

Volume 77
Published on January 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICBioMed 2024 Workshop: Computational Proteomics in Drug Discovery and Development from Medicinal Plants
With the continuous development of society, people's life pressure is increasing; poor daily routines and some other factors make the incidence of cancer increasingly high. Modern medicine typically prioritizes surgical resection, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy for cancer treatment. However, these methods often result in a high recurrence rate, as well as side effects such as nausea and vomiting, which can lead to intolerant patients. Astragalus polysaccharide (APS) is extracted from Astragalus root, a water-soluble heteropolysaccharide formed by concentration and purification. Numerous studies have shown in recent years that APS can achieve anti-cancer effects in various cancers, including lung, liver, breast, and esophageal cancers. It can suppress tumor cell growth, cause tumor cell death, and obstruct tumor cell invasion and metastasis by modulating the body's immune system. Additionally, when combined with other chemotherapy drugs, there is evidence that APS can improve efficacy and reduce toxicity. In this paper, we review recent research on APS in the field of anticancer therapy, aiming to provide a valuable reference for future studies.

 View pdf
View pdf


All mRNA vaccines as a relatively newly developed branch of vaccine have shown a great prosperous future. Unique from the traditional vaccines, mRNA vaccines are fundamentally different in mechanism when promoting immunity for the body. This optimism is built on recently published studies demonstrating the efficacy of mRNA vaccines in combatting several types of cancer and infectious pathogens where conventional vaccine platforms may fail to induce protective immune responses. Traditional vaccines often contain a weakened or inactivated virus that our body can recognize as a real virus without putting us in danger, whereas the mRNA vaccine only carries out the instructions for our body to produce certain types of proteins that counter the virus. With the new Covid vaccine as a great representative, mRNA vaccines carry the genetic codes in messenger RNAs for proteins to recognize the need to build immunity for the virus. One of the most significant developments in progress includes the mRNA vaccine for Zika virus, a single-stranded RNA virus that can cause birth defects and is currently no cure or definite prevention. This review summarizes recent developments in mRNA vaccines from the past few years and discusses the challenges and future directions for the field.

 View pdf
View pdf


Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells can be used to treat B-cell malignancies and represent a novel approach in cancer immune cell therapy. Although the therapy has shown significant clinical success in treating B-cell malignancies, its efficacy in solid tumors is limited by challenges such as tumor antigen heterogeneity, antigen loss, and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. This review understands the shortcomings of CAR-T cell therapy and proposes several optimization strategies to face different dilemmas in treating tumors. Targeting fibroblast activation protein (FAP) to suppress the TME; RNA vaccines that can deliver specific antigens to lymph nodes to activate and expand CAR-T cells to enhance their immune response against solid tumors; and multi-targeting design to target multiple antigens at the same time to effectively mitigate tumor escape due to antigen loss. In addition, this review enumerates the strategies of combining therapies with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and co-stimulatory molecules to improve the durability and targeting precision of CAR-T cells and reduce side effects. Thus, this review demonstrates a series of optimized uses of CAR-T cell therapies and improves the efficacy of CAR-T cells in solid tumors. This has important clinical implications for advancing cancer immunotherapy and driving the development of immune cancer in the future.

 View pdf
View pdf


Thearubigins (TRs) are a class of water-soluble, acidic phenolic compounds that are generated through oxidative polymerization reactions during the fermentation of black tea. As the predominant constituents in black tea, TRs significantly influence its unique color, texture, and potential health benefits. However, compared to polyphenols in black tea with lower molecular weights, research on TRs is more limited due to their diverse and complex nature. This paper reviews the current status of research on TRs production, the progress in isolation and preparation methods, and discusses the pharmacological effects of TRs, including their roles in antioxidant, anti-aging, anti-mutagenic, anti-cancer, and anti-tumor activities, as well as their anti-inflammatory properties and potential in preventing obesity. It also explores the prospects of TRs' application in the fields of food coloring, chemical, and healthcare industries. Despite their potential, the isolation and purification of TRs remain challenging due to their structural complexity and heterogeneity. Future studies should integrate various scientific techniques to further explore the bioactivity and mechanisms of action of TRs. The aim of this study is to provide a comprehensive overview that will serve as a reference for future research and application of high molecular weight polyphenols, such as TRs.

 View pdf
View pdf


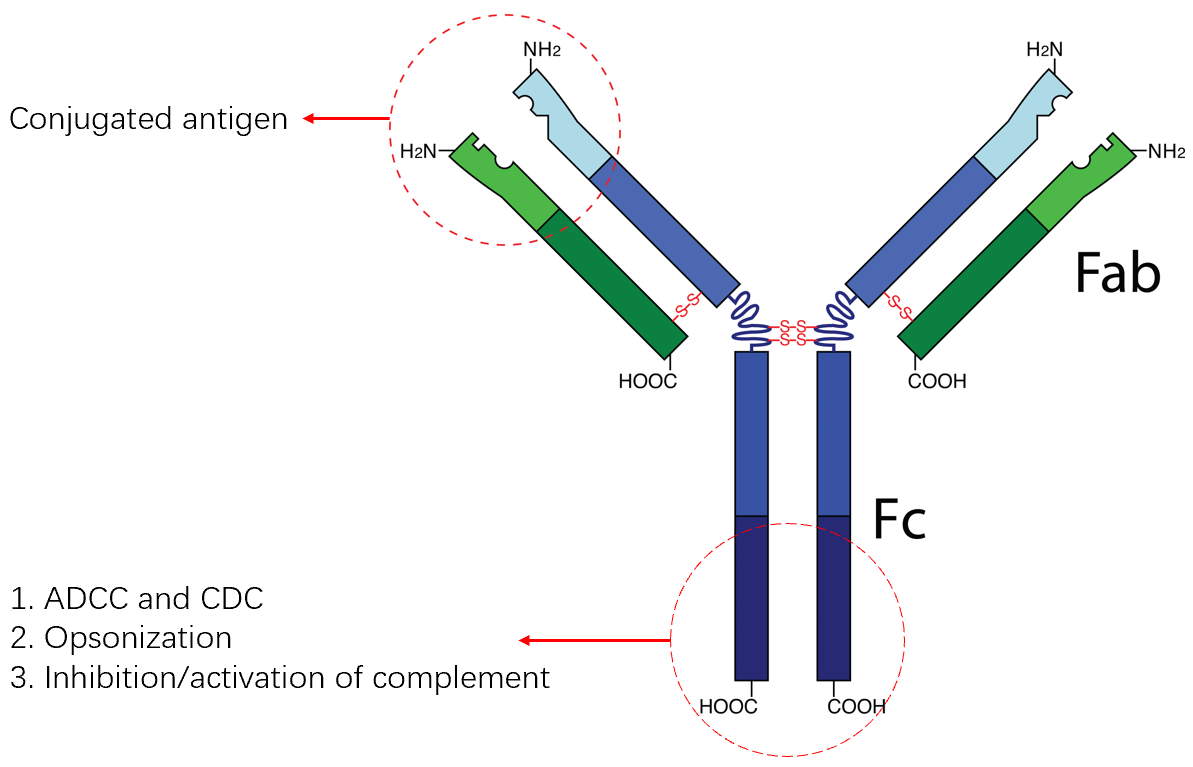
Cancer is a serious public health issue and the second leading cause of death worldwide. It is predicted that the number of cancer diagnoses and cancer-related deaths will continue to rise in the future. Advances in molecular biology and genomics of cancer, combined with an increasing understanding of the molecule phenomena in cancer, have led to the emergence of monoclonal antibodies as key therapeutic strategies in reverse pharmacology. Monoclonal antibodies have high specificity and affinity, allowing them to directly target specific tumor markers and modulate the immune system, thereby providing unique advantages in precision cancer therapy. The purpose of this review is to gain an in-depth understanding of the structure and function of monoclonal antibodies, and to provide a comprehensive overview of the applications and developments of monoclonal antibodies in cancer treatment, as well as their mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses. Furthermore, by analyzing the approved and investigational drugs for different types of cancer and their efficacy, one can gain a deeper comprehension of monoclonal antibodies targeting distinct cancers.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the medical domain, artificial intelligence (AI) pertains to the utilization of machine learning models and algorithms for the analysis of intricate medical data. This paper demonstrates the application of learning models in cancer diagnosis through two innovative approaches: the Hybrid U-Net model and an improved MobileNet-V3 model, as well as a novel Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) model. The combination of these models has achieved significant improvements in cancer diagnosis accuracy, interpretability, and performance. The integration of the Hybrid U-Net with MobileNet-V3 effectively enhances image segmentation and feature extraction efficiency, particularly in analysis of medical imaging tasks such as skin cancer detection. Through hyperparameter optimization, these models perform exceptionally well with complex data, significantly improving performance metrics such as accuracy, PPV, NPV, and AUC. On the other hand, the MIL model, with its innovative attention mechanism, has shown considerable promise in improving the diagnosis of lung cancer by providing greater interpretability and aiding clinical understanding. However, despite the impressive performance of these models, the research also highlights limitations such as small sample sizes and reliance on existing segmentation methods, which affect the stability and broad applicability of the models.

 View pdf
View pdf


Cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are major health problems worldwide, accounting for the majority of morbidity and mortality. Heart failure, hypertension, and coronary artery disease (CAD) are examples of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) that are caused by a combination of lifestyle, environmental, and genetic factors. Dietary treatments as preventive measures have attracted considerable attention due to the increasing prevalence of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disorders. The paper examines the data from ongoing studies to find out the way plant-based diets have an influence on heart and brain health. A substantial amount of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts are features of plant-based diets, which are linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), including obesity, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. Differences in intake of certain types of nutrients are discussed, along with possible pathways via which plant-based diets may help strengthen the heart and brain systems. This passage underlines the promise of these kinds of diets as proactive strategies to reduce the incidence and progression of cardiovascular illnesses and cerebrovascular disease by offering some comparison and analysis based on current studies.

 View pdf
View pdf


Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a kind of neurodegenerative disease, and it usually occurs in senility. The number of people suffering from this disease is increasing every year, which makes AD become a major global public health problem. Once a person is diagnosed with AD, it’s really hard to heal. The early symptoms of AD include memory loss, difficulty with problem solving and planning, confusion about time and place and so on. The moderate symptoms include personality and behavioral changes, restlessness and wandering. The late stage symptoms include physical decline, severe memory loss, and increased vulnerability to infections. So, it's important to write a review paper about it. This paper presents Pathogenesis of AD including A β hypothesis, Tau protein hypothesis, mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroinflammation hypothesis, cholinergic hypothesis and oxidative stress hypothesis. It also presents treatments of AD including RNAi therapeutics, ketogenic diet, probiotic interventions. Lastly, the paper suggests corresponding therapies for each pathogenesis.

 View pdf
View pdf


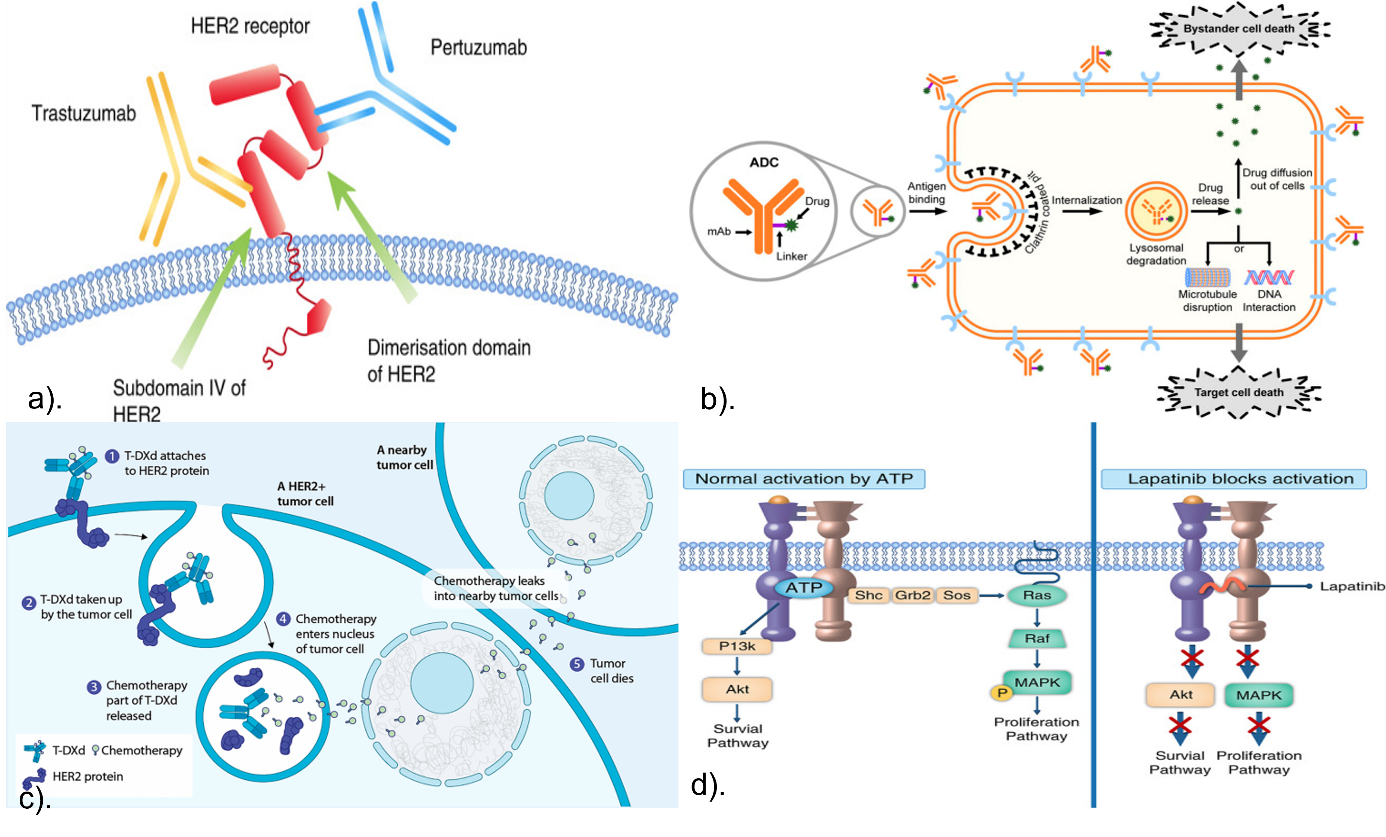
The human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is a member of the ErbB family, a group of four transmembrane glycoproteins with tyrosine kinase activity that are structurally related to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). These proteins are crucial in cell signaling processes that regulate normal cell growth and differentiation. When these signaling pathways become dysregulated, abnormal cell growth can occur, potentially leading to cancer. HER2 was first recognized as a key therapeutic target in breast cancer and has since been studied in the context of other cancers. This review provides an in-depth overview of HER2-targeted therapies and their mechanisms, as well as an analysis of the resistance pathways associated with these treatments. Over the past few decades, the development of HER2-targeted therapies has revolutionized cancer treatment strategies. Advances in understanding HER2 biology, resistance mechanisms, and diagnostic techniques have driven the field forward. This review concludes by discussing emerging anti-HER2 therapies that show great potential in the future treatment of cancer.

 View pdf
View pdf


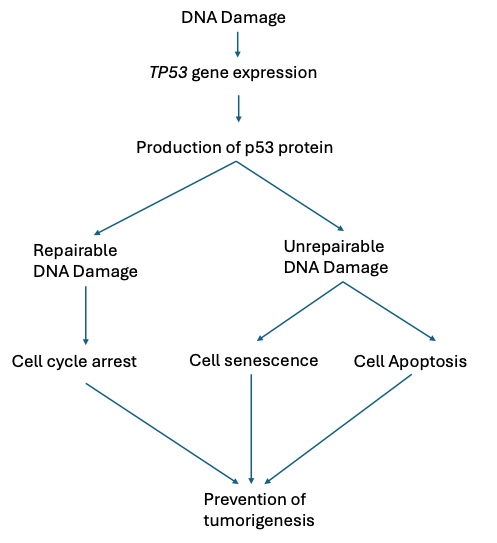
Tumor protein 53 (TP53) is a tumor repressor gene that is highly responsible for activating cell cycle arrest in the event of DNA damage, stopping the replication of damaged cells, which may cause cancer. However, when mutated, TP53 is an oncogene, with mutated variants of it being seen in over half of all cancers diagnosed including the aforementioned four. With groundbreaking CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology coming to the forefront of biotechnological research, the applications to cancer research and gene therapy have been increasing. This review explores CRISPR-Cas9 and its uses for treatment and medication investigation in various cancers, including lung, prostate, breast, and bone cancer through the lens of the TP53 gene. Due to TP53’s commonality in cancer, CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology can be used to its maximum potential in this context as a treatment or investigative tool, with it yielding positive results in reverting tumor growth, as well as great versatility when it comes to screening related genes that inhibit or encourage tumor growth which can be targeted by drugs, or even the screening of the drug’s effectiveness themselves. Thus, CRISPR-Cas9’s applications in TP53-related cancer treatment and chemotherapeutic fields prove this technology to be successful.

 View pdf
View pdf




