

Volume 68
Published on January 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
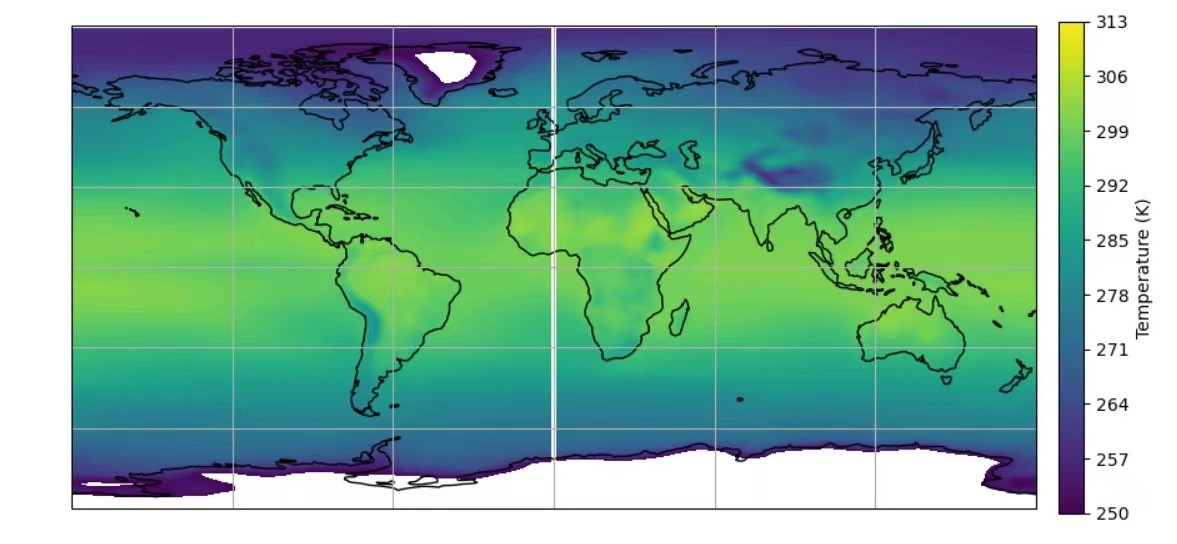
Drought can be defined as a kind of natural disaster, with a series of effects in different aspects of human life, including environment, economic, ecosystem and agriculture. Previous studies has delved more deeply into the impact of drought, examining it through a range of drought indices, including PEI, SPEI, PDSI, and others. Our study is aims to analyze and research the effects of evaporation and precipitation on droughts under global climate change. Through the temperature changing data research the global climate change feature, analyzing the development of droughts using a drought assessment index (P-E) and making use of ‘bucket’ model to analyze the relationship between precipitation rate and soil moisture. Research found that the average land temperature is increasing. On the context of this change, the change of evaporation and precipitation causes dry regions to become drier and wet regions wetter. Furthermore, the 20% decrease of precipitation leads to about a one-fifth decline in soil water content, and a lower precipitation rate would speed up the drought states. Meanwhile, soil moisture can also lead to an increase in precipitation. A coupling phenomenon between precipitation rate and soil moisture is exist. This study provides a new point for predicting future droughts conditions.

 View pdf
View pdf


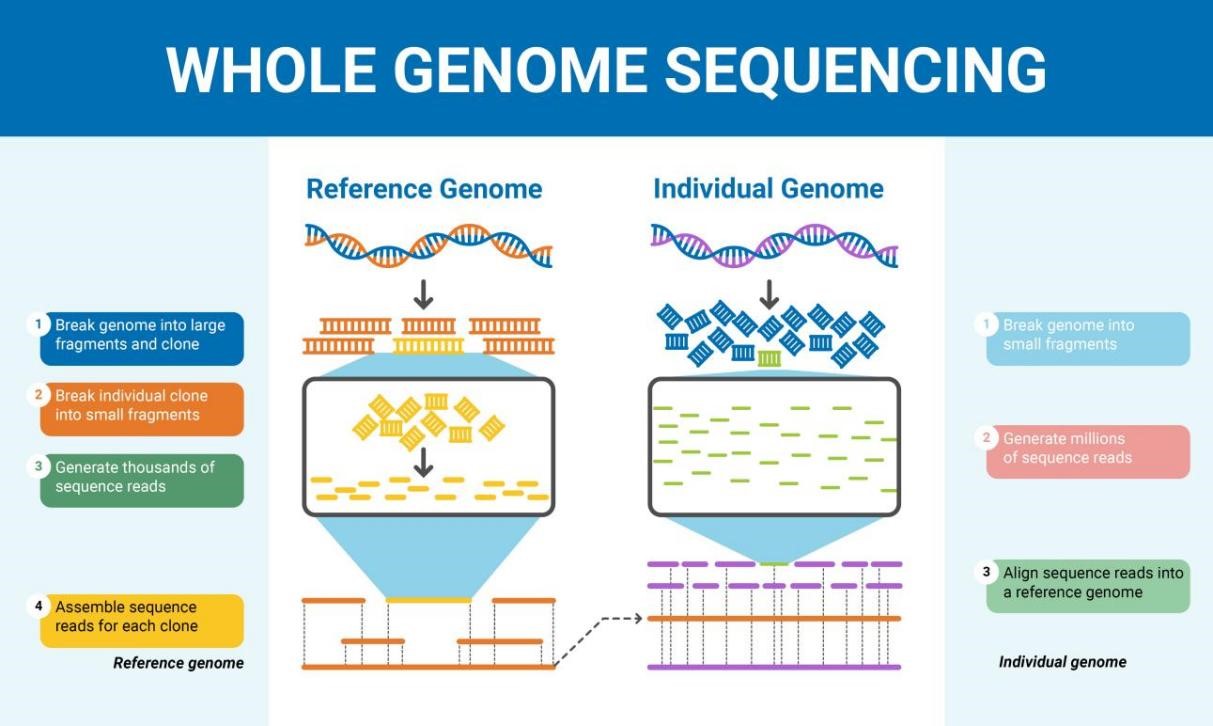
In public health, the arrival of genomic data greatly enhanced infectious disease surveillance, personalised medicine and the global response to pandemics. This Review examines how genomic sequencing became a vital tool for identifying pathogens, tracking virus evolution, and tracing transmission chains, with case studies on COVID-19 variants such as Delta and Omicron. Genomic sequencing has also led to breakthroughs in personalised medicine and pharmacogenomics, whereby drug efficacy and adverse reactions are optimised for individual patients. Genomic surveillance is now a critical tool for detecting emergent threats, monitoring disease spread, and evaluating the efficacy of public health interventions, from contact tracing to vaccines. These genomic approaches have saved thousands of lives during the global COVID-19 pandemic. The paper ends on a positive note about the advances in public health genomics and underscores the value of continuing investment in genomic technologies to safeguard global health security.

 View pdf
View pdf


Obesity has become a major global health issue and is an independent risk factor for several cardiovascular risks. Exercise, as a therapeutic method, is commonly used to improve cardiovascular health in obese populations. This paper reviews and analyzes the effects of five different exercise forms on risk factors for obesity-related cardiovascular diseases: Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training (MICT), High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT), Sprint Interval Training (SIT), aerobic combined with resistance training, and Blood Flow Restriction Training (BFR). The aim is to explore the similarities and differences in health benefits among these exercise forms for individuals with obesity. The review finds that MICT is notably effective in reducing cardiovascular disease risk factors and promoting cardiovascular health in obese individuals. In contrast, high-intensity interval exercises such as HIIT and SIT show even more significant improvements in cardiovascular health. This difference may be attributed to varying biological effects caused by different intensity levels and intervals, though the specific mechanisms require further clarification. Since increased skeletal muscle can enhance basal metabolic rate and positively impact the cardiovascular system, resistance training is often recommended in combination with aerobic training for better results. Additionally, BFR can achieve similar training effects under lower exercise loads, providing a safer training option for obese individuals. Future research should focus on the mechanisms by which different exercise forms affect specific cardiovascular disease risk factors and how to optimize exercise programs based on individual differences to enhance personalization and scientific validity of interventions.

 View pdf
View pdf


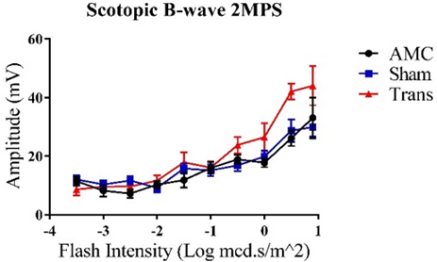
Our research aims to develop a therapy for incurable retinal diseases, such as retinitis pigmentosa (RP) and age-related macular degeneration (AMD), using the retinal degenerate Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) nude rat model. The approach involves transplanting human embryonic stem cell (hESC)-derived retinal organoid sheets. Photoreceptors in RCS nude rats deteriorate over time, leading to impaired vision, similar to RP and AMD. By transplanting hESC-derived retinal organoid sheets, the degenerated host photoreceptors may be replaced or rescued, potentially halting further degeneration and even enhancing visual performance. Electroretinography (ERG), a noninvasive method, is used to measure visual function. Our current project utilizes ERG to monitor visual responses in RCS nude rats and test whether transplantation of hESC-derived sheets leads to improved light response compared to age-matched control (AMC) non-surgery and sham groups. The left eyes of RCS nude rats were exclusively treated with retinal sheet transplants, allowing for internal comparison. ERG data collected every two months over six months showed a significant decline in visual function with age in both low-light scotopic and bright-light photopic tests for AMC and sham groups. Notably, transplanted RCS nude rats exhibited enhanced responses in the treated left eyes. Together with findings from superior colliculus (SC) recordings and Optokinetic (OKN) assessments, the results suggest that hESC-derived retinal organoid sheets improve visual function in RCS nude rats.

 View pdf
View pdf


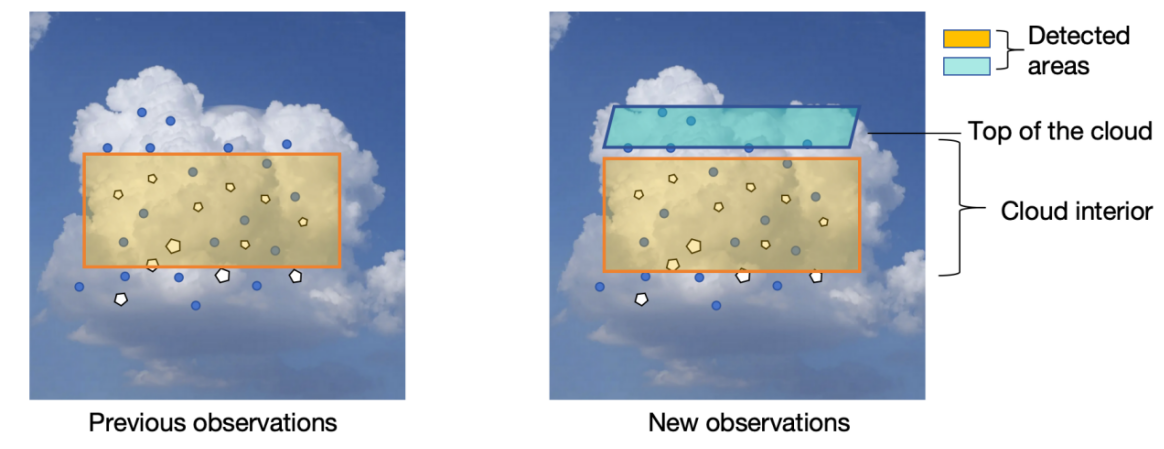
The issue of climate change is hotly debated in today's world. More attention is paid to climate-related issues, including global warming. It is accepted that clouds are responsible for the rise of global surface temperature. People have spent decades trying to develop climate models that are capable of more accurate cloud projections without getting the ultimate solution since clouds are complicated compounds. This review article focuses on clouds' role in global warming, the mechanisms of cloud warming the Earth's surface, uncertainties of cloud parameterizations, and some researches aiming at mitigating the uncertainties . This paper concluded that although advancements are made in adding new constraints and taking new observable variables, uncertainty remains. The majority of new methods and constraints reviewed in this paper are still limited to different extents. Therefore, more complete climate models that can be applied to more conditions and regions could be the direction for future studies in the field.

 View pdf
View pdf


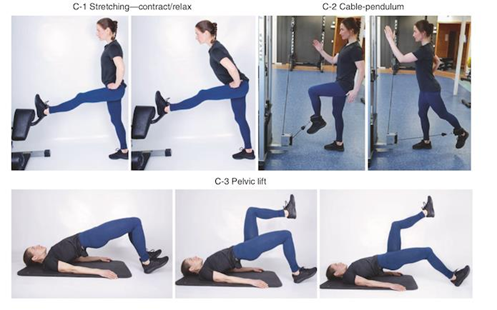
Nowadays, as the injury rate of hamstring injuries increases, it is important to find the effective recovery method. This article is in order to explain the reasons of why soccer athletes get hamstring injuries based on the detailed analysis of the injured structure anatomy of people, and discuss the functions and mechanisms of the injury, which include stretch and sprinting. Then explain both the modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors and risk group of human such as older people who has muscle weakness and the athletes who already experience the same injuries. Finally, the article provides several rehabilitation methods which can help athletes to do the recovery step by step, from soft tissue injuries, to reducing the inflammation and pain, then doing physiotherapy which includes the muscle strength training and flexibility training. Besides, it also gives an evaluation of each rehabilitation program to find the most effective and useful one and it also compare the similar rehabilitation program of L-protocol groups and C-protocol groups in many aspects. The common results show that by doing effective recovery, can help athletes with hamstring injuries return to the sports quickly. After that, several prevention methods are given in the article, such as doing warm up program and stretching before doing the sports, which can help athletes avoiding getting those kinds of injury

 View pdf
View pdf


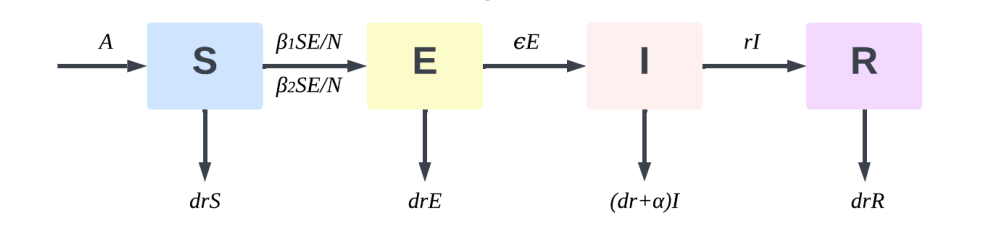
From the Black Death to SARS to influenza A (H1N1), communicable diseases have always been among the uppermost problem endangering human health and have caused crises all over the world countless times. Practical relevance of a thorough knowledge of the transmission pathways and related mechanisms of infectious diseases are complex. Investigating the laws of infectious illness transmission mostly depends on the building of dynamic models. Designing corresponding models based on specific transmission mechanisms can more realistically depict the transmission dynamics of infectious diseases and provide higher accuracy for parameter estimation. This study suggested an enhanced SEIR model and performed a comprehensive investigation of its equilibrium point and stability, acknowledging that individuals infected with the novel coronavirus are contagious in time of their incubation period. Consequently, an empirical investigation was undertaken utilizing this model to analyze the overall trend of the epidemic in China and the outbreak aboard the Diamond Princess cruise ship. Key model parameters, such as the infection rate coefficient, control coefficient, basic reproduction number, and the particular time at which the effective reproduction number declines to 1, were ascertained by the maximum likelihood estimation approach. The cumulative confirmed case fitting curves for the national pandemic in China and the Diamond Princess outbreak were presented concurrently to further validate the model's efficacy

 View pdf
View pdf


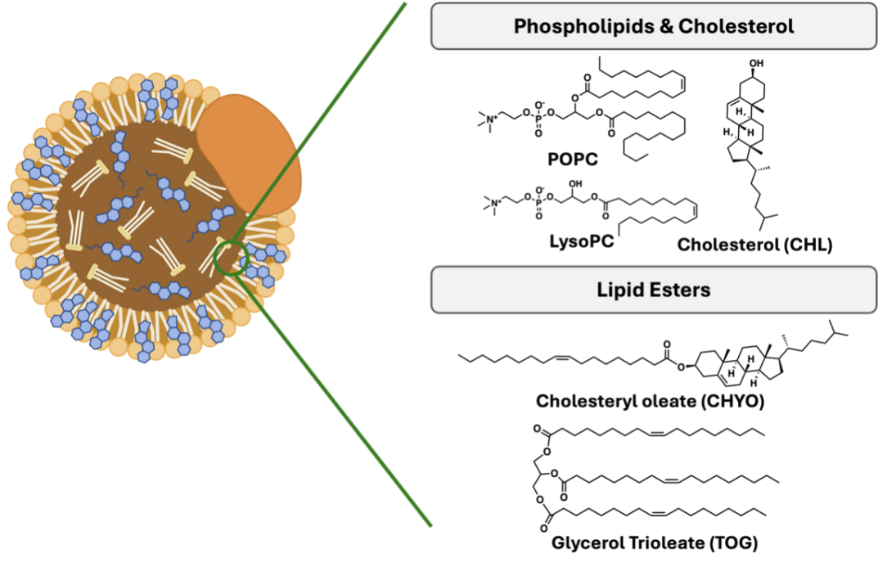
Cancer is a major global health threat and a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Nucleotide analog chemodrugs are commonly used in the treatment of various solid tumors, but their clinical efficacy is often limited by rapid blood metabolization, poor intracellular diffusion and significant side effects due to non-selectivity targeting. To address these challenges, this study investigates the potential of conjugating squalene—a natural triterpene and cholesterol biosynthesis precursor—to two model chemodrugs to enhance the drug's incorporation into endogenous low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) for targeted cancer delivery. By leveraging the natural affinity of lipoproteins for cancer cells with overexpressed lipoprotein receptors, this approach can potentially improve the drug’s specificity to cancer cells and accumulation at tumor sites. Using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, we found that squalene-conjugated drugs have favorable partitioning into LDL interior with a deep negative free energy well. It confirms that squalene-drug conjugates possess the significantly higher affinity to LDL and the potential to exploit LDL for targeting cancer cells. The improved drug behaviors are expected to improve drug circulation and tumor accumulation. The findings provide valuable insights into the potential of squalene-conjugated chemodrugs as a novel strategy for improving the therapeutic efficacy of nucleoside analogs in cancer treatment

 View pdf
View pdf



Objective: This study aims to systematically analyze and screen the main factors affecting injuries of figure skaters and to construct a scientific injury prediction model. Methods: A questionnaire survey was conducted to collect the basic information of 34 figure skaters from Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Shanghai, including the subjects' gender, starting age, years of skating, frequency of on-ice training, duration of each training session, frequency of off-ice training, warm-up time, sleep duration, coach level, ice surface conditions and skate fit during training, as well as the number injuries the subjects had in the past years. The main factors affecting injuries of figure skaters were found through a logistic regression model, and a nomogram was constructed. All data were analyzed in R language. Results and Conclusion: The findings indicate that gender, starting age, height, skating experience, and free skating level are key factors influencing the risk of sport injuries. Based on these factors, this study successfully developed a comprehensive risk assessment model for sports injuries in youth figure skaters. This model can predict and reduce the risk of injuries and provide a scientific basis for personalized training programs

 View pdf
View pdf


With an incidence of 1.2 million new cases reported annually worldwide, 80% of which are non-small cell lung cancer, the majority of which are advanced at the time of diagnosis and have a poor prognosis, lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related mortality in many countries. The effectiveness of chemotherapy for advanced lung cancer is still lacking, despite notable advancements in this area. The most prevalent histologic form of lung cancer is non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Platinum-based chemotherapy is the conventional treatment for individuals with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), although it has a high rate of side effects and is not very effective. In recent years, molecular targeted therapy has become an important therapeutic tool for patients with advanced NSCLC with the continuous development of lung cancer targets and molecular targeted drugs. At present, these drugs have been successfully applied in the clinic and achieved remarkable efficacy, creating a new era of molecularly targeted therapy for NSCLC. The paper summarizes the progress of molecularly targeted therapy for advanced NSCLC. Targeted therapeutic drugs are now widely used in clinical practice and play an important role in tumor treatment, but most of them are resistant after a period of time. In addition, the high price limits their uses in general patients. Therefore, new drugs with lower efficacy, smaller side effects, a longer effective time, and a reasonable price are expected to come out as soon as possible

 View pdf
View pdf




