

Volume 96
Published on April 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science
A common pregnancy problem, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), is caused by impaired glucose and carbohydrate metabolism that is initially identified during pregnancy. Because GDM has a major influence on the health of mothers and infants, its rising prevalence has made it a serious public health concern. The multifaceted pathophysiology of GDM, which includes insulin resistance, genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, and lifestyle variables, is reviewed in this article. It highlights the serious short-term hazards, such macrosomia and gestational hypertension, as well as the long-term effects, like a higher chance of type 2 diabetes in both mothers and their children. Effective management of GDM requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing dietary adjustments, physical activity, regular blood glucose monitoring, and pharmacological interventions when necessary. Public health strategies promoting low-glycemic index and high-fiber diets, alongside interventions targeting obesity and physical inactivity, are vital to reducing GDM incidence. Furthermore, this study highlights gaps in understanding the influence of social, cultural, and economic factors on GDM management and emphasizes the need for future research to develop inclusive, personalized strategies to address these disparities effectively.

 View pdf
View pdf



This study explores biological control strategies for managing Rosa chinensis pests, specifically mites (Tetranychus urticae) and aphids (Macrosiphum rosae), through agroecological approaches such as companion planting and habitat enhancement. Predatory mites (Phytoseiulus persimilis), hoverflies (Syrphidae), lacewings (Chrysopidae), and ladybugs (Coccinellidae) were identified as effective natural enemies for pest suppression. Strategic intercropping with plants like Lobularia maritima, Viburnum tinus, and Vitis riparia was proposed to attract and sustain these predators, reducing pest populations while minimizing chemical inputs. The research highlights the ecological and economic advantages of biological control, including reduced environmental risks, enhanced biodiversity, and long-term sustainability, compared to conventional chemical pesticides. By integrating natural pest control methods, this study provides practical solutions for sustainable Rosa chinensis cultivation and contributes to the broader adoption of environmentally friendly agricultural practices.

 View pdf
View pdf


Neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by the progressive loss of neurons or their myelin sheaths, leading to dysfunction and worsening over time. In Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Huntington's disease (HD), certain specific types of neurons are symmetrically lost in the patient's brain, and these specific neuron losses cause motor, sensory, or conscious disorders of the patient. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are multipotent stem cells obtained through reprogramming of somatic cells. The iPSC of patient origin carries disease-related genetic and epigenetic information, and its differentiation process can reflect the development of the disease to a certain extent. This makes iPSCs an ideal tool for building a variety of disease models, including AD and HD, offering valuable insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies. Since most AD and HD still lack effective treatment methods, clarifying the possible pathogenesis of AD and HD will become a prerequisite and foundation for effective prevention and development of the disease and finding effective treatment methods, which is of great theoretical and practical significance for improving the quality of life and longevity of the elderly.

 View pdf
View pdf


When CRISPR-Cas9, short for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) with CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9), was successfully harnessed for genome editing in the early 2010s, it marked a new era for biotechnology. The high precision, efficiency, and adaptability of CRISPR-Cas9 have unlocked extraordinary potential in medicine, agriculture, and industrial biology, underscored by the awarding of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2020 to its pioneers. This paper reviews follow-on advancements to the technology addressing challenges, including off-target effects and inefficient delivery systems, and explores its transformative applications in treating genetic disorders, including sickle cell disease, transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia, and cystic fibrosis. Additionally, it highlights ongoing hurdles management of such as high costs and safety and efficacy of heritable gene editing. This study shows that addressing these challenges and fostering ethical and collaborative advancements will be essential for CRISPR technologies, which can fulfill their transformative potential in improving human life quality.

 View pdf
View pdf


Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer among women worldwide, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases annually. In the United States, it accounts for 15.5% of all new cancer cases in 2024, with over 42,000 deaths reported annually. Despite advancements in detection and treatment, mortality remains a concern. This paper explores breast cancer’s biological and clinical characteristics, risk factors, and screening strategies, with a particular focus on young women. The disease originates from abnormal cell growth in breast tissue and is classified into various subtypes based on molecular markers. Key risk factors include age, genetic predisposition (e.g., BRCA mutations), and lifestyle influences such as obesity and alcohol consumption. The disease often manifests in a more aggressive form with less favorable outcomes in younger women.Early detection through mammography significantly reduces mortality, but debates persist over the optimal screening age due to concerns about false positives and overdiagnosis. This study examines existing screening guidelines, the economic burden of screening, and barriers to access for young women. This study examines approaches to boost early detection and close the gaps in breast cancer survival rates. It also highlights the critical need for addressing inequalities by increasing diversity in clinical trials and providing equal access to high-quality care and screening.

 View pdf
View pdf


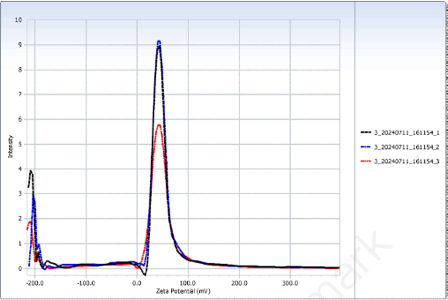
The polymer poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) emulsifies in aqueous conditions to form nanoparticles. Such vesicles are frequently involved in drug delivery, of vaccines for instance, due to several advantages, such as high structural stability, low cytotoxicity and biodegradability. Incorporating lipids onto surfaces of such nanoparticles enhances their effectiveness in cellular internalization. However, the effects on structural integrity in terms of the entire polymer-lipid particle of incorporating lipids onto polymeric nanoparticles is rather less fathomed. In this article we synthesized PLGA vesicles via ultrasonication of suspensions of PLGA as the hydrophobic phase, deionized (DI) water as the inner aqueous phase, and 30% ethanol as the outer aqueous phase. The hydrophobic phase was pre-added 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium propane (DOTAP) in different ratios. The resulting vesicles were presented with scan electron micrographs (SEMs), and were measured their sizes and zeta-potentials. Average zeta potential increased as proportion of lipid to polymer increased, while in all samples there were polydispersion, suggesting the possibility of nanoparticles dissembled. We suggest that the ratio leading to the highest average zeta potential is within the interval between 1:6 and 1:4, or greater than 1:4.

 View pdf
View pdf


Around 10% of pregnant and postpartum women globally suffer from depression, with the incidence of postpartum depression ranging from 10% to 15%. Besides, about 50% to 80% of postpartum women exhibit varying degrees of depressive symptoms following childbirth. And epidemiological data demonstrate that the global prevalence of postpartum depression is 17.22% (95% confidence interval: 16.00-18.51). Despite the effectiveness of antidepressants in relieving depressive symptoms, their use in breastfeeding women may result in transfer via breast milk, potentially affecting infant health. Therefore, this paper presents a review of the safety of using antidepressants during breastfeeding, with a focus on the permeability of different antidepressants in breast milk and their potential risks to infants. The results indicate huge differences in the concentrations of various medications in breast milk, with some drugs exhibiting higher permeability, which may negatively impact infant health. As such, in clinical practice, healthcare professionals should carefully select an antidepressant treatment plan for breastfeeding women according to the pharmacokinetic properties of the drug and the physiological characteristics of the infant, so as to minimize potential risks to both maternal and infant health.

 View pdf
View pdf


Breast cancer is one of the most frequent malignancies affecting women’s health and is the second leading tumor in terms of prevalence globally. However, advanced breast cancer remains incurable, and the prognosis is unfavorable. Identifying prognostic factors in advanced breast cancer is crucial for clinical practice. In this paper, we aim to summarize significant risk factors affecting the prognosis of patients suffering from advanced breast carcinoma, including age, sites of metastasis, molecular typing, and local treatments. Additionally, this paper explores the methods and functions of prediction models for advanced breast cancer, aiming at offering new insights for clinicians and researchers. In the future, with a large body of research, we hope clinical researchers will develop prediction models for advanced breast cancer that are widely applicable in clinical practice. These models could enable patients to have a clearer and more in - depth understanding of their conditions and assist physicians in implementing individualized treatments and precision medicine, ultimately prolonging patient survival.

 View pdf
View pdf


Intestinal tumors pose a significant threat to human health, and existing treatments have limitations, making the exploration of new therapeutic approaches highly important. β-Glucan, a naturally occurring bioactive polysaccharide, has garnered significant interest in anti-tumor research. This paper, using literature review and case analysis methods, systematically elaborates on its mechanisms of action in combating intestinal tumors. β-Glucan is widely sourced, structurally diverse, and possesses various physiological functions, such as immune regulation and anti-inflammatory effects. Its anti-tumor mechanisms primarily include: Immune modulation – activating immune cells, it can trigger the apoptosis of tumor cells, restrain the proliferation of tumors, and prevent tumor metastasis. Modulating gut microbiota - encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria while inhibiting harmful ones; its metabolic byproducts can also inhibit tumor growth. Clinical studies have shown that β-glucan, when used alone, exhibits immune-regulatory and potential tumor-suppressive effects. Moreover, it can work synergistically with chemotherapeutic drugs to boost effectiveness, providing a new approach for the prevention as well as treatment of tumors in the intestine.

 View pdf
View pdf


Telomere dysfunction has emerged as a critical determinant in the pathogenesis of various diseases, particularly in age-related disorders such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). This review delves into the telomere hypothesis, elucidating the function and composition of telomeres, while also acknowledging their intricate relationship with cancer, albeit not as the primary focus. This study employs a comprehensive literature review approach to elucidate the mechanisms linking telomere dysfunction to IPF. The review focuses on the genetic mutations associated with telomere shortening, the role of cellular senescence, and the potential of telomerase activation and TGF-β pathway modulation. Telomere dysfunction is a pivotal determinant in the pathogenesis of IPF, providing new insights into disease etiology and therapeutic targets. The intricate interplay between telomere shortening, cellular senescence, inflammation, and fibrosis underscores the complexity of IPF and highlights the need for multifaceted therapeutic approaches. Future research should focus on elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying telomere dysfunction in IPF, identifying novel biomarkers for early disease detection, and developing safe and effective telomere-targeted therapies.

 View pdf
View pdf




