

Volume 81
Published on November 2024Volume title: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Machine Learning and Automation
Under the background of the development of domestic and foreign manufacturing industries and the increasing demand for industrial products at home and abroad, and under the premise of ensuring and even further reducing the manufacturing cost of manufacturers, how to effectively detect and cool the local temperature of industrial parts is a problem worth studying. After analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of traditional manual control and gear adjustment to adjust the fan, the design will be programmed using Arduino. The fan combines infrared sensor technology to detect the presence and position of parts. A temperature sensor is also set up to detect local temperatures in real-time. A fan with automatic step-less speed change according to temperature is obtained. This fan is used for heat dissipation control of local parts in industrial production, thereby reducing the cost of manual control. It further improves control accuracy and efficiency, improves product quality, and ensures production safety.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the advancement in relative technology, robotics is gaining an increasing amount of attention among engineers and researchers as it is a current focus on enabling people’s lives to become more convenient. However, there is another type of robot designed very differently from functional robots like delivery robots and quadrotors that most people are familiar with, bionic robots. This is a kind of robots that gets design inspiration from real animals in nature, from the design of structure to altitudes and mechanisms of motion. How bionic robots are designed, and how the conceptional difference of bionic robots with other robots is reflected on their physical designs are the focuses of this paper. In this paper, four basic types of bionic robots are introduced and 17 existing designs of bio-inspired vehicles are included. 10 bionic aerial vehicles in 3 smaller classifications are compared to 3 conventional aerial vehicles in order to figure out differences in 3 aspects (structure design, sensors, and control method). The results show that bionic robots usually have more degrees of freedom in order to mimic animals’ attitudes, and are lighter in weight. Typically, bio-inspired aerial vehicles employ different wing systems compared with conventional ones. Additionally, while conventional vehicles favour PID more because of its ease of construction, bionic robots use machine learning techniques. Both types of robots use the same sensors, which is necessary for them to detect their environment. However, their control methods differ due to different purposes.

 View pdf
View pdf


As the need for precision and efficiency grows in industrial manufacturing, the accuracy of industrial robots assumes paramount importance. Nevertheless, factors, such as mechanical structures and assembly processes often introduce errors, compromising robots' positioning and repeatability accuracy. Consequently, precise calibration and compensation of these errors are paramount for optimizing robots’ performance. A thorough analysis of error sources and the establishment of error models in industrial robots are conducted in the present study, with special attention paid to offline calibration methods. This paper reviews the robot error model building methods and offline accuracy calibration techniques, summarizes the technical difficulties of the calibration task, and proposes the future development direction for the difficulties such as the complexity of error modeling, the difficulty of non-motor calibration calculation, and the traditional stiffness compensation that does not meet the needs of the robot's operation process. The importance of this research lies in its potential to improve the accuracy and reliability of industrial robots, thus contributing to the development of industrial automation.

 View pdf
View pdf


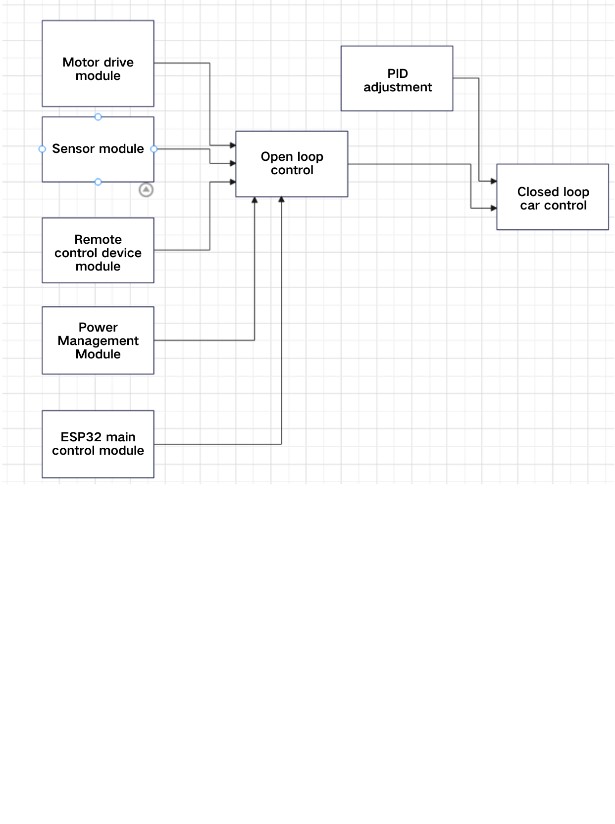
With the rapid advancement of information technology, Bluetooth technology has been widely used in the field of short-range wireless communication, playing an important role in information exchange. As one of the main technologies for short-range wireless communication, Bluetooth technology has broad application prospects, especially in robotic applications such as remote-controlled cars. This paper provides a detailed introduction to the design and implementation process of a Bluetooth remote-controlled car system based on the ESP32. It covers the classic Bluetooth and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) functionalities of the ESP32, the hardware design and assembly of the car (including the DC motor drive module, Bluetooth module, and speed measurement module), and methods for establishing a connection between the ESP32 and Bluetooth module, data transmission, and remote control of the car's movement. The paper also evaluates the system's performance through experiments, discusses the application and parameter adjustment of the PID control algorithm in enhancing speed control, and finally summarizes the research findings and suggests directions for future work.

 View pdf
View pdf


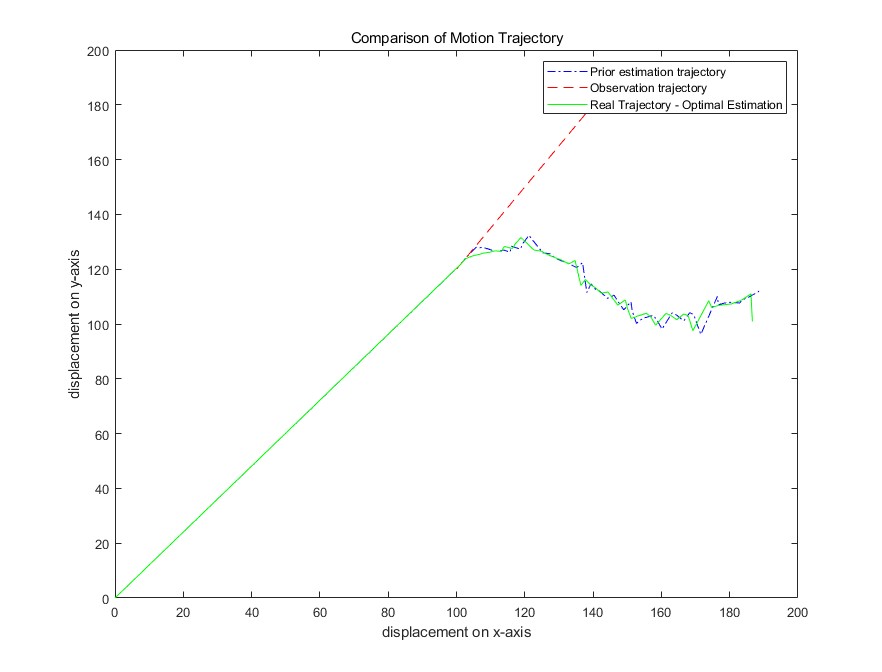
With the popularization of robot technology, various technological developments related to robots have gradually entered a stage of rapid development. Especially path planning technology, which has been a very important and worthwhile part of robot motion and behavior since the concept of robots emerged. In this technology, various obstacles, environmental changes, and efficiency factors usually need to be considered. Whether in the past, present, or future, robot behavior pursues greater precision, reliability, adaptability to the environment, and even anthropomorphism. In order to achieve these goals, the idea of data fusion has emerged in the development of robot data processing. Therefore, the research direction is to use Kalman filtering for noise filtering and data correction to improve the accuracy of fused data. By using a feasible and strongly correlated data fusion method, combined with an improved extended Kalman filter, various data generated by robots can be fused in multiple dimensions and have correlations, reducing the negative impact of data differences and improving the quality and reliability of data fusion.

 View pdf
View pdf


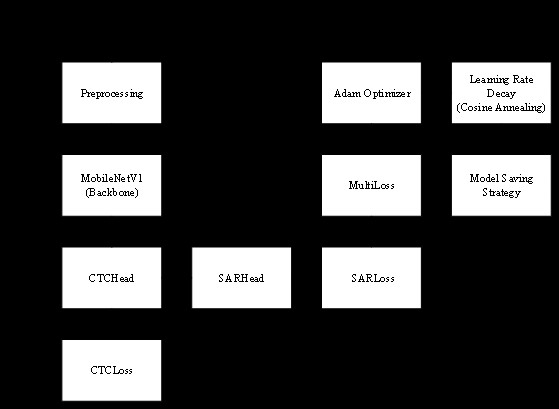
CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart), a security technique widely used on the Internet, can be utilized to distinguish human users from automated programs. The rapid development of deep learning technology has led to the emergence of graph-based recognition techniques that demonstrate excellent performance, which has prompted the investigation of CAPTCHA recognition based on deep learning as a research area of significant interest. This paper addresses the challenging problem of CAPTCHA recognition based on deep learning techniques, reviews the development and classification of CAPTCHA, examines traditional CAPTCHA recognition methods, and delves into the application of deep learning in CAPTCHA recognition. Therefore, a CAPTCHA recognition system is designed and its effectiveness is verified through experiments. This paper makes a significant contribution to the field of CAPTCHA recognition by proposing a deep learning-based approach, which not only enhances the accuracy and efficiency of CAPTCHA recognition, but also provides new ideas and methods for the further development. In the future, further research will be conducted in the field of CAPTCHA recognition to explore additional deep learning models and techniques with the aim of boosting the security and user experience of CAPTCHA.

 View pdf
View pdf


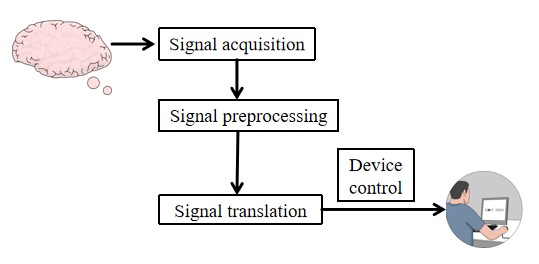
The rapidly aging population faces increasing prevalence of neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and Parkinson's Disease (PD), which significantly impair cognitive and motor functions. There is an urgent need for increased research, awareness, and development of effective treatments to mitigate their impact on the affected individuals and their families. This paper delves into the history, mechanisms, and applications of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) as innovative solutions to mitigate these impacts. BCIs enable direct brain-to-device communication, circumventing conventional neuromuscular routes. We highlight how neurofeedback and neuroplasticity facilitated by BCIs not only restore motor skills and cognitive functions but also enhance the overall quality of life for sufferers. Through applications in cognitive training, motor assistance, and advanced communication aids, BCIs present a significant promise despite the ethical and practical challenges they pose. The continual advancement of this technology promises to a future when its incorporation into treatment plans will be widely used and provide significant advantages for those with PD and AD.

 View pdf
View pdf


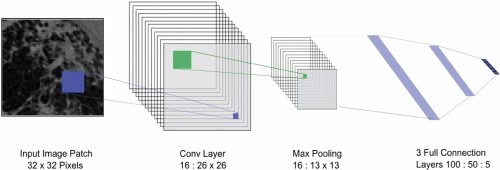
This paper reviews the application and improvement of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in image classification. Firstly, a shallow CNN for interstitial lung disease image classification is presented. This model suppresses overfitting through a unique network architecture and optimisation algorithm. Next, the improved VGG16 architecture and MIDNet18 model are discussed and their superior performance in brain tumour image classification is demonstrated. Subsequently, a CNN-CapsNet model for cervical cancer image classification and its improvement are presented and the customised model is compared with the conventional VGG-16 CNN architecture in the paper. Next, the application of sparse convolutional kernels and hybrid sparse convolutional kernels (HDCs) in solving the problem of computational resource consumption is presented. Subsequently, methods for solving the problem of limited training data through transfer learning and network data augmentation techniques are discussed, as well as GAN-generated datasets for solving the overfitting problem. Finally, the effect of degraded images on the classification effectiveness of CNNs is explored. The results show that the improved CNN architecture and algorithms have significant effects in solving the problems of overfitting and computational resource consumption, and can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of image classification. And degraded images do adversely affect the accuracy of CNN for image classification.

 View pdf
View pdf


The COVID-19 pandemic has forced most schools, including universities, to adopt online courses for teaching. Due to the breaking of the constraints of time and space, online courses still occupy a large proportion in education until now, and large-scale open online education courses will become a major trend in the future. Of course, problems also arise in this process. As teachers cannot receive feedback from students anytime and anywhere in online courses, such as micro expressions, body movements, etc., they cannot know whether students are confused. Therefore, how to effectively detect students' learning status has grown in popularity. In the last few years, machine learning has developed rapidly, and a large number of artificial intelligence have emerged, making it possible to detect whether students are confused by combining electroencephalography with machine learning. In order to determine whether students were confused, this study used a wireless single channel Mindset device to collect Electroencephalography (EEG) signals. Six machine learning models—random forests, eXtreme Gradient boosting, K-nearest neighbors, gradient boosting machines, logistic regression, and support vector machines—were then chosen. The findings indicate that other machine learning models have a high accuracy rate in classifying students' bewilderment, with the exception of the logistic regression model. With a 99.69% accuracy rate, the eXtreme gradient boosting model performs better than a number of other models.

 View pdf
View pdf


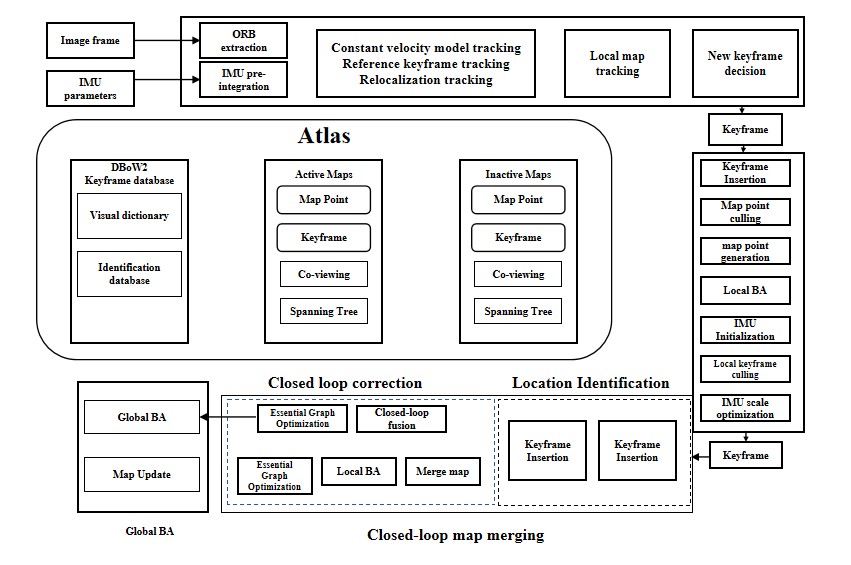
Drones can play a quite crucial role in many walks of life today. Enhancing the visual perception ability of drones is crucial to their intelligence level. Among them, it is necessary to focus on strengthening the detection, tracking and mapping capabilities of drones for dynamic objects. However, the existing visual SLAM systems carried by drones do not perform well in dynamic environments. This project designs a monocular visual SLAM system specifically for drones, aiming to achieve efficient three-dimensional mapping and target tracking, surpassing the limitations of simple static mapping and positioning. Besides, this project constructs a drone dynamic SLAM system developed on the ORB-SLAM3 structure, uses drone images to detect, track and map object motion models, and reconstructs environmental maps to obtain motion parameters with real physical scales. This project strives to optimize the input pre-processing module, improve the validity of data and output environmental maps and raster maps. The outcomes demonstrate the system's strong accuracy and adaptability in dynamic installation procedures.

 View pdf
View pdf




