

Volume 98
Published on April 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Modern Medicine and Global Health
The review highlights recent advancements in mRNA vaccine technology, focusing on the key mechanism of increasing vaccine immunogenicity through lipid nanoparticle (LNP) and its successful application to a COVID-19 vaccine. Optimized mRNA design, coupled with chemical modifications, such as pseudouridine substitution, have enhanced mRNA stability, translational efficiency, and minimized immune-related adverse reactions. Moreover, LNP optimization, through adjusting the ratio of ionized lipid, phospholipid, and cholesterol and regulating the nanoparticle size and surface charge, has proven critical for efficient vaccine delivery and robust immune responses. The review also discusses different administration routes and dosing regimens, emphasizing intramuscular injection as the most effective for systemic immune activation. The successful development of COVID-19 vaccines, as represented by Pfizer and Modena vaccines, supports the importance of those technologies and provides a new paradigm for future vaccine development. Continued optimization of LNP technology and the exploration of novel delivery systems are essential for extending the scope of mRNA vaccines to combat a broader range of diseases, ultimately providing innovative solutions to global health challenges.

 View pdf
View pdf


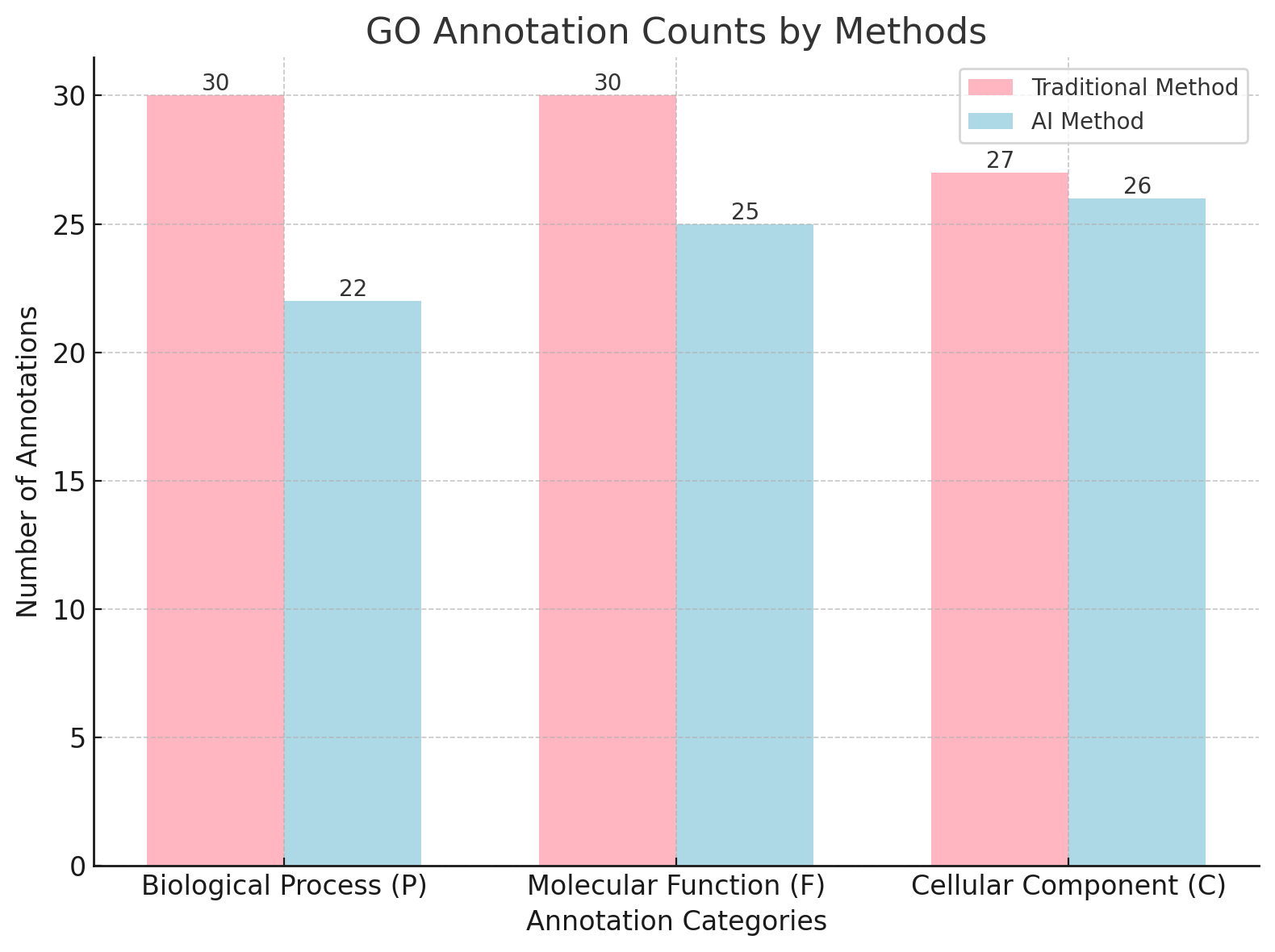
Gene annotation is a critical process in genomics that involves the description of not only the position but also the function of an encoded element of a genome. In general, this provides biological context to sequence data, enabling an advanced level of understanding of genetic information. This is important in areas aligned with genetic engineering, studies of diseases, and evolution. Through ML and DL methodologies, AI enhances functional annotation and gene prediction effectively and accurately. This review focuses on AI in genomic research and assesses its effectiveness compared to traditional annotation tools. Using Escherichia coli as the representative model organism, the study focuses on a systematic approach of gene prediction using web Augustus with functional annotation using DeepGOPlus, an artificial intelligence tool, instead of the conventional BLAST-based annotation using the UniProt database. The study researches the extent of GO term coverage, the specificity of the annotations, and the concordance among these various tools. Artificial intelligence is highly beneficial owing to its speed, scalability, and proficiency in annotating intricate or poorly defined genomic areas. Notable instances include DeepGOPlus, which has demonstrated enhanced coverage by suggesting new terms that were frequently missed by earlier traditional tools. Notwithstanding these, AI tools face challenges such as dependence on high-quality training data, concerns about interpretability, and the need for biological validation to support the predictions. This review emphasizes the transformative impact that artificial intelligence brings to the field of gene annotation by presenting novel applications in many fields, including personalized medicine and synthetic biology, in which traditional methods suffer from severe limitations.

 View pdf
View pdf


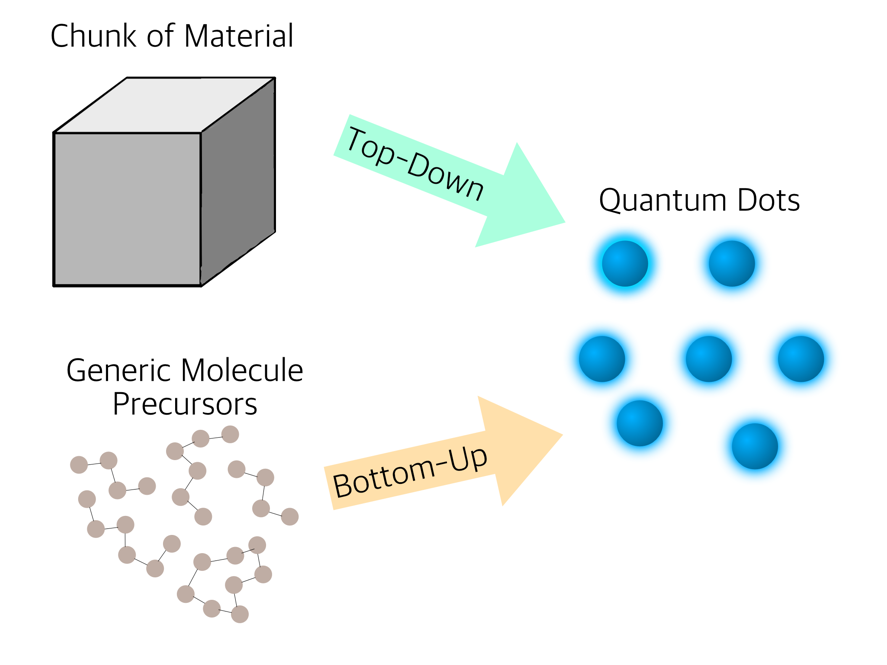
Quantum dots (QDs), a class of zero-dimensional nanomaterials with exceptional fluorescent properties, have emerged as a key component in biosensors. Biosensors are sophisticated devices that measure biological properties and convert them into electrical signals, comprising components such as the analyte, bioreceptor, transducer, electronics, display, and power source. Compared to traditional methods, QDs are more sensitive, less likely to suffer from photobleaching, and customizable. This review explains the properties of QDs, their synthesis methods, and the integration of QDs into biosensors. Additionally, it delves into the various applications of quantum dots-based biosensors, providing a brief overview of multiple QD biosensors, including their use in detecting cancer, coronavirus, tuberculosis, and salmonella. Despite their significant potential, the toxicity of QDs, particularly those composed of heavy metals, poses challenges for their broader application and can harm organisms after entering the environment. Finally, the paper discusses future trends in the development of quantum dot biosensors, such as more carbon QDs, greener synthesis, and more QD sensors. This paper provides information that can be used to improve future QD biosensors.

 View pdf
View pdf


The demand for geriatric nursing in China continues to grow in the context of aging, and the policy support system is gradually improving. However, it still faces challenges such as insufficient service supply and low professionalization. To this end, China is actively exploring innovative methods such as the integrated medical and nursing care model and "Internet + nursing services", and is strengthening talent training and team building to meet the challenges of an aging society.

 View pdf
View pdf


Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is characterized by persistent, excessive worry about everyday situations, lasting for at least six months. Individuals with GAD often experience both psychological and physical symptoms, including restlessness, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances. Freud’s early idea of “anxious expectation” is still a key part of understanding the disorder, along with the more modern concepts of “free-floating anxiety” and panic attacks. Research into the brain shows that Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is tied to issues with certain neurotransmitter systems, like serotonin, norepinephrine, and GABA. These imbalances play a big role in mood changes and anxiety symptoms. To create better treatments, it’s important to dig deeper into how genetic, environmental, and neurochemical factors all work together to cause GAD.

 View pdf
View pdf


Cigarette smoking, while not widely recognized as an established risk factor for various chronic diseases, have also been accumulating findings suggesting its epidemiological association with diabetes mellitus, particularly type 2 diabetes. However, smoking was not widely recognized as a modifiable risk factor in the development of diabetes prevention and screening strategies. This paper, through a method of literature review, has highlighted studies that focused on the physiological effects of smoking on increased type 2 diabetes risk, the association between smoking behavior and diabetes risk in large-populational studies, and the temporal effect of smoking cessation on diabetes risk. This study finds that smoking significantly increases the risk of type 2 diabetes through mechanisms such as insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, and metabolic disruptions, while smoking cessation, despite initial metabolic challenges, reduces diabetes risk over time, with former smokers' risk aligning with that of never-smokers approximately 12 years after quitting. Key future directions are suggested for strengthening public health strategies on smoking cessation, lifestyle interventions, and personalized metabolic management to reduce the global burden of diabetes.

 View pdf
View pdf


Huntington's Disease (HD) is a degenerative neurological condition that requires extensive nursing care because it has a significant influence on a patient's physical, mental, and emotional health. Even though there is a wealth of research on the clinical features of HD, less is known about the holistic nursing interventions that can greatly enhance the outcomes for both patients and caregivers. With an emphasis on specialized interventions that address physical symptoms, emotional support, and patient education, this review emphasizes the critical role that nursing care plays in managing HD. Promoting participation in worthwhile activities, offering emotional support, and highlighting the significance of culturally responsive treatment are some of the key tactics covered. The results highlight how important it is to combine these all-encompassing strategies in order to improve the quality of life for patients and their families dealing with patients' difficulties. This study aims to promote a comprehensive view of nursing care and identifies areas for future research that will focus on creating novel interventions that give HD patients both medical care and psychosocial support.

 View pdf
View pdf


In a recent study, thalidomide has been proved to have positive pharmacological effects in the immune system, such as the treatment of lupus erythematosus and anti-tumor, but 60 years ago, because of its optical isomer, it led to many tragedies. This time, by collecting the data of papers, this paper mainly analyzes and summarizes the connection between stereochemistry and pharmacological action of drugs, and tried to find the main reasons for the isomers of different structures and their effects from the aspects of biology and medicine. 4-aminopyridine, 4-aminoquinoline, thalidomide, and macrolide compounds are mentioned in this article. It comes to the conclusion that the larger the plane structure area of some drugs, the better the efficacy; some drugs have therapeutic effects only in the R configuration and some drugs with different chiral structures have different pharmacological functions.

 View pdf
View pdf


This paper explores the genetic underpinnings of bipolar disorder (BD) to enhance understanding and inform clinical practice. It aims to examine the hereditary components of BD, identify specific genetic markers, and discuss their implications for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. The study synthesizes findings from family and twin studies, molecular genetics research, genome-wide association studies (GWAS), and epigenetic analyses. It also reviews the role of genetic markers such as CACNA1C and ANK3 and their impact on neurobiological mechanisms associated with BD.The analysis confirms a strong genetic component in BD, with family and twin studies showing significant heritability. Specific genetic markers linked to neurotransmitter signaling and synaptic function are identified. The paper also discusses the role of voltage-gated calcium channels and synaptic function in BD pathophysiology, as well as the influence of epigenetic factors and gene-environment interactions.The findings underscore the importance of integrating genetic data into clinical practice for personalized treatment strategies. Future research should focus on rare genetic variants, deeper exploration of neurobiological mechanisms, and the challenges of translating genetic insights into clinical applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


Classic Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) formulas are an essential component of TCM, embodying profound theoretical foundations and unique practical experiences, and serving as a crucial guarantee for the clinical efficacy of TCM. In recent years, with the development of modern medical technologies, research on the modernization of classic formulas has become one of the hotspots in the field of TCM. Among them, Minor Bupleurum Decoction, a representative formula from the Treatise on Febrile Diseases, has demonstrated broad adaptability and excellent therapeutic effects in clinical applications due to its intricate formulation and remarkable efficacy. This article systematically analyzes and summarizes the mechanisms of action and application value of Minor Bupleurum Decoction in areas such as liver diseases and febrile illnesses, starting from the classic theoretical origins, medicinal composition, and traditional effects of the formula, and integrating modern pharmacology and clinical research. Additionally, this article explores the major issues and future directions in the modernization research of classic TCM formulas, aiming to provide scientific evidence for the modernization and internationalization of TCM. By uncovering the intrinsic rules of classic formulas and integrating them with modern science, the exploration of their clinical potential not only promotes the inheritance and innovation of TCM but also provides important ideas for addressing contemporary medical challenges.

 View pdf
View pdf




