

Volume 152
Published on November 2025Volume title: Proceedings of ICMMGH 2026 Symposium: Biomedical Imaging and AI Applications in Neurorehabilitation
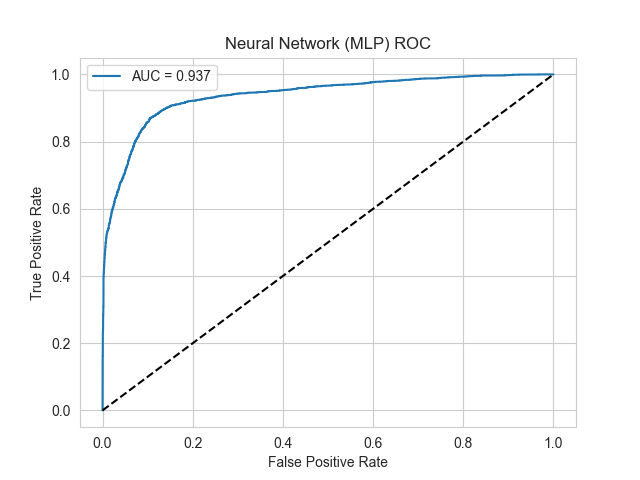
Glioblastoma is the most malignant primary brain tumor with high heterogeneity, making it challenging to achieve accurate diagnosis and evaluate treatment efficacy. With the fast development of single-cell RNA sequencing technology, malignant cells can be identified at the single-cell level to evaluate tumor purity. This study developed a computational workflow that integrated single-cell sequencing data and machine learning methods. Two classification models, XGBoost and a multilayer perceptron, were developed based on 30 selected genes with most differential expression identified by an independent samples t-tests from whole-genome expression data. Subsequently, the performance of two models was evaluated using multiple evaluation metrics. Experimental results showed that the two machine learning models had excellent performance in distinguishing malignant cells in glioblastoma. For distinguishing malignant cells, the AUC, accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of the XGBoost model were 0.941, 0.894, 0.883 and 0.901, respectively; while those of the MLP model were 0.937, 0.883, 0.865 and 0.896, respectively. In addition, the results of the probability distribution experiment showed that the XGBoost model had a more concentrated distribution, while the MLP model had a relatively broader distribution. These results were consistent with the effectiveness of the two machine learning approaches in malignant cell identification. This study validated the effectiveness of using machine learning methods based on single-cell RNA-seq data in identifying malignant cells in glioblastoma. This machine learning workflow could provide a reliable computational tool for subsequent malignant cell identification and tumor purity assessment.

 View pdf
View pdf


The target of Drug Delivery Systems (DDS) is to improve drug bioavailability and reduce side effects, which represents a research focus in modern medicine and pharmacy. Traditional experimental methods have limitations in elucidating low bioavailability and the interaction mechanisms between drugs and carriers. Therefore, this study employs a literature review and case analysis to systematically explore the application of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations in drug delivery systems. Particular emphasis is placed on their unique advantages in nanoparticle design, drug loading, and release mechanisms. This research highlights the progress of MD simulations and further examines the current challenges. It also envisions broad prospects for integrating advanced technologies, such as machine learning and multiscale simulations in the future of drug delivery system development.

 View pdf
View pdf


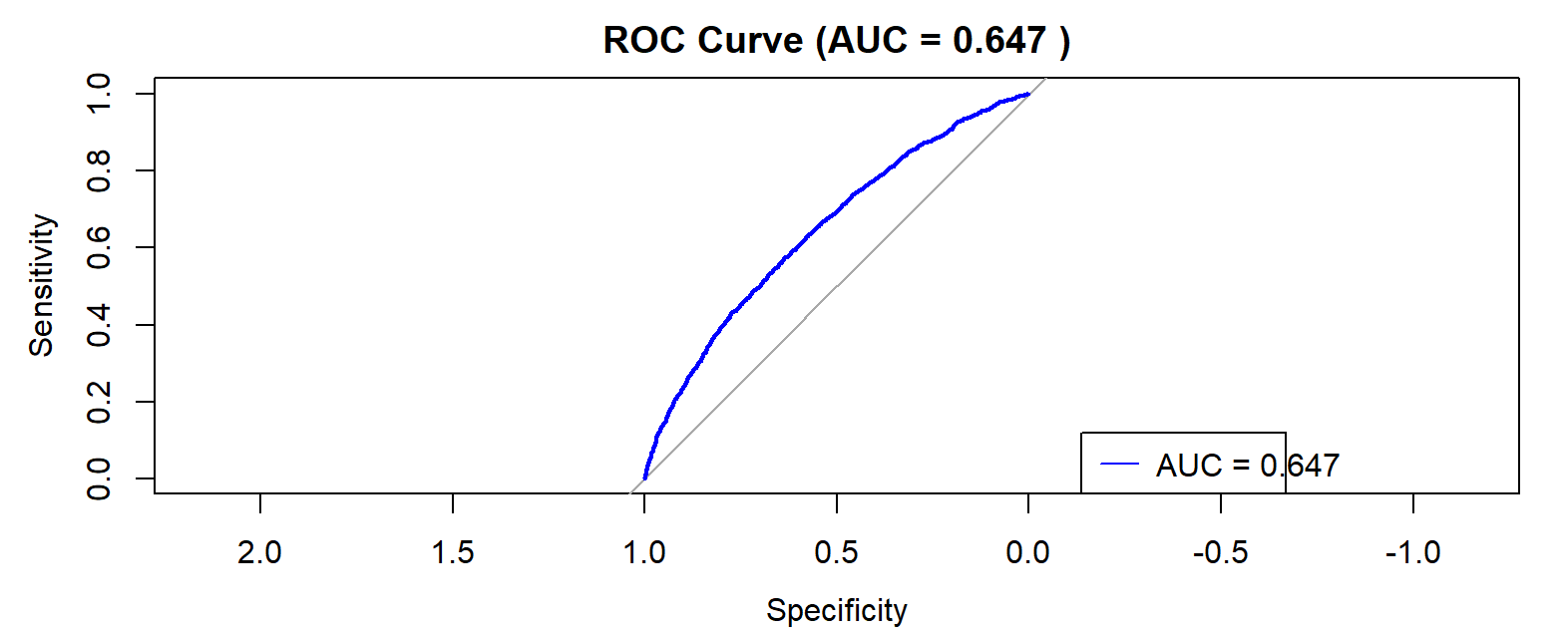
This study was designed to examine the impact of ADL (Activities of Daily Living), average walking speed, and arthritis history on fall risk among middle-aged and older adults aged 45-100 in China. The data for this study come from 7,367 individuals aged 45-100 surveyed in the 2014 China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS). T-tests were used in this paper to explore differences between the fall group and the non-fall group; chi-square tests to examine differences, bivariate analysis for associations among categorical variables, and establish a multivariate logistic regression model to identify independent influencing factors for fall risk in middle-aged and older adults. To explore the moderating effect of age, age-stratified models were conducted. The analysis revealed that ADL, average walking speed, and arthritis history are significant influencing factors for fall risk among middle-aged and older adults aged 45-100. There is a strong graded dose-response relationship between the degree of ADL impairment and fall risk. An increase in average walking speed reduced the risk of falls among middle-aged and older adults. The proportion of individuals with a history of arthritis was significantly higher in the fall group.

 View pdf
View pdf


Immunotherapy holds significant promise in the cancer treatment, but its clinical application is hindered by challenges such as systemic toxicity and limited targeting efficiency. In recent years, biodegradable PLGA nanoparticle have emerged as a promising tool to address the safety and efficacy challenges of immunotherapy, owing to their high biocompatibility and capabilities for drug delivery. This article provides a comprehensive review of the research and application of PLGA nanoparticle in tumor immunotherapy, emphasizing their mechanisms and advantages as multifunctional drug carriers for co-delivering antigens and adjuvants, remodeling the tumor microenvironment, and enhancing immune responses. This review offers new insights for the development of low-toxicity, high-efficiency personalized immunotherapy strategies and holds significant potential for future clinical translation through advanced material design and technological integration.

 View pdf
View pdf


Gynecological malignant tumors seriously threaten the women's lives and also the health, with cervical cancer, ovarian cancer and endometrial cancer being the most common. Traditional treatment modalities (surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy) remain the cornerstone, but their efficacy is often limited by drug resistance and recurrence. New treatment methods need to be explored to save patients' lives. Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have made breakthrough progress in gynecological malignant solid tumors. By blocking the binding of inhibitory receptors on the surface of T cells (such as PD-1 and CTLA-4) to their ligands, they have reactivated the immune response of T cells to tumors, completely changing the treatment landscape. This article aims to systematically review the current clinical application status, key clinical trial evidence and biomarker roles of ICI in cervical cancer, endometrial cancer and ovarian cancer, deeply analyze the challenges it faces, including the limitations of biomarker prediction, drug resistance, management of immune-related adverse reactions and exploration of combination treatment strategies. In order to provide references for its clinical application and future research.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the advancement of sports technology and the evolution of various athletic disciplines, demands for wearable devices in competitive sports settings continue to rise. Wearable technology has become central to performance monitoring in football, yet its accuracy, contextual adaptability, and usability across competitive levels still present areas for development. This paper employs a literature review methodology to examine GPS/GNSS systems, foot-mounted IMU sensors, and ECG/PPG-based heart rate monitors, analysing their efficacy, application scenarios, and limitations. It concludes that each device type demonstrates distinct advantages in specific contexts—GPS for outdoor tracking, IMUs for micro-movement detection, and ECG for physiological monitoring—highlighting the necessity for multi-sensor integration and standardised frameworks to enhance future applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are covalently closed RNA molecules that were once considered transcriptional noise. Yet, in recent years, a variety of regulatory functions have been reported for circRNAs, and even more surprisingly, translation of circRNAs into microproteins has been demonstrated. This emerging field holds great promise for the field of oncology, since circRNA-encoded proteins have been increasingly implicated in processes such as proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of cancer. This review systematically summarizes the current literature on translatable circRNAs in cancer and outlines the experimental approaches commonly used for circRNA translation identification and validation. The translation of circRNAs is mediated via cap-independent mechanisms, mainly IRES and N6-methyladenosine (m⁶A) modifications. The most commonly detected circRNAs and features of their encoded microproteins are being summarized. By synthesizing these findings, this review is intended to serve as a resource for researchers in the field and to encourage further investigation into the hidden proteome and its impact on cancer.

 View pdf
View pdf


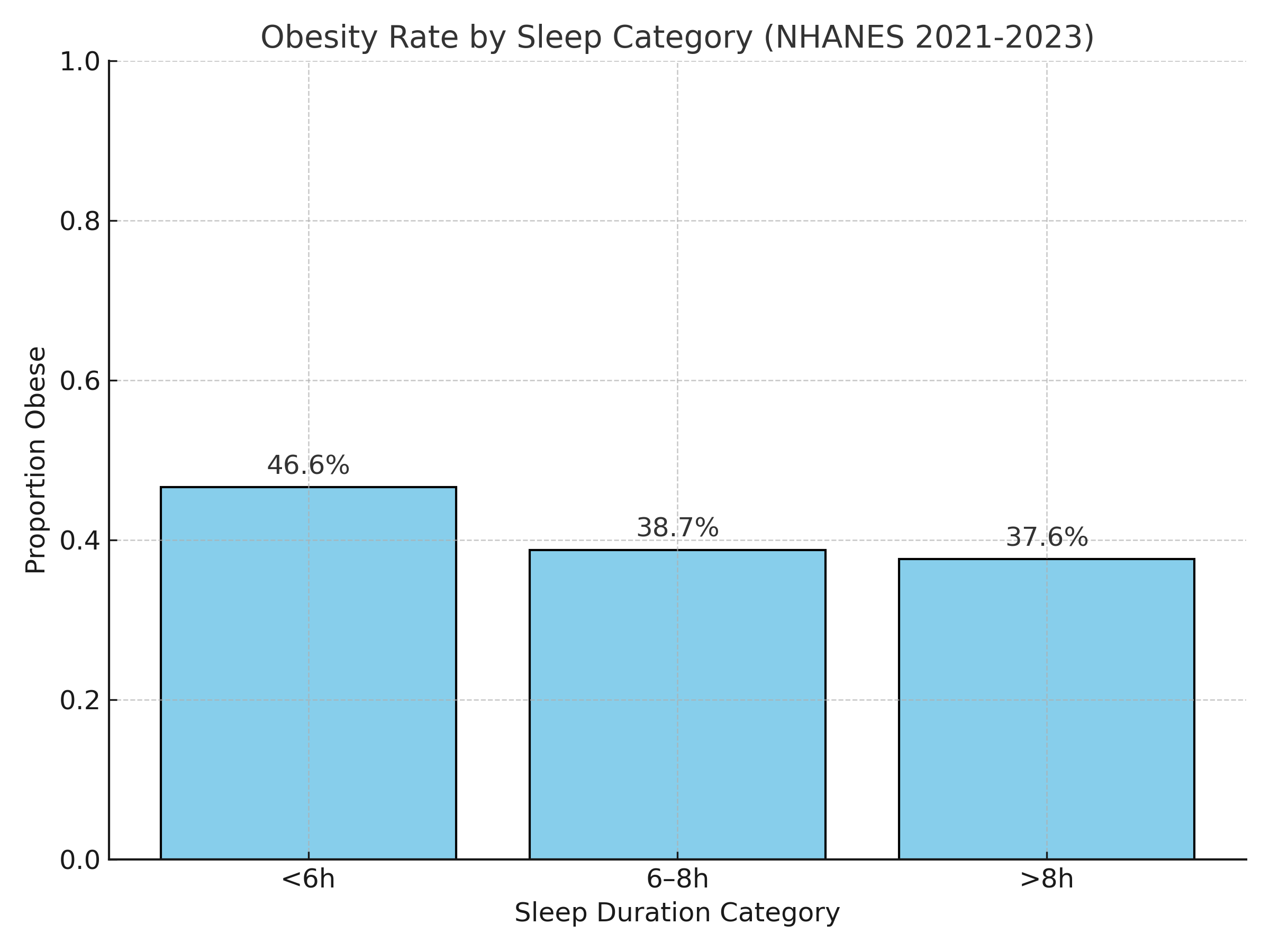
Obesity remains a major public health challenge globally. Sleep length has been identified as a behaviorally adjustable factor that may influence the risk of obesity. Recent research reveals that the effects of sleeping longer hours remain unclear, but it has been shown that poor sleep is linked to an increase in the prevalence of obesity. This study used data from a nationally representative sample for the period between 2021 and 2023 to examines the relationship between nighttime sleep duration and obesity in the adult population of the United States. The sample size of the dataset is 8,000 participants. Sleep duration is classified into three groups: <6 hours, 6-8 hours, >8 hours. Participants reported their usual hours of nighttime sleep using item SLD012 of the sleep questionnaire. Obesity status was determined by calculating body mass index (BMI) from height and weight data collected in the survey; individuals with a BMI of 30 kg/m² or higher were classified as obese. After controlling for age, sex, and race/ethnicity, we used logistic regression, chi-square tests, and descriptive statistics. Based on the analysis, this study confirmed that participants sleeping <6 hours had the highest obesity prevalence (approximately 48%), compared with those sleeping 6–8 hours (42%) and >8 hours (39%). Sleep duration and obesity were significantly correlated (p<0.001), according to chi-square tests. Short sleepers had considerably higher risks of obesity than regular sleepers, according to logistic regression result. There is currently no clear evidence showing a direct connection between long sleep duration and obesity. In contrast, studies have found that getting too little sleep may raise the chance of getting obesity among U.S. adults. These findings emphasize how crucial it is to get the right amount of sleep to prevent becoming overweight.

 View pdf
View pdf


Shenqi Fuzheng Injection (SFI) is a typical single compound from traditional Chinese medicine with a huge potential of SFI is mostly polysaccharide extracts of the substances of astragalus and Codonopsis, and the major three active components of SFI are astragalus polysaccharides, astragalosides and flavonoids. Molecular mechanisms of SFI have been extensively elucidated in gastric cancer, liver cancer, and other digestive system tumors based on recent basic and clinical studies. SFI interacts with multiple molecular pathways and molecular targets to achieve its therapeutic effects. The most prominent one is immune regulation, which is evidenced by the increased production of cytokines and chemokines and the alleviation of chemotherapy-induced immunosuppression. In the adjuvant treatment of digestive system cancers, SFI shows remarkable immunoregulatory and antitumor activities. Combining the SFI with immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies can be further explored to achieve synergistic antitumor effects based on the potential therapy effects of SFI. This review article summarizes the antitumor mechanisms of Shenqi Fuzheng Injection in digestive system cancers that are currently known, intending to help clinical use and future research directions.

 View pdf
View pdf


The COVID-19 pandemic led to physical distancing, thus increasing the use of digital health programs such as artificial intelligence (AI) platforms. Throughout this paper, we will be using AI to describe a system that performs actions that typically require human thinking skills. AI has the potential to transform into a healthcare organization using machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. This review will include AI-based diagnostic and prediction tools, and their potential in changing the detection and management of disease in various fields of medicine. AI algorithms are needed to analyze complex medical data, such as X-ray images and heart signals, and often exceed the accuracy of early human detection. Additionally, there are now AI-based wearable devices and supported systems available for real-time detection and personal management, which could also advance a person’s capability toward earlier detection and prevention of disease. Of course, data privacy challenges, constant data access issues, and algorithmic inequity are still present. Collaboration in addressing data collection, algorithm design, and constant monitoring or evaluation will be needed across disciplines. As institutions of health care, it is critical to ensure that the data collected, and the algorithm designed are transparent for AI to be applied in the real-world healthcare field.

 View pdf
View pdf




