

Volume 173
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Business and Policy Studies
This paper empirically investigates the relationship between management overconfidence, media attention and corporate ESG performance using data from all A-share non-financial listed companies in China between 2017 and 2023.The results of the study show that management overconfidence is significantly negatively correlated with corporate ESG performance, i.e., management overconfidence inhibits the enhancement of corporate ESG performance. Meanwhile, further analyses find that media attention plays a negative mediating role between management overconfidence and corporate ESG performance, and management overconfidence triggers more attention from the media, which in turn increases the corporate ESG performance by increasing the This may be due to the fact that large-scale enterprises are subject to more market attention and media scrutiny, which makes it easier for management overconfidence to be magnified and exposed, thus affecting ESG performance. This may be due to the fact that large-scale firms are subject to more market attention and media scrutiny, and management overconfidence is more likely to be magnified and exposed, thus having a more significant negative impact on ESG performance. This paper enriches the research literature on the relationship between management overconfidence and firms' ESG performanceoffering new insights into the role of media attention in corporate governance.It also provides policy insights for regulators and corporate managers to be cautious of the risks posed by management overconfidence and guide media attention to improve ESG performance.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper analyzes the relationship between digital transformation and green innovation based on the data of A-share listed companies from 2019-2023. It is found that (1) digital transformation enhances the development of green innovation, which still holds after the robustness test. (2) Digital transformation promotes the development of green innovation by enhancing the level of corporate ESG index and then promoting the development of corporate green innovation. (3) Digital transformation has a more significant impact on green innovation in SOEs than in non-SOEs. The purpose of this paper is to provide references and lessons for enhancing enterprises' attention to digital transformation and promoting enterprises' green innovation development.

 View pdf
View pdf


Amid escalating global climate change and environmental challenges, contemporary organizations now prioritize environmentally-conscious technological advancements as a pivotal mechanism to attain enduring ecological equilibrium. While existing studies have explored the role of digitalization on eco-friendly innovation, the mediating role of ESG score between the two is not discussed enough in the prior scholarly investigations, which is mostly from a singular viewpoint analysis and lacks systematic empirical support. This paper takes China's A-share listed companies from 2016 to 2023 as samples to explore the impact mechanism of digital transformation on corporate green innovation and introduces ESG score as a mediating variable to reveal its impact path. The findings indicate that digital transformation has a notable impact on enhancing the level of green innovation within enterprises, and ESG score serves as a moderating factor in this sequence of events. Heterogeneity test shows that digital transformation plays a more significant role in promoting green innovation in non-state-owned enterprises. This research offers an innovative viewpoint for comprehending the intrinsic linkage between the shift to digital and eco-innovative advancements and provides a theoretical basis and practical reference for enterprises to realize green transformation through digital technology.

 View pdf
View pdf


The global industrial structure is accelerating its transformation, and global value chains are being restructured under the differentiation of trade systems and investment. This paper discusses the impact of OFDI on GVC restructuring under the “Belt and Road” initiative, aiming to analyze the resource reallocation of Chinese enterprises in the global market and its role in value chain upgrading. This paper finds that OFDI can significantly increase the degree of GVC embeddedness of enterprises, in which technological innovation, vertical integration adjustment, specialization and industrial chain integration are important mechanisms affecting the upgrading of GVC. The moderating effect of “Belt and Road” is weakly negatively correlated, but the trade facilitation, digital infrastructure improvement and financial support it promotes provide long-term development momentum for enterprise GVC embeddedness. Meanwhile, private firms, manufacturing firms, and non-asset-intensive firms are more likely to benefit from OFDI and enhance GVC embeddedness.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study investigates the dynamic relationship between digital transformation and green technology innovation in China's manufacturing sector, with a focus on the mediating role of total factor productivity. Based on the panel data of A-share listed manufacturing enterprises in Shanghai and Shenzhen from 2010 to 2022, it is found that the digital transformation of manufacturing industry significantly promotes green technological innovation, and total factor productivity plays an important mediating role in it. Specifically, digital transformation provides strong support for green technology innovation by optimising resource allocation and improving production efficiency. Heterogeneity analyses show that large enterprises and state-owned enterprises (SOEs) perform more significantly in the promotion of green technology innovation by digital transformation. The findings provide a new perspective for understanding the intrinsic connection between digital transformation and green technology innovation in the manufacturing industry, as well as policy insights for promoting high-quality development of the manufacturing industry and achieving green development.

 View pdf
View pdf


In the era of knowledge economy, technological progress is a key measure of national strength and a focal point of competition among nations. This paper utilizes data from 285 prefecture-level cities in China from 2009 to 2019, employing the Difference-in-Differences (DID) method to study the impact of policies combining technology and finance on local new quality productivity. The research indicates that the effective integration of technology and finance observably enhances the new quality productivity of prefecture-level cities, mainly achieved by improving regional innovation capabilities and optimizing industrial structures. Heterogeneity tests show that the impact of this integration varies across different regions, with more developed areas benefiting more, while less developed areas experience a lag effect. This may be related to factors such as regional resources, financial infrastructure, and types of industries. Further research will delve into the reasons for these differences and conduct mediation-heterogeneity analysis to propose more effective policy measures.

 View pdf
View pdf


Amidst the current wave of scientific and technological advancements and industrial evolution, digital transformation has become a pivotal strategy for sustainable development and maintaining a competitive edge. As a forward-looking and sustainable development paradigm, green innovation increasingly highlights its key role in helping enterprises to reduce environmental pollution, maximize the efficacy of resource deployment and management, and achieve the win-win goals of economy and environmental protection. This research scrutinizes the impact and implications of digital transformation on green innovation by analyzing data selected from A-share listed firms from 2010 to 2023. Concurrently, the intermediary function of R&D expenditure is explored. The outcomes reveal that digital transformation exerts a markedly beneficial consequences on corporate green innovation, and this impact is partially channeled through its influence on R&D investment. Furthermore, the catalytic effect of digital transformation on green innovation is more pronounced in publicly-held corporate entities & government-operated institutions, non-polluting industries, and high-technology sectors.

 View pdf
View pdf


At a critical juncture where the "dual carbon" goals are guiding enterprises toward green development, ESG performance has garnered widespread attention. This study selects A-share listed companies in China from 2012 to 2022 as a sample and employs textual analysis to measure the degree of enterprise digital transformation. The findings reveal that digital transformation significantly enhances ESG performance, a conclusion that remains robust after a series of robustness and endogeneity tests. Mechanism testing indicates that digital transformation improves ESG performance by enhancing green innovation capabilities, strengthening external supervision, and optimizing resource allocation. Heterogeneity tests show that the enabling effect of digital transformation on ESG performance is more pronounced in firms with high analyst coverage, high-carbon industries, and highly marketized environments. This study enriches the theoretical discourse on enterprise digital transformation and provides practical insights for enterprises to better implement ESG practices.

 View pdf
View pdf


Using data from listed companies in China's A-share market from 2014 to 2023, this paper examines the influence of senior management with an environmental background on corporate environmental performance, considering green investors as a mediating factor. The research shows that senior management with environmental backgrounds significantly and positively enhances corporate environmental performance, specifically manifested in the company's environmental philosophy, environmental target setting and environmental management systems. Furthermore, green investors play a crucial mediating role between the environmental background of senior management and corporate environmental performance, suggesting that the environmental expertise of senior management further enhances corporate environmental performance by attracting green investors. The study also finds that this positive effect is particularly pronounced in non-state owned firms and non-polluting industries. Finally, the paper suggests strategies such as strengthening cooperation with the green investment community and promoting technological innovation in environmental protection to continuously improve corporate environmental performance.

 View pdf
View pdf


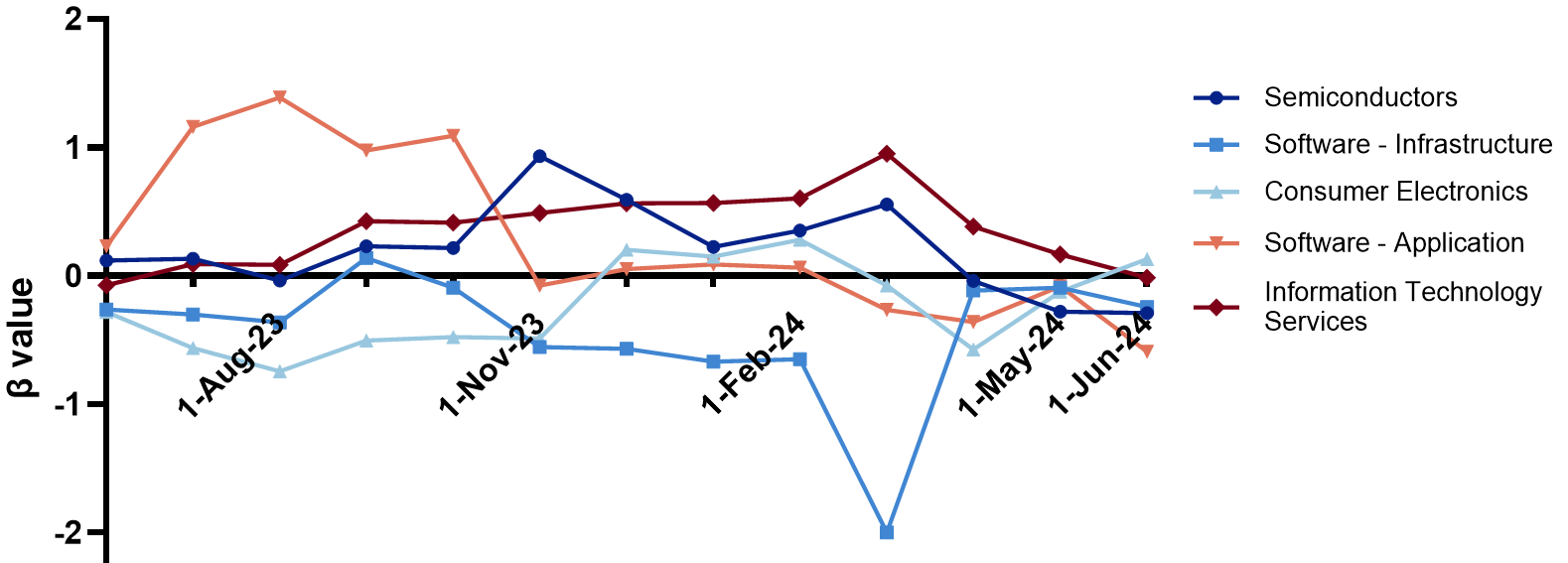
Momentum and reversal effects are critical in understanding stock performance, yet their dynamics within the diverse U.S. technology sector remain underexplored. This study investigates the behavioral dynamics of momentum and reversal, analyzing their effects across the five largest industries by market capitalization in the U.S. technology sector, with particular attention on the top three businesses in each area, as determined by the Yahoo Finance Screener. Using time-series and cross-sectional analyses, this paper examines momentum and reversal effects in the technology sector at the industry and company levels, complemented by Fama-MacBeth regression to control for risk factors. The results reveal distinct patterns: IT services and software applications show strong momentum effects driven by long-term trends (6-month), while consumer electronics and software infrastructure display significant reversal effects linked to short-term (3-month) market volatility. Semiconductors display stable β values with minimal effects. Momentum is more prevalent in large-cap firms (e.g., AAPL, NVDA), while reversal dominates smaller-cap stocks (e.g., HEAR, CRM).

 View pdf
View pdf




