

Volume 94
Published on April 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Environmental Geoscience and Earth Ecology
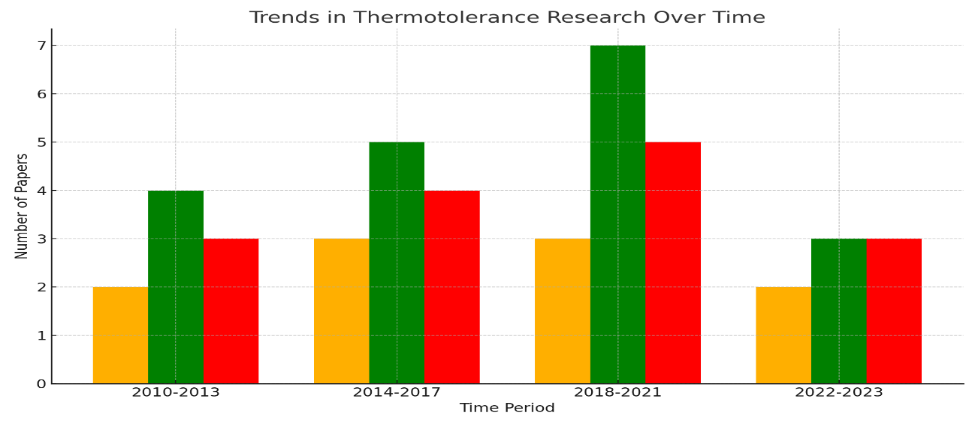
Global warming has significantly altered ecosystems, especially in isolated islands and nearby coastal biomes, where organisms face increased thermal stress and climatic disturbances. These distinctive ecological systems serve as natural laboratories for examining the evolutionary responses of organisms to increased temperatures. This research undertakes a comparative analysis of paleontological evidence and extant species within island ecosystems to elucidate genomic divergences and their evolutionary trajectories, further elucidating the mechanisms underlying thermotolerance adaptation. This study rigorously investigates the roles of natural selection and adaptive mechanisms in enhancing thermotolerance among organisms by integrating palaeobiological datasets and molecular genomic analyses. The review consolidates findings in three primary areas: reconstructing paleoclimatic thermal environments from fossil records, elucidating the physiological and molecular mechanisms of thermotolerance in extant taxa, and assessing climate change as a selective pressure in adaptive evolution. This study consolidates evidence from various perspectives to elucidate the impacts of global warming on evolutionary trajectories and underscores the substantial ecological ramifications of climate-induced selective pressures.

 View pdf
View pdf


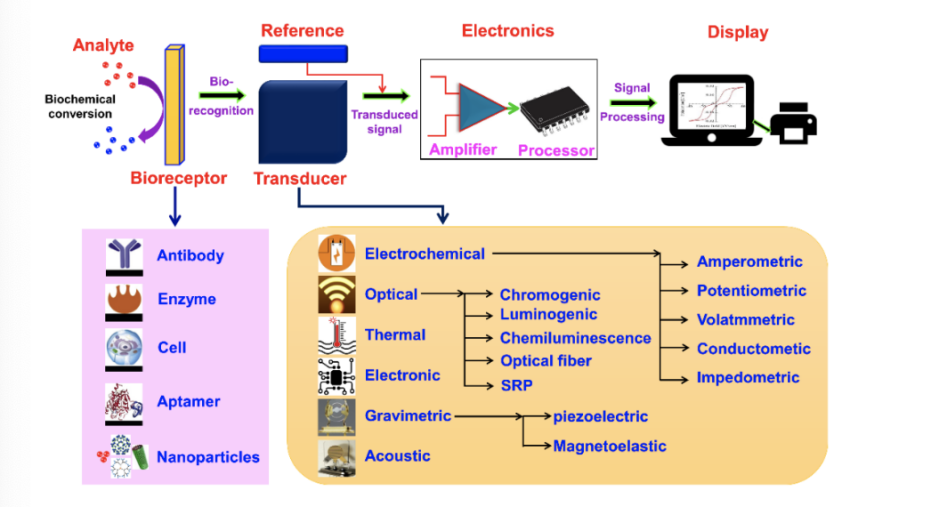
This article expounds that human activities have caused severe marine pollution, and biosensors have become key tools for marine pollution monitoring. It elaborates on their composition, classification, and working principles. It focuses on introducing various sensors and their detection effects in different aspects of marine pollution detection, such as organic pollutants (hydrocarbons, organophosphorus, organic nitrogen compounds), heavy metal ions, microorganisms, and biological toxicity assessment. It also looks forward to the future development of multi-characteristic sensing platforms that can be integrated into various marine platforms to form coastal sensor networks. At the same time, it is necessary to address challenges such as the variability of the marine environment, conduct multi-disciplinary verification, and optimize the quality and performance of sensors. This review found that biosensors are important tools for detecting various marine pollutants, providing effective solutions for marine environmental monitoring and protection. Future advances in sensor technology, multi-characteristic platforms, and artificial intelligence integration will improve their performance and scalability, supporting sustainable marine resource management. However, this study relied on secondary data, which highlights the need for more empirical studies and field tests in different marine habitats to evaluate the actual performance of marine biosensors.

 View pdf
View pdf


Scientifically quantifying and analyzing the nitrogen flow efficiency and its influencing factors in the Taihu Lake basin is of great significance to promote its pollution management and green development. Twenty-one municipalities in the Lake Tai basin were selected as the research objects from 2018 to 2022, and the Super-SBM model was used to reveal the changing characteristics of the nitrogen flow efficiency in the Lake Tai basin from 2 perspectives, namely static and dynamic, and the key factors affecting the nitrogen flow efficiency of the basin were explored through the Tobit model. The results show that (1) from 2018 to 2022, the overall nitrogen flow efficiency of the Lake Tai basin is at a low level, and there is still a large space for nitrogen reduction potential. (2) In terms of dynamic efficiency, the Malmquist trend indicates that the overall trend of nitrogen flow efficiency in the Lake Tai Basin is favorable, and that technological progress remains an important driving force to promote the improvement of nitrogen flow efficiency in the Lake Tai Basin. (3) In terms of influencing factors, environmental regulation and energy structure show positive and significant effects in improving the nitrogen flow efficiency of the basin. Finally, from the commonalities and differences, relevant policy suggestions for improving the efficiency of nitrogen flow in the basin are proposed.

 View pdf
View pdf


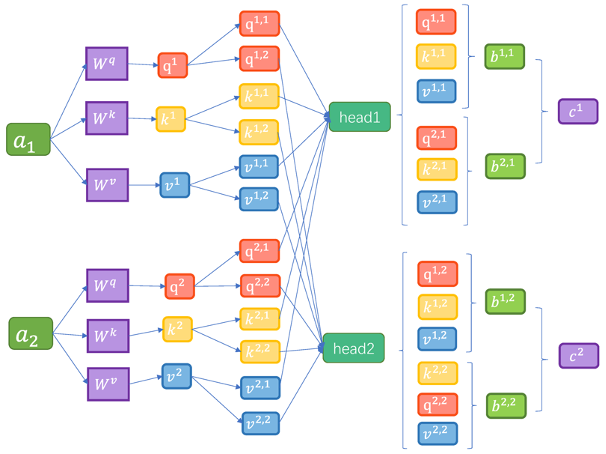
In this study, long short-term memory network (LSTM) model was optimized based on multi-head attention mechanism to effectively predict the survival of agricultural trees. Based on the in-depth analysis of a large number of agricultural tree survival data, the corresponding prediction model was constructed. In the training phase, we analyzed the confusion matrix of the training set, and the results revealed that the accuracy of the model in predicting the survival of agricultural trees was as high as 99.74%. In addition, the performance on the independent test set is also very good, with an accuracy of 99.40%, although there is a slight decrease compared to the training set (0.34%), but both maintain a high accuracy level of more than 99%. This shows that the model has very high prediction accuracy and maintains good generalization ability across different data sets. Further, by drawing the ROC curve and calculating the AUC (area under the curve), the result is 0.9857, which fully reflects the strong ability of the model in the tree survival prediction task. An AUC value higher than 0.9 indicates that the model has a very low error rate on the classification task, which ensures the reliability of the prediction results. This study shows that the LSTM optimization model based on multi-head attention mechanism can provide a high-precision tree survival prediction tool for agricultural management, so as to help farmers make more effective decisions. This result not only has theoretical value, but also has important significance for the growth management and sustainable development of trees in practical application. Through this research, we expect to be able to contribute to the development of smart agriculture.

 View pdf
View pdf


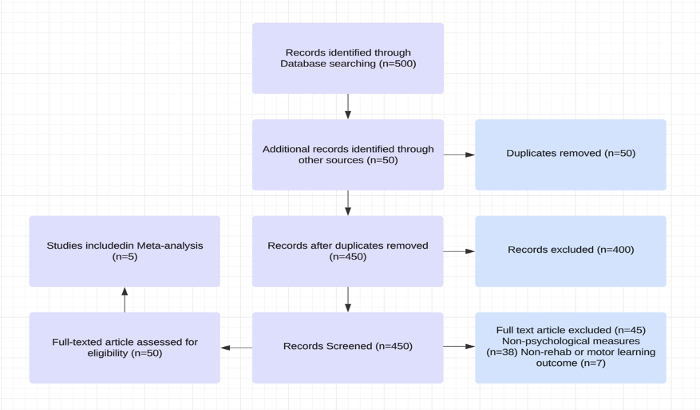
Sport-related concussions significantly impact athletes, affecting psychological health and recovery outcomes. This meta-analysis examined the influence of psychological factors, such as anxiety, depression, and motivation, on rehabilitation adherence and motor learning in athletes recovering from concussions, with subgroup analyses by gender, age, and sport type. A systematic review of PubMed, Web of Science, and PsycINFO identified five studies, revealing that anxiety and depression consistently reduced rehabilitation adherence, while low motivation delayed motor skill reacquisition. Female athletes exhibited higher anxiety and depression levels, younger athletes experienced greater emotional distress, and contact-sport athletes faced more severe psychological effects compared to non-contact sports. Although minimal heterogeneity was found (I² = 0%), potential publication bias was noted in the funnel plot. These findings underscore the critical role of psychological factors in recovery, highlighting the need for integrated mental health interventions and motivational strategies to improve rehabilitation and motor learning. Future research should prioritize longitudinal studies and targeted psychological interventions to enhance recovery protocols for athletes.

 View pdf
View pdf


Gannan is located in the southern red soil hilly region, characterized by concentrated rainfall, interlaced ravines, and poor soil structure, which contribute to severe soil erosion. With rapid economic development, various construction projects have been launched, disrupting the surface and destroying the original landforms, making vegetation restoration extremely difficult. This study takes the Ganzhou Hele Substation as an example, applying “W-OH + soil microbes” to the slopes of the substation, with a control group for comparison. Through soil infiltration tests, soil erodibility modeling, organic matter content analysis, and plant root vitality assessments, the effectiveness of vegetation restoration on erosion-affected land slopes in the Gannan mountainous region under different configuration modes was verified. The results show that the W-OH material significantly reduces water infiltration in the eroded soils of the Gannan mountain area, enhances soil erosion resistance, and the soil microbes effectively increase soil organic matter content and plant root vitality. The combined application of both is complementary. The configurations “soil microbes + 3.0% W-OH” and “soil microbes + 4.0% W-OH” are more beneficial to the rapid restoration of vegetation in the erosion-affected land in the Gannan mountainous region.

 View pdf
View pdf


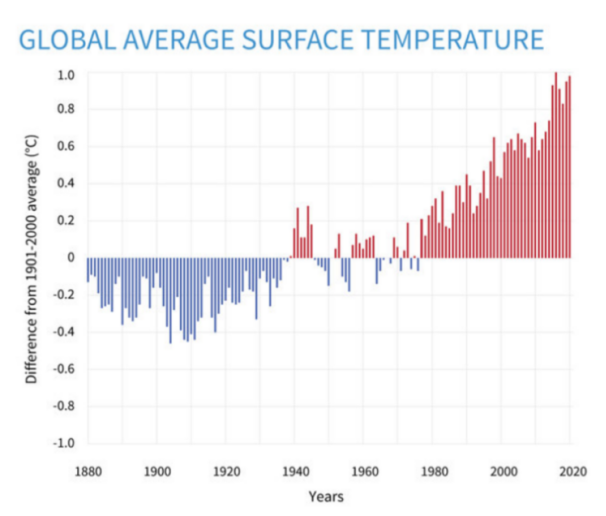
Groundwater is a crucial resource for irrigation and domestic use, particularly in China and the United States. Nevertheless, climate change and excessive extraction threaten its sustainability. Over-exploitation not only accelerates climate change but also heightens groundwater’s vulnerability to its effects. Declining water tables and disrupted aquifer recharge reduce long-term availability, while groundwater pumping releases dissolved carbon and nitrogen compounds, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Deeper extraction demands greater energy input, primarily from fossil fuels, further exacerbating emissions. These dynamics position groundwater depletion as both an environmental and climate challenge. This study reviews the effects of environmental change on groundwater availability and management, explores strategies for regulating its use in irrigation, and proposes effective measures to safeguard the long-term sustainability of this finite resource. By analyzing trends in major groundwater-dependent regions, the study advances understanding of how environmental changes influence groundwater availability and quality. The significance of this research extends beyond regional case studies, offering insights into the global implications of groundwater depletion. The findings underscore the urgent need for policy interventions, including regulated extraction, enhanced recharge methods, and energy-efficient irrigation practices, to safeguard this critical resource for future generations.

 View pdf
View pdf


The optimization of multiplex PCR technology involves factors such as primer specificity, annealing temperature, and buffer concentration. This paper discusses the optimization process of the technology and its performance evaluation in practical detection. The objective of the study is to enhance the sensitivity, specificity, and stability of multiplex PCR technology to more efficiently detect harmful substances in food. The research systematically evaluates the performance of the optimized PCR system by optimizing parameters such as primer design, annealing temperature, and buffer concentration. The sensitivity and specificity of the optimized technique are validated through experimental data, demonstrating advantages in stability and reproducibility. In practical applications, the optimized technology was tested on food samples, providing specific data analysis and comparing its performance with existing detection methods. A comprehensive evaluation of multiplex PCR's application value in terms of detection time, cost, and efficiency was conducted. The results show that the optimized multiplex PCR technology improves the detection sensitivity to 0.1 pg/µL, with specificity exceeding 98%, along with lower background signals and higher stability. The widespread application of this technology is expected to provide a faster, more accurate, and cost-effective detection method for food safety testing.

 View pdf
View pdf


Desert ecosystems characterized by extreme aridity and fragile ecological balance face the dual threat of climate change and escalating anthropogenic activities. Restoration of these ecosystems requires strategic plant protection approaches, particularly drought-tolerant and disease-resistant species selection. This paper focuses on current research on plant protection strategies for restoring desert ecosystems, with the discussion focusing on the selection of drought-resistant vegetation in the Horqin Sand. The main findings of this paper reveal that species such as and Artemisia halodendron exhibit superior drought adaptability, with significant variations in leaf traits (e.g., specific leaf area, dry matter content) influencing their survival. Soil potassium dynamics and microbial interactions further modulate plant resilience. Community succession studies highlight the transition from annual to perennial dominance over 30 years, enhancing ecosystem stability. However, challenges persist in balancing ecological restoration with agricultural demands. This study underscores the integration of multi-disciplinary insights to optimize species selection to ensure sustainable desert rehabilitation.

 View pdf
View pdf


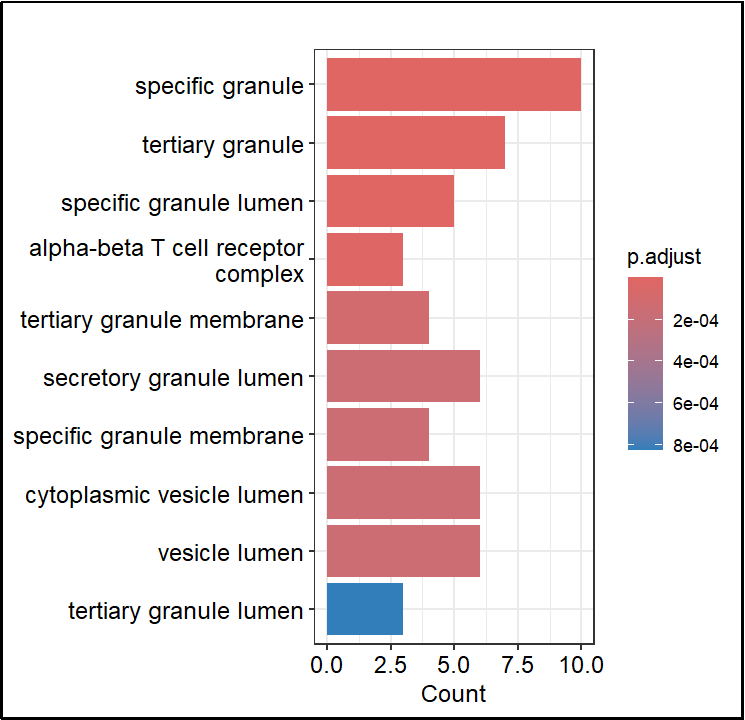
Recent advancements in understanding the pathogenesis and therapeutic approaches for septic shock have been made; however, research elucidating genetic-level mechanisms remains limited. This study aims to explore genetic contributors to septic shock pathogenesis and evaluate differentially expressed genes as potential diagnostic targets. Utilizing the GSE95233 dataset from the GEO database, we compared blood samples from 51 septic shock patients and 22 healthy controls via R language and GEO2R tools. We identified 38 differentially expressed genes (21 upregulated, 17 downregulated). GO functional enrichment analysis of differential genes was carried out using the Cluster Profiler package in R language, and the results showed that most of the differential genes were distributed in T cells, which were related to the development, differentiation, recognition, and clearance of T cells, and the regulation of inflammatory cytokines, which directly affected immune signaling and immune killing pathways. We also analyzed the interaction network between differentially expressed proteins with the help of string online website and MCODE plug-in in Cytoscape 3.8.2, and identified 9 core genes, including BCL11B and TBX21 genes related to immune cell development and differentiation, CD247, CD3G, CD8A and S1PR5 genes related to T cell signaling, PRF1 and GNLY genes related to immune cell killing activity. Through the evaluation of gene function and the prediction of the mechanism of action, we determined that BCL11B, TBX21, S1PR5, CD247, PRF1 and other differential genes can be used as new targets for research to prevent the exacerbation of sepsis and treat septic shock.

 View pdf
View pdf




