

Volume 101
Published on May 2025Volume title: Proceedings of CONF-MPCS 2025 Symposium: Mastering Optimization: Strategies for Maximum Efficiency
With the improvement of people’s living standards in the new era, tourism consumption has gradually become a hotspot of popular entertainment. Beijing faces the challenges of high tourist carrying capacity at attractions and uneven distribution of tourism resources. There is a growing need for personalised travel path planning. This study aims to develop a one-stop personalised intelligent recommendation model for tourist attractions in the Beijing area to enhance tourists’ travel experience. By integrating data from mainstream travel websites such as Ctrip, Tongcheng, and Qunar, the paper uses natural language processing (NLP) technology to conduct analyses of online reviews to derive user sentiment and personalisation indicators. The entropy weight method is used to comprehensively consider the user’s personalised travel preferences, combined with the Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to an Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) method to scientifically rank the attractions and select the candidate set. Finally, the path planning algorithm with distance factor is implemented based on a greedy algorithm to optimise the travel path according to the user’s interest and achieve the recommendation of personalised travel routes. The model proposed in this study shows high accuracy and user satisfaction in empirical tests, which strengthens the user information processing support and personalisation needs in the era of big data, and contributes new solutions to the field of travel path recommendation.

 View pdf
View pdf


Many physics and mathematics problems generate linear equation systems, and solving linear equation systems has become an important proposition. Therefore, combined with the characteristics of modern computers, various methods for solutions need to be sought. This article introduces applications of linear equation systems in different fields, as well as representative figures and works with outstanding achievements. It focuses on providing formulas and corresponding Matlab codes for Gauss elimination, Jacobi iteration, and G-S iteration to solve equation systems, and rigorously proves the sufficient and necessary condition for convergence of iterative formula and also proves the convergence of different iteration methods under different types of coefficient matrices. Based on these solving methods, two examples are practiced in Matlab, the running time and iteration times of different methods are comprehensively compared. Thus, the superiority of the G-S iterative method is obtained. Finally, when there are zero elements in the diagonal elements of the coefficient matrix, the article proposes an improved method to solve this problem.

 View pdf
View pdf


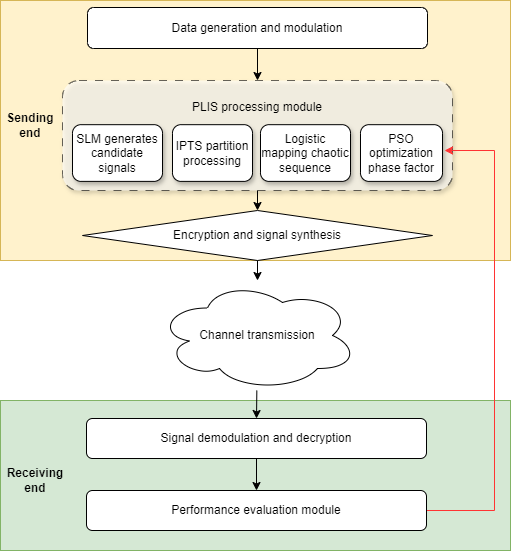
In the context of the booming development of wireless communication technology today, although orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) technology is widely used, the high peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) issue significantly constrains its performance enhancement. This paper is dedicated to studying the OFDM transmission system based on PLIS (Particle Swarm Optimization-Logistic mapping-Improved Partial Transmit Sequence-Selected Mapping) to overcome this problem. First, this study had sorted out the relevant theories and previous achievements, and accurately located the defects of existing research in solving the PAPR problem of OFDM system. Then, the system model was constructed in detail and the research method was introduced, covering precise parameter settings and rigorous data processing procedures. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed PLIS-based method achieves remarkable improvements in reducing PAPR, improving bit error rate and improving spectrum efficiency, and its advantages are obvious compared with traditional methods. Finally, the research findings are deeply discussed, the limitations are analyzed, the important contributions to theory and practice are explained, and the future research directions such as performance optimization under frequency-selective fading channels and algorithm hardware implementation are prospected, providing valuable reference and reference for the sustainable development of OFDM technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


Precision agriculture offers a promising solution to enhance crop productivity and sustainability amidst global agricultural challenges. This paper reviews the development and application of computer vision technologies in modern farming, with a focus on deep learning techniques such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), including Residual Network (ResNet), You Only Look Once (YOLO), and Segmentation Network (SegNet), applied to disease detection, weed classification, and crop health monitoring. The integration of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has significantly advanced agricultural efficiency. However, challenges such as data scarcity, computational limitations, and environmental variability continue to impede large-scale adoption. Emerging solutions, such as lightweight AI models, edge computing, and multi-source data fusion, offer potential pathways to overcome these hurdles. These innovations are critical for scaling, adapting, and sustaining precision agriculture technologies. This paper provides an overview of the current state of computer vision in precision agriculture, identifies key challenges, and outlines future research directions aimed at advancing the field.

 View pdf
View pdf


Utilizing data from Chinese A-share listed companies between 2013 and 2022, this study investigates the governance effect of digital transformation on corporate environmental information misrepresentation and its underlying mechanisms. The empirical findings reveal that (1) digital transformation significantly inhibits corporate greenwash behavior; (2) Organizational dynamic capabilities act as a partial mediator between digital transformation and greenwashing behavior, with digital advancements curbing information distortion by strengthening knowledge integration, innovation mechanisms, and external environmental responsiveness; (3) the heterogeneity analysis reveals that the inhibition effect is more pronounced for non-state-owned enterprises and enterprises in the eastern region, which indicates that the degree of marketization and the institutional environment are the important boundary conditions. The study reveals the non-economic benefits of digital transformation in environmental governance, and provides theoretical and practical basis for policy makers to promote green transformation of enterprises.

 View pdf
View pdf


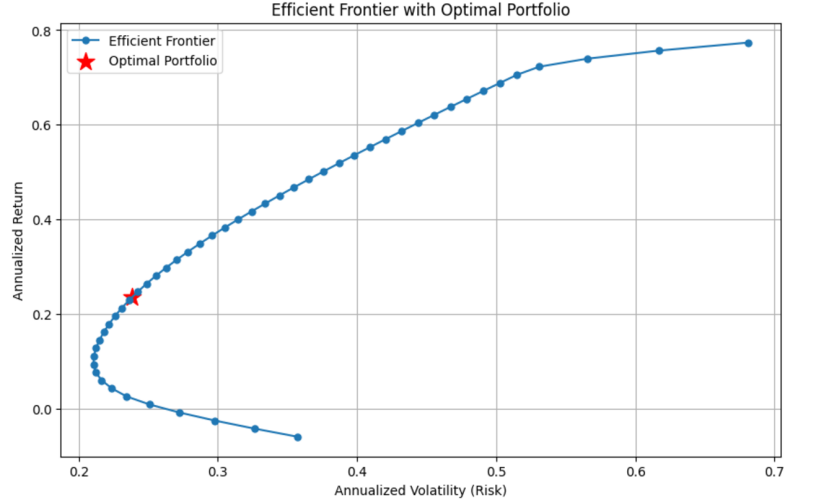
The US stock market remains a focal point for both institutional and individual investors, with portfolio optimization being a critical need. Traditional approaches to asset allocation often rely on single models or incremental improvements, which struggle to address the complexity and instability of financial markets. Hence, this study adopts a model-based analytical framework to address these limitations. First, theoretical models are collected and derived to establish the research foundation. Second, the financial market is analyzed using quantitative data from the Yahoo Finance database. Third, econometric models are constructed, parameters are estimated, and models are optimized. Fourth, data visualization techniques are employed to generate analytical charts. Finally, model results are evaluated and compared to provide investment strategy recommendations. Advanced models, including the mean-variance model, Black-Litterman model, and genetic algorithm, are introduced to enhance adaptability to market complexity. The mean-variance model provides intuitive risk-return insights but relies heavily on historical data. The Black-Litterman model incorporates investor views but overlooks asset-specific risks. The genetic algorithm offers flexibility in handling constraints but requires significant computational resources. While these models provide valuable insights, investors should integrate their own market understanding to optimize portfolio decisions. This study highlights the importance of combining model-based analysis with investor expertise to navigate financial market uncertainties effectively.

 View pdf
View pdf


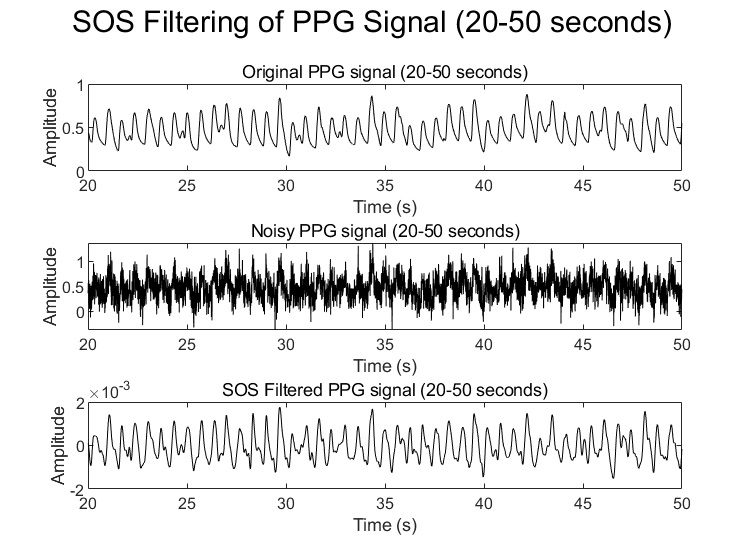
Signal denoising is an important research direction in the field of signal processing, with widespread applications in communication, audio processing, medical signal analysis, and other areas. With the development of technology, traditional noise reduction methods are gradually facing bottlenecks in efficiency and accuracy, especially in dynamically changing noise environments. Adaptive filtering algorithms have become effective tools for solving noise elimination problems due to their ability to adjust filter parameters in real time based on the characteristics of the input signal. However, classical adaptive algorithms, such as Least Mean Square (LMS) and Normalized Least Mean Square (NLMS) algorithms, despite their success in many applications, still face issues such as slow convergence and insufficient performance when handling different types of noise. This study aims to explore the application of adaptive filtering algorithms in signal denoising, particularly those based on second-order statistics, evaluate their performance in different noise environments, and optimize their enhancement. Initially, simulations were undertaken to implement the LMS, NLMS, and second-order statistics-based adaptive filtering algorithms for noise removal experiments. These experiments employed various noise power levels and signal types to assess the performance of each algorithm, focusing on metrics such as Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR), Mean Squared Error (MSE), and the convergence speed of filter parameters. The research results show that the adaptive filtering algorithm based on second-order statistics has significant advantages over LMS and NLMS algorithms in various noise environments, especially in cases of higher noise power, where its denoising effect is more significant, and the convergence speed is also faster. Additionally, to address the computational complexity of the algorithm, this study proposes a simplification strategy to optimize the practical application performance of the algorithm.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of the rapid development of artificial intelligence technology, the issue of fair use in AI data training has sparked widespread attention and discussion. Large model training relies on massive amounts of data, whose technical characteristics differ significantly from how traditional works are used. However, market failures are prevalent, with high licensing costs and difficulties in obtaining rights holders' permissions hindering the effective operation of traditional authorization mechanisms. Therefore, the use of works in large-scale model training should be considered as fair use, since it has a limited impact on the legitimate rights of copyright holders while offering significant social and public benefits. In addition, within the framework of copyright law, it is essential to clarify the rules and criteria for fair use in machine learning and to define the obligations and responsibilities of AI data trainers. This will help balance the interests of copyright holders, society, and data trainers, thereby promoting the healthy and sustainable development of AI technology and the adaptive evolution of copyright law.

 View pdf
View pdf


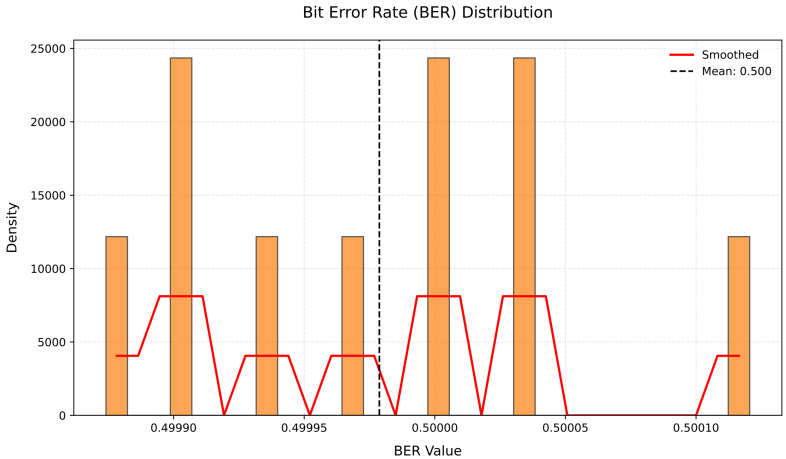
With the rapid development of video applications and increasing demands for secure transmission, traditional video encryption methods face challenges in balancing security and efficiency. This paper proposes a novel multi-level secure video encryption scheme that combines Scalable Video Coding (SVC) with source-Joint encryption. The scheme first analyzes the limitations of direct source-Joint encryption in video protection, then introduces a layered approach based on SVC principles. By decomposing video frames into YUV color spaces and applying wavelet transform, the content is structured into base and enhancement layers. A threshold secret sharing mechanism is implemented to provide differentiated security levels, where the base layer ensures basic visual quality while enhancement layers offer progressive improvements. The experimental results demonstrate superior performance compared to traditional methods, achieving a bit error rate (BER) close to 0.5 for unauthorized access while maintaining high reconstruction quality (PSNR > 40dB) for authorized users. Security analysis shows effective resistance against statistical and differential attacks. The proposed scheme successfully achieves flexible access control, efficient transmission, and robust security, making it particularly suitable for scenarios requiring multi-level security in video applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


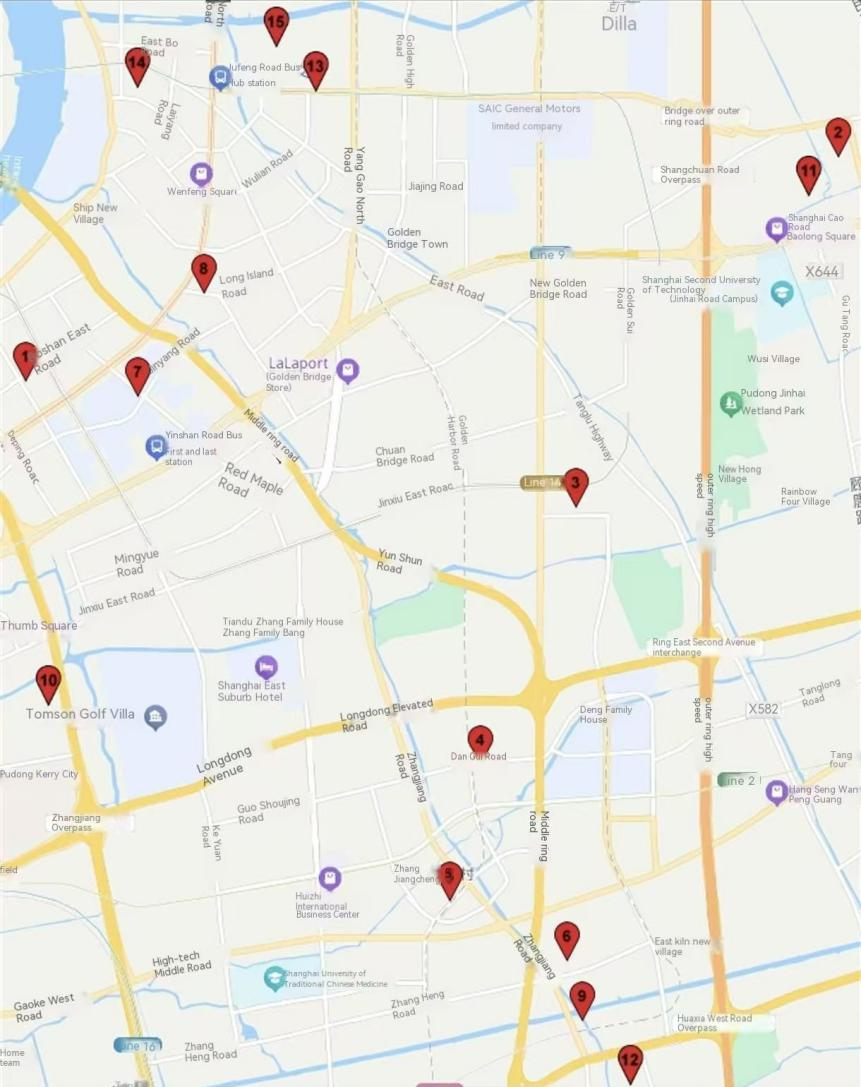
The optimization of logistics delivery routes plays a crucial role in reducing transportation costs and improving delivery efficiency. This paper focuses on the problem of logistics delivery route optimization, taking 20 Hema Fresh stores in Pudong New Area, Shanghai as the research object. By analyzing factors such as vehicle load limits and variable costs generated during the delivery process, a suitable mathematical model is constructed. Subsequently, the greedy algorithm and the genetic algorithm are applied to solve the model respectively, aiming to find the optimal delivery routes. The performance differences of different algorithms in practical applications are compared in detail. The research results show that different algorithms have different effects on the optimization of logistics delivery routes and need to be selected according to the actual situation. This paper provides a feasible solution and useful reference for the logistics delivery route planning of Hema Fresh and other fresh - food e - commerce enterprises.

 View pdf
View pdf




