL, normalized to nanomolar units, filtered at IC50≤100 nM, standardized to canonical SMILES, and consolidated into a high-quality training table; pIC50 values were computed and a top-100 reference set was exported for down- stream novelty control. A REINVENT prior was adapted to the DPP-4 chemical space via maximum-likelihood fine-tuning on 173 nonredundant, high-activity SMILES. The adapted generator was then optimized with an RL objective that combined predicted potency (pIC50), drug-likeness (QED), synthetic accessibility (SA), and novelty penalties relative to the top-100 reference inhibitors. Relative to the transfer-learned baseline, RL increased mean QED by ~ 10%, improved normalized synthetic accessibility (1 - SA)/10 by ~ 15%, and maintained diversity with ~60% novelty, while the composite reward showed a clear upward shift. Structure-based evaluation further corroborated these gains: 100 RL-generated molecules achieved a mean docking score of -9.8 kcal/mol, surpassing both pre-RL de novo samples (-7.7 kcal/mol) and the top 100 reference actives (-8.5 kcal/mol). These results demonstrate that RL fine-tuning can steer a pretrained generator toward DPP-4–relevant regions of chemical space with improved developability surrogates and predicted binding. Future work will integrate ADMET predictors into the reward and prioritize wet-lab validation to confirm biochemical potency and advance selected designs toward lead optimization.

 View pdf
View pdf


Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a widespread health problem, especially in the elderly. Dietary strategies are essential for effective glycemic regulation and extra virgin olive oil is considered to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation, which could offer more advantages than other vegetable oils. This study examined the differential effects of EVOO and rapeseed oil supplementation on glycemic control and metabolic risk factors in 38 elderly Chinese women with T2D. The main detection indicators were FPG and HbA1c; and the secondary testing indicators were postprandial glucose, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, lipid profile, and C-reactive protein. The results showed that EVOO had more significant advantages than rapeseed oil in improving blood glucose control and cardiovascular risk markers in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes.

 View pdf
View pdf


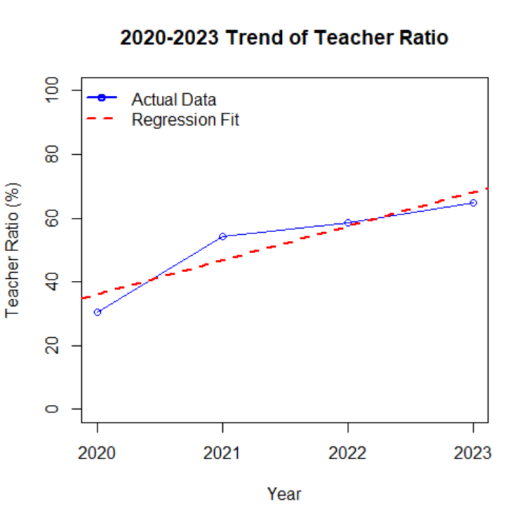
With millions of young people affected by depression and related conditions, adolescent mental health has become a growing concern in China. In response, national policies have emphasized strengthening school-based mental health education and expanding the allocation of dedicated teachers. This study uses macro-level data from the China Statistical Yearbook and the annual reports of the Ministry of Education (2020–2023) to analyze trends in mental health teacher allocation and its potential association with student well-being. Descriptive statistics and linear regression show a steady increase in teacher allocation, with an estimated annual rise of approximately 10 percentage points, though statistical significance was limited by small sample size. Exploratory regression using available outcome data from 2020 and 2022 suggests a positive relationship between teacher allocation and the proportion of students reporting good mental health. To further illustrate methodological approaches, a logistic regression model incorporating education expenditure, GDP, student–teacher ratio, and urbanization rate was applied to simulated data, yielding moderate discriminatory capacity (AUC = 0.798). While these findings are preliminary due to restricted data availability and reliance on macro-level statistics, they provide initial evidence that the expansion of mental health teacher resources may support improvements in adolescent mental health outcomes. Future research should incorporate larger, multi-year, and individual-level datasets to more rigorously evaluate the policy’s impact.

 View pdf
View pdf


Breast cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women globally, with treatment facing significant challenges due to drug resistance and metastasis. RNA interference technology, particularly via siRNA, offers a novel strategy for precision therapy. This review comprehensively examines the mechanisms and applications of nanotechnology-mediated siRNA delivery systems. Methodologically, it involves systematic analysis of the design principles underlying polymeric, lipid-based, and metallic nanocarriers to evaluate their efficacy in enhancing cellular uptake, promoting endosomal escape, and protecting siRNA from degradation; additionally, it combines preclinical and clinical data to evaluate these delivery platforms' pharmacodynamic characteristics and therapeutic results. Results demonstrate that siRNA nanocarriers significantly enhance targeted gene-silencing efficiency, exhibiting potent anti-tumor activity in breast cancer models. However, clinical translation is hampered by limitations in specificity, immunogenicity, and evolving regulatory frameworks. To advance clinical application, future research should focus on developing stimuli-responsive nanovectors and combining them with immunotherapy or chemotherapy regimens.

 View pdf
View pdf


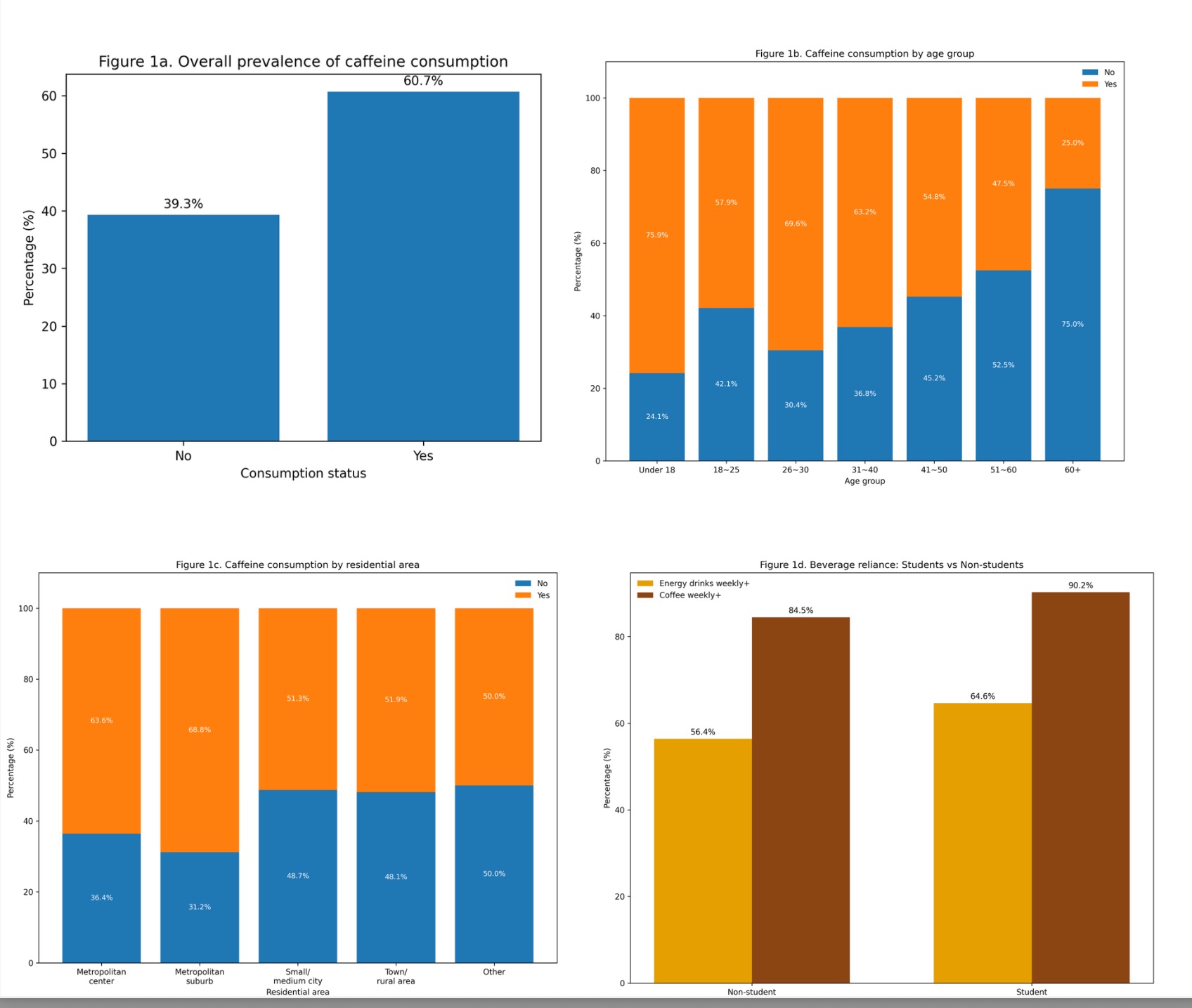
Caffeine is among the most consumed psychoactive substances worldwide, with well-documented benefits –such as reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases and neurodegenerative diseases --and risks, including sleep disturbances and other side effects. It has become integral to daily life, and consumption patterns vary across population groups and over time. This study investigated caffeine consumption pattern in coastal China through a comprehensive online questionnaire. The survey assessed demographics, consumption behaviors, knowledge, attitudes, and perceived effects. A total of 481 valid responses were collected from individuals aged 12 years and older without restrictions on gender, education, or occupation. Data were analyzed using chi-square tests, independent-sample t-tests, ANOVA, kruskal–wallis tests and regression models, as appropriate. Findings revealed that caffeine consumption was widespread and significantly associated with younger age groups and metropolitan residence. Student reported relatively higher energy drink use, which non-students consumed more coffee and tea. Importantly, higher knowledge and concern about caffeine were linked to regular use, indicating that awareness may reflect lived experience and self-regulation rather than acting as a deterrent. This study highlights the complexity of caffeine-related behaviors and underscore the need for targeted health strategies that address the specific motivations and contexts of different consumer groups. This study contributes valuable evidence for scholars, public health education, and local policy initiatives in Chinese context.

 View pdf
View pdf




