

Volume 48
Published on August 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Environmental Geoscience and Earth Ecology
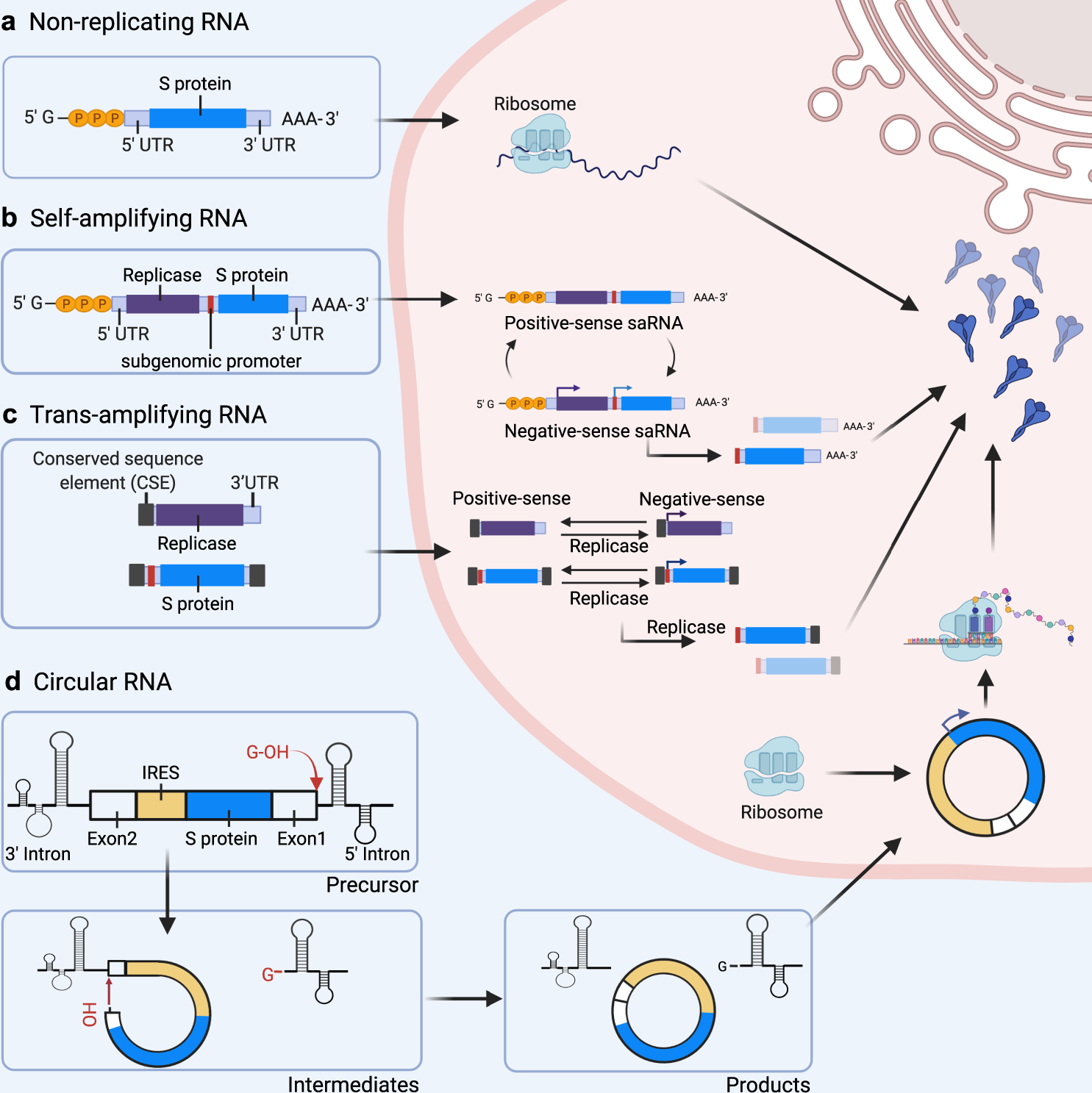
Over the period from 2020 to 2023, a four-year non-military battle drew to a close, marking the end of the COVID-19 pandemic that will be etched into history. During this time frame, policies and technologies aimed at combating the virus were developed, ultimately saving numerous lives and enhancing people's efficacy in battling the virus while demonstrating unwavering determination. However, some less mature biological nucleic acid technologies and some controversial policy bases are still being improved. Through the development of biotechnology levels and policies, the research and development of three mRNA vaccines, health codes and RT-PCR nucleic acid detection methods have greatly improved the efficiency of epidemic prevention and control. The government's policy of controlling speech and behavior at the initial stage of the outbreak brought people together to fight against the virus. These technologies are being researched to reduce the number of casualties and minimize losses. For example, circRNA or saRNA vaccines are still in the research stage. If these more advanced techniques are put into use, it will undoubtedly greatly increase the means of fighting against the virus. This is also the direction and key for future research and development.

 View pdf
View pdf


Anorexia nervosa, as a psychiatric disorder with a progressively high prevalence, is characterized by the following features: high mortality rate, serious harm, long-lasting effects, difficult to cure and easy to relapse. In recent years, Awareness of anorexia nervosa is different than in the past, going deeper: it is a complex disorder involving multiple systems. Many disciplines are also actively exploring it. However, there are still problems such as Pathologic mechanism unclear, no clear indicators of disease, no targeted drugs, and insufficient public awareness. This article analyses research in the fields of social environment, immunology and brain science in the order of disease onset, evolution and treatment (including difficulties in the treatment process, such as in Refeeding syndrome), and puts forward some recommendations for earlier intervention, comprehensive treatment, and optimization and maintenance of therapeutic efficacy in anorexia nervosa. It is also hoped that public awareness and attention will be raised. There are still many gaps in the road to overcoming anorexia nervosa, which has a large research space and is also not less challenging. Future research could focus on finding objective indicators for diagnosing anorexia nervosa or suggesting recovery, and finding targeted drugs from the perspective of multi-system interactions.

 View pdf
View pdf


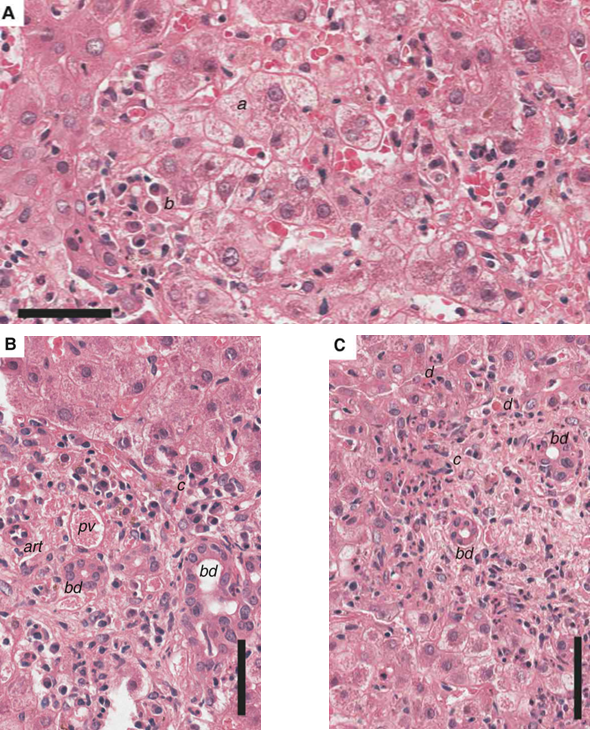
This study explored the globally prevalent pathogens, hepatitis viruses, and their significant impact on human health. This article mainly focuses on HAV, HBV, and HCV, aiming to provide a comprehensive reference for future studies. HAV is mainly transmitted through the gastrointestinal tract, while HBV and HCV are mainly transmitted through blood, body fluids, sexual contact, and mother-to-child transmission. Pathologically, HAV is mostly acute, while HBV and HCV tend to be chronic, which can easily lead to cirrhosis and even liver cancer. Analyzing the transmission mechanism and pathological changes of HAV, HBV, and HCV is crucial for preventing and controlling viral transmission, accurate diagnosis and treatment, formulating public health policies, and public health education. Understanding this information will help reduce the prevalence of hepatitis, improve treatment outcomes, and promote public health. However, the analysis of the structure of these viruses in existing studies is not sufficient. Future studies will further deepen the understanding of HAV, HBV, and HCV, promote vaccine and treatment innovation, and provide stronger support for the prevention and treatment of hepatitis.

 View pdf
View pdf


As cancer has gradually become the world's deadliest long-term disease, the impact on the public health has been devastating. Especially the Melanoma which is a cancer with a very high malignant and a high fatality rate. With the emergence of adoptive cell therapy(ACT) based on T Cell Receptor-Gene Engineered T Cells (TCR-T), good results have been obtained in scientific research and clinical fields for a variety of malignant tumors. As TCR-T continues to enter the clinic, the FDA also has approved the first case of TCR-T in 2022, and more and more basic researches and clinical trial projects based on TCR-T are gradually being carried out. However, TCR-T therapy still has some defects, such as non-tumor tissue damage caused by off-target effect and insufficient affinity with tumor tissue. Therefore, the affinity and anti-tumor effectiveness of TCR-T should be improved in multiple aspects, and multi-field cooperation should be carried out to promote the development of basic research, a number of products should be introduced into the clinic, and the intervention of economic means to improve the accessibility of TCR-T. Not only brings the Gospel of cure to patients in the field of solid tumors, but also produces innovation in the field of non-solid tumors.

 View pdf
View pdf


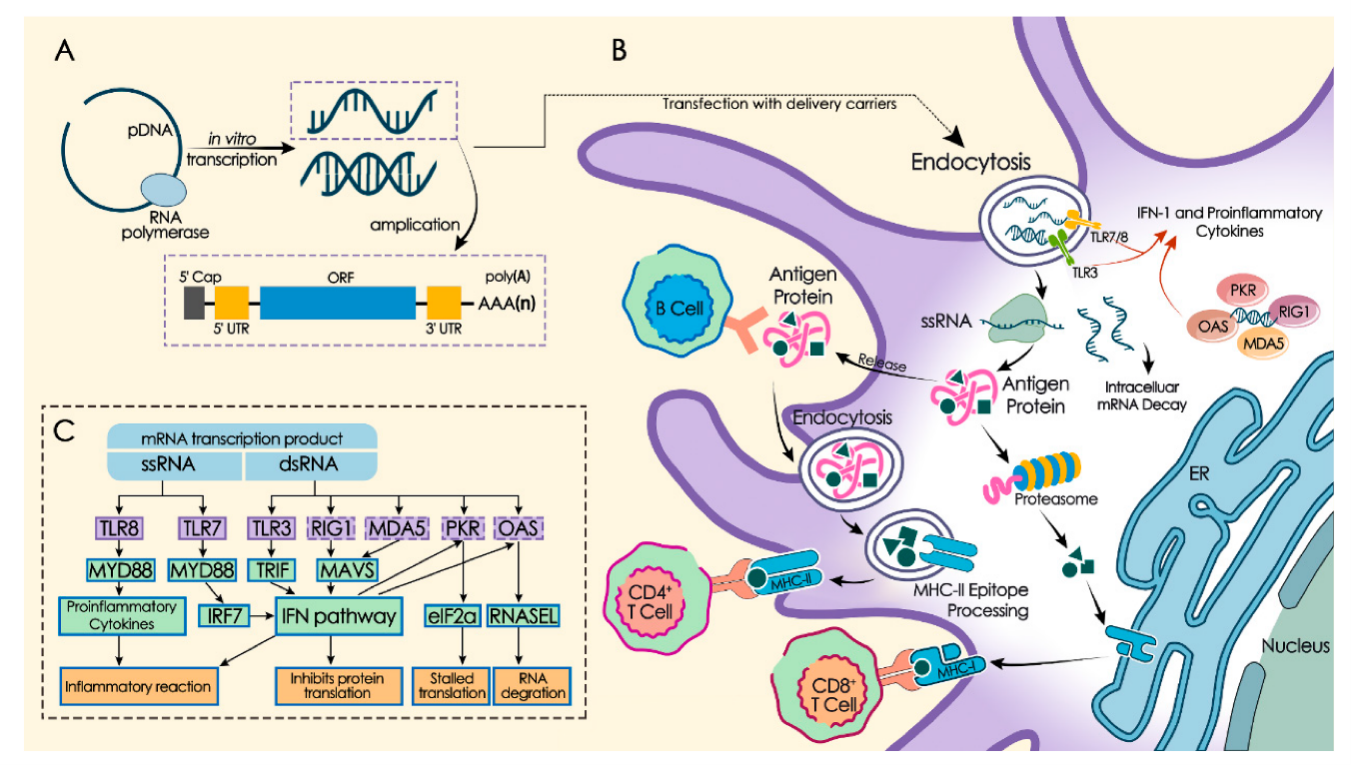
Following the COVID-19 outbreak, two mRNA vaccines were marketed in late 2020 after receiving FDA-approved emergency access, pioneering the use of mRNA vaccines in humans. Since then, more and more companies have joined the development and clinical trials of mRNA vaccines. At this stage, the development of mRNA vaccines is not only limited to COVID-19, but also covers infectious diseases, influenza, and cancer. Up to now, the regulation of immunogenicity of mRNA vaccines is a problem to be solved, and the controversy is mainly about typeⅠIFN. This paper mainly introduces the classification, mechanism and characteristics of mRNA vaccines to show the basic principle of mRNA vaccines, and lists the applications of mRNA vaccines and the types of vaccines that are undergoing clinical trials, which reflects their huge application potential. The potential of mRNA vaccines is shown. With this paper, the author summarizes the current status of mRNA vaccines in order to show readers the basic principles and potentials of mRNA vaccines.

 View pdf
View pdf


Considering the unsuccessful results and lack of sustainable efficiency of previous cancer therapies, T-immunotherapy's clinical success has led to a revolution in cancer treatments. Blood cancers, characterized by abnormal blood cells and metastasis, result in severe health issues and cause high mortality rates. Conventional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation often result in poor prognoses due to cancer cell resistance and have a high relapse rate. This paper focuses on how Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy removes tumor cancerous cells with genetically engineered T-cells. The specific targeting ability of T-cell allows it to overcome the difficulty unresolved by traditional treatments. Despite its significant progress, CAR-T cell therapy also experienced new challenges brought by its specific treatment: cytokine release syndrome and logistical complexities. This paper provides a comprehensive review of T-cell therapy's novel enhancement of blood cancers, including its mechanisms, applications, and side effects after therapy. Various data underline T-cell therapy's potential as a novel cancer treatment, though further research is needed to address its limitations and improve patient outcomes. This research paper provides valuable insights into CAR-T therapy application, minimizing toxicity, and expanding its applicability, offering a reference for future research. Unresolved issues such as managing side effects and improving accessibility continue to be focused for future investigation.

 View pdf
View pdf


Population aging is a significant medical and sociodemographic issue facing the world today. While the financial circumstances of older adults have seen some progress in recent decades, a significant number of senior citizens in the United States still grapple with the challenges of affording daily necessities and encounter inadequacies in their health insurance coverage. Current research has explored the challenges in elderly care, including shortages of medical staff and the need for integrating medical care with nursing care. However, there is still a lack of comprehensive policy approaches to address these issues. This article analyzes the current landscape of elderly care policies and proposes strategies to improve the independence and caregiving abilities of older people. The key findings suggest that increasing fertility rates through government policies and promoting the integration of nursing and medical care can significantly improve the quality of life for the elderly. The proposed "medical care and elderly care" model combines medical treatment with principles of elderly care, offering a more comprehensive approach to meet the health and well-being needs of older adults. The insights from this article provide valuable references for future policymaking and research in elderly care. However, further studies are needed to explore the implementation and effectiveness of these proposed strategies in various contexts. Future research should also focus on developing innovative solutions to address the growing challenges in elderly care as the global population continues to age.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper explores the complex relationship between aging and inflammation and its impact on the development of chronic diseases. Aging is an important contributor to elevated levels of inflammation, with mechanisms including changes in immune regulatory function, chronic low-grade inflammation, cellular aging and tissue damage, changes in gene expression, and increased oxidative stress. These inflammatory processes not only accelerate aging itself, but also promote the development of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease (CVD) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The article goes on to address other modern anti-inflammatory treatment approaches, such as biologics, JAK inhibitors, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications. These treatments help manage and mitigate aging-related pathologies by targeting key molecules and pathways of inflammation. A better comprehension of the relationship between inflammation and aging may serve as the foundation for the creation of novel therapeutic approaches that, in addition to reducing inflammatory reactions, may also prevent or slow the advancement of illnesses associated with age. This article aims to improve medical and scientific understanding of the relationship between inflammation and aging and to encourage the development and use of more potent therapies to lessen the burden of chronic illnesses and enhance the quality of life for the aged.

 View pdf
View pdf


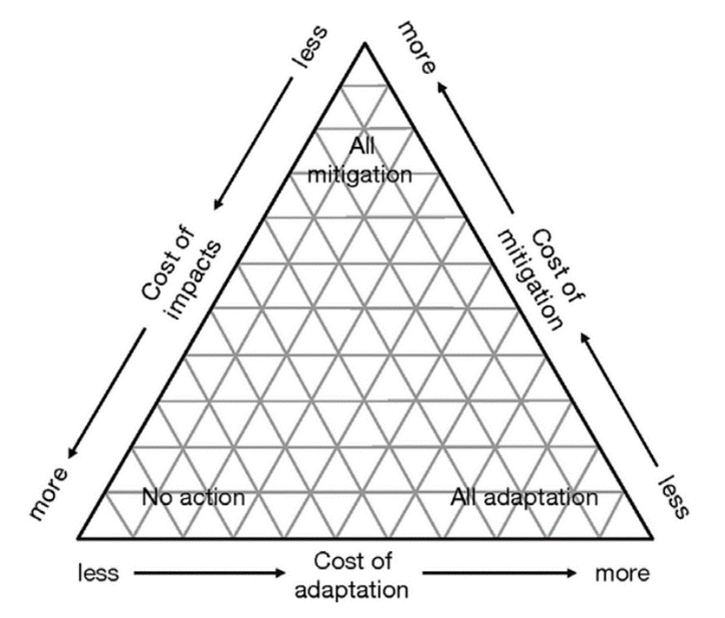
Global warming is a severe environmental problem which caused by human activities such as damage to the environmental an overuse of resources. In order to control the global warming under 2°C, net zero, especially net zero CO2 has been a goal that must be pursued. The net zero is a goal that all the countries can reduce the emission of greenhouse gases to zero. This article uses FaIR climate model to study the effect of different greenhouse gases on temperature anomaly so that to find the main contributor. The effect of net zero CO2 also be estimated. The model concluded that carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels is the most important contributor to global warming, and zero emissions of CO2 would greatly help mitigate it. In addition, global warming is an inevitable trend, so while reducing CO2 emissions to mitigate the global warming, adaptation to the long-term global warming can also be combined with mitigation.

 View pdf
View pdf


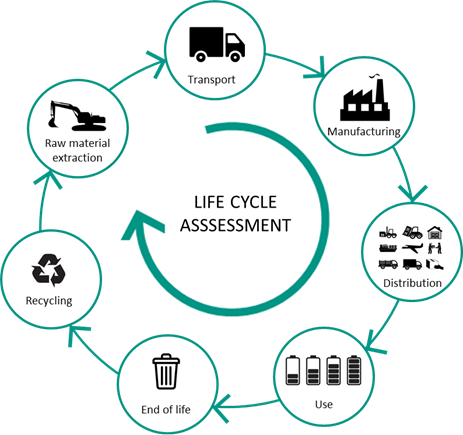
This comprehensive study delves into the integration of green building practices, smart technologies, and ultra-low energy consumption strategies in modern architecture. Through a meticulous examination of existing green buildings, the implementation of smart technology, and the achievements of ultra-low energy structures, this paper highlights the pivotal role these practices play in promoting environmental sustainability and operational efficiency. By analyzing life cycle assessments, energy efficiency models, and the application of renewable energy sources, we provide a quantitative and qualitative overview of the benefits and challenges associated with sustainable architectural practices. The analysis reveals significant environmental impacts, including reduced carbon emissions and lower water usage, alongside notable economic benefits such as decreased operational costs and enhanced property values. Furthermore, the paper explores the technological integration of smart systems, emphasizing the importance of innovative solutions for optimizing building performance. Through detailed case studies and real-world applications, we demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of these integrated approaches in achieving sustainable, efficient, and comfortable living and working environments. This study not only underscores the necessity of adopting sustainable practices in architecture but also provides a roadmap for future developments in the field.

 View pdf
View pdf




