

Volume 44
Published on August 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
Cancer, as the second leading cause of death in the world, caused an estimated 9.6 million deaths in 2018, accounting for one-sixth of all deaths. Early detection and early treatment is the best solution for cancer, and now, through machine learning methods, we can achieve accurate judgment of cancer so as to realize precise treatment and reduce the mortality rate of cancer. During this discussion, we will focus on the applications of machine learning methods to diagnose breast cancer, prostate cancer, oral cancer, which use machine learning methods including neural convolutional networks, K-clustering, support vector machine (SVM), and so on. As of now, machine learning has achieved better results than other methods, but due to the importance and complexity of cancer diagnosis and the cost of human computational capacity for diagnosis, we still hope to find a more accurate and effective method to realize the accurate judgment of cancer, and then introduce it into real-life applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


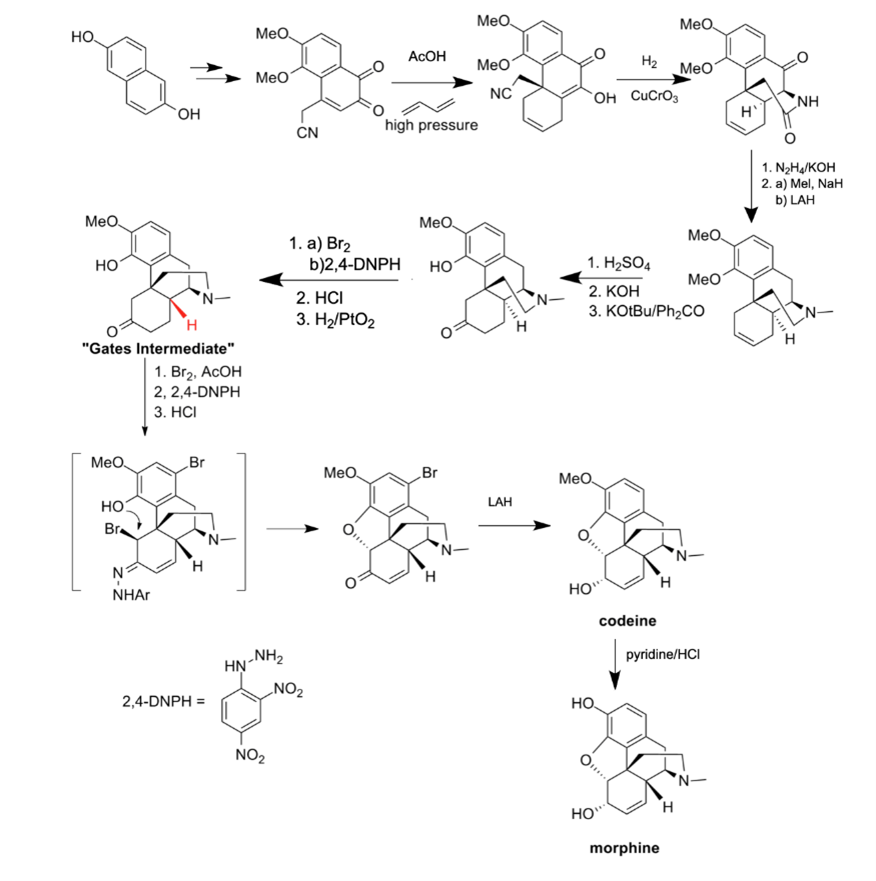
Throughout history, painkillers have played an integral role in human’s day-to-day lives. Used to relieve pain in various ways throughout the body, painkillers have gone through many years of development to keep up with the demands of modern medicine. More specifically, opioids, one type of pain killer that works with the human central nervous system, have been at an all-time high in demand. Its use for treating both acute and chronic pain is indispensable in medicine. However, the neural pathways associated with its pain-relieving effects make these substances highly addictive. In the past, morphine, one type of opioid, had been mainly grown and extracted in its plant form, opium poppy. But due to the highly addictive nature of these plants, numerous countries have strictly regulated the growth of any morphine plants, including China and Afghanistan. These regulations lead to the inability to obtain morphine-like opium through natural purification. Because of this, scientists have been in search of the most efficient and effective methods of synthesizing morphine. This review aims to provide the history, techniques, and further analysis of existing morphine opioid synthesis processes.

 View pdf
View pdf


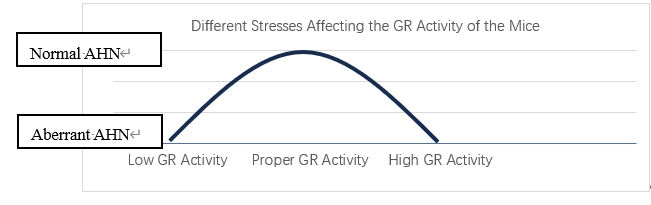
Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis, short for AHN, is an essential yet foundational process of producing new nerve cells in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. It is a fact that increasing AHN will enhance people’s ability to learn, memorize, regulate mood, etc. Therefore, scientists strive to pursue the factors which influence AHN. Until now, research had proved that GR activity is associated with the degree of AHN. Additionally, a high GR activity will potentially reduce the level of ANH and an optimal level of GR activity will create the optimized level of AHN. Consequently, how a low level of GR activity will possibly influence AHN will be examined in this paper. For Experiment 1, the GR antagonist reduces the GR activity in 8-year-old male mice: C57BL/6 and BrdU highlights the newly generated neurons in the dentate gyrus. As an ideal result compared to the control group, low GR activity will lead to a decrease in the AHN. For Experiment 2, 3 minor experiments will be constructed to test the GR activity and AHN of the mice in 3 different conditions (low, controllable, and uncontrollable stress). And Nanobit Assay that is separately attached to the GR and the ligands will present fluorescent when combined. Additionally, the method of CRISPR-CAS9 is used to knock down either GRα or GRβ when the other one is measured, and BrdU is also used to light up the neurons to measure the degree of AHN. The ideal result will present a number greater than 1 for the ratio between GRα/GRβ and AHN decreases for the low-stress group and uncontrollable-stress group. Oppositely, the ratio will be smaller than 1 for the controllable stress group, meaning AHN increases. Conclusively, the output will demonstrate a reversed “U” shape with the x-axis being the level of GR activity and the y-axis presenting the level of AHN. Despite the experiments that have proceeded on mice, the significance of them is people will have certain references to the influences of AHN to prevent those conditions or stress which will negatively affect AHN.

 View pdf
View pdf


Reward prediction error (RPE) refers to the discrepancy between expected and actual rewards received during an event, signaling the difference between what was predicted and what actually happened. Dopaminergic neuron encodes RPE signals in the brain, and is responsible for updating reward expectations and influencing decision-making processes. The relationship between RPE and dopamine has led to research in understanding reward-driven learning and its implications on cognition and behavior. In this review, I will provide an overview of the principles, and task models used to quantify RPE. I will also discuss about the neural mechanisms underlying RPE generation, with a particular focus on the role of dopamine in encoding and transmitting RPE signals and enhance learning. Overall, this review highlights the importance of RPE in reward processing, decision-making, memory and so on, emphasizing its connection to dopamine.

 View pdf
View pdf


Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is the most common kind of liver cancer, which has a relatively high fatality rate. The main cause of this type of cancer is liver inflammation, which leads to disorder in the tumor microenvironment. There are some current treatments, including liver transplants, radiofrequency, microwave ablation, and transarterial chemoembolization. However, the treatments still have limited disadvantages, which cannot be ignored. Recently, a traditional Chinese medicine - Chebulae Fructus, has been proven to have an inhibition ability on HCC cells. One of the main constituents, ellipticine, is found to have therapeutic targets that can treat HCC: PTGS2, CYP1A2, CCNB1, and RASGRF1. Moreover, the essay also mentioned that another type of constituent ellagic acid could also have an inhibition effect on tumor progression by binding to Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 6 (CDK6). This study will further investigate the HCC inhibition effect of ellagic acid by providing an overview of the predicted results of the experiment. It will also provide the possible research direction of ellagic acid HCC treatment.

 View pdf
View pdf


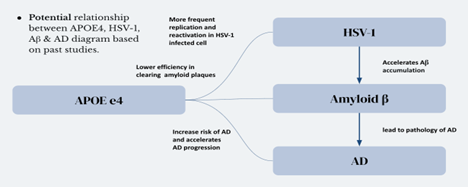
The role of APOE4 in Alzheimer’s disease progression is an area of ongoing research. The core objective of this paper is to investigate the intricate interplay between APOE4, HSV-1, Aβ, and AD progression. Methodology involves assessing Aβ Levels, Spatial Recognition Memory, and Exploratory Behavior in HSV-1-infected Fx5AD Mice with APOE4, alongside monitoring specific biomarkers to confirm HSV-1 activation status. Our expected experimental outcomes suggest that APOE4 accelerates latent HSV-1 activation, leading to heightened Aβ aggregation. Thus, we hypothesize that APOE4 may expedite latent HSV-1 activation, thereby facilitating Aβ accumulation and AD advancement. The investigation of relationship between APOE4, HSV-1, Aβ, and AD progression could give valuable insights into further experiments and treatments of AD.

 View pdf
View pdf


One of the most prevalent kinds of cancer is lung cancer, and rates have been rising since the early 1900s. Non-small cell lung cancer is the most often diagnosed of all the many forms of lung cancer. Smoking plays a large role in contributing to cancer due to tobacco that damages DNA in epithelial cells. Moreover, it is rare yet proven that lung cancer can be inherited through a mutation in the EGFR gene. While Afatinib is used especially for non-small cell lung carcinoma, including the EGFR mutation, many cancers are initially treated with Carboplatin. What makes them unique, then? In essence, through their various chemical structures, they react in the body through separate mechanisms but share the same property of halting cell proliferation. Consequently, they lead to different side effects and have unique limitations when treating certain kinds of lung cancer. This review provides information about non-small cell lung cancer along with the two categories of medications that are used to treat it.

 View pdf
View pdf


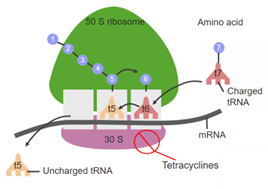
In this piece of writing, we will be addressing the following factors: properties of antibiotics, mechanism of action, clinical safety profile, as well as toxicity, adverse event profile, and case fatality rate. From our evaluation, in terms of properties of the two groups of antibiotics, protein synthesis-inhibiting antibiotics displays a like number of lipophilic and hydrophilic properties, with the majority of Anti-30S inhibitor drugs being predominantly hydrophilic, and a higher number of lipophilic drugs amongst Anti-50S inhibitors. Anti-50S inhibitors could therefore be preferred in oral intake drug development. DNA synthesis-inhibiting antibiotics show a limited trend in their properties. The mechanism of action for protein synthesis-inhibiting antibiotics generally follows four steps: activation of amino acids, initiation, extension, and termination of peptide chain synthesis. On the other hand, DNA synthesis-inhibiting antibiotics exhibits a range of different mechanisms, all of which results in the damage of DNA structure of the bacterium. In both clinical safety and toxicity studies, it is concluded that the two groups of antibiotics have previous cases of side effects, with the DNA synthesis-inhibiting drug, fluoroquinolones, more dangerous due to its potential to result in ventricular fibrillation on a patient. By assessing and comparing all the factors, this review aims to present a precise comparison of the similarities and differences between the protein and DNA synthesis inhibitors, and an evaluation of the effectiveness of the two groups against bacterial infections, along with their safety for regular medication use.

 View pdf
View pdf


The emergence and rapid spread of carbapene-resistant klebsiella pneumoniae has become a severe clinical concern. The acquisition of carbapenemase enzymes is a common mechanism contributing to resistance. Alterations in outer membrane permeability and upregulation of efflux pumps, have also been implicated. In addition, approaches to combat CRKP infections may involve the use of combination therapy, development of new antibiotics, scientific prevention and phase therapy which targets multiple bacterial mechanisms simultaneously. This review aims to look into the drug resistant mechanism and some possible therapies of anti-CRKP infection, provided valuable information on the mechanism of Carbapenem Resistance, enhancing the progress of novel strategies targeting CRKP.

 View pdf
View pdf


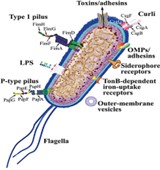
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is one of the most prevalent bacterial infections in the world, and 80% of reported UTI cases are derived by gram negative bacteria Escherichia coli. Uropathogenic Escherichia coli is strongly adaptive and resilient against immune response, forming Intracellular Bacterial Communities (IBC) inside uroepithelium cells that constitute the urethra and the bladder. Their rapid absorption of cellular nutrients enables them to advance upward toward the kidney and cause inflammation. Hence, based on the perceived severity of UTI, multiple antibiotics are used to treat UPEC-causing UTI. This article provides a detailed review on the contemporary performance of amoxicillin and trimethoprim, both widely used to treat UPEC-causing UTI for decades. Amoxicillin is a penicillin-derivative that produces bactericidal by inhibiting transpeptidase to disrupt peptidoglycan synthesis, causing rapid-growing bacteria to lyse. It is a well-tolerated drug that can be used on pregnant patients. Resistant UPEC develop beta-lactamase to counter amoxicillin. Trimethoprim, on the other hand, is a dihydropyrimidine antibiotic that impedes the production of tetrahydrofolic acids, producing either bacteriostatic or bactericidal effects. Resistant UPEC transforms the shape of tetrahydrofolic acids-producing enzyme, dihydrofolic reductase, to resist trimethoprim. Although amoxicillin and trimethoprim are competitive inhibitors are effective against a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative species, trimethoprim, in statistical study, is proven to be more effective than amoxicillin in treating gram-negative UTI. Today, the wide-spread resistant strains of UPEC exists for both drugs. Thus, amoxicillin and trimethoprim are implemented mainly through combination therapies, amoxicillin/clavulanate and trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole, respectively. These combinations are more effective than the drugs to be used alone and are able to counter some resistant strains, but UPEC that are resistant to combinations also exists. Regardless, both amoxicillin and trimethoprim are still used as first-line antibiotics, while more powerful antibiotics are reserved for special multi-resistant superbugs.

 View pdf
View pdf




