

Volume 97
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
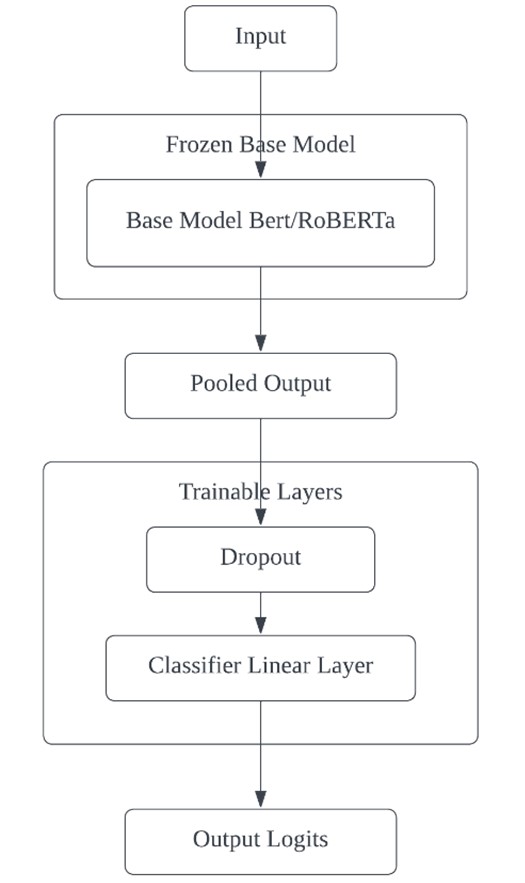
This paper presents an advanced approach to sarcasm detection in online discourse using state-of-the-art language models. The study systematically evolves Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) and Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach (RoBERTa) architectures from baseline to optimized versions, demonstrating significant improvements in sarcasm detection accuracy. Utilizing a balanced subset of 30,000 samples from a Reddit sarcasm dataset, the research implements gradual unfreezing, adaptive learning rates, and sophisticated regularization techniques. The final RoBERTa model achieves 76.80% accuracy, outperforming BERT and showing balanced precision and recall across sarcastic and non-sarcastic classes. The comparative analysis reveals interesting learning dynamics between BERT and RoBERTa, with RoBERTa demonstrating superior performance in later training stages. The study highlights the importance of architectural innovations and advanced training strategies in capturing the nuanced linguistic cues of sarcasm. While computational constraints limited the dataset size, the research provides valuable insights into model behavior and sets a foundation for future work. The paper concludes by discussing potential avenues for advancement, including scaling to larger datasets, exploring multi-modal approaches, and developing more interpretable models, ultimately contributing to the broader field of natural language understanding and affective computing.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper explores the application of Stable Diffusion model and LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) model in AI-generated artwork. The authors introduce the foundational principles of Stable Diffusion model and LoRA, as well as their application in high-quality image generation. Using three popular datasets — ImageNet, COCO, and CelebA — we apply various image quality assessment metrics, including PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio), IS (Inception Score), and FID (Fréchet Inception Distance), and further validate their potential in artistic creation through subjective evaluations. By comparing the performance of these two models across different datasets, we examine their strengths, weaknesses, areas for improvement in image generation tasks, along with user experience considerations. The experimental results show that the Stable Diffusion model excels in terms of image quality and diversity, while the LoRA model offers significant benefits in computational efficiency and resource usage. Through comprehensive experimental evaluations, this paper provides a scientific basis for model selection in AI art creation and offers insights for the future development of hybrid models.

 View pdf
View pdf


The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly influenced various industries, including software engineering. This paper explores the integration of AI into software engineering, focusing on its applications across different stages of the software development life cycle, including design, development, testing, project management, and maintenance. AI's ability to automate tasks, enhance efficiency, and improve code quality is revolutionizing how software is built and maintained. The paper also addresses the challenges and risks associated with AI-driven software engineering, such as dependency on AI tools, ethical concerns, and security vulnerabilities. Finally, the paper highlights future trends in AI-powered software engineering, including adaptive and self-healing systems, AI-enhanced collaboration, and full software automation. The role of AI in shaping the future of software engineering is both profound and transformative, making it a critical area of study.

 View pdf
View pdf


Large language models (LLM) have made significant achievements in the field of natural language processing, but the generated text often contains content that is inconsistent with the real world or user input, known as hallucinations. This article investigates the current situation of hallucinations in LLM, including the definition, types, causes, and solutions of hallucinations. Illusions are divided into different types such as factual and faithful, mainly caused by factors such as training data defects, low utilization of facts, and randomness in the decoding process. The phenomenon of hallucinations poses a threat to the reliability of LLM, especially in fields such as healthcare, finance, and law, which may lead to serious consequences. To address this issue, this article investigates methods such as managing training datasets, knowledge editing, and enhancing retrieval generation. Future research should classify and evaluate illusions more finely, explore multimodal strategies, enhance model stability, and integrate human intelligence and artificial intelligence to jointly address challenges, promoting the continuous progress of LLM.

 View pdf
View pdf


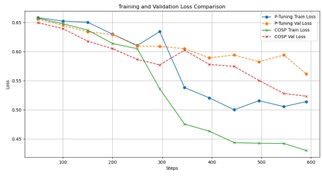
The field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) has seen remarkable advancements with the development of large pre-trained language models, which excel in various tasks, especially through in-context learning. However, the increasing size of these models presents significant challenges for widespread deployment, particularly in resource-constrained environments. This study introduces Context-Optimized Soft Prompts (COSP), a new approach that can improve the performance of smaller language models in few-shots learning scenarios. COSP uses information from the presentation to initialize soft prompts, effectively addressing the limitations of smaller models when performing contextual learning. COSP is evaluated on multiple tasks in the SuperGLUE benchmark and showed significant performance improvements. Results show that COSP not only enhances model performance but also generates more diverse and evenly distributed soft prompts, contributing to robust and generalizable model behavior. Additionally, COSP accelerates the training process, potentially reducing computational resources for model adaptation. By enabling smaller models to perform complex tasks competitively, COSP opens up new possibilities for deploying complex language understanding techniques in resource-constrained environments.

 View pdf
View pdf


Smart wearable devices have rapidly evolved to become essential components of modern technology, transforming the way users interact with the digital world. This paper explores the design and development process of smart wearable devices, focusing on the Apple Watch as a case study. Key design principles such as sensor integration, power management, user interface, and connectivity are discussed in detail. Apple Watch, as one of the leading devices in this field, is examined through its hardware architecture, software environment, and communication protocols. Through this research, we delve into the technical challenges faced during its development and the solutions that make the Apple Watch a successful wearable product. Additionally, the paper highlights future trends in wearable device design, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and enhanced human-computer interaction. The findings indicate that the success of wearable devices, such as the Apple Watch, hinges on achieving a fine balance between performance, user comfort, and energy efficiency, while continuously innovating in the areas of sensor technology and machine learning integration. Ultimately, this study contributes to the understanding of how modern wearable devices are designed and how they can be further improved for future applications in health monitoring, entertainment, and productivity enhancement.

 View pdf
View pdf


The emergence of AI-generated content (AIGC) can be traced back to as early as 1950, when Alan Turing introduced the famous "imitation game" in his paper Computing Machinery and Intelligence, which proposed a method to determine whether a machine possesses "intelligence." Since the introduction of the GAN model by Goodfellow et al. in 2014, the issue of autonomy in AIGC has not seen any breakthroughs. However, due to the challenges posed by robustness and the lack of explainability, society is already beginning to anticipate the social issues and anxieties that might arise with the advent of autonomous artificial general intelligence (AGI). The increasing influence of AI technology on society has further driven concerns about the ethical implications of both AIGC and AGI. Specifically, the relationship between human-computer interaction (HCI) and AI ethics—particularly the role of explainable AI—has become increasingly crucial. Merely understanding the issue of non-explainability from a technical standpoint is no longer sufficient to form a principled basis for AI ethics. In fact, Turing to some extent foresaw the possibility that AI's future development would face such issues. This paper seeks to offer a direction that moves beyond the traditional AI ethics research framework by reinterpreting Turing's original question and analyzing some of the objections he raised. The goal is to provide a new mindset for exploring the necessary modes of thinking for human-computer interaction in the era of AGI.

 View pdf
View pdf


The deep learning technology is becoming widely used in the sectors of safety monitoring and intelligent transportation management, and this has made license plate recognition systems crucial. However, these systems also face security challenges from antisample attacks. This study examines the literature on antisample assaults on license plate recognition software, with a focus on recent advancements and methodologies. First, this paper analyzes several major adversarial sample generation methods, especially gradient-based methods, which can significantly reduce the accuracy of license plate recognition systems without being detected by the naked eye. Then, this paper introduces the basic working principle of the license plate recognition system and its importance in practical applications and finally summarizes the research progress and related methods in recent years. Through a comprehensive analysis of the existing literature, this paper aims to provide researchers with a comprehensive overview of license plate recognition systems against sample attacks and their defense strategies for further development in the field.

 View pdf
View pdf


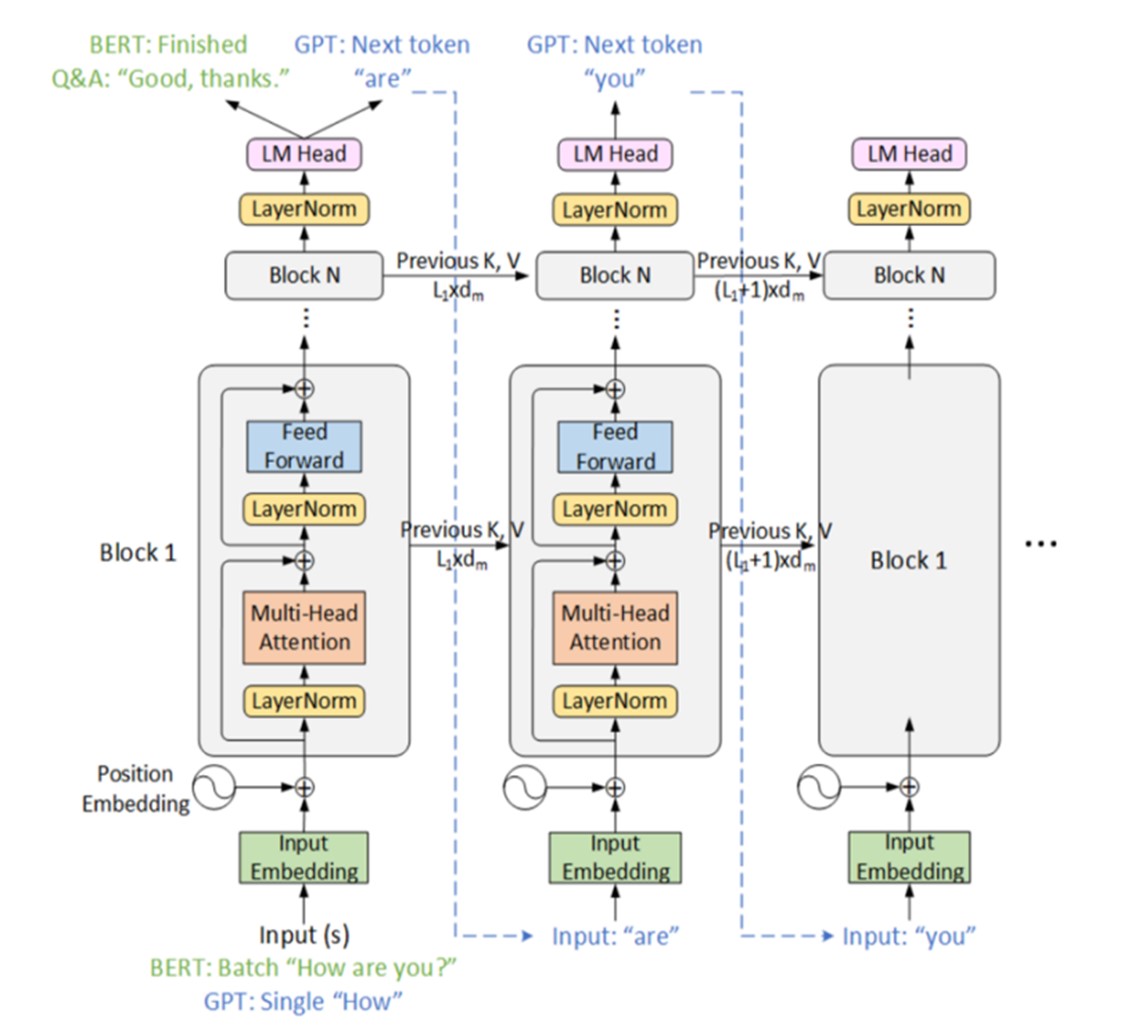
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the field of natural language processing (NLP), demonstrating remarkable capabilities in understanding, generating, and manipulating human language. This comprehensive review explores the development, applications, optimizations, and challenges of LLMs. This paper begin by tracing the evolution of these models and their foundational architectures, such as the Transformer, GPT, and BERT. We then delve into the applications of LLMs in natural language understanding tasks, including sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, question answering, and text summarization, highlighting real-world use cases. Next, we examine the role of LLMs in natural language generation, covering areas such as content creation, language translation, personalized recommendations, and automated responses. We further discuss LLM applications in other NLP tasks like text style transfer, text correction, and language model pre-training. Subsequently, we explore techniques for optimizing and improving LLMs, including model compression, explainability, robustness, and security. Finally, we address the challenges posed by the significant computational requirements, sample inefficiency, and ethical considerations surrounding LLMs. We conclude by discussing potential future research directions, such as efficient architectures, few-shot learning, bias mitigation, and privacy-preserving techniques, which will shape the ongoing development and responsible deployment of LLMs in NLP.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the development of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, predictive analytics and data-driven decision making are becoming increasingly common across industries. While the widespread use of AI has brought many conveniences, it has also led to profound discussions about user privacy and data protection. This study aims to explore the application of privacy protection design principles to machine learning data collection and its impact on user experience. The study found that embedding privacy protection measures early in system design can significantly reduce privacy management vulnerabilities and enhance users' trust and satisfaction with the system. This study provides theoretical support and practical guidance for privacy protection in machine learning data analysis and provides a feasible design framework for future user experience optimization.

 View pdf
View pdf




