

Volume 195
Published on July 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICMRED 2025 Symposium: Effective Communication as a Powerful Management Tool
This study analyzes the 128 companies listed in the "China's 500 Most Valuable Brands" ranking released by the World Brand Lab from 2020 to 2023 to investigate the correlation between equity structure and brand value. The empirical findings suggest that a higher concentration of equity can have a positive effect on brand value, whereas a balanced equity structure may impede its development.Furthermore, when examining corporate nature and regional distribution separately, it is observed that the positive influence of equity concentration is more pronounced in state-owned enterprises compared to non-state-owned ones. Moreover, the beneficial impact of equity concentration on brand building appears to diminish in the eastern regions as compared to the central and western ones.

 View pdf
View pdf


The Rust Belt region, which includes the heavy industry towns and cities alongside the railroad and the Great Lakes in the central United States, has faced severe crises after iron companies quit. Significant changes in population structure and local communities happened in the next 30 years that changed everything in these cities; hundreds of smoking factories, jobs, and unions vanished, leaving a rusted town where everyone was escaping. This essay analysed the local communities in the Rust Belt region and cities like Youngstown, Ohio and Gary, Illinois. Deeply analysed local communities' racial structure and the change in regional minimum wage suppliers, finding that the rust belt area has lost population, decreased income, and worsened social security. These combined features caused the crisis of the local community.

 View pdf
View pdf


Based on data from the China Family Panel Studies (CFPS 2014-2018), Peking University’s Digital Financial Inclusion Index, and the National Bureau of Statistics, this paper empirically examines how digital finance impacts online consumption among youth (aged 18-35) and its mechanisms. The study reveals that digital finance significantly boosts youth online consumption through enhanced payment convenience, credit accessibility, and expanded consumption scenarios. This effect is more pronounced in economically developed eastern regions, while weaker in central and western regions due to digital infrastructure gaps and financial exclusion, highlighting regional heterogeneity shaped by economic structures, digital literacy, and infrastructure development. Robustness tests using internet and mobile payment penetration rates confirm the findings, offering micro-level evidence for national strategies like "integrating the digital and real economies."

 View pdf
View pdf


This study delves into the intricate relationship between retail investor sentiment and stock market volatility through the lens of behavioral finance. The massive spread of social media platforms including Twitter and Reddit during modern times has led to retail investor behavioral biases such as herding and overreacting which today significantly affect market movements. The research uses the literature review approach as its primary method but it mainly presents previous research findings in addition to explanation of theoretical frameworks and investigation methods. Once negative retail market sentiments appear in the market the study shows volatility levels intensify. Market volatility transmission occurs because investors combine price differences with washroom actions related to changing market sentiment. The proposed solution contains two components for investor distortion management which combines educational measures with circuit breaker safeguard protocols. The research offers real-world directions to financial market stakeholders who need to handle sentiment-caused economic risks across various market cycles of today's interconnected financial system.

 View pdf
View pdf


Extreme climate not only poses severe challenges to social security issues but also becomes an important factor threatening the stability of the proportion of household financial assets. This paper uses the data from the China Household Finance Survey (CHFS) and the statistical data of climate disasters. By combining the heterogeneity analysis and mechanism test, it systematically explores the impact paths and differential influences of extreme climate events on the allocation of household financial assets. The study finds that extreme climate significantly reduces the proportion of household financial assets, and this effect shows significant heterogeneity among different groups and regions. The mechanism analysis reveals that the frequent occurrence of climate disasters intensifies households' concerns about future economic uncertainties, and their risk appetite is significantly reduced. This paper not only enriches the existing literature on climate financial risks but also provides suggestions and references for households to prevent the impacts of climate disasters and maintain household financial stability.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of the maturation of sustainable development concepts and ESG metrics, research on their impact on firm value has become increasingly significant. This not only helps enterprises enhance their value while balancing sustainable development but also amplifies their environmental externalities. This study employs a sample of A-share listed companies in China from 2017 to 2023, grounded in stakeholder theory, sustainable development theory, and resource management theory, to construct a time-fixed effects regression model. The aim is to explore the impact of ESG performance on firm value. The findings reveal a positive correlation between ESG performance and firm value. Further analysis indicates that R&D investment serves as a mediating factor in this relationship. Heterogeneity analysis demonstrates that the positive effect of ESG performance on firm value is more pronounced in enterprises located in western China. This research provides theoretical insights into corporate sustainable development and offers empirical guidance for enhancing firm value within a sustainable framework.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study investigates the dynamic interplay between ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) public sentiment and investment risk through big data analytics, using Haidilao's 2023 "man urinating in hotpot" incident as a case study. Leveraging text mining and machine learning techniques—including Jieba segmentation, SnowNLP sentiment analysis, LDA topic modeling, and random forest algorithms—the research quantifies public opinion intensity, polarity, and dissemination patterns across social media platforms. Findings reveal that negative ESG incidents trigger immediate financial repercussions (e.g., a 4.2% stock price drop) but can be mitigated by rapid, technology-driven crisis management, as evidenced by Haidilao's 3.5% price rebound within a week. The study highlights the asymmetrical impact of ESG dimensions, with Environmental and Social factors exerting stronger market effects than Governance. Theoretically, it advances ESG analytics by integrating unstructured text data with standardized frameworks like GRI. Practically, it demonstrates how AI-enhanced monitoring systems reduce crisis response time by 48 hours, offering actionable insights for corporate risk mitigation and investor decision-making. Limitations, such as semantic ambiguity in sentiment classification, suggest future directions for adopting Transformer-based models and cross-industry validation.

 View pdf
View pdf


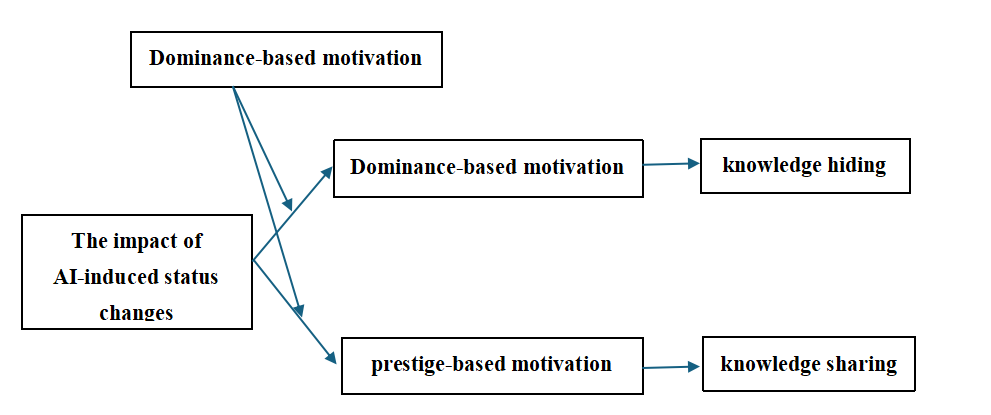
This study, from the perspective of status competition motivation, investigates the impact of AI-induced status changes on employee knowledge behavior. Experimental findings indicate that AI-induced status changes do not significantly stimulate dominance-based motivation but rather decrease prestige-based motivation in some employees. Prestige-based motivation positively influences knowledge sharing, whereas dominance-based motivation (contrary to initial expectations for its direct impact on hiding) was found to have a complex role, with the overarching context suggesting that when technological advancements threaten universal job security, employees, regardless of their dominant or prestige-oriented motivations, are compelled to adapt their knowledge strategies for survival. A highly politicized organizational climate also strengthens AI’s positive impact on prestige-based motivation. Additionally, it reinforces the dominance-based motivation pathway.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study explores the relationship between capital structure and corporate performance in the non-bank financial industry. By analyzing non-bank financial firms across multiple regions and industries, it is found that capital structure generally exhibits a negative correlation with corporate performance. As the debt-to-asset ratio increases, the net return on assets decreases. The empirical results show that the negative correlation is particularly evident in the eastern regions, remains significant in the western regions, but is no longer significant in the central regions. For state-owned enterprises, a moderate increase in debt can enhance corporate performance to some extent, whereas for private enterprises, a moderate reduction in debt can promote corporate performance. Based on these findings, this paper proposes corresponding policy and practical recommendations to optimize capital structure investment, improve corporate performance, and promote the sustainable development of the industry.

 View pdf
View pdf




