

Volume 139
Published on January 2025Volume title: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Financial Technology and Business Analysis
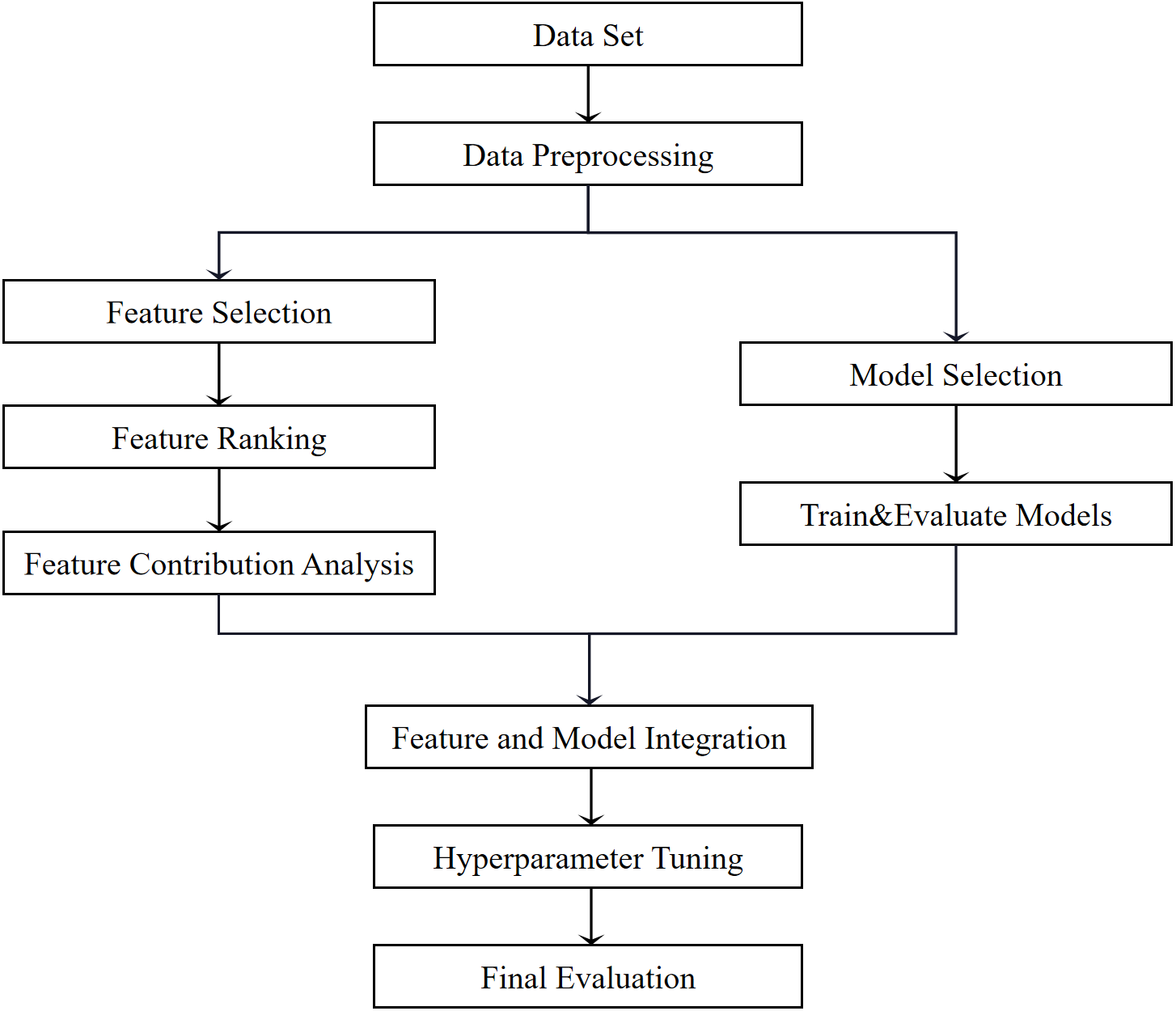
The quality of red wine is crucial for both consumers and producers, influencing purchasing decisions and product improvements. This study aims to enhance red wine quality prediction models through effective feature selection and model optimization. By employing feature engineering to construct and assess feature contributions, the study identifies the best feature combinations and utilizes a five-dimensional evaluation framework of accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, and Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUC-ROC) to screen various models. The research integrates new feature combinations with the optimal model and compares performance before and after feature selection through cross-validation, focusing on stability and generalization. The findings reveal that the Random Forest model, when combined with feature selection, outperforms models using original features in terms of generalization and stability. Key features such as alcohol content and free Sulphur dioxide significantly enhance prediction accuracy. However, new feature construction does not always improve model performance and may introduce noise. These results not only offer practical insights for production and quality control but also underscore the importance of careful feature selection in model prediction, contributing valuable academic knowledge to the field.

 View pdf
View pdf


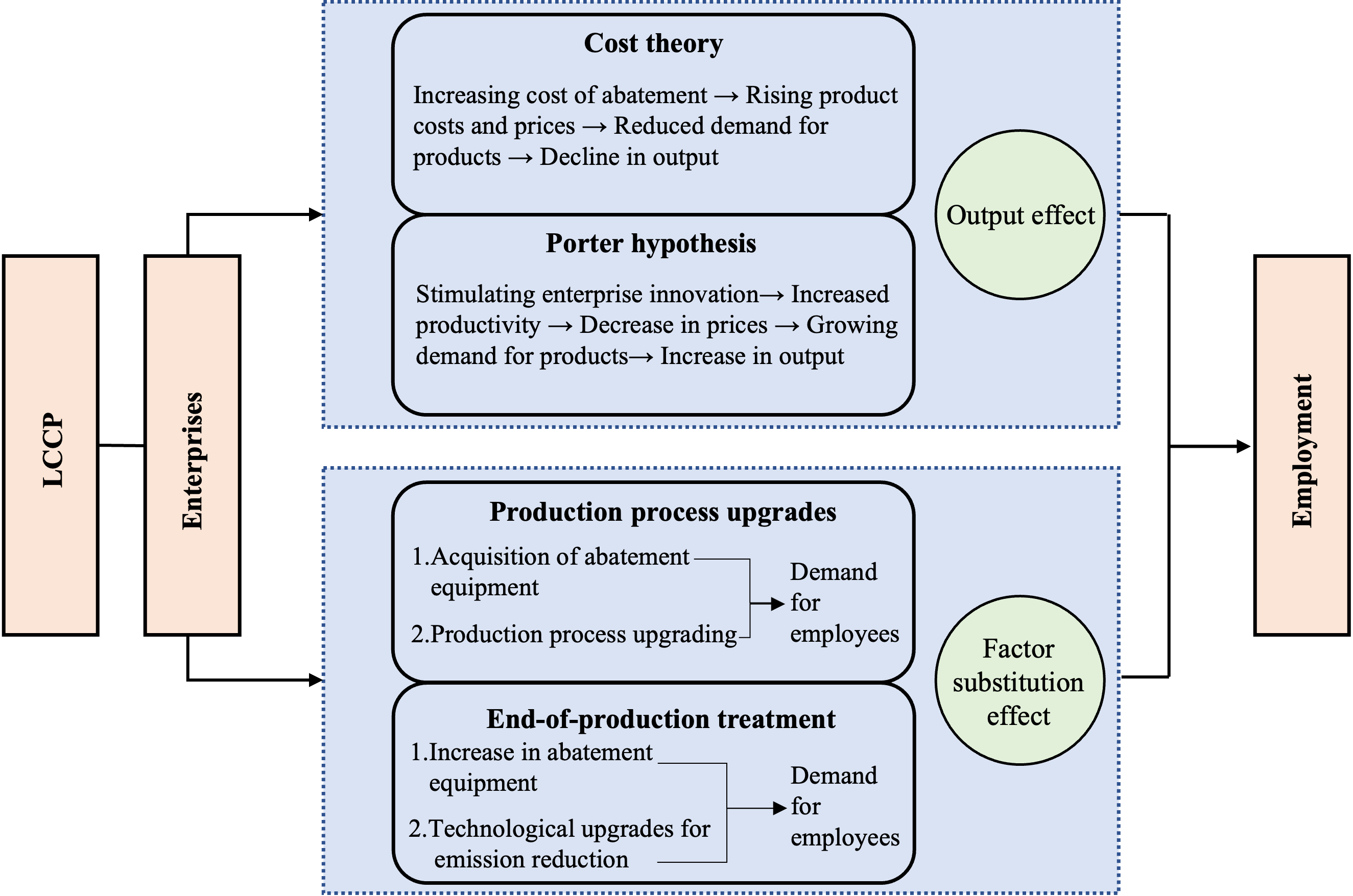
To fulfill the “carbon peak and carbon neutrality” targets pledged in the 2016 Paris Agreement, China implemented the Low-Carbon City Pilot Policy (LCCP) in 2010, expanding its scope in 2012 and 2017. However, its effect on employment in manufacturing remains unexplored. This paper employs a difference-in-differences (DID) model and a micro-panel dataset of Chinese listed manufacturing firms from 2007 to 2021 to identify the casual effect of the LCCP on manufacturing employment. The findings reveal that (1) the LCCP leads to an average 3.9% increase in manufacturing employment; (2) this impact operates through output and factor substitution effects. These conclusions are validated through a series of endogeneity and robustness tests. The study provides new evidence supporting a win-win outcome between environmental protection and employment growth under low-carbon development initiatives.

 View pdf
View pdf


Against the backdrop of increasingly stringent global climate change and environmental protection requirements, shipping enterprises, as a vital component of global trade, face significant pressure from environmental regulations. This paper analyzes the impact of environmental regulations on the integration strategies of shipping enterprises and their underlying mechanisms from the perspective of the Resource-Based View (RBV). As representatives of high carbon emission industries, shipping enterprises must integrate internal and external resources based on their unique characteristics to address the growing stringency of global environmental policies. This study reveals that the formulation of environmental strategies for shipping enterprises is driven by both environmental regulations and resource integration, emphasizing the critical role of integrating technological resources, fleet size, external collaboration, and financial resources in responding to environmental regulations. Based on case analysis, this paper further elucidates the pathways through which shipping enterprises can achieve long-term competitive advantages via green technological innovation and strategic cooperation, exploring how companies can optimize resource allocation under environmental regulations to reduce operational costs and carbon emissions. Finally, this paper summarizes the practical application value of integration strategies for shipping enterprises and offers suggestions for future research.

 View pdf
View pdf


Green finance, defined as supporting the development of green and low-carbon projects, serves as a mechanism for tackling resource shortages and environmental damage caused by Chinese economic reform and opening up. The reason for studying Chinese green finance development path by region is that each region has different economic development policies, investment in education and environment, and investment in scientific and technological innovation. This article employed the entropy method and DEA-Malmquist model to measure the efficiency of Chinese green finance development. The entropy method assigned values to each green financial development efficiency evaluation indicator and determined the weight. Then the DEA-Malmquist method was conducted to calculate the weight of each indicator to measure the dynamic development scale and efficiency. Based on the above research results, three policy recommendations are put forward to improve economic development, enhance innovation capabilities, and improve the green financial system.

 View pdf
View pdf


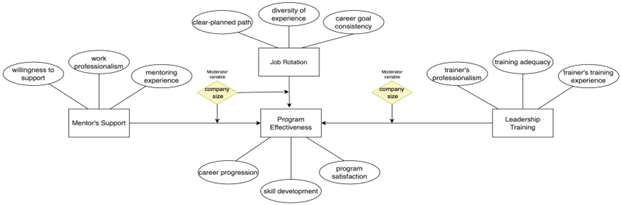
The research examines the factors influencing the overall effectiveness of management trainee (MT) programs in the career progress of trainees and evaluates the suitability of MT programs for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) within the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) industry in China. The study identifies perceived leadership training, perceived mentor support and perceived job rotation as the key variables affecting overall program effectiveness. Using a sample of 400 FMCG employees who have participated in MT programs and data collected via online questionnaires, the study conducted a comprehensive analysis employing correlation and regression techniques to determine the significance and impact of the key variables. The results revealed that, perceived leadership training, perceived mentors support and perceived job rotation all have positive and significant impacts on overall program effectiveness. Furthermore, the positive coefficient levels and strong statistical significance indicated that, the key variables, considerably enhances career progression of trainees and also make MT programs suitable and beneficial for SMEs in the Chinese FMCG industry.

 View pdf
View pdf


With the development of the digital economy and the emergence of digital financial products, some traditional theories of monetary demand face challenges in explaining current financial environments. Emerging digital financial tools and models within the digital economy have effectively alleviated traditional conflicts, impacting financial products, consumer behavior, corporate marketing strategies, and government policies on a wide scale. Regarding financial products, new digital financial products continually challenge traditional ones, while simultaneously creating new opportunities. Consumer behavior has also shifted, with lower psychological barriers leading to impulsive consumption and decreased savings rates. In response, companies should leverage this trend by enhancing corporate efficiency through data-driven precision marketing and by utilizing various digital financial products to support financing, thereby creating better investment opportunities and improving profitability. At the same time, governments face challenges such as data misuse by corporations, leading to discriminatory pricing, and insufficient regulation of emerging financial products, resulting in financial risks. To address these issues, governments should adopt measures such as strengthening data protection legislation, drawing on international financial regulatory frameworks, and improving credit systems to respond to these challenges actively, achieving a win-win for economic and social benefits.

 View pdf
View pdf


This study investigates the influence of social media sentiment on stock market performance by analyzing investor comments on the Snowball platform for Yunnan Baiyao (00538.SZ) and CICC (601995.SH) (China International Capital Corporation) between July and September 2024. Using web-scraping technology and sentiment analysis, the research categorizes comments into positive, neutral, or negative, applying regression models to investigate the relationship between the number of posts reflecting investor sentiment and stock trading performance, while controlling for variables such as company assets, P/E ratio, and market turnover rate. The results reveal that both positive and negative sentiments significantly affect stock trading behavior, with negative sentiment having a stronger impact. Additionally, company size and market fundamentals consistently influence trading volume and turnover rate. The study concludes by recommending that investors rely more on fundamental analysis rather than short-term sentiment fluctuations to achieve long-term stability in their investments.

 View pdf
View pdf


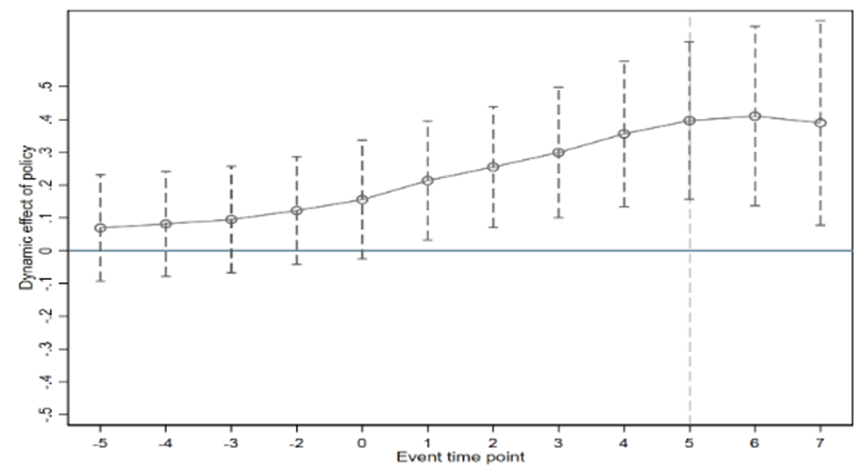
This research aims to investigate how China's high-speed rail system affects Chinese cities' appeal to foreign direct investment. This study uses the multi-time point difference to difference model to investigate the consequences in relation to foreign direct investment in high-speed rail in Chinese cities using panel data from 300 prefecture-level cities in China between 2008 and 2021.The findings indicate that the appeal of foreign direct investment is significantly impacted by the introduction of China's high-speed rail. Placebo test and delayed single-stage regression are also used in this paper, which proved that result is robust. In a further heterogeneity test, Chinese cities are classified according to center-periphery, high-speed railroads and city type. The findings indicate that the FDI influx into nearby cities, non-main line cities, and agricultural cities is significantly impacted by high-speed rail’s opening. There is no significant effect on FDI inflow in central cities and Cities with high-speed rail main lines The influence of FDI inflow on the service cities is negative. Construction of high-speed rail should be prioritized by the government in the nation's agricultural and comparatively underdeveloped cities, and encourage the building of high-speed rail that is not main line.

 View pdf
View pdf


As global attention to environmental protection intensifies, an increasing number of companies are engaging in greenwashing practices, which misrepresent their sustainability efforts. This paper presents an empirical analysis examining the impact of corporate innovation on greenwashing behavior. The findings reveal that innovation serves a crucial role in suppressing such misleading practices, as demonstrated by a fixed effects model. Furthermore, moderation effect analysis indicates that the relationship between innovation and greenwashing becomes more pronounced under imitative competitive pressure, suggesting that firms may enhance their commitment to sustainability when influenced by competitors. However, heterogeneity analysis indicates that this suppressive effect is less pronounced among state-owned enterprises and high-pollution industries, thereby underscoring the necessity for tailored strategies in these sectors. In sum, the findings offer valuable insights for corporate managers, market regulators, and investors, enabling more informed decision-making and promoting a more transparent and sustainable business landscape.

 View pdf
View pdf


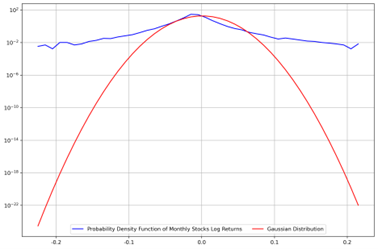
Investment portfolio optimization has been a commonly discussed topic. This paper compared the differences between two established models regarding such topic, the Markowitz Model and the Index Model, by comparing the optimized portfolio outcomes formed by ten stocks, one equity index (the S&P 500 Index), and a proxy for the riskless asset (1-month Fed Funds Rate) under five different scenarios that each simulates a particular real-life circumstance, and concluded that while the Markowitz Model produced more optimistic results under situations with no constraints, with an arbitrary box constraint, and with a constraint of excluding the broad index, the Index Model outperformed the Markowitz Model under the constraints that simulate Regulation T and the U.S. mutual funds industry. This paper provided an analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of each model under different schemes by comparing the total returns, risks, and reward-to-volatility rate of each portfolio. It may also guide the investors who aim to optimize their portfolios to some extent.

 View pdf
View pdf




