

Volume 51
Published on March 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning
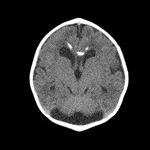
Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to scan the brain and using the image to identify whether the patient has a brain tumor or not is the common way doctors use it today. However, as this may potentially add to the workload of healthcare professionals, it becomes crucial to explore methods for automating image identification. One effective algorithm for this purpose is the utilization of a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) network. However, when applying a CNN network to discern whether an individual has meningioma or not, it becomes evident that the available data may be limited. Meningioma is relatively uncommon, and not all associated images have been made accessible for analysis. The shortage of original samples makes it hard to train the CNN network and has relatively low accuracy. In this case, this study tries to use DCGAN to generate more images based on the original sample. By comparing the accuracy and f1 score of the CNN network, this study finds that implementing images has improved the performance of the CNN network. By implementing the images, the DCGAN generates, the accuracy for the same CNN network to identify whether the images have meningioma or not is increased from 93.53 percent to 97.75 percent. The f1 score also increased from about 0.9187 to about 0.9738.

 View pdf
View pdf


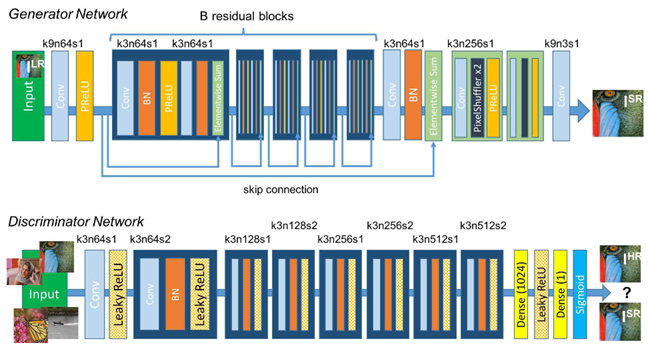
QR codes have become an integral part of our daily routines, simplifying tasks ranging from accessing websites to making payments. However, the quality of QR codes, especially their resolution, can significantly impact their functionality. Low-resolution QR codes may lead to misinterpretation during scanning and even decoding failures. To address this issue, researchers have explored various techniques to enhance the resolution of QR codes. Traditional image processing methods, such as interpolation and filtering, have been used in the past for resolution enhancement. However, these methods often result in overly blurry images with poor perceptual quality. Conversely, solutions based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) can introduce clarity but may compromise the sharpness of image edges. This paper presents an effective approach to improve QR code resolution using a Super-Resolution Generative Adversarial Network (SRGAN). The results are impressive, with SRGAN achieving a Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) of 30.06, significantly outperforming the 17.48 achieved by the SRCNN method. Additionally, in terms of Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), SRGAN reaches 0.936, surpassing SRCNN's 0.473. These metrics demonstrate that SRGAN is highly effective in enhancing the resolution of QR codes, ensuring better scan accuracy and overall functionality in practical applications.

 View pdf
View pdf


Medical images play a crucial role in modern healthcare diagnostics and treatment. However, many medical images suffer from limitations in resolution, potentially impeding a comprehensive understanding of a patient's condition by healthcare professionals. This comprehensive review delves into the applications of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in medical image super-resolution reconstruction to address this challenge. In the Methods section, this paper first focused on the direction of medical image classification, including cell classification of histopathological images and synthetic data enhancement using GANs to improve liver lesion classification. Subsequently, this paper focused on the direction of medical image segmentation, looking into the use of Structure-Corrected Adversarial Networks (SCAN) for organ segmentation in chest radiographs and Deep Adversarial Networks for biomedical image segmentation using unannotated images. In the Applications and Discussion section, this paper thoroughly examined the current progress of GANs in telemedicine diagnosis and disease state generation and prediction. This paper emphasized the significant potential of GAN technology in telemedicine while outlining the current constraints and challenges. Furthermore, this paper highlighted the prospects of GANs in medical image super-resolution reconstruction and how they affect the discipline of medical imaging. This comprehensive review consolidates the latest research findings on GANs in medical image super-resolution reconstruction, underscoring their importance in the realm of healthcare. By critically analysing existing literature, this paper provides valuable insights for medical image analysts are researchers while inspiring future research directions and innovations.

 View pdf
View pdf


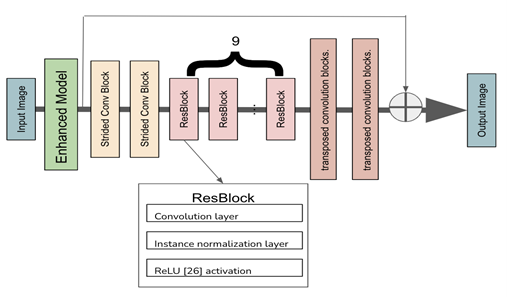
This article aims to address the challenge of eliminating low-light motion blur, a problem that lacks effective solutions, despite being crucial in various application scenarios. For instance, it can help in the identification of moving individuals or license plates during nocturnal surveillance, filming running videos after dark, and managing animals in rural areas at night. These examples represent commonplace and significant scenarios. These are all important domains, but few approaches are effective at handling such specific cases simultaneously. This paper utilizes a fusion model to increase the brightness of an image while preserving the photographic details. The motion blur is subsequently eliminated from the brightness-enhanced image. This results in the enhancement of image details and the removal of motion blur. Comparing the model proposed in this paper with the commonly used Deblur model, it becomes apparent that the new model effectively enhances brightness in low-light motion blur while preserving image details and reducing much of the blur. This implies that the model is more versatile, as it can be used not only for images but also for low-light videos.

 View pdf
View pdf


Recommendation systems play a crucial role in enhancing user satisfaction and driving sales for businesses. They are essential in today’s marketplaces, as they are able to suggest products and services that may interest a particular individual based on their past purchases. In this paper, empirical research is conducted on three distinct subsets of the Amazon dataset, namely Sports & Outdoors, Movies & TV, and Video Games, to comprehensively evaluate the performance of three distinct recommendation methods based on deep learning algorithms. These methods include the dot product method, (an updated version of the singular value decomposition algorithm), the neural network method, and the neural collaborative filtering model with natural language processing method. The results of this study reveal that deep learning-based recommendation systems can achieve more accurate results compared to traditional recommendation systems for three types of products. The implementation of these methods on Amazon’s dataset can help improve sales by correctly identifying customers’ interests and suggesting relevant items.

 View pdf
View pdf


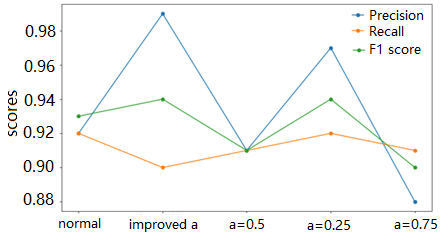
With the continued progress of the Internet, network security has become an increasingly significant issue that requires constant attention and research. Network traffic classification is a key technology used to detect and prevent malicious network activity, and it has accordingly received increasing attention and research. However, datasets related to malicious network traffic classification often have imbalanced characteristics. In conventional traffic classification problems with multiple categories, the sample size characteristics of small categories are often overlooked. To address this issue, the focal loss function was proposed, which focuses on small samples by modulating the trade-off between the positive and negative samples through two hyperparameters α and γ. This article uses convolutional neural networks (CNN) to tackle traffic classification problem and explore the optimal values of α parameters in this application scenario. Additionally, this work proposed a novel weight allocation formula to replace α, which allowed small class traffic to obtain higher accuracy.

 View pdf
View pdf


Artificial Intelligence (AI) has a significant impact on empowering autonomous driving systems to perceive and interpret the environment effectively. However, ensuring data privacy and security in autonomous driving systems is a critical challenge. To surmount these hurdles, federated learning has emerged as an effective strategy. Federated learning is a decentralized machine learning approach that facilitates the cooperative training of models across a diverse set of connected devices, enabling them to collectively learn and improve their performance, while preserving data privacy. This approach eliminates the necessity of sharing raw data and only involves sharing model updates with a central aggregator, thereby ensuring privacy and minimizing data exposure. This paper examines the implementation of federated learning in autonomous driving. It explores the principles of federated learning, including decentralized training, local model updates, model aggregation, privacy preservation, iterative learning, and heterogeneity handling. Two specific approaches, Deep Federated Learning (DFL) and End-to-End Federated Learning, are discussed, highlighting their benefits in enhancing privacy and maintaining prediction accuracy. The paper also discusses the applications of federated learning in communication and control aspects of autonomous driving. It emphasizes the scalability, adaptability, edge computing, real-time learning, federated transfer learning, and privacy-preserving data sharing as potential future prospects for federated learning in autonomous driving. Overall, federated learning offers a unique opportunity to address privacy concerns in autonomous driving systems while harnessing the collective intelligence of a fleet of vehicles. It has the potential to revolutionize the field and contribute to the development of safe and secure autonomous driving technologies.

 View pdf
View pdf


The conventional method of coloring comics can be quite arduous and time-consuming, particularly within the realm of animation, where each frame necessitates individual coloring. Over the past few years, the advent of deep learning technology has introduced fresh prospects for comic coloring. Nonetheless, it's worth noting that deep learning typically demands a substantial volume of data to effectively train models, giving rise to legitimate concerns regarding data privacy. This study proposes an innovative approach that applies federated learning to comic coloring to improve efficiency and address privacy issues. In this research, an existing neural network European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV16) model was employed using federated learning to partition and train the model on segmented databases. To better quantify the color differences between the original images and the colored images, this study designed a custom loss function. Experimental results demonstrate that this approach has been effective in comic coloring, demonstrating the feasibility of applying federated learning to the task of comic coloring.

 View pdf
View pdf
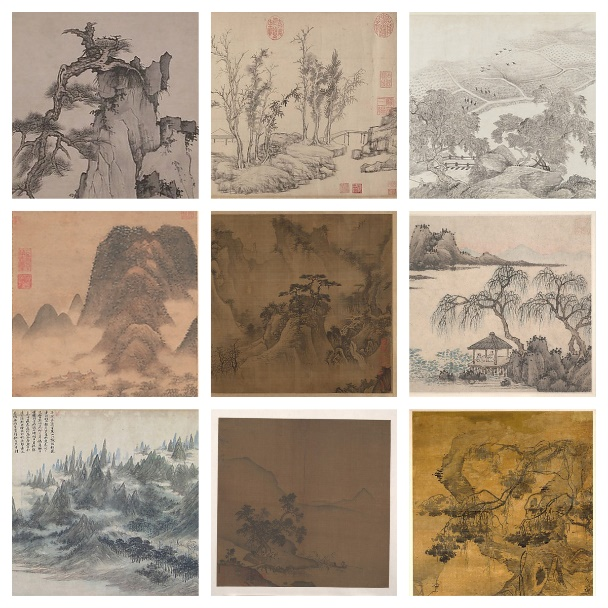



Chinese landscape painting is a prevalent and unique mode of artistic expression within traditional Chinese art. It boasts intricate techniques and demands a relatively high level of artistic skill. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence have ushered in the era of image style transfer techniques, making it feasible to convert landscape photographs into stunning Chinese landscape paintings. In this study, the author has developed an image translation model that enables mutual transformation between images of landscapes and Chinese landscape paintings. This technology significantly reduces the difficulty of creating Chinese landscape paintings, allowing more ordinary people in China to experience and appreciate the joy brought by traditional Chinese art. Experimental results indicate that the style transfer model based on CycleGAN has achieved significant success in this scenario. The generated artworks successfully integrate the style of Chinese landscape painting into the original images without altering the original composition and details. As a result, the original photos gain a certain level of artistic value. Additionally, this study innovatively explores the goal of reverse restoration of Chinese landscape paintings into images, highlighting both the similarities and differences with the current research, thus laying the foundation for future studies.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the rapid development of the Internet and the rise of e-commerce, commercial enterprises are faced with a large amount of data and a complex market environment. In this situation, machine learning, as a powerful tool, is widely used in the field of business analysis. In this dissertation, we take Amazon and eBay as examples to study the application of machine learning in the company's business analytics, focusing on its role in market prediction, customer behavior analysis and operation optimization. By analyzing the relevant cases, we find that machine learning technology plays an important role in helping companies make more accurate decisions and improve efficiency. Studying the application of Amazon machine learning in business analytics can promote in-depth research on the application of machine learning in business in academia, and promote the application and development of machine learning technology in other business scenarios. Overall, the application of machine learning in business analytics can help companies understand customer behavior, optimize operations, and improve sales results. However, there are still some challenges, such as data quality, algorithm selection and privacy protection. Therefore, further research and innovation are necessary to advance the development of machine learning applications in business analytics.

 View pdf
View pdf




